В случае, если вам потребовался доступ из Windows к данным на разделе диска с файловой системой Linux — ext4/ext3/ext2, встроенными средствами системы сделать это не получится. Однако, возможности есть, причем реализовать это можно встроенными средствами системы или с помощью сторонних инструментов.
В этой инструкции подробно о способах подключить раздел диска в файловой системе Linux в Windows 11 и Windows 10 для доступа к данным на этом разделе как для чтения, так и для записи.
Ext2 File System Driver (Ext2Fsd) — самый простой способ открыть раздел ext4/ext3/ext2 в Windows
Ext2 File System Driver или Ext2Fsd — сторонний и полностью бесплатный драйвер для подключения разделов Linux во всех версиях Windows начиная с XP. Несмотря на название, поддерживаются не только разделы не только с файловой системой ext2, но и более новые ext4 и ext3.
Порядок использования Ext2 File System Driver для доступа к дискам Linux будет следующим:
- Загрузите установщик Ext2Fsd с сайта https://sourceforge.net/projects/ext2fsd/
- Установите драйвер, в параметрах установки как правило не требуется ничего изменять.
- По завершении установки вам будет предложено запустить Ext2 Volume Manager (менеджер томов), запустите его.
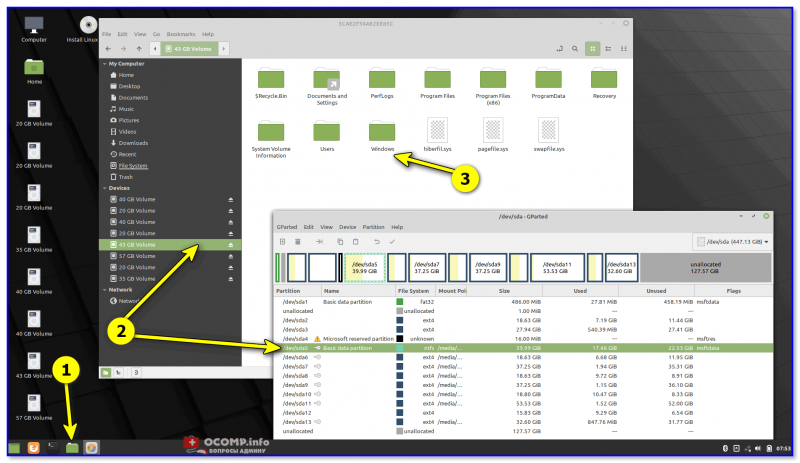
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по разделу Linux ext4, ext3, ext2 и выберите пункт «Assign Drive Letter» — назначить букву диска.
- Для раздела будет автоматически назначена буква диска, и вы увидите раздел в Проводнике Windows с возможностью чтения и записи файлов на нём.
В дальнейшем вы тем же способом сможете удалить букву диска с раздела (опция «Change letter» — «Remove»).
Доступ к разделам Linux средствами Подсистемы Windows для Linux (WSL)
Подсистема Windows для Linux (WSL) также может быть использована для подключения дисков Linux в Windows таким образом, чтобы доступ к ним был возможен из проводника. Шаги будут следующими:
- Запустите командную строку, Терминал или PowerShell от имени администратора и по порядку введите команды
wsl --install wsl --set-default-version 2 dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart wsl --install -d Ubuntu
- После выполнения последней команды откроется окно консоли Linux (командную строку при этом не закрывайте, она еще пригодится) с предложением настроить имя пользователя и пароль, сделайте это. Если в окне консоли вы увидите сообщение об ошибке, скачайте и установите обновление WSL, перезагрузите компьютер и запустите Ubuntu из меню «Пуск».
- В консоли Ubuntu введите команду
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/ext-drives/
для создания папки, к которой будут монтироваться диски.
- В консоли Windows (командная строка, терминал, Powershell) введите команду
wmic diskdrive list brief
- Обратите внимание на DeviceID диска, который нужно подключить и введите команду (так же в консоли Windows) указав соответствующий номер в имени PHYSICALDRIVE
wsl --mount \\.\PHYSICALDRIVE
- В консоли Ubuntu введите команду lsblk — это отобразит список подключенных дисков, разделов на них и их размер. В следующей команде используем имя нужного раздела для монтирования:
sudo mount /dev/sdИМЯ /mnt/ext-drives/
- После успешного выполнения всех указанных шагов вы можете зайти в Проводник Windows, выбрать пункт «Linux» в панели быстрого доступа, перейти в папку mnt\ext-drives и получить доступ к файлам на подключенном разделе Linux с возможностью записи и чтения.
В дальнейшем для отключения диска от WSL можно использовать ту же команду, которая использовалась на 5-м шаге, заменив mount на unmount.
Есть и другие программы (драйверы) для доступа к разделам Linux из Windows, но не полностью бесплатные. Среди них:
- DiskInternals Linux Reader — в бесплатной версии доступно только чтение данных с разделов.
- Paragon Linux File Systems for Windows — бесплатная работа в течение пробной версии, затем необходимо приобретать лицензию.
Свежая инсайдерская сборка Windows 10 с индексом «20211» позволяет монтировать физические диски внутри WSL 2, тем самым открывая возможность получить доступ к файловым системам, не поддерживающимся Windows нативно (например, ext4). Если вы используете две системы параллельно на разных дисках, то теперь вы сможете получать доступ к файлам Linux из под Windows.
Подготовка
Для монтирования диска, необходимо открыть PowerShell с привилегиями администратора и выполнить следующую команду:
wsl —mount <Путь к диску>
Для отображения всех доступных дисков надо выполнить:
wmic diskdrive list brief
Демонтировать диск из WSL 2 можно командой
wsl —unmount <Путь к диску>
Пути к дискам можно узнать в колонке DeviceID. Обычно он представлен в виде \\.\\\.\PHYSICALDRIVE*.
Доступ к файлам через «Проводник»
Как только диск смонтирован, к нему можно получить доступ через «Проводник», перейдя по пути \wsl$ и смонтировав папку.
Ограничения
По стандарту wsl —mount пытается смонтировать диск как ext4. Для того, чтобы указать другую файловую систему, необходимо использовать команду
wsl —mount <Путь к диску> -t <Тип файловой системы>
Список всех доступных файловых систем можно узнать, введя
cat /proc/filesystems
Также важно отметить, что только целые физические диски могут быть смонтированы в WSL 2. На текущий момент невозможно присоединить только один раздел. Кроме того, хотя и есть поддержка дисков USB, устройства USB Flash не могут подключаться к WSL 2.
Внимание: Это перевод статьи из блога Microsoft.
Содержание статьи:
- Как «прочитать» информацию на разделах с файловыми системами Ext2, Ext3, Ext4
- Способ 1 (через спец. драйвер)
- Способ 2 (через дополнения к TC)
- Способ 3 (с помощью LiveCD)
- Вопросы и ответы: 4
Доброго дня!
К сожалению «обычная» версия Windows не позволяет работать с дисками, отформатированными в файловые системы (ФС) Ext2, Ext3, Ext4 (используются в Linux). Всё, что доступно — это узнать о их существовании в управлении дисками, а вот скопировать файл — уже проблема…
Что делать?
Наиболее сподручный и самый удобный вариант (на мой взгляд) — установить в Windows спец. драйвер, который позволит ОС работать с дисками Ext2/3/4 также, как если бы они были отформатированы в NTFS (скажем). Т.е. любая программа в Windows (тот же проводник) сможет в обычном режиме работать с диском. Удобно?
Теперь о том, «что» выбрать…
*
Как «прочитать» информацию на разделах с файловыми системами Ext2, Ext3, Ext4
Способ 1 (через спец. драйвер)
Подобные «драйверы» есть от нескольких производителей. Я бы выделил продукт от Paragon (ссылка на офиц. сайт с драйвером). Почему:
- поддержка ФС: Ext2, Ext3, Ext4 (чтение + запись); Btrfs, XFS (только чтение);
- после установки драйвера — ничего «делать» не нужно: просто Windows начинает видеть накопители с Ext4+;
- совместим с ОС Windows 7/8/10 (плюс есть пробный период, которого хватает для возникшей задачи (обычно)).

Драйвер от Paragon
Обратите внимание, что «ненужные» разделы диска можно откл. и не монтировать. Настройка драйвера позволяет это сделать.
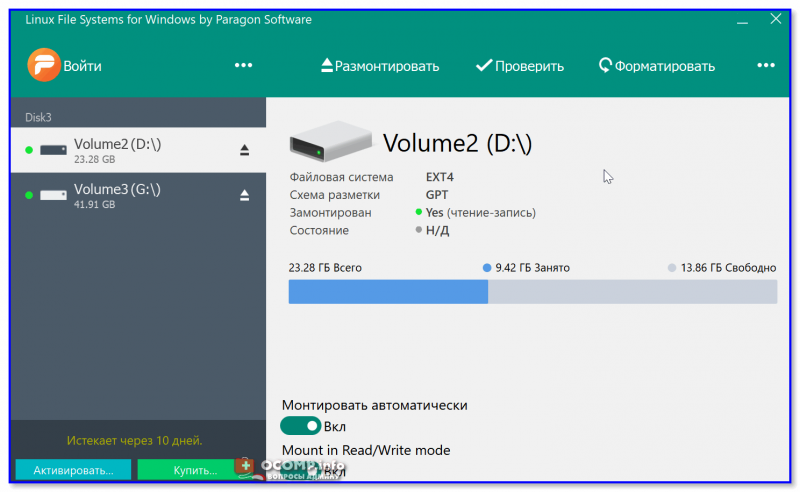
Главное окно (Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon Software)
На скрине ниже привел окно проводника: как видите, раздел отображает как «обычный» — на него также можно что-нибудь скопировать / удалить.
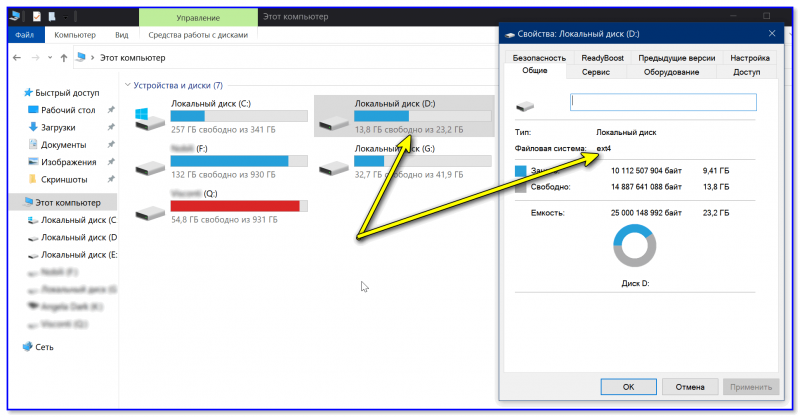
Этот компьютер — диски с ФС EXT4 появились в проводнике
👉 Дополнение!
На Sourceforge можно также найти бесплатный драйвер файловой системы Ext2/3/4 для Windows 7/8/10* (ориг. название: Ext2Fsd).
Сразу отмечу, что на некоторых ОС Windows 10 — драйвер этот ведет себя нестабильно, и не позволяет прочитать информацию с нужного раздела…
Продукт от Paragon, конечно, выигрывает…
*
Способ 2 (через дополнения к TC)
TC — это сокращенное название файлового коммандера Total Commander (некая замена проводнику). К этой программе есть очень много плагинов, и, разумеется, для чтения Ext2/3/4 ФС тоже есть!
Покажу по шагам, как в нем открыть подобный раздел диска…
1) Сначала устанавливаем сам Total Commander. Ссылка на офиц. сайт.
2) Далее необходимо загрузить плагин DiskInternals Reader с офиц. сайта (он идет в архиве ZIP — извлекать не нужно).
3) После необходимо запустить TC от имени администратора (просто кликните правой кнопкой мыши по значку…). 👇
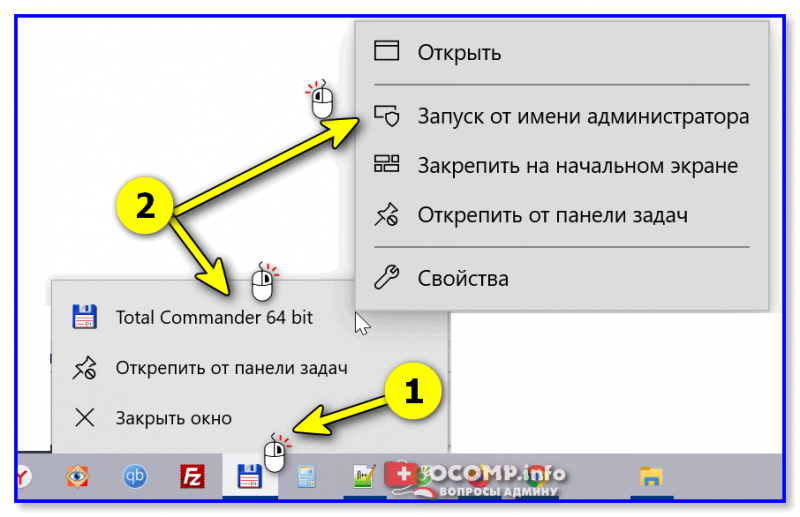
Запуск TC от имени админа
4) Затем необходимо открыть архив ZIP с плагином DiskInternals Reader в Total Commander — тогда он предложит вам установить плагин. Разумеется, соглашаетесь! 👌
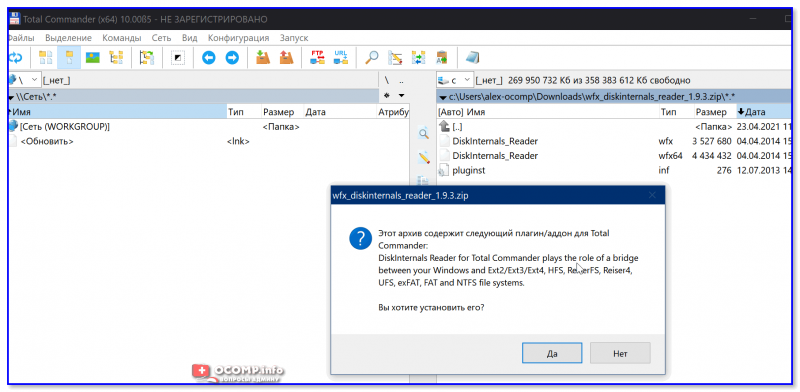
Установка плагина
5) Далее необходимо закрыть TC и снова его запустить от имени админа. В меню выбора диска укажите вариант «Сеть / FS-плагины» — далее кликните по значку DiskInternals Reader (см. стрелки 1, 2 на скрине ниже 👇).
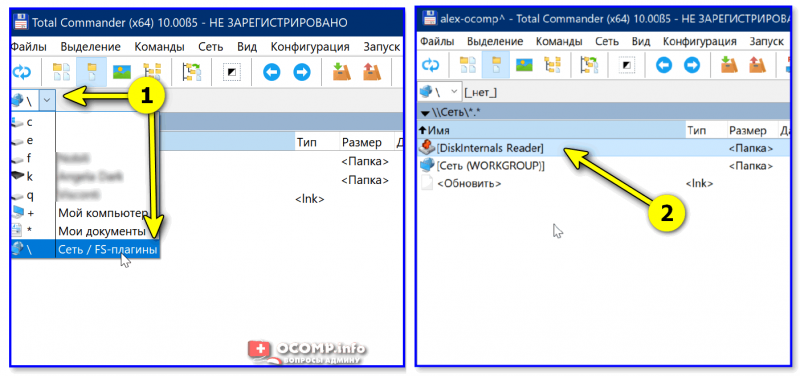
DiskInternals Reader
6) Собственно, далее появиться список всех дисков (в том числе и Ext2/3/4) — их можно открыть и скопировать с них нужную информацию. Задача решена?! 👌
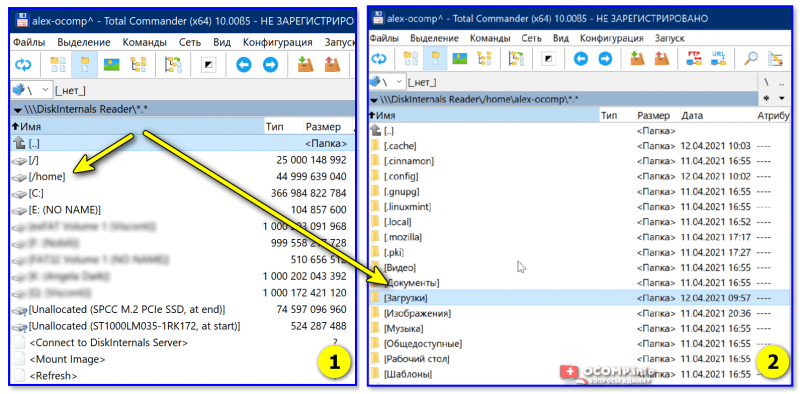
Файлы читаются, можно копировать
*
Способ 3 (с помощью LiveCD)
Вообще, этот вариант, конечно, не относится к работе из-под Windows… Однако, он вполне себе годен для какой-то разовой работы (например, для копирования и переноса папки с файлами). К тому же аварийный LiveCD с Linux никогда не помешает — вдруг чего… 👌
1) Дистрибутивы Linux с поддержкой работы LiveCD — 👉 можете найти в моей подборке
2) Загруженный ISO-файл с нужной версией дистрибутива Linux необходимо правильно записать на флешку.
3) Далее останется только загрузиться с этой флешки с помощью Boot Menu (вызывается сразу после вкл. ПК). Если вы выберите дистрибутив Linux для новичка — то работать с ним весьма просто (ничуть не сложнее, чем с проводником Windows).
Linux Mint загружена с LiveCD
*
Дополнения приветствуются!
Успехов!
👌
In this article, we will be discussing five different ways to access Linux files from Windows. We’ll work on Ubuntu in this article, but you can use any distribution. Just identify the partition type that you’re using on your system and download the appropriate tool from this list.
Ubuntu supports Windows NTFS partitions but Windows can’t access Ubuntu partitions i.e. Ext4, Ext3, Ext2, etc. To access these partitions from windows when dual-booted with Ubuntu, this can only be done using third-party software. We will discuss some of the software to read and write Linux partitions.
Here are some free tools to access Linux files from windows without booting into Linux:
1. ext2fsd
ext2fsd can read Ext4, Ext3, Ext2 file systems and can even provide write access on enabling write support during the setup. You have to start it manually in Tools > Service Management and click on Start or you can set it to start automatically when the system boots. It is free and easy to install.
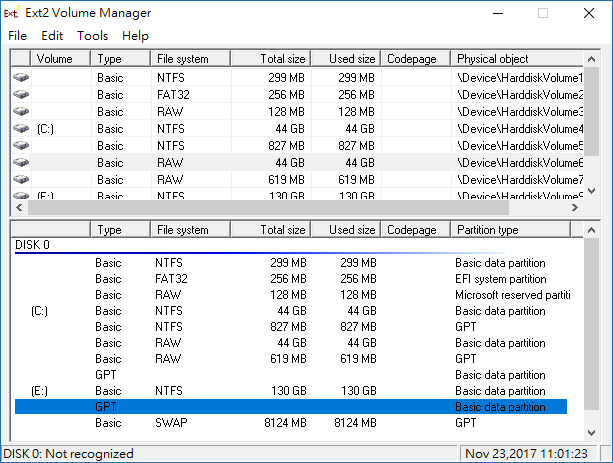
It assigns a drive letter to the Linux partitions or you can set it manually using Ext2 Volume Manager and can change ext2fsd’s settings. You can choose to assign the drive letter automatically in Tools > Service Management. Assigning a drive letter to Linux partitions allows apps to directly access Linux Files on Windows!
2. DiskInternals Linux Reader
Unlike ext2fsd, Linux Reader also supports ReiserFS, Reiser 4, HFS, HFS+(Apple’s file system), APFS, XFS, etc along with Ext4, Ext3, Ext2. It provides read-only access to keep the original files secure. It previews the contents of the files and bypasses the security policies of files which gives you access to any file on your Linux partition. It is free software for non-commercial use and works on Windows 7, 8, and 10.
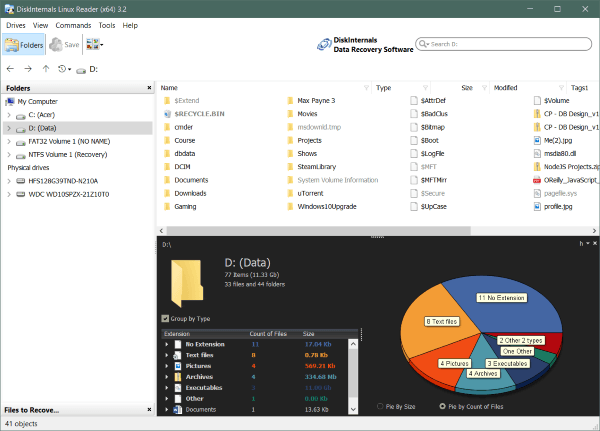
It also has a pro version i.e. Linux Reader Pro which provides some extra features such as remote access via SSH, Exporting files to an FTP server. You can download it through this link. Instead of assigning a drive letter, it shows the files in its application window. You can save the files to windows which you want to use.
3. Ext2Read
Ext2read is a free and open-source utility that works the same as the Linux Reader. It provides read-only access only to Ext4, Ext3, Ext2, and Ext4 Extents. It does not need to be installed, It is just a .exe file that should be run as an administrator. You can copy folders and even whole directories from Linux partitions. You can download the .exe file through this link.
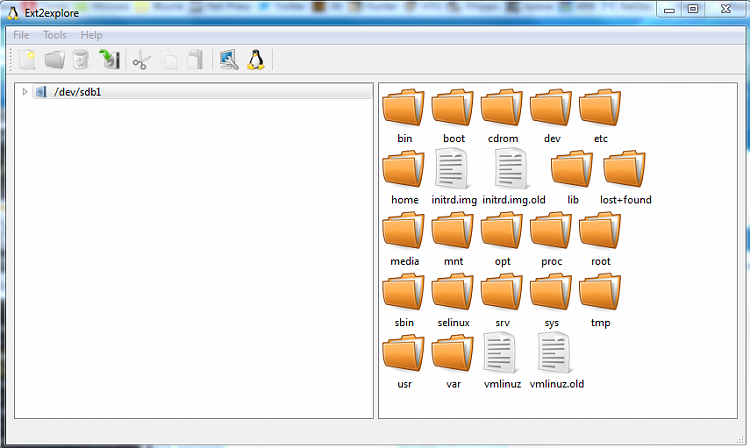
4. Explore2fs
Explore2fs is a tool that gives you access to Ext2 and Ext3 file systems. It supports all versions of windows, especially the older versions. This tool is used for the old hardware as it supports Floppy disks, CD-ROM, Jazz Disk and can export files as binary, text, or even directories. While not the best option, if you need to access Linux files on Windows on a old device, go for this one. You can download it from here.
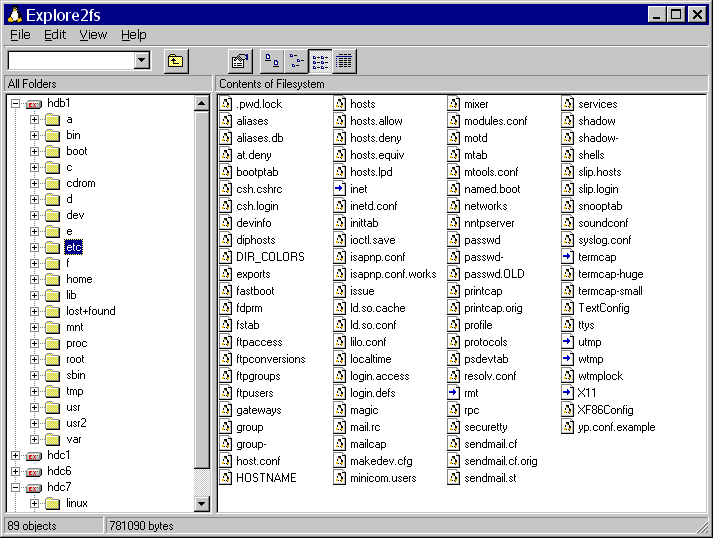
5. Ext2 IFS
Ext2 IFS is a tool used to access the Ext2 file system with read and write access. You can read, write, rename, move and delete files or directories. It works on Windows 7 and 8, Windows Server 2003, 2008, 2012, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and other old versions.
During installation, it will give the option to choose a drive letter for your Linux partition and after the installation, you will find the Linux file system in your file explorer.
Unlike other software discussed above, this tool can only access Ext2 file systems. You can download it through this link.
FAQs
What are some tools to access Linux files on Windows?
You can use tools like DiskInternals Linux Reader, Ext2Fsd, Explore2fs, WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux), and Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon to access Linux files on Windows.
How can I access Linux partitions from Windows?
You can use tools like Ext2Fsd or Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon to access Linux partitions from Windows. These tools allow you to browse and save files from Linux partitions on your Windows system.
Can I access Ext4 partitions from Windows?
Yes, you can access Ext4 partitions from Windows using tools like Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon which supports the Ext4 file system and allows you to access files from Ext4 partitions on your Windows PC.
Does Windows 10 have built-in support for accessing Linux files?
Windows 10 does not have built-in support for accessing Linux files. However, you can use third-party tools like DiskInternals Linux Reader or Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon to access Linux files from Windows 10.
How can I transfer files between Windows and Linux systems?
You can transfer files between Windows and Linux systems by using tools like WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) or third-party applications like DiskInternals Linux Reader or Linux File Systems for Windows by Paragon.
Conclusion
So, We discussed different ways to access Ubuntu files from Windows without shutting windows and booting into Linux. Explore2fs and Ext2 IFS can be used for older versions of windows and can access old hardware as discussed.
On Windows 11, the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) ships with a new feature that allows you to attach and mount physical drives to access Linux file systems (for example, ext4) not natively supported on Windows.
The new feature allows users to access Linux files using File Explorer on a dual-boot system running Windows 11 and a Linux distro on a different drive.
In this guide, you will learn the steps to mount and unmount drives using the Windows Subsystem for Linux.
- Mount Linux file system on Windows 11
- Mount any Linux file system on Windows 11
- Access Linux file system on Windows 11
- Unmount Linux file system on Windows 11
To mount a Linux file system using WSL, use these steps:
-
Open Start on Windows 11.
-
Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
-
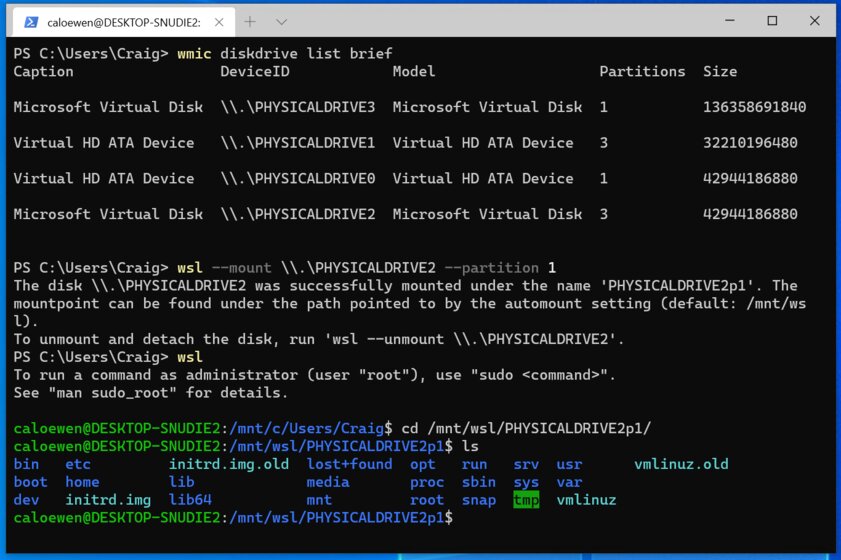
Type the following command to list the available physical disks and press Enter:
wmic diskdrive list brief
-
Confirm the drive path under the “Device ID” column.
-
Type the following command to mount the Linux file system and press Enter:
wsl --mount DISKPATH
In the command, make sure to replace DISKPATH for the drive path with the Linux distribution you want to mount. For example,
wsl --mount \\.\PHYSICALDRIVE2. If you’re going to mount a specific partition, you’ll need to use the--partitionoption with the partition number. For example,wsl --mount \\.\PHYSICALDRIVE2 --partition 1.
Once you complete the steps, the drive with Linux files will mount, and it’ll be visible from Windows 11.
Mount any Linux file system on Windows 11
The previous steps only attempt to mount a physical drive as ext4. If you want to specify another file system, you will need to use a different command with the Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL2).
To mount a specific Linux file system on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
-
Type the following command to list the available physical disks on Windows 11 and press Enter:
wmic diskdrive list brief
-
Confirm the drive path under the “Device ID” column.
-
Type the following command to mount a drive and press Enter:
wsl --mount DISKPATH -t FILESYSTEM
In the command, make sure to replace DISKPATH and FILESYSTEM for the path of the Linux drive and file system you want to mount. For example, to mount a disk as
fat, use this command:wsl --mount DISKPATH -t vfat.
After you complete the steps, the drive with Linux files will mount, and it will be accessible using File Explorer.
Access Linux file system on Windows 11
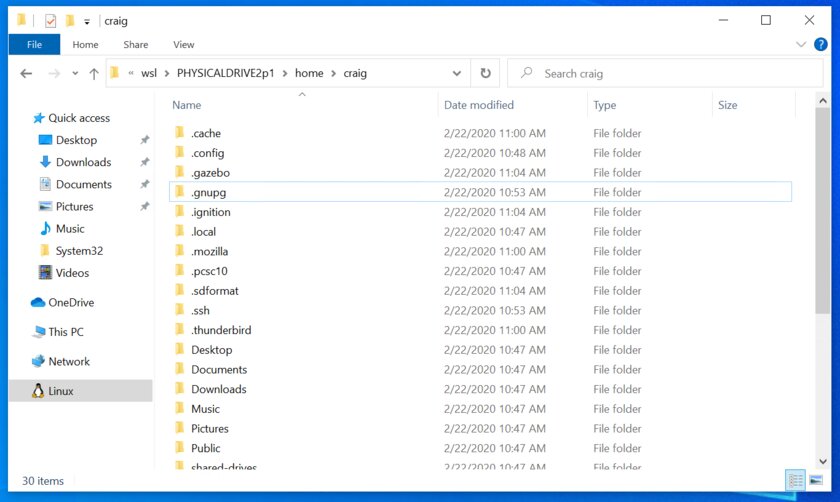
To access files from a Linux file system on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open File Explorer.
-
Click the Linux item from the left navigation pane.
-
In the address bar, navigate to
\wsl$and then access the mount folder. For example,\\wsl$\\DISTRO-NAME\\MOUNT-POINT.
Once you complete the steps, you should be able to browse the Linux files from a natively unsupported file system on Windows 11. In addition to using File Explorer, you can access file systems like “ext4” from the WSL2 console using command lines once the drive is mounted.
Unmount Linux file system on Windows 11
To unmount the Linux file system on Windows 11, use these steps
-
Open Start.
-
Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
-
Type the following command to unmount and detach the drive and press Enter:
wsl --unmount DISKPATH
In the command, make sure to replace DISKPATH for the Device ID of the drive you want to unmount.
After you complete the steps, the drive with the Linux file system will unmount and detach from Windows 11.
Why You Can Trust Pureinfotech
The author combines expert insights with user-centric guidance, rigorously researching and testing to ensure you receive trustworthy, easy-to-follow tech guides. Review the publishing process.










