В случае, если вам потребовался доступ из Windows к данным на разделе диска с файловой системой Linux — ext4/ext3/ext2, встроенными средствами системы сделать это не получится. Однако, возможности есть, причем реализовать это можно встроенными средствами системы или с помощью сторонних инструментов.
В этой инструкции подробно о способах подключить раздел диска в файловой системе Linux в Windows 11 и Windows 10 для доступа к данным на этом разделе как для чтения, так и для записи.
Ext2 File System Driver (Ext2Fsd) — самый простой способ открыть раздел ext4/ext3/ext2 в Windows
Ext2 File System Driver или Ext2Fsd — сторонний и полностью бесплатный драйвер для подключения разделов Linux во всех версиях Windows начиная с XP. Несмотря на название, поддерживаются не только разделы не только с файловой системой ext2, но и более новые ext4 и ext3.
Порядок использования Ext2 File System Driver для доступа к дискам Linux будет следующим:
- Загрузите установщик Ext2Fsd с сайта https://sourceforge.net/projects/ext2fsd/
- Установите драйвер, в параметрах установки как правило не требуется ничего изменять.
- По завершении установки вам будет предложено запустить Ext2 Volume Manager (менеджер томов), запустите его.
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по разделу Linux ext4, ext3, ext2 и выберите пункт «Assign Drive Letter» — назначить букву диска.
- Для раздела будет автоматически назначена буква диска, и вы увидите раздел в Проводнике Windows с возможностью чтения и записи файлов на нём.
В дальнейшем вы тем же способом сможете удалить букву диска с раздела (опция «Change letter» — «Remove»).
Доступ к разделам Linux средствами Подсистемы Windows для Linux (WSL)
Подсистема Windows для Linux (WSL) также может быть использована для подключения дисков Linux в Windows таким образом, чтобы доступ к ним был возможен из проводника. Шаги будут следующими:
- Запустите командную строку, Терминал или PowerShell от имени администратора и по порядку введите команды
wsl --install wsl --set-default-version 2 dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart wsl --install -d Ubuntu
- После выполнения последней команды откроется окно консоли Linux (командную строку при этом не закрывайте, она еще пригодится) с предложением настроить имя пользователя и пароль, сделайте это. Если в окне консоли вы увидите сообщение об ошибке, скачайте и установите обновление WSL, перезагрузите компьютер и запустите Ubuntu из меню «Пуск».
- В консоли Ubuntu введите команду
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/ext-drives/
для создания папки, к которой будут монтироваться диски.
- В консоли Windows (командная строка, терминал, Powershell) введите команду
wmic diskdrive list brief
- Обратите внимание на DeviceID диска, который нужно подключить и введите команду (так же в консоли Windows) указав соответствующий номер в имени PHYSICALDRIVE
wsl --mount \\.\PHYSICALDRIVE
- В консоли Ubuntu введите команду lsblk — это отобразит список подключенных дисков, разделов на них и их размер. В следующей команде используем имя нужного раздела для монтирования:
sudo mount /dev/sdИМЯ /mnt/ext-drives/
- После успешного выполнения всех указанных шагов вы можете зайти в Проводник Windows, выбрать пункт «Linux» в панели быстрого доступа, перейти в папку mnt\ext-drives и получить доступ к файлам на подключенном разделе Linux с возможностью записи и чтения.
В дальнейшем для отключения диска от WSL можно использовать ту же команду, которая использовалась на 5-м шаге, заменив mount на unmount.
Есть и другие программы (драйверы) для доступа к разделам Linux из Windows, но не полностью бесплатные. Среди них:
- DiskInternals Linux Reader — в бесплатной версии доступно только чтение данных с разделов.
- Paragon Linux File Systems for Windows — бесплатная работа в течение пробной версии, затем необходимо приобретать лицензию.
Position: How Tos — Partition Management — How To Fully Read & Write Ext4 Partition and Data in Windows 11/10/8/7?
Table of Contents:
If your computer is dual-boot with Linux and Windows, you are probably very clear that default file systems used in Windows and Linux are different. Partitions used in Windows are formatted as FAT32 or NTFS, while they are formatted as EXT4, EXT3 or EXT2 in Linux. Linux system is able to access Windows partition, but Windows cannot access Linux partitions.
Sometimes we may need to access data of Linux partition from Windows, but Windows does not support Linux file system. In this case, we’ll have to reboot computer to Linux and access desired data. It would be better if we can read and write Linux EXT4/3/2 partition from Windows. The rest part of the instruction is going to explain how to create, format, delete, write, resize and recover EXT4 partition from Windows 11/10/8/7.
Linux file system types
File system is the way how files are stored and organized on storage device. Windows and Linux use different file system formats, and the most widely used file system in Linux is EXT4, EXT3 and EXT2. EXT means Extended Filesystem and it was mainly introduced for MINIX. EXT2 (the second extended version) was improved based on the original version, and EXT3 improves performance over EXT2. EXT4 is current the default file system of Linux and it improves performance and reliability and adds additional features over EXT3.
EXT3 VS EXT4
Ext3 became available since the year 2001 together with Linux Kernel 2.4.15 and it is a logical extension of Ext2. Ext3 can be converted to Ext3 directly without backup / restore. Ext3 file system was designed with the ability to journal write to the files system, which allows quite fast crash recovery time. It uses indirect block mapping scheme, which makes it efficient to manage small files. However, it does not work effectively when dealing with large files especially when carrying out deletion task, for the mapping retains an entry for each single block and large file usually has many blocks.
Ext4 was available in 2008 with Linux kernel 2.6.1.19. It is a progressive revision of Ext3 file system and overcomes limitations on Ext3. Ext4 works similarly to Ext3, but it becomes able to store large files much more efficiently than ext3 due to the extend based layout. In Ext4, you are allowed to disable the journaling feature. Ext4 is the default file system in most modern Linux distributions
EXT4 VS NTFS
NTFS (New Technology File System) is the default file system of hard drives used under Windows system since Windows XP. It has complicated structure and can be regarded as a journaling file system, as it retains records of all operations on the device. This feature is capable of detecting errors and restoring from them. NTFS is primarily used on hard drives and external hard drive even though USB media can still be formatted to NTFS.
EXT4, the accessor to Ext3, is the most used filesystem type on Linux system for the moment. It is best suited for hard drives, but it can also be used on removable disks. However, it is not supported by Windows system, thus Ext4 partition is not visible under Windows system.
Linux reader for Windows 10
Since Windows system does not support reading or writing any Linux partition, we need to use third-party Linux reader software to access Linux drives from Windows. DiskGenius Professional Edition is an efficient tool which enables full access to Linux Ext4, Ext3 or Ext2 storage devices under Windows operating system. Just connect your hard drive with Linux partitions to computer and launch DiskGenius and you can easily access and manage ext4 partitions in Windows 11/10/8/7/XP. Main features related to Ext4/3/2 drive provided by DiskGenius:
Partition management: Create, delete, format, resize, clone, image, hide Linux-formatted partition. Support LVM (Logical Volume Management).
Disk management: Check and repair bad sectors, clone & image disk, wipe disk, convert GPT/MBR, convert dynamic disk to basic, etc.
Data recovery: Recover deleted or lost data from ext4 partition, restore lost Linux partition.
Data backup: back up an ext4 partition to an image file, supporting incremental backup.
Supported file systems: Read/write: Ext2, Ext3, Ext4, NTFS, exFAT, FAT32, FAT16, FAT12.
When it comes to reading or writing Ext4 drive, you can do following actions with the help of DiskGenius:
- View and open files and folders stored inside the Ext4/3/2 drive, which is the same as accessing a normal partition.
- Write files or folders from a local drive to the Ext4/3/2 drive.
- Rename files or folders stored inside the Ext4/3/2 drive.
- Export data from the EXT4/3/2 drive to another storage device on the computer.
- Resize/extend/split/shrink the EXT4/3/2 partition without losing data.
- Format any partition into EXT4/3/2 file system.
- Create a new partition as EXT4/3/2 on unallocated disk space.
- Clone or image the EXT4/3/2 partition.
- Recover deleted or lost files from EXT4/3/2 partition and recover lost EXT4/3/2 partitions.
- Edit hex raw data on the EXT4/3/2 partition.
- Check and repair bad sectors for EXT4/3/2 drives.
Guide #1: Format NTFS to EXT4 in Windows
The process of converting NTFS to EXT4 will format the partition so that file system can be changed. Due to partition formatting causes data loss, you need to back up crucial data on the drive before formatting it.
Step 1. Launch DiskGenius, select the NTFS partition you want to change file system and click Format button from toolbar. Also, you can right-click on the partition and select Format Current Partition from context menu.
Step 2. The partition formatting window pops up, and you can choose file system types you need from the dropdown list. Currently, DiskGenius can format partition to NTFS, FAT32, exFAT, EXT2, EXT3 and EXT4 file system.
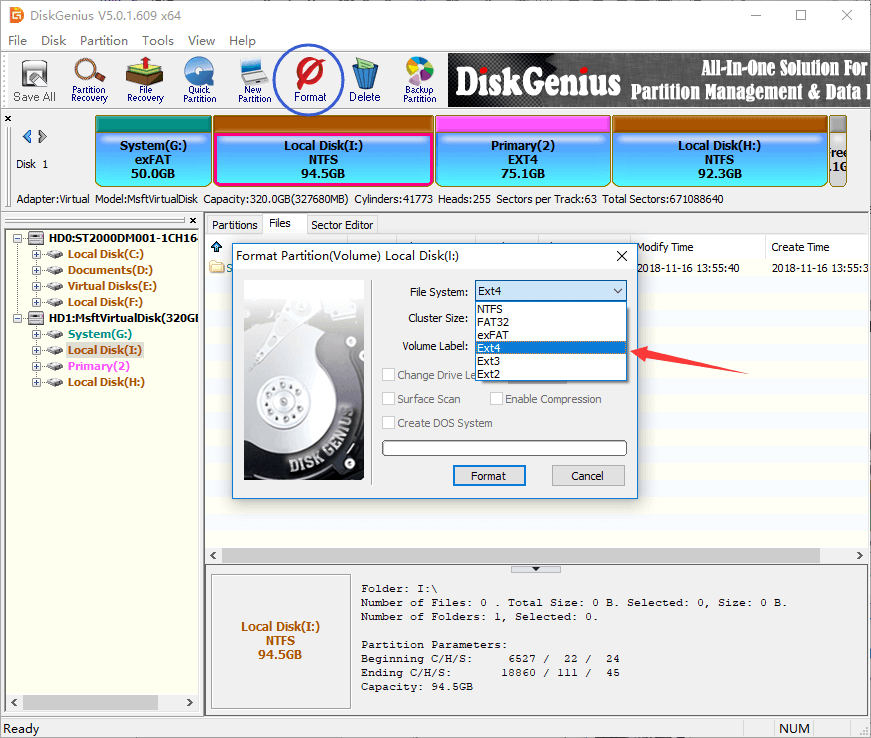
Step 3. Click Format button and you’ll receive a message box asking confirmation. Click Yes to continue and DiskGenius starts to format partition.
Once formatting process completes, the NTFS partition will change to EXT4 file system. Since Windows does not support EXT4 file system, the partition won’t be assigned drive letter and it is not visible to Windows system. If you want to access the partition, you can use DiskGenius to complete required tasks.
Guide #2: Create & delete EXT4 partition in Windows 10/11
DiskGenius is full-featured partition manager which enables you to manage Ext4 partition under Windows. It is quite easy to create an Ext4 partition or format NTFS partition to EXT4.
1. Create EXT4 Linux partition in Windows
Step 1. Launch DiskGenius from your computer, right-click on free disk space (unallocated disk space) and choose Create New Partition, as below:
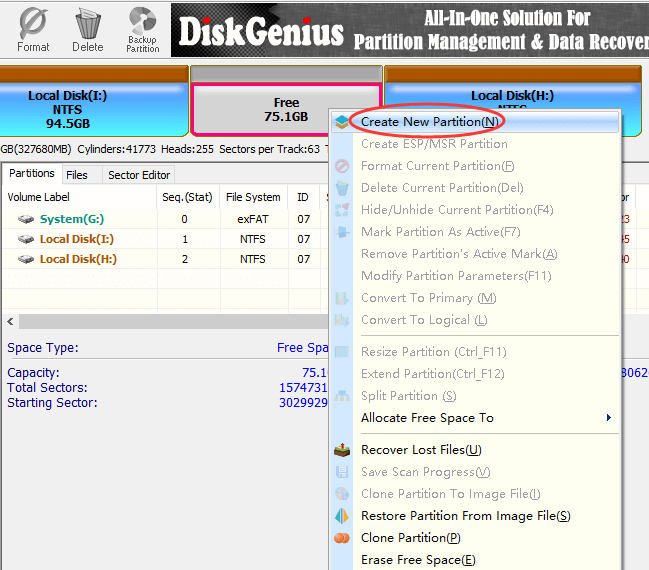
Step 2. On the Create New Partition widows, you can select partition and file system type, set partition size, set 4K sector alignment, etc. There are around a hundred types of file system available here, just choose the one you need. Then click OK button.
Step 3. Click Save All button from toolbar to save the new partition to partition table. Click Yes when DiskGenius asks whether to format the partition. The Ext4 partition will be created successfully after formatting process finishes.
2. Delete Ext4 partition in Windows
Step 1. Right-click on the Ext4 partition you want to delete and choose Delete Current Partition option.
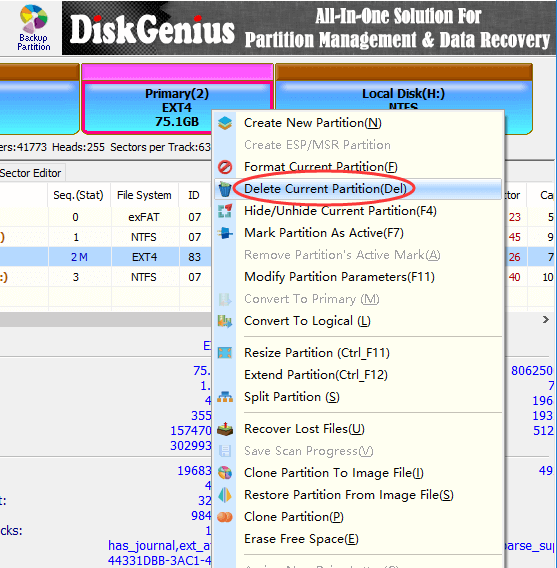
Step 2. Click Yes when DiskGenius asks confirmation for the deleting operation. Then click Save All button to save changes on partition table.
Guide #3: Read & write EXT4 partition data in Windows 10/11
Windows partition manager DiskGenius provides full access to Ext4, Ext3 and Ext2 partition. Thus, you can read or write data in Linux partition via DiskGenius in Windows 10/8/7/XP without rebooting computer to Linux system.
1. Read files of Ext4 partition from Windows 10/11
Install and launch DiskGenius from computer, and you can view all disks and partitions connected to the computer. In the middle area, there are three tabs: Partitions, Files and Sector Editor. Select a disk or partition and click Partitions tab, you can view disk or partition parameters in details, such as partition table type, sector count, SN, adapter type, S.M.A.R.T. information, file system, reserved blocks, volume GUID, etc.
Step 1. Select a partition and click Files tab, you can view files and folders stored on the root directory of the selected partition. Click a file and there will be a thumb preview of the selected files on the lower area, as below:
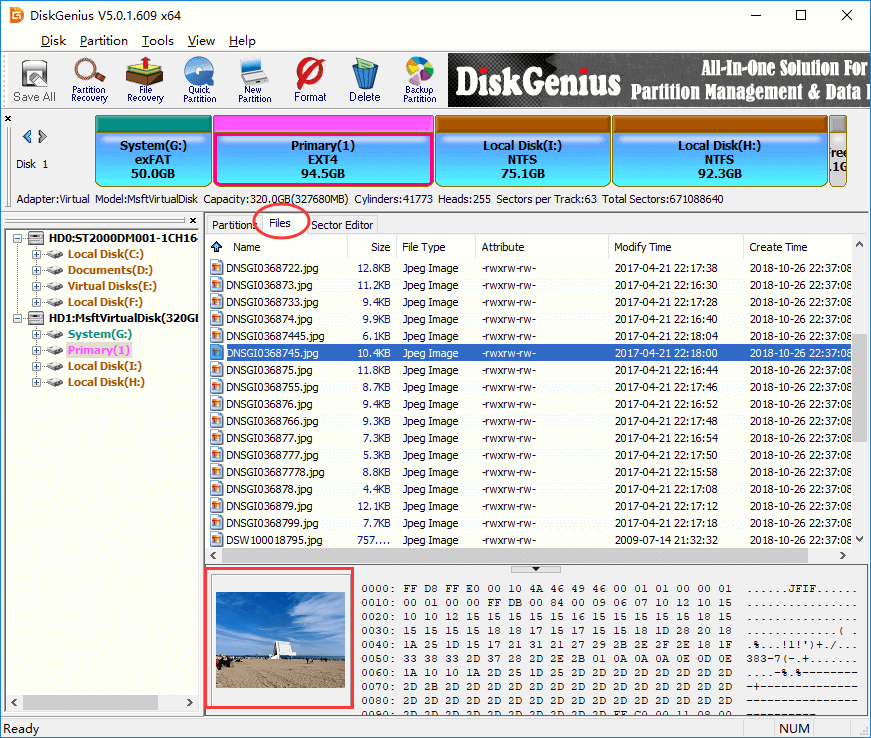
Step 2. Double-click the file and you can view the file content in its original size. The following screenshot shows DiskGenius is viewing a JPG file.
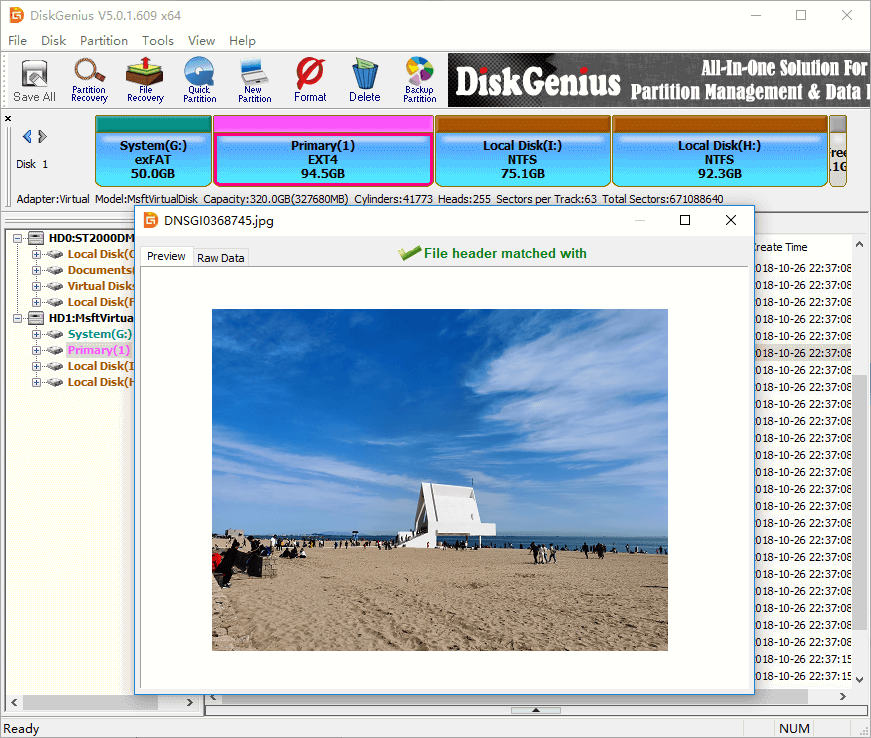
2. Write data to EXT4 partition
Writing an EXT4 partition includes too many operations, such as, delete data, create folder, modify file, rename data, store new data, etc. DiskGenius has full access to write ext4 partition and it can do all operations related to writing, but in this section, we only explain how to store data to ext4 partition.
Step 1. Select an Ext4 partition to which you want to store new data, and click Files tab.
Step 2. Right-click on the empty area and choose Copy Files To Current Partition.
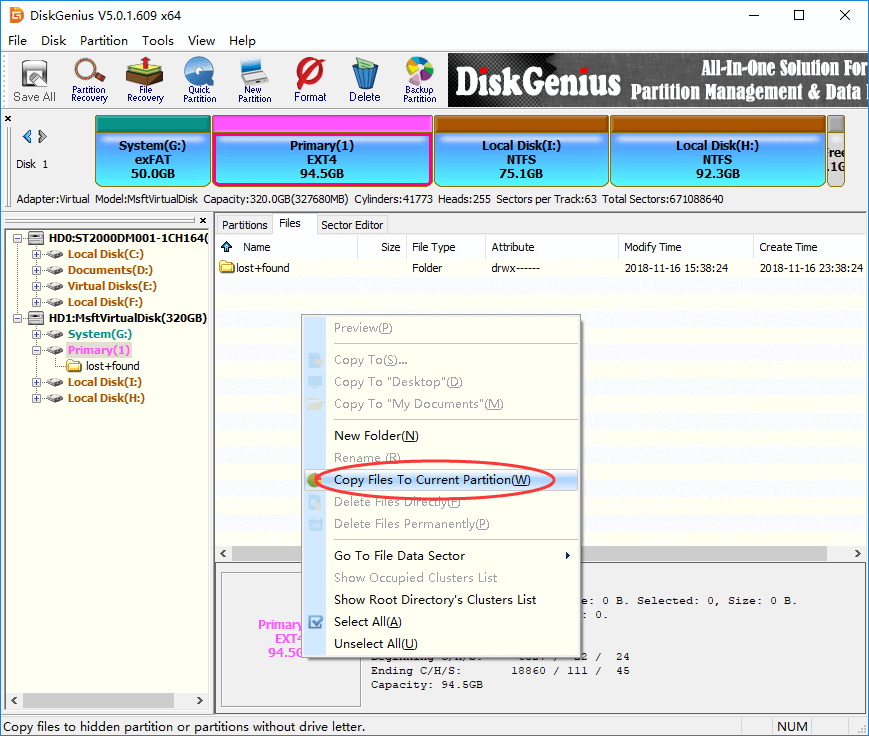
Step 3. Select files you want to copy to the EXT4 partition and click Open.
Guide #4: Resize EXT4 partition without losing data
Apart from resizing Ext4 partition, DiskGenius is also able to split and extend Ext4 partition without losing data.
Step 1. Right-click on the Ext4 partition you want to change its size and choose Resize Partition.
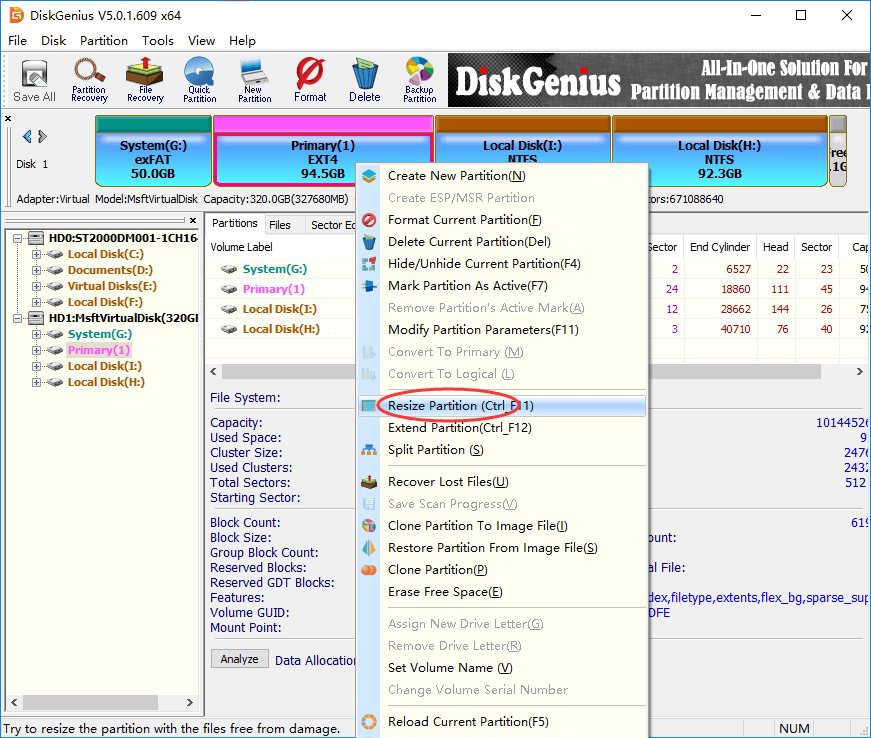
Step 2. Set partition capacity you want to move between partitions and click Start button.
As shown in the screenshot below, DiskGenius is going to move 36.53GB disk space from Ext4 partition to the adjacent NTFS partition Local Disk (I:). The disk space spared from the Ext4 partition can be either kept as unallocated or added to other partitions.
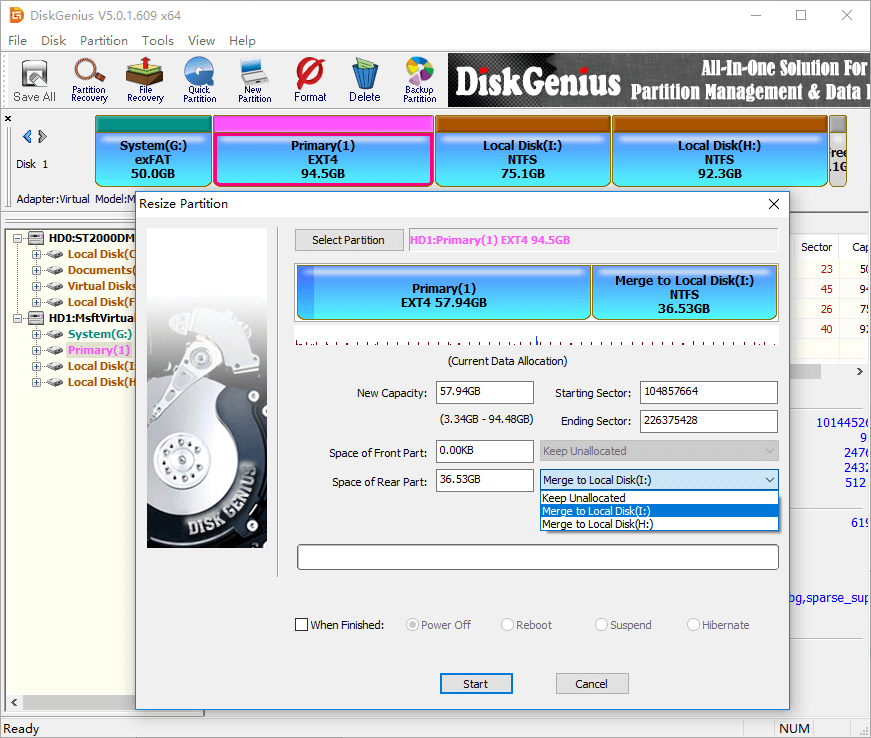
Step 3. Click Yes when DiskGenius prompts rest operations to be done, and it will starts resizing partition.
Guide #5: EXT4 data recovery
Ext4 file recovery and partition recovery is now available for the latest version of DiskGenius. It supports recovering deleted files from ext4 partition, retrieving lost data from formatted or corrupt ext4 partition, and restoring lost or deleted ext4 partition. The following instruction will show you how to recover lost or deleted files from ext4 partition.
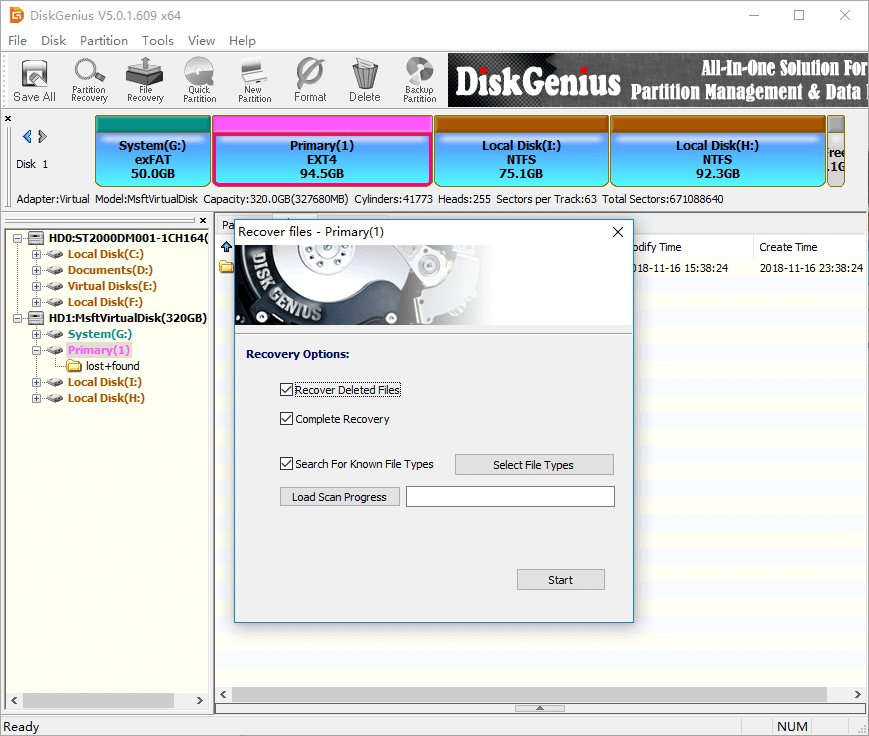
Step 1. Select the ext4 partition where lost files were stored and click File Recovery button from toolbar. This will open Recover Files window, as below.
Step 2. Select recovery options and file types you need and click Start button. Then DiskGenius starts to search for lost data from selected drive.
There are three options on the file recovery window: Recover Deleted Files, Complete Recovery and Search For Known File Types. The default setting gets all of them selected, which can guarantee the software can find out as many files as possible.
Step 3. Preview files during or after scanning process to check if your files can be recovered correctly.
DiskGenius enables users to preview recoverable files listed in scanning result so that you can make sure whether your files are found or overwritten.
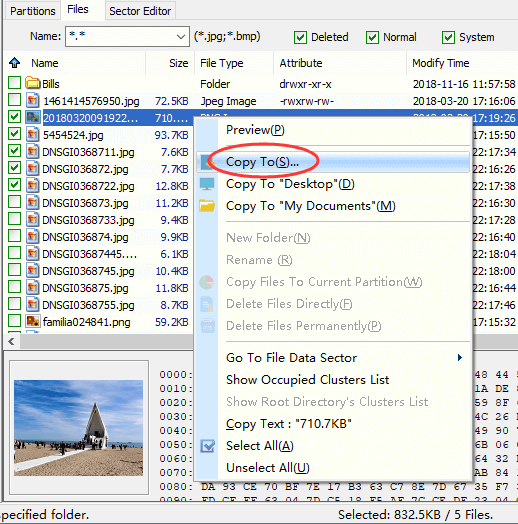
Step 4. Copy and save files you need to get files recovered.
You can select files and folders you want to recover from file list, right-click on selected data and choose «Copy To» option. Then you can select a location which is different from the partition being recovered data, for the recovery process is read-only to original device.
These steps above apply to deleted or lost file recovery only, and you need to perform partition recovery if entire partition gets lost due to hard drive partition, hard drive failure, partition deletion, partition table, etc. Partition recovery function searches for lost partitions and restore them to partition table directly.
Conclusion
With the help of DiskGenius, you can easily and efficiently access and manage Ext4 partition in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8 and Windows 7. So, reading or writing Ext4/Ext3/Ext2 Linux partition from Windows is no longer a complicated thing. Fee download DiskGenius and manage Ext4 partition in Windows now.
FAQs on reading Ext4 in Windows 10
1. Can Windows 10 read Ext4?
By default, Windows 10 does not have native support for reading or accessing Ext4 file systems. The Ext4 file system is commonly used in Linux-based operating systems. However, there are third-party tools and software available that allow Windows 10 to read and access Ext4 partitions.
2. How to format Ext4 in Windows 10?
Formatting an Ext4 partition directly within Windows 10 is not natively supported because Windows does not have built-in tools for formatting Ext4 file systems. However, you can use third-party software DiskGenius to format an Ext4 partition in Windows 10.
3. Why Windows doesn’t recognize Ext4?
Windows doesn’t natively recognize or support the Ext4 file system for a couple of reasons: Windows and Linux operating systems use different file system architectures; Microsoft, the developer of Windows, has not integrated Ext4 support into their operating system, likely due to licensing and compatibility considerations.
4. How do I transfer files from Ext4 to Windows?
To transfer files from an Ext4 partition to Windows, you can follow these steps:
Step 1. Connect the Ext4 drive to a Windows computer and launch DiskGenius.
Step 2. In DiskGenius, select the Ext4 drive, and you can view all files and folders.
Step 3. Select files you want to transfer, right-click selected data and choose «Copy To».
Step 4. Specify a location on your Windows computer and start outputting files.
5. Is EXT4 only for Linux?
The Ext4 file system is primarily associated with Linux and is the default file system for many Linux distributions. It was developed as an extension of the Ext3 file system, introducing improvements in performance, scalability, and reliability. In summary, while Ext4 is primarily associated with Linux, there are options available to enable access to Ext4 partitions from non-Linux operating systems.
6. How do I manage ext4 partition in Windows?
Managing Ext4 partitions in Windows requires the use of third-party software or tools specifically designed for Ext4 file system support. For instance, DiskGenius can help you manage EXT4/3/2 partitions in Windows 11/10/8/7, including, format partition to EXT4/3/2, resize/clone/backup EXT4/3/2 drive, recover lost EXT4/3/2 partitions, etc.
7. How do I view ext4 SD card in Windows?
To view the contents of an Ext4-formatted SD card in Windows, you can use DiskGenius to do the job, for example, write data to SD card, output data from ext4 SD card to another drive, format SD card to EXT4, etc.
Подключение ext4 в Windows
Подключение ext4 в Windows
Если вы используете Windows рядом с Linux, рано или поздно может возникнуть необходимость скопировать файлы из одной операционной системы в другую. При копировании с Windows в Linux проблем не возникнет так как Linux отлично открывает файловые системы семейства NTFS, но вот открыть файловую систему ext4 в операционной системе от майкрософт будет не так то просто.
В этой инструкции я опишу несколько способов подключения ext4 в Windows. Вы можете либо добавить поддержку этой файловой системы в Windows либо просто извлечь из неё файлы с помощью специальной программы.
Подключение ext4 в Windows 10
Сообществом открытого программного обеспечения был разработан открытый драйвер ext4 для windows под названием ext2fsd.
1. Установка драйвера ext2fsd
Загрузить установщик для вашей версии ОС можно с официального сайта программы. Процесс установки не должен вызвать никаких трудностей и сводиться к нажиманию кнопки Далее в мастере установки, как обычно при установке программ в Windows. Интерес представляет только это окно:

Здесь:
- Make Ex2Fsd automatically started when system boots — автоматическая загрузка драйвера во время загрузки системы, желательно включить.
- Enable write support for ext2 partitions — поддержка записи в файловую систему ext2
- Enable force writing support on Ext3 partitions — поддержка записи в файловую систему ext3
Установите необходимые галочки и еще несколько раз нажмите кнопку Далее.
2. Подключение ext4
Главное окно программы выглядит вот так:

Здесь в в списке показаны все доступные разделы, их размер и файловая система. Для того чтобы примонтировать любой из разделов выполните на нем двойной щелчок:

Здесь есть два варианта монтирования:
- Automaticly mount via Ext2Mgr — раздел будет подключен сейчас, но только до перезагрузки
- Mountpoint for fixed disk — постоянное автоматическое подключение раздела при старте системы.
С права от поля способа монтирования можно выбрать букву диска для монтирования.
Также в поле Hiding files with prefix можно указать с какими префиксами файлы нужно считать скрытыми, как вы знаете в Linux считаются скрытыми файлы с префиксом точка. Когда укажите все необходимые параметры нажмите кнопку Apply.
Теперь открыв Мой компьютер вы увидите подключенный диск:

С помощью драйвера Ext2fsd вы можете работать с вашими разделами Linux как с обычными NTFS или FAT.
Извлечение файлов из Ext4 в Windows
Это самый простой способ открыть ext4 в windows 10. С помощью программы DiskInternals Linux Reader вы можете извлечь файлы из раздела с файловой системой Linux не добавляя её поддержку в ядро системы. Скачать программу можно на официальном сайте. Установка программы аналогично предыдущей сводится к нажатию кнопки Далее:

Главное окно программы выглядит вот так:

Здесь вы можете выбрать нужный раздел с файловой системой ext4 и просмотреть все файлы, что там есть:

Чтобы извлечь любой из файлов или папку, кликните по ней правой кнопкой мыши и выберите Save As, затем выберите папку, в которую будет сохранен ваш файл:

Чтобы сохранить структуру папок нужно отметить флажок Save directory structure. Затем дождитесь завершения процесса копирования и можете делать с полученными файлами все что нужно уже в проводнике.
Source
На чтение 4 мин Просмотров 13.2к. Опубликовано Обновлено
В этой статье рассказывается о том, как вы можете получить доступ к разделам файловой системы Linux Ext2, Ext3 и Ext4 в Windows 10 и автоматически сохранить их в проводнике, как все другие разделы NTFS или FAT32. Вы даже можете копировать файлы и записывать новый файлы на эти разделы.
Хотя Windows использует файловую систему NTFS и FAT32, Linux (например, Ubuntu) использует расширенные архитектуры файловой системы Ext 3, Ext4 и т. д. Самое интересное то, что Linux может получать доступ, читать и записывать файлы в файловые системы Windows, а Windows не может получить доступ к файлу Linux — системы. Я имею в виду, что Windows не имеет поддержки для чтения или доступа к разделам Ext3 или Ext4.
Таким образом, если у вас есть система с двойной загрузкой или более, в которой вы можете переключаться между Windows и Linux из меню загрузчика, иногда вам может понадобиться доступ к Linux-дискам / разделам. Или предположим, что вы находитесь в Windows, и у вас есть съемный / жесткий диск, который отформатирован в Ext3, и теперь вам нужно открыть файл внутри него. Или ваша система Linux «зависла», и вам необходимо восстановить важные файлы с помощью Windows. В таких случаях вам необходимо прочитать эти файловые системы без переключения с Windows.
Хотя Windows никогда не интересовалась файловыми системами Linux, к счастью, существуют сторонние диски и инструменты для открытия и чтения разделов Linux из Windows. Мы рассмотрим несколько инструментов в этой статье. Однако здесь мы будем использовать драйвер файловой системы Linux с открытым исходным кодом под названием Ext2Fsd, который предназначен исключительно для поддержки Ext2/3/4 в Microsoft Windows. При этом вы можете автоматически монтировать разделы Ext при загрузке диска, когда вам нужно.
- Размонтируйте разделы Linux Ext4/3/2 в проводнике Windows
- Загрузите Ex2Fsd из sourceforge.net/projects/ext2fsd/.
Содержание
- Подключение EXT4 в Windows 7/8/8.1/10
- Восстановление личных файлов
- Выводы
Подключение EXT4 в Windows 7/8/8.1/10
При установке отметьте «Make Ext2Fsd автоматически запускается при загрузке системы» и нажмите «Далее» и завершите настройку. Он будет автоматически запускать драйвер Ex2Fsd с Windows после следующей перезагрузки.
Запустите диспетчер томов Ext2Fsd. С помощью этого вы можете установить точку монтирования и настройки.
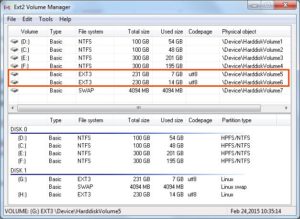
Чтобы назначить последний том, дважды щелкните раздел (или выберите раздел и выберите «Инструменты»> «Управление томами Ex2»), включите «Mountpoint for fixed disk» и назначьте букву диска. Затем нажмите Применить.
При следующей перезагрузке Windows вы увидите, что ваш желаемый раздел Linux монтируется в Проводнике в качестве других стандартных разделов.
Вы также можете указать свое имя, переименовав имя по умолчанию «Локальный диск». Готово!
Примечание 1: Рекомендуется хранить ваши разделы Linux только для чтения, чтобы вы или ваша система не могли повредить системе Linux.
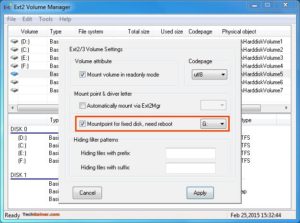
Примечание 2: Если вы не хотите, чтобы Ext2Fsd автоматически монтировал диск в проводнике при загрузке, вы можете отметить «Автоматически монтировать через Ex2Mgr». При этом ваш раздел будет монтироваться только при открытии диспетчера томов Ex2Fsd, как показано ниже:
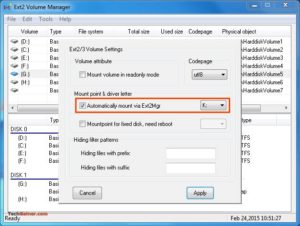
Примечание 3: Во время установки Ext2Fsd, если вы не устанавливали службу Ex2Fsd для автоматического запуска с Windows, вам необходимо вручную запустить службу из меню «Сервис»> «Управление службами»> «Пуск», как показано ниже:
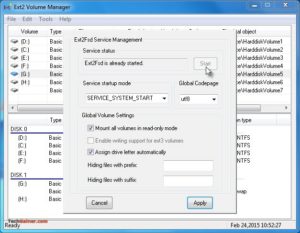
Восстановление личных файлов
Про подключение EXT4 в Windows поговорили, теперь узнаем что делать дальше. Если вы ищете доступ к своим личным файлам, хранящимся в Linux, перейдите в home\name\, как показано ниже:
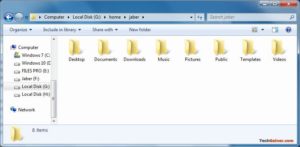
Хотя это руководство сделано в Windows 7, я протестировал его на Windows 10 и способ должен также работать с Windows 8.x в соответствии с его редакциями. Возможность просмотра и чтения всех разделов в обеих ОС — это, безусловно, классная функция для тех, кто использует Linux и Windows на одной машине.
Выводы
Подключение EXT4 в Windows является очень простым. Надеемся, Вам была интересна наша статья об этом — расскажите нам в комментариях.
Также, не забудьте поделится ссылкой на статью в Google+, Facebook, Twitter, Одноклассники или, например, ВКонтакте.
If you’re trying to access ext4 file systems on your Windows 10 machine, you’re not alone. Windows doesn’t natively support ext4, which is commonly used by Linux, but there are ways around this. By using third-party software, you can mount and read ext4 partitions just like any other drive on your computer. Here’s a quick guide: Download and install a tool like Ext2Fsd, start the program, mount your ext4 partition, and voila, you can read your Linux files on Windows. Easy peasy!
Let’s walk through the simple steps to access your ext4 files on Windows 10. By following this guide, you’ll be able to read and manage your Linux partitions effortlessly.
Step 1: Download Ext2Fsd
Head over to the Ext2Fsd website and download the software.
Ext2Fsd is a free tool that acts as a bridge between Windows and Linux file systems. It’s safe and widely used, making it a reliable choice for this task.
Step 2: Install the Software
Run the downloaded installer and follow the on-screen instructions to install the software.
The installation process is straightforward. Just make sure you choose the correct installation folder and agree to the terms and conditions.
Step 3: Launch Ext2Fsd
Open the software after installation is complete.
Once launched, the software interface will display your system’s available storage devices, including those with ext4 partitions.
Step 4: Mount ext4 Partition
In Ext2Fsd, locate your ext4 partition and click “Mount.”
Mounting the partition assigns it a drive letter, allowing Windows to access it just like any other drive.
Step 5: Access Your Files
Open File Explorer and locate the newly mounted drive to access your files.
You can now browse, copy, or move files from your ext4 partition as easily as from any other drive on your system.
After completing these steps, your ext4 partition will appear as a regular drive in Windows Explorer. You’ll be able to access files, transfer data, and manage the contents as needed.
Tips for Reading ext4 on Windows 10
-
Always back up important data before accessing ext4 partitions, as third-party tools can sometimes cause data corruption.
-
Use read-only mode if you’re unsure about writing to the ext4 partition to avoid accidental file changes.
-
Regularly update your Ext2Fsd software to ensure compatibility with the latest Windows updates.
-
Consider using a virtual machine for a more integrated Linux experience on Windows if you frequently use ext4 partitions.
-
Explore other tools like DiskInternals Linux Reader if you encounter issues with Ext2Fsd.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ext4?
Ext4, or the fourth extended file system, is a journaling file system used by Linux. It’s known for its improved performance and reliability over its predecessors.
Can I write to ext4 partitions with Ext2Fsd?
Yes, Ext2Fsd supports writing to ext4 partitions, but use caution as writing can sometimes lead to data corruption if not done properly.
Is using Ext2Fsd safe for my data?
Ext2Fsd is generally safe for reading data, but always backup critical files before writing to an ext4 partition to prevent data loss.
Are there alternatives to Ext2Fsd?
Yes, alternatives like DiskInternals Linux Reader and Paragon ExtFS offer similar functionality for accessing ext4 partitions on Windows.
Why doesn’t Windows support ext4 natively?
Ext4 is a Linux file system, and Windows is designed to support its own file systems like NTFS and FAT32. Third-party tools bridge this gap.
Summary of Steps
- Download Ext2Fsd.
- Install the software.
- Launch Ext2Fsd.
- Mount ext4 partition.
- Access files in File Explorer.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of file systems can feel a bit like traveling to a foreign country. You’re not quite sure how things work, but once you get the hang of it, it’s smooth sailing. Accessing an ext4 file system on Windows 10 might seem daunting at first, but with tools like Ext2Fsd, it’s actually quite straightforward.
While Windows doesn’t natively understand ext4, using the right software makes it possible to bridge the gap, bringing your Linux files right into your Windows environment. Remember, though, with great power comes great responsibility—make sure to back up your data to avoid any potential mishaps.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast eager to explore or someone who just needs to get the job done, learning how to read ext4 on Windows 10 is a nifty skill to have. As technology continues to evolve, so too do the tools at our disposal, offering endless possibilities for cross-platform compatibility and ease of use. So, go ahead—give it a try and unlock the full potential of your dual-OS setup!
Matt Jacobs has been working as an IT consultant for small businesses since receiving his Master’s degree in 2003. While he still does some consulting work, his primary focus now is on creating technology support content for SupportYourTech.com.
His work can be found on many websites and focuses on topics such as Microsoft Office, Apple devices, Android devices, Photoshop, and more.







