,
In Windows, drive letters and labels (or both) are used to make it easy for the end user to identify partitions (volumes) on installed disks.
Instead of that the operating system uses a Global Unique Identifier (GUID) that identifies each volume (partition) individually, for internal purposes. This is because it is difficult to identify specific volumes using only letters and disk labels, and also because some disk partitions (such as the «System» and the «Recovery») are not mapped with letters.
The volume GUID is a unique volume name that is assigned the first time you attach a volume to the operating system and does not change even if the drive letter of the attached volume changes.
The Volume GUID path has the form «\\?\Volume{GUID}\«, where GUID is a globally unique identifier (GUID) that identifies the volume. *
* e.g. \\?\Volume{3558506b-6ae4-11eb-8698-806e6f6e6963}\
In this tutorial you will learn how to find the GUID of all Volumes on your system and how to find out on which physical disk each Volume GUID resides (if you have two or more physical disks). *
* Note: If you want to find out the GUID partition table (GPT) identifier or the master record (MBR) signature of a physical disk, open Command Prompt as administrator and give these commands in order:
- diskpart
- list disk
- select disk number
- uniqueid disk
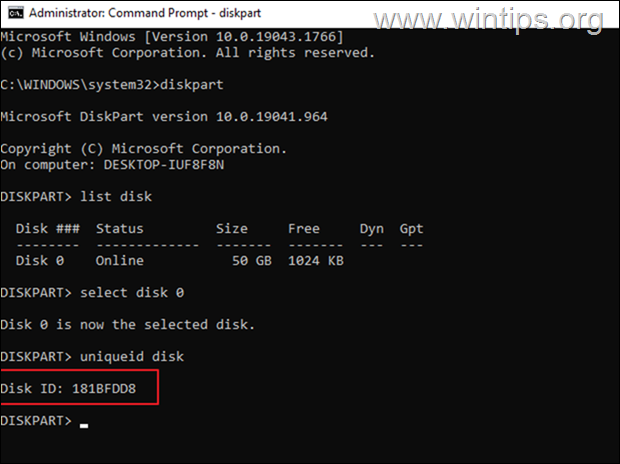
How to Find Volume GUID & View all Volume GUIDs for Each Disk. *
* Note: To find the GUID of all Volumes you can use the method-1 or the method-2 below. But, keep in mind that these methods doesn’t show in which disk each volume GUID located when you have more than one physical disks. If you want to find out that information, use the instructions on method-3.
- Find Volume GUID from Command Prompt.
- Find Volume GUID from PowerShell.
- Find Volume GUIDs per Disk.
Method 1. View all Volume GUIDs on Windows with MOUNTVOL command.
The easiest way to view all volume GUIDs on your system, is to run the «mountvol» command in command prompt.
- mountvol.exe
* Note: «mountvol» command is used to create, delete, or list a volume mount point. But if you give the command with any arguments lists all the Volume GUIDs.

Method 2. View Volume GUIDs with PowerShell.
The second method to find the GUID of all volumes on your system is to use the following PowerShell command: *
-
GWMI -namespace root\cimv2 -class win32_volume | FL -property DriveLetter, DeviceID
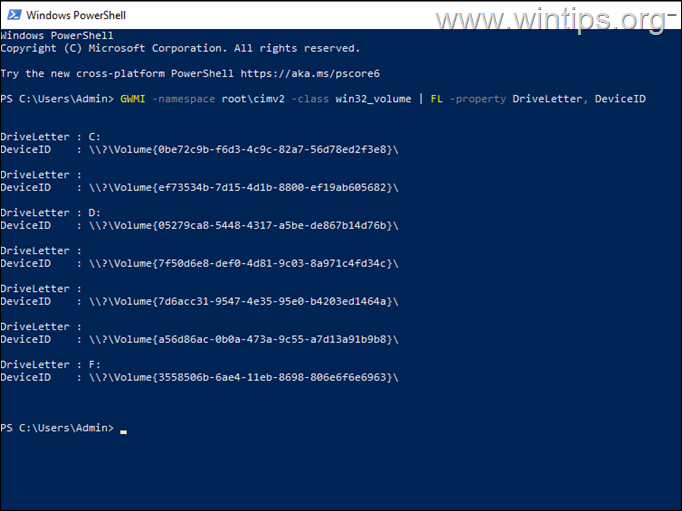
* Note: Additionally you can use the following command, that displays also information about volume’s capacity and free space:
-
GWMI -namespace root\cimv2 -class win32_volume | FL -property Label,DriveLetter,DeviceID,SystemVolume,Capacity,Freespace
Method 3. List Volume GUIDs per Disk.
The above methods help you to view the GUID of each volume on your system, but they do not help you to identify in which physical disk each volume is on when you have more than one hard disks on the system and when the volumes does not have a drive letter (e.g. the «System» or the «Recovery» volume hasn’t not a drive letter).
Since (as far I know), Windows does not offer a single command to retrieve the physical location of each Volume GUID on one or more disks (in which disk the Volume GUIDs are located), I use the DiskExt utility from Sysinternals to perform that task:
1. Download and extract DiskExt to a folder.
2. Open the extracted folder «DiskExt» and select and copy its path to the clipboard.
3. Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
4. In the command prompt window, type CD, press the space bar once, and press CTRL + V to paste the copied path. When done press Enter.
5. Then give this command and press Enter.
-
diskext
6. After executing the command you’ll see all the Volume GUIDs on your system and in which disk is located each of them .(e.g. in Disk 0, Disk 1,etc.)

That’s it! Let me know if this guide has helped you by leaving your comment about your experience. Please like and share this guide to help others.
If this article was useful for you, please consider supporting us by making a donation. Even $1 can a make a huge difference for us in our effort to continue to help others while keeping this site free:
- Author
- Recent Posts
Konstantinos is the founder and administrator of Wintips.org. Since 1995 he works and provides IT support as a computer and network expert to individuals and large companies. He is specialized in solving problems related to Windows or other Microsoft products (Windows Server, Office, Microsoft 365, etc.).
Disks and volumes on Windows 10 have a unique identifier called a GUID. The GUID for volumes is stored somewhere in the registry but you’d have to go digging around to find it. If you need to find either or both the disk and volume GUID on Windows 10, and you prefer the simplest method possible, you can use the Diskpart utility and a simple PowerShell command.
Open Command Prompt with admin rights and enter the following. If you need to find the GUID for an external drive, connect it first.
Diskpart
This will run the Diskpart utility. You now need to list all the disks connected to your system with the command below
list disk
You will get a list of disks that are connected and each disk will be assigned a number. The number is how you will reference a disk in a command so, if you want to find the GUID for disk 0, you need to select it with the command;
select disk number
Once the disk has been selected, run this command to find its GUID.
uniqueid disk
Volume GUID
The easiest way to find the GUID of a volume on your system is to go through PowerShell.
Open PowerShell with admin rights and run the following command. You do not need to modify it in any way. The command will return a list of all volumes and their GUIDs.
GWMI -namespace root\cimv2 -class win32_volume | FL -property DriveLetter, DeviceID
Running the commands listed in the above two sections will not result in any sort of data loss. You can run them for your system’s disk while it is still in use. If you’re apprehensive about running commands from Command Prompt or PowerShell, you can always find an app that can read this data from your system.
It’s also important to mention here that volumes are not the same as drives. A drive may have multiple volumes, and Windows 10 doesn’t assign a GUID to drives. It instead assigns them to volumes. If you run the PowerShell command in the volume GUID section of this article, you will see that the results return more than one GUID for the C and D drive. This is because while the disk in question only had two drives, those drives were divided into multiple volumes.
Once you have the GUID for the disk and volumes on your system, use them wherever you need to.

Fatima Wahab
Fatima has been writing for AddictiveTips for six years. She began as a junior writer and has been working as the Editor in Chief since 2014.
Fatima gets an adrenaline rush from figuring out how technology works, and how to manipulate it. A well-designed app, something that solves a common everyday problem and looks
The disks and volumes in Windows 10 have a unique identifier called a GUID. If you need to find the GUID of a disk or volume in Windows 10, and you prefer the easiest possible way, you can use the Diskpart tool and the simple PowerShell command. Execution of the listed commands will not lead to any data loss. You can run them on your system disk while it is still in use.
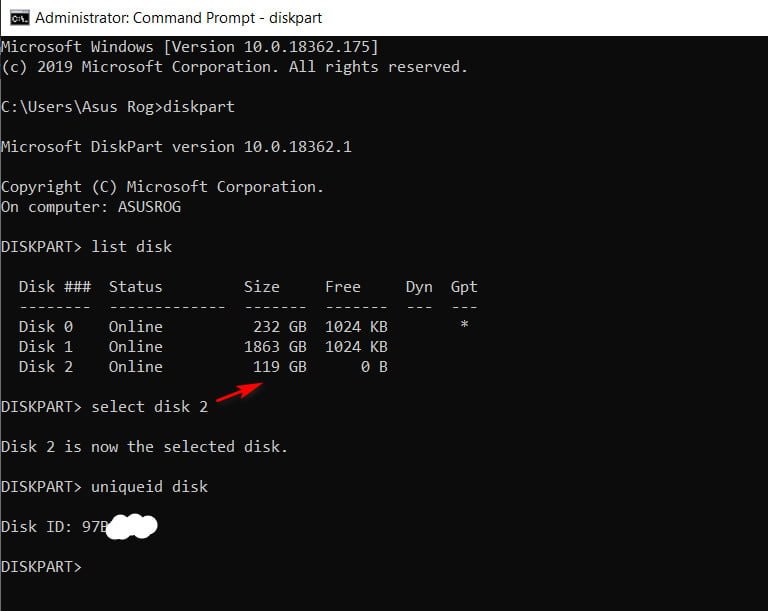
If you need to find the GUID for an external hard drive or is currently in use, then open a command prompt as an administrator and enter the following commands:
Diskpart – Run the tool.
list disk – Shows a list of all currently mounted disks.
select disk 1 – Select the disk you need. The picture shows that I have two of them. I chose the number 1, external hard drive.
uniqueid disk – Shows the hard disk ID.

Related post : How to disable pop-up push-notification sites in browsers
How to find the volume GUID
If you need to find the volume GUID, open PowerShell as administrator and enter the command:
GWMI -namespace root \ cimv2 -class win32_volume | FL -property DriveLetter, DeviceID
Related post : How to Trim a Video in Windows 10 without Using a…
Back to top button
The use of letters to identity volumes and partitions in Windows is something we have inherited from MS-DOS. Drive letters are still used today due to their ubiquity and for compatibility. However, the Windows operating system does not depend on them. Instead Windows uses a GUID to identify each volume or partition. (Windows Home Server, which is actually a custom version of Windows Server 2003 has done away with the use of drive letters completely.)This GUID is called the Volume GUID or the Unique Volume Name. The Volume GUID is assigned the first time the OS encounters a volume and it does not change. This ensures that Windows can always uniquely identify a volume, even though its drive letter has changed.
On systems with a lot of storage you will often run out of drive letters for your partitions and volumes. You can work around this by using mount points e.g., but you can also reference the volume by its GUID directly. This is actually the recommended practice in some situations. When configuring highly available virtual servers in Hyper-V with Windows Failover Clustering, for example.
So how do we find the Volume GUID? The easiest way I have discovered is by the use of the mountvol.exe utility. Running mountvol.exe without any arguments will show you help for the utility, but also the current Volume GUID to drive letter/mount point relationships.
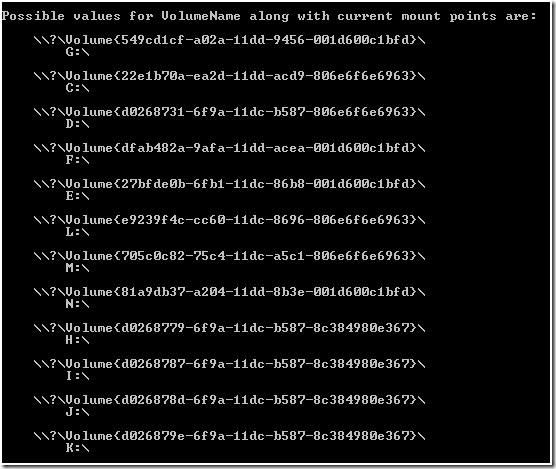
To prove that the volume GUIDs really are the “true” path to the volume, copy one of the strings and past it into Explorer or the Run dialog.
Press enter and you will see the contents of the volume displayed.

(Notice the question mark by the drive icon in the navigation bar and the info pane.)
I have not been able to use the Volume GUID from the command line, but that is also the only limitation I have found. Not strange if you consider the command prompt’s origins.
You can also see all the volume GUIDs for every volume the OS has ever seen under the registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\MountedDevices
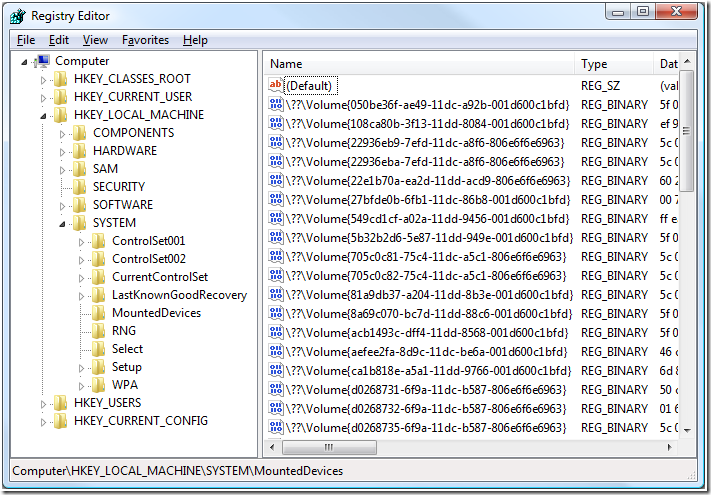
At this location you will also find the “regular” drive letter assignments. They have the form \DosDevices\<drive letter>. If you compare the data in this key for the Volume GUID and the DOS drive letter for a given volume, you will see that they match meaning that they point to the same volume.
Strangely enough, the Swiss army knife of disk and volume management in Windows; diskpart.exe can’t display the Volume GUID. This is something that will change in future releases, hopefully. Diskpart can, however, display another interesting piece of data which resembles the Volume GUID, namely the disk signature. Just as volumes have unique IDs, so do disks (or what Windows perceives as disks). The DETAIL command in diskpart will display the disk signature as the Disk ID. It is an 8 digit hexadecimal number.
The string \\?\ is present in all volume GUIDs and it tells Windows to turn off path parsing. Windows NT/2000/XP/Vista have a maximum path length of 255 characters. It is possible to use more that 255 characters by prefixing the path with \\?\. This enables you to use paths that are up to 32,000 characters long, and is called using the “wide” version of a function. The \\?\ itself is ignored as part of the path. E.g.:
“\\?\C:\Users\Aquaman\Documents\test.docx” will be processed as “C:\ Users\Aquaman\Documents\test.docx”
Various problems with the Volume GUID may occur under some circumstances making Windows unable to boot or access the volume. Some of these situations are documented here: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/959573
В этой небольшом посте, мы рассмотрим основные возможные способы узнать текущую используемую таблицу разделов целевого диска, в операционной системе Windows.
1. Только для Windows 10. Нажимаем комбинацию клавиш Win + X (аналогичного эффекта можно добиться выполнив правый клик по кнопке пуск панели задач) и в открывшемся меню выбираем Windows PowerShell.
2. Выполнить поиск по фразе powershell среди программ в меню пуск. В Windows 10 достаточно нажать комбинацию клавиш Win+Q и в строке поиска ввести powershell.
3. Нажимаем сочетание клавиш Win+R, в открывшемся окошке Выполнить, вводим powershell нажимаем OK.
Чтобы получить информацию о типе таблицы разделов имеющихся дисков системы, в открывшемся окне командной оболочки PowerShell нужно ввести всего лишь одну команду.

Результатом выполнения введенной команды будет таблица, содержащая в себе список всех дисков системы с информацией о них. Последняя колонка «Partition Style«, будет содержать информацию о типе таблицы разделов каждого из имеющихся дисков системы.
Данный способ хорош тем, что не требует прав администратора для выполнения данной команды.
Diskpart
Консольная утилита Diskpart входит в стандартный набор операционной системы Windows начиная с 2000-й версии. Данная утилита так же включена в среду предустановки WinPE, и среду восстановления WinRE операционных систем Windows.
Предназначена данная программа для работы с дисками и разделами системы. И соответственно, она способна выводить информацию о них. Для работы данной программы потребуются права администратора.
Запустить Diskpart можно несколькими способами:
1. Через любую, удобную вам командную оболочку, запущенную с правами администратора. Вводим diskpart и нажимаем ENTER.

2. Нажимаем комбинацию клавиш Win+R, и в открывшемся окне Выполнить, вводим команду diskpart и нажимаем OK.

3. С помощью поиска программ в меню пуск, или поиска в Windows 10. Нажимаем комбинацию клавиш Win+Q и вводим diskpart.

Итак, запустив утилиту Diskpart мы попадаем в ее командный интерфейс. Далее достаточно ввести одну команду.
rem Запускаем Dispart
diskpart
rem Выполняем вывод списка дисков
list disk
Команда выведет список дисков в виде таблицы. Обращаем внимание на последний столбец именуемый GPT, содержащий символ звездочки, если диск указанной строки имеет соответствующую таблицу разделов.
По сравнению с предыдущим способом, определить целевой диск будет немного проблематично, так как из доступной информации, по которой можно определить нужный диск, только его размер. Но из этой ситуации есть выход.
К примеру, вы знаете букву тома (та что отображается в проводнике) целевого диска, и вы хотите посмотреть к какому из дисков он принадлежит. Продолжаем ввод команд.
rem Выводим список томов системы
list volume
rem Выставляем фокус на том под номером 3
select volume 3
rem Снова выводим список дисков
list disk
После повторного вывода дисков, диск с выбранным томом, будет отмечен символом звездочки в качестве префикса. Замечу, что третий том выбран для демонстрации.
В итоге. Если целевой диск содержит в столбце GPT звездочку, то данный диск имеет таблицу разделов GPT. Если звездочки нет, то таблица разделов для данного диска MBR.
Управление Дисками
Оснастка «Управление дисками» это графический инструмент для работы с дисками и разделами. И как свойственно подобному инструменту, он способен отображать свойства выбранных дисков.
Запустить оснастку «Управление дисками» можно запустить, так же, несколькими способами:
1. Для операционной системы Windows 10. Нажимаем комбинацию клавиш Win+X (или правый клик по кнопке пуск), и в открывшемся меню выбираем пункт «Управление дисками«.
2. Нажимаем комбинацию клавиш Win+R, и в открывшемся окне Выполнить, вводим команду diskmgmt.msc и нажимаем OK.

Запустив оснастку «Управление дисками«, нажимаем правой клавишей мыши по интересующему вас диску, и в открывшемся меню выбираем пункт Свойства.
В открывшемся окне свойств выбранного диска, переходим на вкладку «Тома«, в которой обращаем внимание на секцию «Сведения о диске«, а конкретно на пункт «Стиль раздела«.
Значение «Таблица с GUID разделов …» означает, что диск использует таблицу разделов GPT. А значение «Основная загрузочная запись (MBR)» означает, что диск использует таблицу разделов MBR.
Итог
В статье было рассмотрено: Как узнать тип используемой таблицы разделов в ОС Windows? Как узнать тип используемой таблицы разделов в ОС Windows с помощью PowerShell? Как узнать тип используемой таблицы разделов в ОС Windows с помощью Diskpart? Как узнать тип используемой таблицы разделов в ОС Windows с помощью оснастки «Управление дисками«?
