-
Home
-
News
- 2 Ways to Replace GRUB with Windows Boot Manager
By Amy | Follow |
Last Updated
If you are going to replace GRUB with Windows Boot Manager, this post is what you need is it offers you a full tutorial. It collects 2 available methods. Explore the content with MiniTool Partition Wizard now!
Why Do You Need to Replace GRUB With Windows Boot Manager
GRUB is often set as the bootloader when you dual-boot a Linux distro with Windows. This can ensure that there’re no conflicts between the two operating systems in the load-up process. Though GRUB is a versatile and easy-to-use bootloader, you may still want to set Windows Boot Manager as the default because of errors like GRUB not showing in dual boot setup or something else.
Here comes the question: how to switch from GRUB to Windows Boot Manager. Well, you don’t have to worry about it. This post would illustrate the whole process for you.
Further reading:
Windows Boot Manager (BOOTMGR) is a small piece of software that is loaded from the volume boot code. It enables you to boot operating systems including Windows Vista/7/8/10. However, it can prompt you with various errors.
For instance, you will receive errors like BOOTMGR is missing, Boot Manager failed to find OS loader, BOOTMGR is compressed, etc. If you are bothered by issues like that, try using MiniTool Partition Wizard to fix them.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
This free partition manager enables you to rebuild MBR, set the partition as active, check the hard drive for errors, copy disks, and perform other operations that are related to partitions or disks.
How to Replace GRUB With Windows Boot Manager
There are 2 methods to switch from GRUB to Windows Boot Manager for you.
Method 1: Change the Boot Priority Order
A simple way to switch from GRUB to Windows Boot Manager is to change the boot priority order in the UEFI settings of the motherboard. The following steps will show you how to do that in detail.
Step 1: Open Settings by pressing Windows and I keys.
Step 2: Then click Update & Security > Recovery > Restart now (under the Advanced startup section).
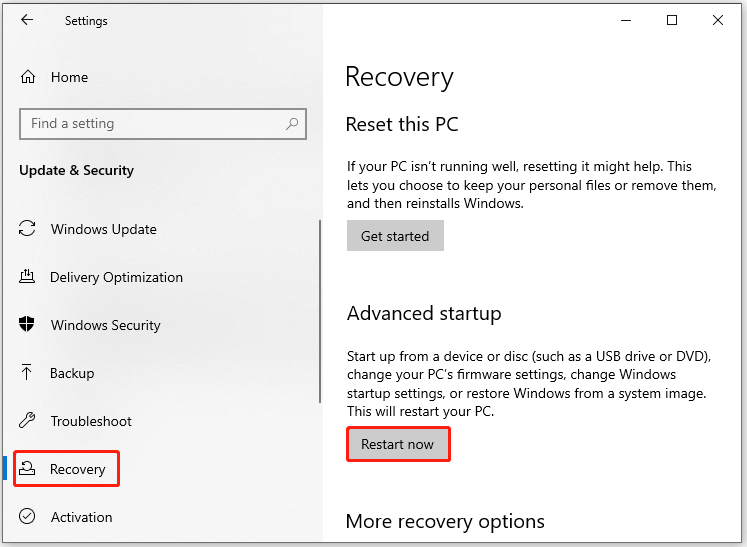
Step 3: Click on Troubleshoot > Advanced options > UEFI Firmware Settings and tap Restart.

Step 4: After the computer restarts, it will enter the UEFI/BIOS setup utility.
Step 5: Navigate to the Boot section and set Windows Boot Manager as the first boot. To do that, click on Windows Boot Manager and keep pressing the “+” key until the option is placed at the first order.
Step 6: Then press F10 and Enter keys to confirm the change and exit the utility.
Method 2: Use EasyBCD to Add Linux to Windows Boot Manager
You can also replace GRUB with Windows Boot Manager via EasyBCD. It is a tool that is capable of controlling your system’s boot process. To be specific, you are able to modify bootloader settings through EasyBCD.
Step 1: Download and install EasyBCD on your computer.
Step 2: Run EasyBCD to enter its main interface and click the Add New Entry option.
Step 3: Click the Linux option under the Operating System tab.
Step 4: Choose GRUB2 in the Type field and type in the name of your Linux distro.
Step 5: Under the Drive tab, select the Linux partition where your Linux system resides. You need to take care because choosing the wrong drive will cause data loss.
Step 6: Tap on the Add (“+” icon) button to confirm your settings and add the Linux distro to the Windows Boot Manager.
Step 7: Restart your computer.
How to replace GRUB with Windows Boot Manager? This post has collected 2 available methods for you. Simply choose one from them to switch from GRUB to Windows Boot Manager.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Having writing articles about computer tech for a long time, I am rather experienced especially on the aspect of computer optimization, PC enhancement, as well as tech terms explanation. The habit of looking through tech forums makes me a great computer issues collector. And then, many articles related to these issues are released, which benefit plenty of users. Professional, effective, and innovative are always the pursuit of an editing worker.
Context
I have Windows 11 installed in the internal SSD of a Lenovo Yoga 710 laptop and Ubuntu is installed on an external USB SSD.
Lenovo UEFIs are known by having lots of bugs and vulnerabilities. One of the bugs is that Lenovo’s UEFI won’t boot from USB drives even when it is configured in the Firmware.
That creates a scenario in which every time I wanted to boot Linux from USB I had to boot into windows, reboot into advanced boot mode, select Ubuntu, and reboot again. These are too many steps for a simple task!
So, I decided to replace Windows Bootloader with GRUB2 to be able to select USB boot or Windows boot directly when computer boots.
Next you have the steps I did to replace the Windows bootloader with Grub2 in the internal SSD.
Steps
Note: These steps have been tested in Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS.
Windows installs the bootloader in a special partition that contains the EFI system. To locate it execute execute fdisk -l /dev/xxxx where xxxxx is the hard drive that contains Windows bootloader.
In this example Windows bootloader is in disk ‘/dev/sda’:
root@ubuntu-builder:~# fdisk -l /dev/sda
Disk /dev/sda: 465,76 GiB, 500107862016 bytes, 976773168 sectors
Disk model: Samsung SSD 860
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: 2E3258621-234G-4452-9851-5AGY98O8C0P8
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/sda1 2048 1085439 1083392 529M Windows recovery environment
/dev/sda2 1085440 1288191 202752 99M EFI System
/dev/sda3 1288192 1320959 32768 16M Microsoft reserved
/dev/sda4 1320960 877888002 876567043 418G Microsoft basic data
/dev/sda5 975566848 976771071 1204224 588M Windows recovery environment
Output shows that EFI System partition is /dev/sda2
Now let’s check if EFI partition is mounted with the command mount -l | grep /dev/yyyyy where yyyyy is EFI System partition
Example:
root@ubuntu-builder:~# mount -l | grep sda2
root@ubuntu-builder:~#
If the output of the command does not show anything it means that partition is not mounted. Create a folder and mount it.
Example:
root@ubuntu-builder:~# mkdir /mnt/efi
root@ubuntu-builder:~# mount /dev/sda2 /mnt/efi
And check it again:
root@ubuntu-builder:~# mount -l | grep sda2
/dev/sda2 on /mnt/efi type vfat (rw,relatime,fmask=0022,dmask=0022,codepage=437,iocharset=iso8859-1,shortname=mixed,errors=remount-ro)
Add the line GRUB_DISABLE_OS_PROBER=false at the end of the file /etc/default/grub. You can edit the file with any text editor like nano /etc/default/grub or vi /etc/default/grub
Example:
# If you change this file, run 'update-grub' afterwards to update
# /boot/grub/grub.cfg.
# For full documentation of the options in this file, see:
# info -f grub -n 'Simple configuration'
GRUB_DEFAULT=0
GRUB_TIMEOUT_STYLE=hidden
GRUB_TIMEOUT=0
GRUB_DISTRIBUTOR=`lsb_release -i -s 2> /dev/null || echo Debian`
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash"
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=""
# To add an entry for Windows 11 using os-prober
GRUB_DISABLE_OS_PROBER=false
Now execute the command os-prober. It will detect the Windows Bootloader and prepare the configuration file for GRUB2:
root@ubuntu-builder:~# os-prober
/dev/sda2@/EFI/Microsoft/Boot/bootmgfw.efi:Windows Boot Manager:Windows:efi
Create a backup of EFI System partition with dd command: dd if=/dev/sda2 of=./efi_backup.image
Example:
root@ubuntu-builder:~# dd if=/dev/sda2 of=./efi_backup.image
202752+0 records in
202752+0 records out
103809024 bytes (104 MB, 99 MiB) copied, 0,438207 s, 237 MB/s
It’s a good idea to copy the file efi_backup.image to a pendrive to be able to restore the partition easily. See ‘Rollback’ section at the end of this page for details.
Install GRUB2 to EFI System partition with grub-install --target=x86_64-efi --efi-directory=/mnt/efi /dev/yyyyy
Example:
root@ubuntu-builder:/mnt/efi# grub-install --target=x86_64-efi --efi-directory=/mnt/efi /dev/sda2
Installing for x86_64-efi platform.
Installation finished. No error reported.
Execute grub-mkconfig -o /mnt/efi/EFI/ubuntu/grub.cfg to create GRUB2 boot menu:
Example:
root@ubuntu-builder:/mnt/efi/EFI/ubuntu# grub-mkconfig -o /mnt/efi/EFI/ubuntu/grub.cfg
Sourcing file `/etc/default/grub'
Sourcing file `/etc/default/grub.d/init-select.cfg'
Generating grub configuration file ...
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-5.15.0-43-generic
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-5.15.0-43-generic
Found linux image: /boot/vmlinuz-5.15.0-30-generic
Found initrd image: /boot/initrd.img-5.15.0-30-generic
Memtest86+ needs a 16-bit boot, that is not available on EFI, exiting
Warning: os-prober will be executed to detect other bootable partitions.
Its output will be used to detect bootable binaries on them and create new boot entries.
Found Windows Boot Manager on /dev/sda2@/EFI/Microsoft/Boot/bootmgfw.efi
Adding boot menu entry for UEFI Firmware Settings ...
done
Reboot you computer and it will show the GRUB2 boot menu. In case it didn’t, do a rollback as explained next.
Rollback
Boot the computer with an Ubuntu Live USB.
Insert the pendrive with the file efi_backup.image that you created in backup step, mount it, and go to the directory where file is stored.
Next execute the command to restore the EFI Partition with the backup dd if=./efi_backup.image of=/dev/yyyyy
Example:
root@ubuntu-builder:~# dd if=./efi_backup.image of=/dev/sda2
202752+0 records in
202752+0 records out
103809024 bytes (104 MB, 99 MiB) copied, 1,52248 s, 68,2 MB/s
Reboot you computer and it will use again the Windows bootloader.
You are here: Home / Windows / How To Install Grub Bootloader In Windows 10? – Complete Guide
Plenty of users have dual boot in their PCs. Most Ubuntu users have a Grub bootloader for booting. However, many users have recently reported that a Windows update overrides their Windows Boot Manager. This prevent users from booting in Ubuntu after updating Windows.
In this article, I have discussed how to install Grub bootloader in Windows 10 after a Windows update overrides it. By following the steps in this article, you will be able to fix Grub after Windows 10 upgrade.
Also learn how to convert MBR to GPT using MBR2GPT Windows 10 tool from here.
It is nuisance that a Windows update overrides the Windows Boot Manager to default boot using NT bootloader. After the Windows Boot Manager is overridden, it cannot recognize Ubuntu and thus cannot boot into it. Not only Windows update, but installing Windows after Ubuntu also does the same thing.
There is another case why your PC won’t boot into Ubuntu and that’s due to a faulty Grub file. In this case, you will have to repair Grub in order to fix this problem. I have given steps for both the cases below. Follow them carefully and you should be able to fix Grub after Windows 10 upgrade, fresh install, or a faulty Grub file.
1) Faulty Windows Boot Manager
The first case is the faulty Windows Boot Manager that occurs due to a Windows update or fresh Windows installation. To fix this issue, you will have to repair Grub from Windows. To do that, follow the steps given below:
- Boot into Windows 10.
- Press the Windows + R keys to open the Run utility.
- Type cmd and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open an elevated Command Prompt.
- Now, type the following command and press Enter:
bcdedit /set {bootmgr} path \EFI\ubuntu\grubx64.efi
- After you run the above command, it will change the bootloader back to Grub.
- Restart your PC and you should be greeted with the Grub Menu.
However, there is a chance that after following the above steps you get the “System Bootloader not found” error. To fix this, you will have to disable the secure boot through UEFI firmware. To do it, follow the steps given below:
- Reboot the PC.
- Press the F2 or F10 key to open the Firmware settings during the boot screen.
- Disable the secure boot. This option will differ for each system as the firmware settings will be different.
After you have disabled the secure boot, you should now boot into the Grub menu. From there you can boot into Ubuntu.
2) Repair Faulty Grub File
Sometimes a faulty Windows Boot Manager is not responsible for the Grub bootloader not working. It can also be due to a faulty Grub file. If the above step doesn’t allow you to use the Grub boot loader, it is likely for this reason. Now to fix it, you will have to use the Boot Repair. To use it, you will have to boot into Ubuntu, which you cannot do currently.
So, you will need a bootable USB or Ubuntu live CD. Download the Ubuntu ISO image from here and use any Bootable USB software to flash the image on your USB. Now, plug in the bootable USB or enter the Ubuntu live CD and restart your computer. After the computer restarts, follow the steps given below:
- After you restart, select the Try Ubuntu without installing option in the booting screen to boot into Ubuntu.
- Once, you boot into Ubuntu, open the Command line.
- Type the following command and press Enter after finishing it:
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair && sudo apt-get update
This command will add all the Boot Repair tool’s repositories and also update them. - Now, type the following command and press Enter to download the Repair tool:
sudo apt-get install -y boot-repair - Once the boot-repair file is downloaded, type the following command and press Enter to run it:
boot-repair
The above steps will run the Boot Repair tool and it will automatically scan the disks in your system. After the scan is finished, the Boot Repair dialog will provide you with two options. Click on the Recommended repair option. Follow the on-screen information to complete the process. Once the repair tool is finished running, restart your PC.
Wrapping Up
That’s it. Now you know how to install Grub bootloader in Windows 10 after a Windows update. The above steps should do the job. If you have any questions related to this article, ask them in the comment section below.
Как вернуть меню выбора ОС после установки Windows рядом с Linux? Рассказываем о двух способах восстановления загрузчика GRUB — для новичков (с утилитой boot-repair) и для продвинутых пользователей (с помощью chroot).
Поставили Windows рядом с Ubuntu, и теперь можете запустить только ОС от Майкрософт? Рассказываем, как восстановить загрузчик GRUB после установки Windows 10 или 11 — вам хватит 20 минут, даже если вы новичок в администрировании VPS.
Аренда VPS/VDS виртуального сервера от AdminVPS — это прозрачная и честная услуга с доступной ценой
Представьте: вы установили Ubuntu, настроили систему, а потом решили поставить Windows рядом. Но после перезагрузки вместо привычного меню GRUB (grand unified bootloader) вы увидите только загрузчик Windows. Это происходит потому, что Windows не дружит с альтернативными загрузчиками: при установке она перезаписывает главную загрузочную запись (MBR) или заменяет файлы в разделе EFI. И если GRUB, стандартный загрузчик для Linux, может работать с несколькими ОС, то загрузчики NTLDR (Windows 11) и Bootmgr (Windows 10) не умеют. Когда вы ставите Windows после Ubuntu, они просто «не видят» ОС, установленную первой.
Что нужно знать перед восстановлением GRUB
Прежде всего разберёмся с базовыми понятиями — это поможет избежать ошибок и сэкономит время.
UEFI или BIOS
Современные компьютеры используют два типа firmware (микропрограммы для управления железом):
- BIOS — это устаревший стандарт, загрузчик записывается в первый сектор диска (mbr);
- UEFI — современная замена BIOS, работает с разделом EFI (fat32), где хранятся файлы загрузчиков в формате .efi.
Чтобы проверить, какой режим на вашем компьютере, зайдите в bios/uefi (нажмите клавишу del, f2 или f12 при запуске). Если в настройках есть пункты Secure Boot, UEFI Mode — значит, у вас используется UEFI.
Или выполните в Linux:
ls /sys/firmware/efi Если директория существует — система загрузилась через UEFI.
Live USB с Linux
Чтобы восстановить GRUB, понадобится загрузочная флешка с любым дистрибутивом (Ubuntu, Fedora, Mint).
Как создать Live USB:
- Скачайте iso-образ с официального сайта ОС.
- Создайте Live USB с помощью специальных программ:
- Rufus (на Windows) — выберите «GPT для UEFI» или «MBR для BIOS» в зависимости от прошивки вашего компьютера;
- BalenaEtcher (на Linux/Mac).
- Проверьте целостность образа после записи (в некоторых программах есть опция «verify»).
Как восстановить GRUB из-под Windows: два способа
Восстановление через boot-repair (для новичков)
Если вы не хотите работать в терминале, воспользуйтесь утилитой boot-repair. Она автоматизирует 90 % работы.
Шаг 1. Загрузка с Live USB
- Вставьте флешку, перезагрузите компьютер.
- Нажмите клавишу выбора загрузочного устройства (обычно f12, ESC или f8).
- Выберите флешку в меню.
Если у вас UEFI, загружайтесь в режиме UEFI, а не в Legacy! Иначе раздел EFI не будет обнаружен.
Шаг 2. Установка boot-repair
- Откройте терминал в Live-системе.
- Добавьте репозиторий и установите утилиту (далее все команды выполняются в режиме суперпользователя):
add-apt-repository universe # добавляйте репозиторий в Ubuntu до версии 22.04
apt update
apt install -y boot-repair Шаг 3. Запуск и настройка
- Запустите boot-repair:
boot-repair - Выберите «recommended repair».
- Следуйте инструкциям на экране: утилита сама определит установленные ОС, восстановит GRUB и обновит конфигурацию.
Если возникли ошибки:
- проверьте подключение к Интернету (boot-repair иногда скачивает дополнительные пакеты);
- убедитесь, что live-система загружена в правильном режиме (uefi/bios).
Ручное восстановление через chroot (для продвинутых пользователей)
Если первый метод не сработал или вы хотите понять процесс изнутри, восстановите GRUB вручную.
Шаг 1. Определение разделов
- Загрузитесь с Live USB.
- Откройте терминал и узнайте список дисков:
fdisk -l или
lsblk -f Команда lsblk -f показывает типы файловых систем и точки монтирования.
- Пример вывода lsblk:
NAME FSTYPE LABEL UUID MOUNTPOINT
sda
├─sda1 ntfs Windows ABCD-1234
├─sda2 ext4 Ubuntu 5678-90AB
└─ sda3 vfat ESP CDEF-1234 Обратите внимание на:
- корневой раздел Linux (ext4, btrfs и т. д.) — нам нужен именно он;
- раздел EFI (vfat) — если система на UEFI;
- раздел подкачки (swap) — не нужен для восстановления.
Шаг 2. Монтирование разделов
- Создайте точку монтирования:
mkdir /mnt/Linux - Примонтируйте корневой каталог с Ubuntu:
mount /dev/sda2 /mnt/Linux Для UEFI примонтируйте каталог EFI:
mount /dev/sda3 /mnt/Linux/boot/efi Если у вас отдельный раздел /boot, монтируйте его:
mount /dev/sdaX /mnt/Linux/boot Шаг 3. Вход в chroot
Chroot (change root) — это команда, которая изменит видимый корневой каталог, чтобы вы вошли в систему из live-окружения.
- Привяжите системные директории:
mount --bind /dev /mnt/Linux/dev
mount --bind /proc /mnt/Linux/proc
mount --bind /sys /mnt/Linux/sys - Войдите в среду chroot:
chroot /mnt/Linux Шаг 4. Установка GRUB
- Если прошивка BIOS (MBR):
grub-install /dev/sda # здесь sda — диск, а не раздел
update-grub - Если прошивка UEFI (GPT), убедитесь, что пакет grub-efi установлен:
apt install grub-efi-amd64Перед grub-install нужно обновить загрузочный список в efibootmgr, иначе в некоторых UEFI-системах GRUB не будет загружаться:
efibootmgr -c -d /dev/sda -p 1 -L "GRUB" -l "\EFI\GRUB\grubx64.efi"Здесь -d /dev/sda — диск, -p 1 — номер EFI-раздела (уточните их с помощью lsblk).
Установите GRUB в раздел EFI:
grub-install --target=x86_64-efi --efi-directory=/boot/efi --bootloader-id=GRUB- Обновите конфигурацию:
update-grub - После update-grub в выводе должны появиться строки «found Windows» или «found os probe entries».
Шаг 5. Выход и перезагрузка
- Выйдите из chroot:
sync # запись данных
exit - Отмонтируйте разделы:
sudo umount -R /mnt/Linux- Перезагрузите компьютер.
Возможные проблемы и их решение
Даже если вы всё сделали правильно, могут возникнуть проблемы.
GRUB не видит Windows
Причина: os-prober не активирован (утилита для автоматического обнаружения установленных ОС).
Решение. В /etc/default/grub раскомментируйте строку:
GRUB_DISABLE_OS_PROBER=false Установите os-prober:
apt install os-prober Обновите загрузчик (update-grub).
Ошибка «grub-install: error: cannot find efi directory»
Причина: неправильно указан путь к разделу EFI.
Решение. Проверьте, примонтирован ли раздел EFI в /boot/efi. Проверьте тип раздела: он должен быть vfat (FAT32).
Загрузчик установился, но система не загружается
Причина: неверный порядок загрузки в uefi/bios или повреждённые файлы GRUB. Также включённый Secure Boot может блокировать работу GRUB.
Решение. Зайдите в настройки UEFI/BIOS и выберите GRUB в качестве первого загрузочного устройства. Отключите Secure Boot в UEFI. Если это не помогло — переустановите GRUB через chroot.
Как избежать проблем в будущем
- Если планируете устанавливать две операционные системы, то сначала установите Windows, потом Linux.
- Создайте резервную копию EFI/MBR.
Для BIOS:
dd if=/dev/sda of=backup.mbr bs=512 count=1 Для UEFI — просто скопируйте содержимое раздела EFI в место для хранения.
- Создайте отдельный раздел EFI для Linux. Это минимизирует конфликты с Windows.
Заключение
Восстановить загрузчик GRUB после установки Windows — задача, которая кажется сложной только на первый взгляд. Даже если вы новичок, boot-repair справится за пару кликов. Для тех, кто хочет глубже разобраться в процессе, подойдёт ручной способ через chroot.
Наши технические специалисты помогут вам определиться с конфигурацией и настроят ваш VPN-сервер под ключ, если это будет необходимо.
Читайте в блоге:
- Как поменять TTL для раздачи Интернета: настройка Default TTL и изменение значения на 64 или 65
- Что такое директория в Linux
- Как сменить владельца папки и изменить права доступа в Linux
GNU GRUB is a powerful bootloader that can be used to boot almost any operating system on your computer. It can even boot operating systems directly from an ISO file stored on your hard drive. It is regularly updated by open-source community of developers and is completely safe to use on your Windows PC. The only problem with GRUB is that is it not so easy to install on a system that already has Windows installed.
Fortunately, you can manage to install GRUB on any Windows PC running Windows 10 without any hassles using an open-source tool called Grub2Win. From the installation to the setup of boot menu, it makes everything easy for users of all experience levels. It supports both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows. It supports older BIOS and newer EFI systems. It supports both GPT and MBR partitions.
Based on your hardware and operating system, it downloads the relevant GRUB files automatically saving the user from all the headache. During the setup, you can choose a folder on your system drive where GRUB files are kept, you can choose to create a desktop shortcut and if you want to copy GRUB modules to the EFI partition.

After the installation, you can launch Grub2Win and it will display you the GRUB menu as it appears at the boot. From this interface, you can change the order of the menu entries as they are displayed at boot time. You can also manage, add, edit or delete entries from this list.
You can add entries for a number of supported operating systems like Windows, Android, Debian, Fedora, Manjaro, Mint, Slackware, Suse, Ubuntu, etc. You can also add many tools like BootInfo and Clover to the boot menu. It supports IsoBoot using which you can boot directly from an ISO file containing Linux.
Using Grub2Win makes is very easy to install GRUB on Windows. Furthermore, it helps you manage all the GRUB entries and settings. This way you can boot into dozens of operating systems on the same PC without any hassles.
You can download Grub2Win from https://sourceforge.net/projects/grub2win/.
