Уровень сложностиПростой
Время на прочтение8 мин
Количество просмотров300K

Каждый владелец компьютера сталкивался с шумом вентиляторов. Хорошо, когда они качественные, не шипят и не гудят, а материнская плата каким-то чудом сама управляет ими в оптимальном режиме, и все довольны.
Но зачастую всё совсем не так. Запуская даже лёгкую нагрузку, вентиляторы взвывают на пару секунд, а иногда какой-то Карлсон на определённых оборотах входит в резонанс с корпусом, и здесь хоть вешайся.
Казалось бы, скачай софт от материнской платы, настрой всё и будь доволен? Все те, кто реально пользовался софтом от материнских плат, прекрасно понимают, насколько ошибочно это предложение, а также насколько софт от вендоров громоздкий, кривой и негибкий.
В этой статье я опишу очень небольшую утилиту для управления вентиляторами в ПК, которая поразила меня своей гибкостью, и вот уже многие годы является второй в списке на установку в свежую систему. Почему второй? Потому что первым делом в систему ставится браузер, желательно огнелис.
Загрузка и установка
Для скачивания софта можно пройти как на официальный сайт приложения, так и на GitHub-страницу, где выкладываются релизы. Да, к сожалению, софт закрытый и не имеет открытого исходного кода, но зато на том же гите можно открыть Issue, если какая-то из ваших железок не поддерживается или работает неправильно.
Как и любой софт, который попадает на мой ПК, этот не оказался исключением и перед запуском был просканирован антивирусами. Единственная угроза была в исполняемом файле и то от ноунейм-антивируса с приставкой AI в названии (отчёт virustotal).
Никаких специальных установщиков здесь нет. Просто распаковываем архив в папку, которая никуда не будет перемещаться (например, C:/FanControl) и запускаем FanControl.exe. Программа требует права администратора!
Перед работой я советую как минимум выключить софт от материнской платы, который позволяет управлять вентиляторами! Но лучше всего будет его удалить насовсем, так как он более не пригодится.
Если вы также планируете управлять вентиляторами ВИДЕОКАРТЫ, то сто́ит удалить софт для видеокарты от вендоров, а при использовании MSI AFTERBURNER заранее выключить программное управление вентилятором в настройках!
После запуска программа просит единожды согласиться с условиями её использования.

Сканирование устройств и начало работы
А далее предложит произвести автоматическое определение доступных к управлению вентиляторов, их датчиков оборотов, а также температурных датчиков в системе. Обязательно соглашаемся, иначе всё это придётся делать вручную.

На следующем этапе нам предложат выбрать сенсоры, которые будут определены программой.
Чем больше сенсоров знает софт, тем больше времени и производительности ПК будет уходить на сбор их данных (на самом деле там абсолютные копейки), но при этом больше датчиков будет доступно для более гибкой настройки.
Здесь выбор зависит от конкретных задач компьютера. Например, на скриншоте ниже стоят дефолтные галочки, которые идеальны для обычного домашнего ПК.
Если планируется управлять охлаждением у NAS, где нет видеокарты, но при этом важны температуры дисков, то можно поставить галку на Storage. Если вы занимаетесь разгоном DDR5-памяти или у вас горячая серверная ECC-память, то галка Memory позволит собирать данные с планок, которые имеют датчики температуры.
Отдельно стоит сказать про галки для видеокарты Nvidia. По стандарту сбор данных и управление идёт через NvApiWrapper. Это абсолютно нормальный способ управления вентиляторами в рамках разрешённых параметров, НО иногда эти заводские рамки не очень адекватные. Например, ваша видеокарта начального уровня и так слабо греется, но не имеет функции Fan Stop, которая может полностью выключить вентилятор, дабы карта работала в пассивном режиме.
В таком случае здесь предусмотрена галка Nvidia 0% hardware curve override, которая позволяет полностью игнорировать все ограничения производителя и управлять вентиляторами на полную. Но будьте с ней осторожны! Вентиляторы требуют разгона перед запуском, и неправильная настройка кривой вентилятора может обернуться повреждением железа!

После выбора нужных датчиков программа проведёт тестирование и соотношение датчиков и вентиляторов. Этот процесс обычно занимает не более 2 минут.

По прошествии процесса калибровки нам предложат назвать каждый из вентиляторов. Для удобства есть ползунки, которые управляют оборотами вентилятора в данный момент.
Тянем ползунок на максимум, слушаем/смотрим, какой вентилятор закрутился быстрее остальных, определяем его и вписываем удобное нам название.

Когда все вентиляторы определены и названы как нам надо, можно нажать ОК. Тогда откроется следующее окно с базовыми настройками приложения.
Полезно будет включать его автозапуск в свёрнутом виде, а также поставить галку на скрытие несуществующих вентиляторов (это можно сделать далее).
К сожалению, здесь нет возможности поставить автозапуск приложения, но о том, как это сделать, я также напишу далее.

Быстрый старт
Перед подробным и скучным описанием каждого из элементов, я опишу простейший процесс настройки процессорного вентилятора, который будет брать температуру с самого горячего ядра процессора и настраивать вентилятор по графику.
Нажимаем на зелёную кнопку + в правом нижнем углу и выбираем Graph.
Для удобства меняем его название на что-то понятное, и в графе Temperature Source выбираем CPU CORE MAX (температура самого горячего ядра).

Теперь в карточке процессора выбираем наш график и нажимаем на переключатель, дабы процессорный вентилятор начал соблюдать значения из этого графика.
Далее на карточке с графиком нажмём на кнопку EDIT и настроим график как душе угодно.
В открывшемся окне можно настроить кривую соотношения скорости вентилятора и температуры процессора (или другого узла, который вы выбрали в поле источника температуры).

Поздравляю, вы прекрасны! Теперь ваш вентилятор процессора управляется графиком, который вы выставили сами!
Ну и под конец настройки стоит добавить софт в автозагрузку. К сожалению, никаких галочек в софте нет, поэтому делаем по старинке. Вызываем запуск приложения через Win-R, вписываем shell:startup и жмём Enter. У нас откроется папка автозапуска. В неё можно положить ярлык, ведущий на EXE-файл программы.
ОБЯЗАТЕЛЬНО СОХРАНЯЕМСЯ (CTRL+S), так как программа не сохраняет ничего сама!
Изучаем разделы подробнее
На главном экране программы всё минималистично, и пользователю открывается вид на 3 набора карточек.
- В первом (Controls) будет список вентиляторов, которыми программа смогла управлять.
- Во втором (Speeds) будут отображаться обороты того или иного вентилятора, которые программа смогла найти в системе.
- В третьем (Curves) можно увидеть созданные нами карточки для управления вентиляторами.

Описание карточек из раздела Controls
▍ Раздел Controls
Как уже говорил ранее, в панели Controls расположены карточки вентиляторов, которыми программа смогла управлять.
На само́й карточке доступны базовые данные:
- Поле ИМЯ, которое можно редактировать после нажатия на него
- Поле Curve, в которое мы далее будем указывать кривую для работы вентилятора
- Переключатель поля Curve (если он выключен, то вентилятор управляется материнской платой, а не программой)
- Текущий процент оборотов
- Текущие обороты в секунду
- Стрелка у поля оборотов, которая открывает подробные настройки поведения вентилятора
- Многоточие, открывающее дополнительные настройки вентилятора
Если нажать многоточие, то откроется список настроек.
- Manual control — переключает управление вентилятором в простой ползунок 0–100% без какой-либо привязки к датчику
- Force apply
- Hide — прячет вентилятор из списка
- Remove paired sensor — «развязывает» сенсор и вентилятор, просто убирая значение RPM из карточки
- Pair speed sensor auto… — автоматически привязывает сенсор к вентилятору
- Detect fan start auto… — автоматически настраивает минимальные обороты, с которых стартует вентилятор
- Detect fan stop auto… — автоматически определяет обороты, на которых вентилятор выключается

Если же нажать на стрелочку в карточке, то откроются настройки вентилятора. Некоторые из них были определены ещё при первом запуске программы при калибровке.
- Step UP — максимальная скорость повышения оборотов % в секунду
- Step UP — максимальная скорость понижения оборотов % в секунду
- Start % — с какого %PWM вентилятор стартует
- Stop % — с какого %PWM вентилятор останавливается
- Offset % — сдвиг %
- Minimum % — минимальный процент оборотов ниже которого нельзя выставить значения
Я бы не трогал все настройки, кроме первых двух, так как эти параметры были подобраны софтом во время первичной калибровки вентиляторов.
А вот первые настройки можно и нужно покрутить. Например, можно настроить так, что при резкой нагрузке (вы открыли тяжёлую программу, но её загрузка длилась буквально пару секунд) вентилятор наращивал свои обороты не резко, а очень плавно, буквально по паре процентов в секунду, за счёт чего вы не услышите резкий и секундный взлёт самолёта.
Вторая настройка (step Down) позволяет настроить скорость снижения оборотов вентилятора после активной нагрузки. Например, вы скомпилировали программу, нагрузка на процессор резко упала, как и его температура, вентилятор как обычно сбросил обороты, но при этом VRM-платы, SSD, чипсет и даже диски могут всё ещё быть разогретыми. Плавное падение оборотов позволит продуть систему после такой активной нагрузки, что точно лишним не будет (есть другой способ сделать это же плавное затухание, но сохранив «отзывчивость» вентилятора, об этом поговорим далее).
▍ Раздел Speeds
Карточки в разделе Speeds буквально отображают скорость того или иного вентилятора. Настроек здесь нет, можно разве что переименовать карточку, либо совсем скрыть её.
Подробное описание карточек из разделов Curves и Sensors
▍ Раздел Curves
Карточки здесь можно переименовывать, скрывать, а также удалять и создавать.
Сто́ит сказать, что здесь очень гибкая система, которая позволяет брать данные с нескольких датчиков температуры, применять базовую математику к значениям, а потом использовать полученные данные и по кривой конвертировать их в процент вентилятора, притом любого!
▍ Раздел Sensors
Данный раздел появится, когда мы добавим новые карточки, которые выступают в качестве сенсоров. Их значения можно использовать в карточках Curves как источник температуры. При этом карточки этого раздела позволяют манипулировать данными с сенсоров.
Изучаем карточки Curves и Sensors
Начнём с раздела Sensors, так как здесь меньше всего карточек, но именно они позволяют манипулировать данными с нескольких датчиков.
▍ Sensors — Mix
Данная карточка является одной из основных при настройке корпусных вентиляторов. Она позволяет взять данные с неограниченного числа датчиков в системе и произвести базовую математику с этими данными.
- Average — среднее значение температуры между выбранными датчиками
- Max — максимальное значение температуры между выбранными датчиками
- Min — минимальное значение температуры между выбранными датчиками
- Sum — сумма температуры всех выбранных датчиков
- Sabstract — вычесть значение темперы всех датчиков
При этом в карточку MIX можно добавлять не только реальные сенсоры, но и результаты других SENSOR-карточек.

▍ Sensors — Time Average
Название карточки говорит само за себя. В настройках карточки можно указать датчик и время усреднения его результатов.
▍ Sensors — Offset
Данная карточка позволяет добавить значение к температуре с датчика. Офсет может быть как положительный, так и отрицательный. Это полезно в случае таких устройств, как чипсет, который на бюджетной плате может быть часто разогрет до 50 градусов, но при этом греется под нагрузкой в редких ситуациях (например, чтение и запись дисков, подключённых через чипсет), но при этом есть желание реагировать на его температуру при помощи вентиляторов.
▍ Sensors — File
Очень интересная карточка, которая позволяет считывать значение из файла и предоставлять его как сенсор в программе FanControl.
Достаточно прямо в программе создать и сохранить файл в любое удобное место. Поддерживаются как целые числа, так и числа с плавающей запятой, но кол-во знаков после запятой ограниченно одним.
▍ Curves — Linerar
Позволяет получить простейший график из двух точек. Бонусом доступна настройка гистерезиса, а также скорости реакции.
▍ Curves — Graph
Более сложный график с неограниченным кол-вом точек.

▍ Curves — Mix
Всё та же карточка MIX, как из сенсоров, но теперь позволяет манипулировать оборотами, полученными из карточек curve. Все настройки также идентичны карточке Sensors — mix.
▍ Curves — Trigger
Карточка переключает значение оборотов между IDLE и LOAD состояниями, по преодолению порогов IDLE TEMP и LOAD TEMP.
▍ Curves — Flat
Просто значение оборотов в процентах. Можно использовать для внесения значения в дельнейшие расчёты в остальных кривых или сенсорах.
▍ Curves — Sync
Позволяет получить скорость вентилятора (в процентах) и использовать его в дальнейших расчётах. Также можно указать офсет.
▍ Curves — Auto
Простейшая и буквально линейная кривая между минимальным и максимальным значением. Отличается от Linear карточки, чуть более гибкими настройками и гистерезисом.
Заключение
Поздравляю! Теперь вы знаете об удобной программе, которая позволяет получить один из самых простых, быстрых и гибких способов управления охлаждением в системе.
Скидки, итоги розыгрышей и новости о спутнике RUVDS — в нашем Telegram-канале 🚀

All the major hardware components of a PC, majorly CPU & GPU, generate an immense amount of heat during their working, especially when heavy resource-consuming applications are running. Heat is the main culprit behind permanent hardware damage due to over-heating, as dust just works as a catalyst for it. Primarily, an effective cooling system is required to handle the heating issues. To solve this issue, CPU fans are introduced, which cools down the heating effectively & efficiently. Today, a large variety of fans are available in the market, from small capacity to high capacity. And the PC fan speed is controllable by using various applications. So, keep reading this article to know how to perform fan control Windows 10 in detail.

A CPU fan is a crucial part of the computer hardware found in the motherboard, which can be a life-saver. Its most heroic function is to continuously cool down the hot CPU and prevent it from permanent damage due to burning out. It’s the CPU fan that saves the CPU and other nearby components from damage due to overheating and keeps the PC running.
- It not only provides cooling but also prevents dust from accumulating in the CPU.
- The power of CPU fans is measured in RPM, which decides the PC fan speed.
- It can be detached from the CPU and then attached back to the motherboard after cleaning.
- Higher the RPM higher the power of cooling. Also, gamers, graphic designers, animators, and VFX designers need the highest capacity and high-power fans to cool down their scorching CPU.
Fans are connected to the motherboard by:
- 3-pin DC connector: Speed can be altered by limiting the voltage.
- 4-pin PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) connector: Speed can be controlled using software easily.
We are here with the guide on how to control fan speed in Windows 10 and how to change CPU fan speed without BIOS. Follow these methods to control pc fan speed:
Method 1: Change Fan Speed Through Power Options
It is the only method in Windows 10 to optimize the fan speed. Follow these steps to perform the same.
1. Press Windows + X keys to open the Quick Link menu and select the Power Options.
2. Under Power & sleep menu, click on Additional power settings situated in the right pane.

3. This will open Power Options, and now click on Change plan settings beside Balanced (recommended).

4. Now, the Edit Plan Settings window appears. Click on Change advanced power settings.

5. This action will open a dialog box of Power Options containing services of different system components.
6. Scroll down and double-click on Processor power management.
7. Then, double-click on System cooling policy and choose Active from the drop-down menu in both On battery & Plugged in modes.

8. Now click on Apply then OK.
Note: Make sure to Activate the system cooling policy on both Battery & Plugged-in mode to fetch maximum fan performance.
It is the only method in Windows 10 OS that will help you in fan control Windows 10.
Also Read: 7 Ways to Fix CPU Fan Not Spinning
Method 2: Use SpeedFan Software
SpeedFan is a hardware monitoring program that is able to change fan speeds according to system temperatures. SpeedFan can read S.M.A.R.T. values and temperatures from the hard disk and can change the fan speed.
Note: This application will not detect all fan models. If you can’t find the fan listed there, then this method will not work. Also, do not alter the default CPU clock settings and other important settings of CPU, GPU & HDD to avoid causing trouble in the system.
1. Download SpeedFan 4.52 from the official website.

2. Then, install the downloaded app on your PC and launch it.
3. Now click on Configure.

4. Navigate to the Fans tab and see if the system fan is listed there.
Note: If any fan is detected by the program, then it will show it under the red-highlighted area, as shown below.

5. If you found the system fan listed there, then select it and explore the options it shows. After modifying the speed of the fan. Click OK.
Also Read: How to Check Your CPU Temperature in Windows 10
Method 3: Use HWiNFo Software
HWiNFo is an award-winning professional hardware analysis, monitoring, diagnosing, and reporting software for Windows and DOS. It is a highly trusted software that is even used by NASA. This real-time system monitoring software has won several awards and is trusted by Intel, AMD, Dell, and Asus. It is also totally free.
Follow the upcoming steps to install this software on your PC to learn fan control Windows 10:
Note: Do not change default system settings related to CPU, GPU & HDD. It may result in system instability. Only alter fan speed if you are sure about it.
1. Download HWiNFo portable or installer version from the official website.
Note: Portable versions run directly without installation.

2. Launch the application. Now, select the Sensors-only option and click on Run.
3. Wait for the program to fetch all the hardware-related information.
Note: This software does not detect the fan in our laptop due to some other reasons. That doesn’t mean it will not work for others also.
4. Once it is open, locate a Fan logo on the bottom and click on it.

5. Here you’ll find the specifications of the CPU fan, including its speed, RPM, temperature, etc. Choose the settings carefully and alter them with caution and follow the on-screen instructions.
Here, we explained the most possible working methods which can be the solution of how to change CPU fan speed without BIOS and that can be helpful in controlling PC fan speed in Windows 10.
Recommended:
- How to Test PSU with Multimeter
- 11 Best WiFi Temperature and Humidity Sensor
- Top 18 Best Fan Speed Controller Software
- Fix Windows 10 Bluetooth Mouse Lag
We hope that this guide was helpful and you were able to learn to control fan speed in Windows 10. Let us know which method worked the best for you. If you have any queries or suggestions, then feel free to drop them in the comments section.
Want to keep your PC running smoothly and quietly? Understanding how to control fan speed on Windows can be crucial, whether you’re trying to reduce noise or prevent overheating. While your computer’s fans automatically adjust speed based on system demands, you might sometimes want more control.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the built-in methods for managing fan speeds using the Control Panel and BIOS and explore some of the best fan control software options available. Read on to learn how to fine-tune your PC’s cooling system for optimal performance and comfort.
The Ultimate Guide to PC Fans: Types, Functions, and More
It can be helpful to understand the kinds of fans that are in your PC, and what they do, before you learn how to control fan speed on Windows. Most fan controls are specific to the CPU, but knowing all the options can be handy if one of them malfunctions. Most PCs have the following fans:
- CPU fans: These fans are located on the central processing unit. They move air away from the processor. They may also bring in cool air, as they move the hot air that is blown out by the case fan.
- Case fans: They get rid of the hot air released into the PC casing by other fans, keeping it from overheating.
- GPU fans: These also bring cooler air into the PC, pushing hot air out, which will then be blown out by the case fan.
- PSU fans: These are for the power supply unit, which creates a lot of heat due to its heavy power demands. This fan moves cooler air into the PC and moves heat out.
- Laptop fans: This guide will be discussing PC fans, specifically, but it is worth noting that laptop fans work very differently, with fans usually located beneath the laptop, blowing the air inside.
How to Find out What Kind of CPU Fan You Have
Locating your fans can be useful for troubleshooting or repair purposes. Here are the steps:
- Turn off your computer and unplug the power cable.
- Remove the PC panel on the left side (when you are facing the computer). You will likely see a few screws that will need to be removed.
- Locate your CPU cooler. It should have a fan on it with an attached cable. It is likely mounted on top of your CPU.
- Look for any model number, brand information, or other identification. This will help you research specific troubleshooting tips and can even be useful when you need to replace this part.
- If you’re having trouble identifying the CPU fan, or it’s too difficult for you to see, contact the manufacturer of your PC for information. Be sure to have your PC model information close by, so they can look up the corresponding hardware for you.
Simple Ways to Manage Fan Speed on a PC
Now that we have all the basics out of the way, it is time to get into the nitty-gritty details. If you are eager to learn how to control fan speed on PC Windows, be careful. This is a delicate system and if your PC or laptop overheats, you might permanently damage the hardware. That being said, there are several troubleshooting tactics to control your CPU fan speed.
Method #1: Control Panel
By adjusting your laptop or PC’s power settings, you can lower the workload placed on your system. This means the fan doesn’t have to work as hard to keep everything cool, which improves performance. Here are the steps:
- Search for Control Panel from the Start menu, then click it in the results.
- Within the Control Panel, search for and click on Hardware and Sound.
- Find and click Power Options and a new window will pop up.
- Click Change Plan Settings.
- Click Change Advanced Power Settings and a new box opens
- Go to Process Power Management and click the + sign to reveal options
- Click System Cooling Policy and make sure it is set to Active
- Save changes by clicking Apply and then Ok
Method #2: BIOS
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), is a program motherboards use to manage data between the computer’s OS (operating system) and attached devices, such as the keyboard, mouse, and printer. There’s a lot more to it, but for our purposes we’ll discuss how BIOS helps control fan speed. UEFI (unified extensible firmware interface) is very similar to BIOS but is found in newer computer models. It does mostly the same things, it’s just more advanced. For this article, we’ll be using the term BIOS, but UEFI could easily be substituted.
Most BIOS allow you to see and adjust the speed of your CPU fan. Here’s how:
Warning: Always be careful when dealing with the BIOS utility. It’s easy to do something wrong and cause a huge headache for yourself. Follow these steps carefully and you’ll be fine.
1. Turn off your computer.
2. Turn your computer back on, and repeatedly press whatever key launches the BIOS settings. Depending on the model of your system, the key might be different. Try F2, F10, F12, Delete, or ESC. You should be able to look up the exact key if you know your model information.
3. Find the menu that shows the settings for the fan. Every PC is different. It could be under Overclocking, Advanced, Hardware Monitor, PC Health, Fan Control, etc.
4. Find something similar to CPU Fan Speed Control, then toggle this to enabled if it isn’t already.
5. Select your desired fan speed, which is often expressed in a percentage, meaning 100 percent is maximum speed. Note: There are other fans in your system besides the CPU, such as a GPU (graphics processing unit) fan, etc. to take note of.
6. Save your changes before leaving BIOS.
Method #3: Third-Party Software
Another method to consider for how to control fan speed on Windows is through the use of a third-party app. Which one you use depends on your hardware and Windows version. There are various kinds of third-party apps out there that can help control your fan speed. We’ve narrowed down the most popular and helpful options, but feel free to do your own research and pick what you think is best.
Here’s how to control fan speed on a PC using SpeedFan, which is said to work with really old Windows versions up through more modern ones, including Windows 10:
1. Install SpeedFan and run it.
2. Select Configure from the Readings tab.
3. Select the Fans tab and wait for the app to find and list your fans.
4. Select the fan you want to control.
5. Use the response curve to control the fan speed.
Tip: Fans turn on when your system heats up. The response curve maps heat with fan speed. The hotter the system runs, the faster the fans will run. Many of the software options will have response curves represented.
If SpeedFan isn’t the right fit for you, consider another free option, appropriately named Fan Control. This one works on Windows 11 and Windows 10. Follow these steps to use this portable fan control software:
- Download and extract the contents of the ZIP download and open FanControl.exe from the folder.
- Accept the default prompts that display upon opening the program.
- Press the plus sign on the right and create a linear curve.
- Name the fan curve and then select it. You’ll need the name later.
- Choose Min. fan speed and then pick a percentage to set its idle speed, or click Max. fan speed. You can also set the temperature range.
- Toward the top of the app, find the fan that corresponds with the fan in your computer, and press Enable to ensure it’s on.
- Click the Selected fan curve menu and pick the name for the fan curve you just made.
Method #4 Using the Manufacturer’s Proprietary Software
Depending on the model of your PC, some manufacturers have specific software that is designed to monitor their hardware, such as fan speeds and system temperatures. This is often called OEM (original equipment manufacturer) software.
Look into your PC model and type and see if there is software you can download to help you gain information about your fan speeds and internal temperatures. Your motherboard may also come with its own software for these purposes, so look into your make and model and see if there are any downloadable utilities. You may not be able to directly control the fan speeds this way, but at least you’ll have an idea of what is going on and why it may be overheating.
Other Troubleshooting Methods
Other possibilities for how to control fan speed on PC Windows could include:
- Swapping out your fans can be a quick solution when the fan itself is faulty.
- If your system sensors are misreading the temperatures of your PC, the fans may not be at the right speed for the actual temperature needs. Look for third-party software or other solutions to see if your temperatures are being misread by the standard sensors.
- If applicable, see if the thermal paste has degraded or needs to be reapplied. This will help to keep the CPU cooler and negate the need for the fan to work as hard.
- Contact customer support from your PC manufacturer. They may have some insight into common malfunctions or next-steps.
Why is it Important to Manage Fan Speed on PC?
Managing a PC’s fan speed is crucial for maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of your hardware components. When your computer’s internal temperature rises, which is common during intense gaming or heavy processing tasks, fans work harder to cool down the system. By controlling fan speed, you can ensure that your computer remains at a safe temperature, preventing overheating that could otherwise damage your hardware, or cause unwanted instability.
Effective fan management also contributes to a quieter overall experience. If your fans are running at full speed constantly, they can be quite noisy, which might be distracting or annoying. By adjusting fan speeds based on the actual temperature needs, you can reduce unnecessary noise, making your PC quieter when it’s not under heavy load and only ramping up when necessary.
Proper PC fan speed also helps with energy efficiency. Fans that run at full speed all the time consume more power, which can lead to higher energy bills and increased wear and tear on the fan itself. Optimizing its speed to align with your PC’s temperature requirements not only means extending the lifespan of your components, but it also helps manage your energy consumption.
Tip: Depending on the type of computer you have, it might be possible to easily remove the case and access the fan yourself for cleaning. You’ll need to be cautious not to disturb any other components, and if you’re not comfortable, you can find a professional to do so for you. If you’re feeling brave, however, use compressed air or a soft cloth to eliminate debris, dust, or even animal hair. Eliminating this debris improves fan function.
Frequently Asked Questions About Fan Speed for PC
How do I control the RPM of my computer fan?
To control the RPM of your computer fan, adjust the settings in your BIOS/UEFI or use software like SpeedFan, HWiNFo, or MSI Afterburner.
What is the best fan curve for CPU temp?
The best fan curve for CPU temperature typically increases fan speed as the temperature rises, starting from a lower speed at idle and ramping up to maximum as temperatures approach the CPU’s thermal limits.
Why is my CPU fan so loud?
Your CPU fan may be loud due to dust buildup, high speeds, or because it’s running at maximum RPM to cool a high-temperature CPU.
Why does my PC fan speed automatically increase?
If you have unexplained fan speed increases, wait until this happens again and then open Task Manager by pressing the Control + Shift + Escape keys. From there, look at the currently running programs and processes and see if there is a culprit for excess CPU usage or similar resource drains. It could be an app or demanding software that is putting a strain on the system.
There could be other processes running in the background that cause the fan speed to increase without obvious explanation. Think antivirus scans, updates, and other applications that suck up plenty of resources.
How do I reduce the temperature of my CPU?
We already covered checking the thermal paste and cleaning out dust and debris from the PC, but here are some additional possible fixes for reducing your CPU temperature:
- Put your PC somewhere with better ventilation. If it’s in an enclosed cabinet or space without airflow, this could cause it to overheat and overwork your fan.
- For better ventilation, you could try taking off your PC’s side panel and see if this increased air exposure resolves the problem
- Make sure the heat sink is positioned correctly. Otherwise, the CPU will not get the full cooling benefit
- Replace your CPU cooler if necessary
Can overclocking cause issues with fan speed?
Absolutely. Overclocking is a way to improve your PC performance by intentionally pushing the default clock speed of the CPU past the manufacturer’s parameters. This boosts PC performance, allowing relatively outdated computers to improve their response times and functions. It’s especially common for PC gamers who don’t have the best CPU for gaming to get the most out of their system. Unfortunately, it can also lead to increased heat production and other CPU strains. If you’ve started having issues after overclocking your PC, try returning to default settings and see if that resolves the fan problem.
Heidi Edwards
Generalist/Tech Writer
Versatile copywriter Heidi Edwards, a marketing graduate from WGU, crafts compelling content across diverse sectors, from eco-conservation to tech. Self-taught in WordPress and graphic design, she runs the successful Aultman Group.
Желающим выжать максимум из технических возможностей своего ПК потребуется специализированный софт, включая программы для управления скоростью вращения вентиляторов. О восьмерке лучших вы узнаете из нашего материала.
SpeedFan
Источник: SpeedFan
- Разработчик: Альфредо Милани Компаретти
- Официальный сайт
Бесплатная утилита для мониторинга температуры и скорости вращения вентиляторов на компьютерах с процессорами Intel. В ней также есть функции для контроля скорости вращения жестких дисков.
Позволяет управлять скоростью вращения вентиляторов вручную или автоматически, основываясь на температуре самой системы. Позволяет создавать профили для управления вентиляторами и другими настройками, основываясь на разных параметрах, например, активности приложений.
Argus Monitor
Источник: Argus Monitor
Позволяет следить за нагрузкой на систему и оптимизировать работу приложений для повышения производительности. Управление кулерами в ней осуществляется во вкладке с материнской платой. Нам нужен подраздел «управление вентилятором»
Помогает отслеживать напряжение на различных компонентах компьютера, включая процессор, оперативную память и жесткий диск. С ее помощью пользователи могут диагностировать проблемы с питанием и предотвратить возможную поломку системного блока.
- Разработчик: Argotronic UG
- Официальный сайт
MSI Afterburner

Источник: MSI
- Разработчик: MSI
- Официальный сайт
Несмотря на то, что MSI Аfterburner позиционируется как программное обеспечение для разгона видеокарт, софт все же предусматривает настройку скорости вращения вентиляторов.
Для этого нам необходимо найти кнопку с надписью Auto, расположенную в правой части ползунка Fan Speed. Скорость вентиляторов устанавливается в процентном соотношении. После нужного значения нам необходимо нажать на кнопку «Применить».
NoteBook FanControl
Источник: Softpedia
- Разработчик: Rémi Mercier
- Официальный сайт
Бесплатная утилита для управления вентиляторами на ноутбуках на Windows. Дает возможность контролировать скорость вращения вентиляторов в зависимости от температуры различных компонентов ноутбука, включая процессор, видеокарту и жесткий диск.
Поддерживает настройку профилей, позволяя создавать и сохранять профили для разных режимов работы ноутбука, например, «Тихая работа» или «Максимальная производительность».
Open Hardware Monitor
Источник: Open Hardware Monitor
- Разработчик: Epic Games
- Официальный сайт
Позиционируемая как программа для разгона компьютеров, Open Hardware Monitor поддерживает и более тонкие параметры, например, нужную нам настройку вентиляторов. Этот параметр можно найти в основной вкладке ключевого компонента.
Отображая текущую скорость вращения вентиляторов, программа позволяет убедиться, что вентиляторы работают правильно и обеспечивают достаточное охлаждение компонентов системы.
HWMonitor
Источник: HWMonitor
- Разработчик: CPUID
- Официальный сайт
Еще одна программа для разгона компонентов ПК, предусматривающая контроль и мониторинг скорости вращения вентиляторов. Позволяет отображать текущую скорость вращения вентиляторов, установленных на компьютере.
Позволяет сохранять данные о мониторинге в виде журнала для дальнейшего анализа. Вдобавок дает возможность отслеживать напряжение, подаваемое на различные компоненты компьютера.
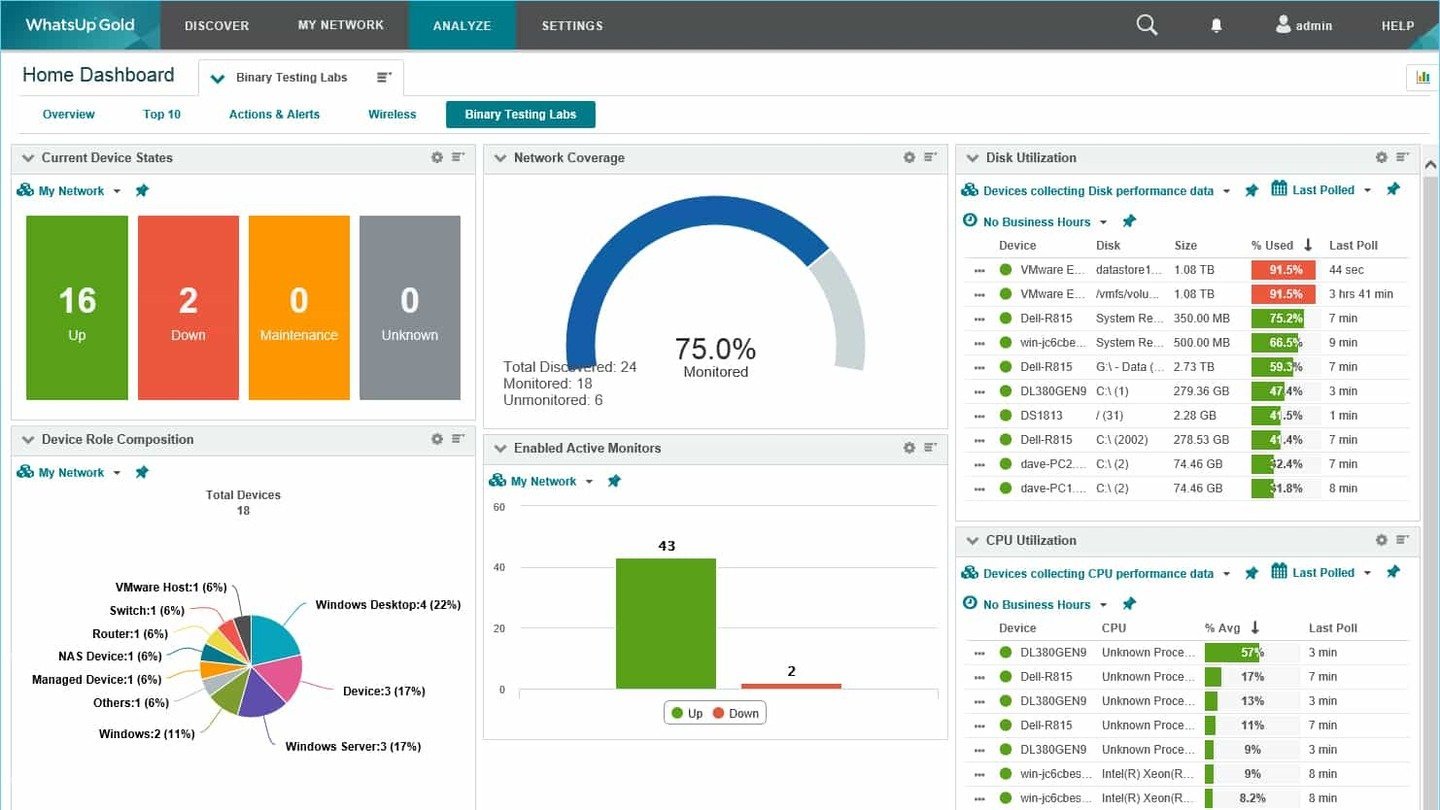
Easy Tune
Источник: Easy Tune
- Разработчик: MSI
- Официальный сайт
Еще одно приложение для настройки и оптимизации работы компьютера, разработанное Intel. В приложении доступны различные инструменты для мониторинга и управления параметрами компьютера, но нам ведь интересны настройки охлаждения?
Easy Tune предлагает инструменты для настройки системы охлаждения компьютера. Вдобавок софт предоставляет инструменты для диагностики и устранения неполадок системы.
Aorus Engine
Источник: Gigabyte
- Разработчик: Gigabyte
- Официальный сайт
Утилита для настройки и мониторинга периферийных устройств, разработанная компанией Gigabyte для своих брендов Aorus и Gigabyte. С помощью нее можно настроить параметры мыши, клавиатуры, наушников и других компонентов ПК.
Aorus Engine также позволяет создавать и сохранять профили для разных игр и приложений, чтобы быстро переключаться между настройками программы. Совместима с большинством моделей Aorus и Gigabyte.
Источник фото: Tech4gamers
Download Article
Download Article
- Using SpeedFan
- Using the BIOS
- Video
- Tips
|
|
|
This wikiHow teaches you how to adjust the fan speeds on your Windows 10 laptop. While it is possible to increase or decrease the speed of your PC’s fans on some models, the feature is not widely available. If your fan speed can be managed manually, you can typically adjust fan speeds in the BIOS/UEFI or using a third-party utility like SpeedFan within Windows.
-
-
Once the app is installed, you’ll find it in your Windows Start menu.
- You may have to click Yes to give SpeedFan permission to access your PC’s settings.
- After a few moments, you will see some information about your PC on the main screen. The fans and their current speeds should appear in the box just below the «CPU usage» bar. If you don’t see any fans here, or the only fans you see are listed as «0 RPM,» your motherboard is not supported by SpeedFan.
Advertisement
-
It’s in the upper-right area of the window.
-
It’s at the top of the window.[1]
-
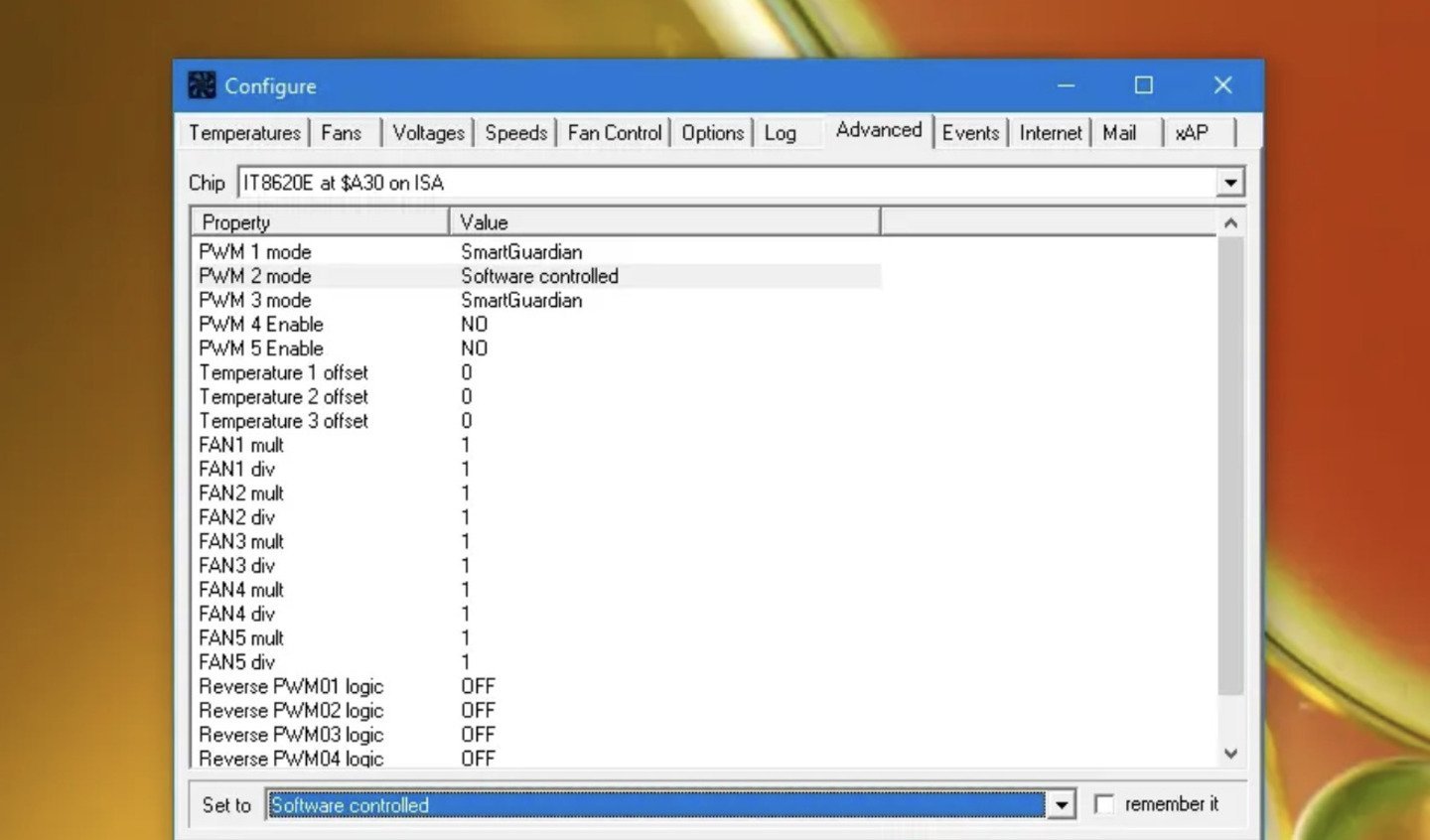
It’s at the top of the screen. It’s the entry that begins with «IT» and ends with «ISA.[2]
» In the bottom section, you’ll see several properties, a few of which should begin with «PWM (a number) mode.»- If you don’t see your CPU in the menu, go through the other options and look for one with «PWM mode» entries in Property box. If you don’t see any options that display a «PWM mode» option in the Property box, you won’t be able to change your fan speed.
-
To do so, click the first PWM mode entry, and then select Software controlled from the drop-down menu at the bottom. Repeat this for each PWM mode entry (PWM 1 mode, PWM 2 mode, etc.).[3]
- The default option, Smart Guardian, stands for chip-based control. When this default option is set for any PWM modes, your PC will self-regulate the fan speeds instead of allowing you to make changes.
-
This takes you back to the main SpeedFan screen.
-
Take a look at each fan speed in the box on the left side of the window. You’ll also see each of the PWMs listed just beneath this box, each with its own percentage value. Grab a sheet of paper or open a blank text file and log the following:
- Write down the percentage of the first PWM setting.
- Now set the first PWM to 0%. After a moment or two, one of the temperatures in right-hand box will begin to rise and turn red. The component with the raised temperature is the one affected by that PWM. Write that down.
- Enter the original percentage back into the box.
- Repeat for all other PWMs until you know a) which PWM controls which components’ fans, and b) what the default values are for each PWM.
-
Start by making small adjustments, raising or lowering the speed by just 1 or 2 at first. Watch the temperatures in the right panel to make sure you don’t cause any overheating, while also paying attention to how your changes affect performance.
Advertisement
-
Depending on your laptop’s model and motherboard, you may be able to control fan speeds in the BIOS or UEFI.[4]
Save any work you have open, and then do the following:- Press the Windows key + i to open your Settings.
- Click Update & security.
- Click Recovery in the left panel.
- Click Restart now under «Advanced startup» in the right panel.
- Click Troubleshoot and then Advanced options.
- Click UEFI Firmware settings and select Restart. This reboots your PC into the BIOS/UEFI.
-
The location will vary, but check the various menus for anything having to do with fans, fan speed, cooling, or temperature. You may have to select a menu called Advanced first.[5]
-
The options you can select also vary by manufacturer.
- You will typically have the option to adjust the temperature at which the fan will speed up, and often the speed itself. If your issue is that the fans are too loud and come on too often, you’d want to increase the temperature at which they activate. Just be careful not to let your PC run too hot, as you could damage your hardware.[6]
- You will typically have the option to adjust the temperature at which the fan will speed up, and often the speed itself. If your issue is that the fans are too loud and come on too often, you’d want to increase the temperature at which they activate. Just be careful not to let your PC run too hot, as you could damage your hardware.[6]
-
The exact key you’ll need to press will appear with «Save Changes and Exit» toward the bottom of the screen. Press that key to save and exit. When your PC boots back up, it will be using the new fan settings you’ve set.
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
-
Some gaming PCs offer power management software that lets you control fan speeds from within Windows. If your laptop model is a gaming-specific laptop, check your manufacturer’s website for available downloads.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Install and open SpeedFan.
2. Click Configure.
3. Click Advanced.
4. Select your CPU from the Chip menu.
5. Set each PWM Mode value to «Software controlled.»
6. Click «OK.»
7. Raise or lower each PWM speed.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 236,386 times.













