Download Article
Download Article
To delete unwanted or corrupt .dll files, you will need to find them by making hidden files visible, unregister them through the command prompt, and then delete them manually from their source folder. It is very important that you know that the file is not a required Windows system file. Removing DLLs that your computer relies on can render your PC unbootable, so don’t delete a file unless you know exactly what it is and why you don’t want it on your PC.
-
This ensures that if you have an unwanted app, such as spyware, that relies on the DLL to work, it won’t prevent you from deleting the file. To boot your computer up into Safe Mode:
- Click the Windows menu and select Settings.
- Click Update & Security.
- Click Recovery.
- Click Restart now’ under «Advanced startup.»
- When your PC reboots, click Troubleshoot.
- Click Advanced options.
- Click Startup Settings and select Restart.
- When you see the list of startup options, press 4 or F4 as indicated to boot into Safe Mode.[1]
-
You can do this by pressing the Windows key + E simultaneously, or by clicking the File Explorer in the Start menu.[2]
Advertisement
-
It’s at the top of the File Explorer.[3]
-
It’s near the top-right corner of the window.[4]
-
It’s at the top of the Folder Options window.
-
It’s the second option under the «Hidden files and folders» header.[5]
-
Both options are a bit below the selection you made in the previous step.
-
You can now work with hidden DLL files on your PC.
-
You can use the Windows Explorer to do so. For example, if you want to delete a DLL that a virus left on your flash drive, select your flash drive in the left panel.
- If you’re not sure where the file is located, click This PC in the left panel, and then type the file name (or part of the file name) into the «Search This PC» field at the top-right corner of the window. Click the purple arrow to display the search results—when you find the file, right-click its name, and then select Open file location from the menu.
-
This is the bar at the top of the window that contains the full path to the folder that’s currently open. This will save the path to your clipboard.
-
Here’s how:
- Type cmd into the search bar next to the Windows start button (you may have to click a magnifying glass first to see it).
- In the search results, right-click Command prompt and select Run as administrator.
- Click Yes.
-
Here’s how:
- Type cd and then press the space bar. Don’t press Enter just yet.
- After the space, right-click the command prompt and select Paste. Depending on your settings, simply right-clicking may automatically paste the copied path, but some may still need to click Paste to see it.
- Press Enter to run the command.
- You can use the dir command at the prompt to view a list of all files in the folder. To see just the DLL files, use dir *.dll instead.
-
At the prompt, type regsvr32 /u filename.dll. Replace filename.dll with the name of the file you want to delete, and then press the Enter key to run the command. This makes it possible to delete the DLL.[6]
-
You’ll use the Command Prompt to do so:
- Type del /f filename.dll, replacing «filename.dll» with the name of the file. The /f flag tells Windows to delete the file even if it’s read-only.[7]
- Press Y to confirm if prompted.
- Once the file is removed, undo the changes you made in the File Explorer options and reboot your computer as normal.
- Type del /f filename.dll, replacing «filename.dll» with the name of the file. The /f flag tells Windows to delete the file even if it’s read-only.[7]
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
How can I remove permissions from IDM properties so I can delete the setup of IDM?
You need admin privileges. If it is a key system file, it will not let you delete it. If you do you delete it, your PC will not work properly.
-
Question
It says, «The action can’t be completed because the file is open in Windows Explorer.» How do I close Windows Explorer?
You can boot into safe mode and do this modification. But make sure that this dll does not deal with Windows booting or else the PC will get frozen at the start screen.
-
Question
It says, «The action can’t be completed because the file is open in Windows Explorer.» How do I close Windows Explorer? And how do I boot into Safe Mode?
You can close Windows Explorer from Task Manager. Press Ctrl-Alt-Del and select «Start Task Manager.» Click on Windows Explorer to highlight it, then click the «End Task» button. For Safe Mode boot, restart your computer and press F8 as soon as Windows starts loading. If you find the timing difficult (as it can be on faster machines), you can restart your computer in Safe Mode when in Windows by holding the Shift key while clicking Restart.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
-
On modern operating systems, you should make sure you have a strong antivirus program in place to protect against viruses in .dll format.
-
Never delete or alter system files on any computer other than your own personal machine.
-
A large number of .dll files are system files. Deleting the wrong one may cause your computer to crash, so never delete a .dll file unless you’re absolutely sure of its function.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. In Safe Mode, open the File Explorer and go to View > Options > View.
2. Enable «Show hidden files and folders.
3. Remove the checkmarks from «Hide extensions for known file types» and «Hide protected operating system files.»
4. Click OK.
5. Go to the folder containing the DLL.
6. Right-click the address bar and select Copy as text.
7. Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
8. Type «cd » followed by the copied path and press Enter.
9. Use regsvr32 /u filename.dll to unregister the file.
10. Use del /f filename.dll to delete the file.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 554,198 times.
Is this article up to date?
Windows relies on several .dll files, also known as Dynamic Link Library files, to perform common functions. From time to time, you may need to delete a .dll file because of a software conflict or because you’re updating an older .dll with a newer version. When you do this, you must be careful to not only move the file to the Recycle Bin, but also to unregister it from Windows.
Step 1
Click the «Start» button in Window,s and select «Search» from the Start Menu.
Step 2
Click the «All files and folders» link in the Search window, and type the name of the .dll file you want to delete into the empty field. Click the «Search» button to begin the search.
Step 3
Locate the file in the search results and take note of the file path, which indicates where the file is stored. This is very important, because you will need to know the file path for the last steps, so you may want to write it down. Typically, .dll files will be found in «C:\Windows\System32,» but this can vary depending on the specific type of .dll file and the version of Windows you’re using.
Step 4
Right-click on the .dll file in the search results, and select «Delete» from the options that pop up. This will move the file to the Recycle Bin.
Step 5
Click the «Start» button in Windows, and select «Run» from the Start Menu. Type «cmd» into the empty field, and click the «Run» button.
Step 6
Type «regsvr32 /u C:\filepath\filename.dll» into the command line, substituting the specific file path and name of the file for «filepath» and «filename,» respectively. For example, if you wanted to delete the file «windows.dll» from the file path «C:\Windows\System32,» you would type «regsvr32 /u C:\Windows\System32\windows.dll.» Press «Enter» after typing this line to unregister the .dll file from your system, completing the process.
Hello! How are you? A DLL file is an essential part of many applications developed for Windows. In fact, inside a DLL there is an executable code that allows a software to work properly. However, removing certain DLL can have disastrous results. That’s why it is necessary to know that the files to be deleted are not essential. Otherwise, the operating system could stop working. It could even come to a complete standstill. On the other hand, removing DLL that are no longer used can be beneficial to the performance and health of your computer. Since they are usually residues of already deleted programs. For that reason, today we will see how to delete DLL files in Windows 10.
How to delete DLL files with DLL Archive
As mentioned, it is possible to delete DLL files. This can be done manually. However, the user runs the risk of disabling the system. For this reason, today we will use a tool that allows you to select the files that are no longer needed. This application is DLL Archive and you can download it for free from this link. Then run it like any other Windows program. What this tool does is locate the DLL files on your computer. It then determines which ones are not needed and extracts them into a folder. Well, the first thing you must do is click on Configuration.

Then, enable the Only display 0-hits option. You must set it to Enabled
Now, start the DLL file search with the Search button.

Please wait while the hard disk scan is finished. After a few minutes, the wizard will display a list of orphaned files. Please note that the files have to show 0 in the hits section. After verification, please click on Archive all. This will cause the files to be hosted at the following address:
C:\Windows\DLLArchive

After having all the DLL files isolated, it is time to restart the computer. Then check that the system is working properly. If so, then the removal of DLL libraries has been completed successfully. In that case, it is enough to delete the contents of the folder mentioned above. On the contrary, if any error persists, please check the text file filelist.txt to consult the original path of each DLL. And consequently, you will be able to restore them if necessary.
Conclusion
Thus, we have seen how to delete DLL files in Windows 10. This is very interesting since lightening the system is always welcome. All right, this is all for the moment. Before saying goodbye, I invite you to see our post about how to install MinGW on Windows 10.
— Advertisement —
Everything Linux, A.I, IT News, DataOps, Open Source and more delivered right to you.
Subscribe
«The best Linux newsletter on the web»
A DLL file is an indispensable part of many applications developed for Windows. Within a DLL, there is an executable code that lets a software work correctly, either in its entirety or partially. DLL stands for Dynamic Library Link.
Removing certain DLLs can have disastrous results. Therefore, before doing anything, you must be sure that the DLL files you are going to delete are no longer necessary. Otherwise, the operating system could stop working, in the worst case, completely. On the other hand, removing DLL files that are no longer used can be beneficial to the performance and health of your computer. The latter are usually residues of programs you have already removed. For this last task, we recommend the DLL Archive.
This tool is responsible for locating all the DLLs on your computer, determining which ones are no longer needed, extracting them, and archiving them in a folder. After its simple installation, just run it and click on Configuration.
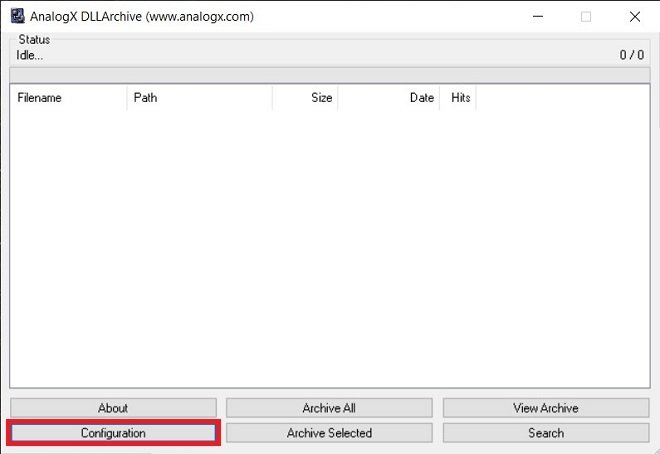
Configure the search
Then, enable the Only display 0-hits option. You must set it to Enabled.
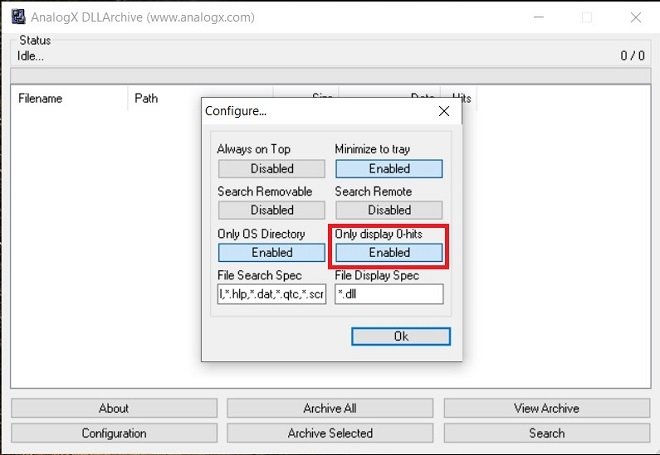
Search only for orphan DLLs
Now, start the DLL file search with the Search button.
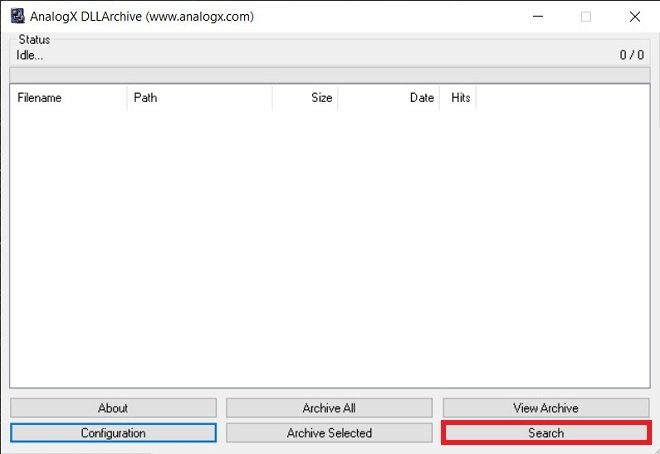
Start searching
Wait for the hard disk scan to finish. When it is finished, you will see a complete list of all the orphaned DLL files. Simply click on Archive all to archive them permanently.
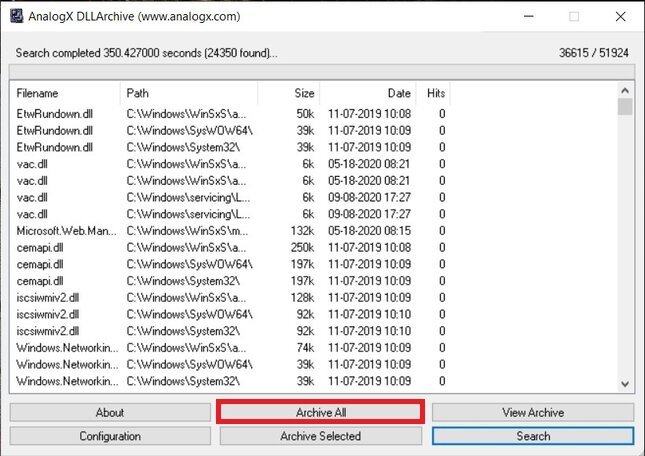
Remove all the DLLs
You must check that, in the list, only those unnecessary DLLs are shown, marked with a 0 in the Hits section. Otherwise, you may end up archiving important DLLs. The copy of all your unused DLLs is located in C:\Windows\DLLArchive.
Once you have all the unnecessary DLLs isolated, restart your computer and check that everything works correctly. If this is the case, it means that the library extraction has been performed satisfactorily. In that case, you can delete the DLL Archive folder permanently. If something has gone wrong, go to the same folder and open the text file filelist.txt to check the original path of each DLL. This way, you can restore them if necessary.
To remove unwanted DLLs we must clean the registry, and for this purpose we will use CCleaner. It is a great tool that comes in both Installer and Portable versions, and apart form cleaning the registry it can also remove temporary files of various browsers and 3rd party tools. Alternatively we will also use DLLArchive.
Run CCleaner and from the left sidebar select Registry, now you will find Shared DLLs on top, make sure it’s checked. Now click Scan for Issues, and after the scan is complete click Fix Selected Issues to remove the DLLs.
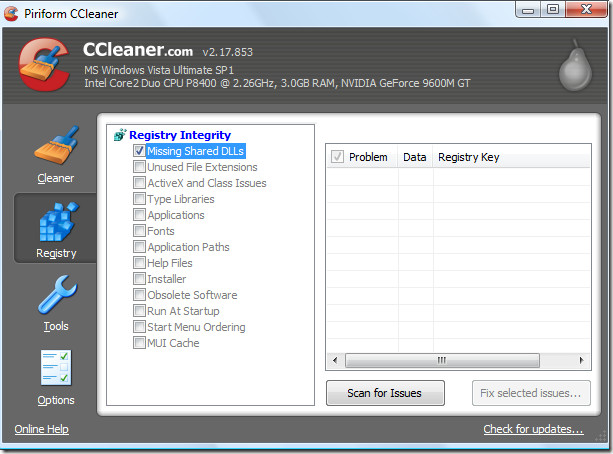
Alternative – DLLArchive
DLLArchive is a great tool that presents the list of all the DLL’s that don’t have references in the system. You can select the ones that you think are not necessary and archive them. If you made some mistake, you can always restore it back again using this tool.
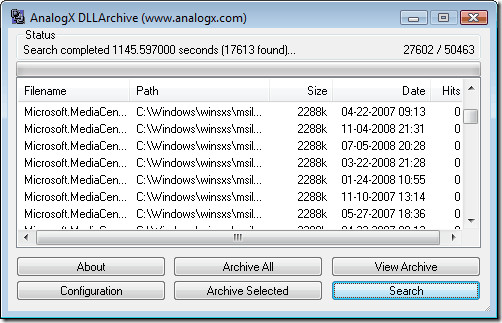
Since this tool does not automatically remove the DLLs, it helps a user by telling which DLLs are unwanted. You can then manually delete them later. Enjoy!















