Applies ToWindows 11 Windows 10
Чтобы узнать, сколько ядер и логических процессоров имеет процессор на устройстве с Windows, выполните следующие действия.
-
Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши меню Пуск и выберите Диспетчер задач.
Совет: При нажатии клавиш CTRL + SHIFT + ESC на клавиатуре также открывается диспетчер задач.
-
Когда откроется окно диспетчера задач , выберите вкладку Производительность в левой части окна, а затем убедитесь, что выбран параметр ЦП .
-
Количество ядер и логических процессоров на устройстве с Windows указано рядом со следующими значениями:
-
Ядер:
-
Логические процессоры:
-
Нужна дополнительная помощь?
Нужны дополнительные параметры?
Изучите преимущества подписки, просмотрите учебные курсы, узнайте, как защитить свое устройство и т. д.
Используем Диспетчер задач, Диспетчер устройств и дополнительное ПО для поиска информации о процессоре
Ядро процессора — физический блок, находящийся внутри процессора, который предназначен для вычисления арифметических операций. Чем больше ядер, тем быстрее процессор обрабатывает информацию.
Существует несколько способов, чтобы узнать сколько ядер в процессоре на нашем ПК, но самый простой — через диспетчер задач.
Способ 1. Диспетчер задач
Вызываем диспетчер задач, нажав одновременно клавиши «Ctrl+Shift+Esc». Затем переходим во вкладку «Производительность» и на закладке «ЦП» (активность ЦП) находим информацию о ядрах процессора.
Способ 2. Диспетчер устройств
В окне «Выполнить» (запускаем через «Win+R») вводим команду «devmgmt.msc» и нажимаем клавишу «Enter».
Откроется окно со списком устройств, для отображения списка ядер разворачиваем раздел «Процессоры». Число строк = количеству ядер.
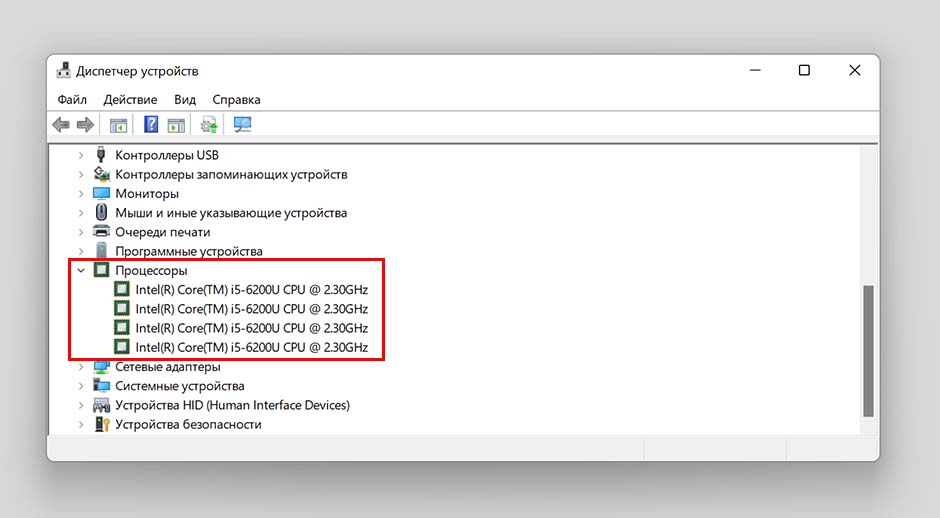
Почему количество ядер различается в диспетчере задач и диспетчере устройств? Дело в том, что в диспетчере устройств отображается 4 потока, то есть на 1 ядро приходится 2 виртуальных, в итоге реальное количество ядер = 2. В названии процессора чаще всего уже имеется подсказка о количестве ядер.
Способ 3. Стороннее программное обеспечение
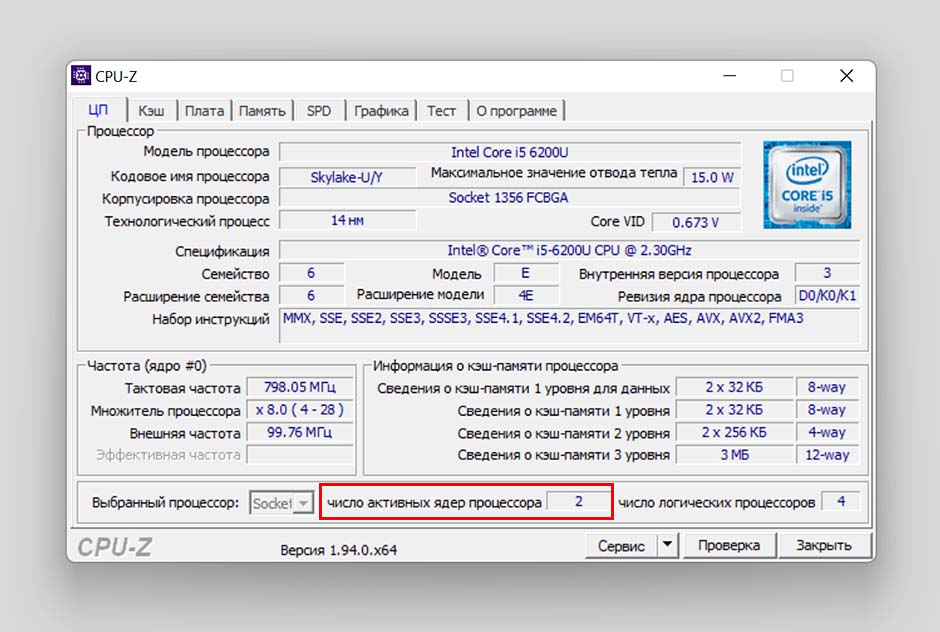
Число ядер процессора можно узнать в таких ПО, как — «CPU-Z», «AIDA64», «HWiNFO», «Hardinfo» и другие.
Например, в CPU-Z число задействованных в работе ядер можно увидеть в разделе «ЦП», там же справа — число логических процессов.
This gearupwindows article will guide you through several methods to find out how many CPU cores and threads are in a Windows 11 or 10 PC. The number of CPU cores and threads (Logical Processor(s)) on Windows 11/10 can be found in several ways, and we’ll explain the most popular ones.
Everyone eventually discovers that a CPU has a variable number of cores, and that number influences its performance. The next logical step is to figure out how many cores your CPU has. Windows 11 and 10 make that process extremely simple.
Based on its model, core count, generation, and whether it supports simultaneous multithreading (SMT) like hyperthreading, your CPU will have a different number of threads. Since newer generation processors have more cores, they have more threads than older generation CPUs. Having more threads means your CPU has more workers (resources) available to it, so the better the performance is. An increased thread count is advisable when multitasking, playing multithreaded games and rendering professional videos.
How to Find CPU Cores and Threads in Windows 11 or 10?
There are multiple ways to find CPU cores and threads in Windows 11/10. Follow these steps to find CPU cores and threads in Windows 11/10:-
Using the System Information panel
As the name implies, the System Information panel displays all information regarding your system hardware, including the processor, so it is probably the easiest way to find the CPU cores and threads on Windows 11 or 10.
Here’s how to find the CPU cores and threads in Windows 11/10:-
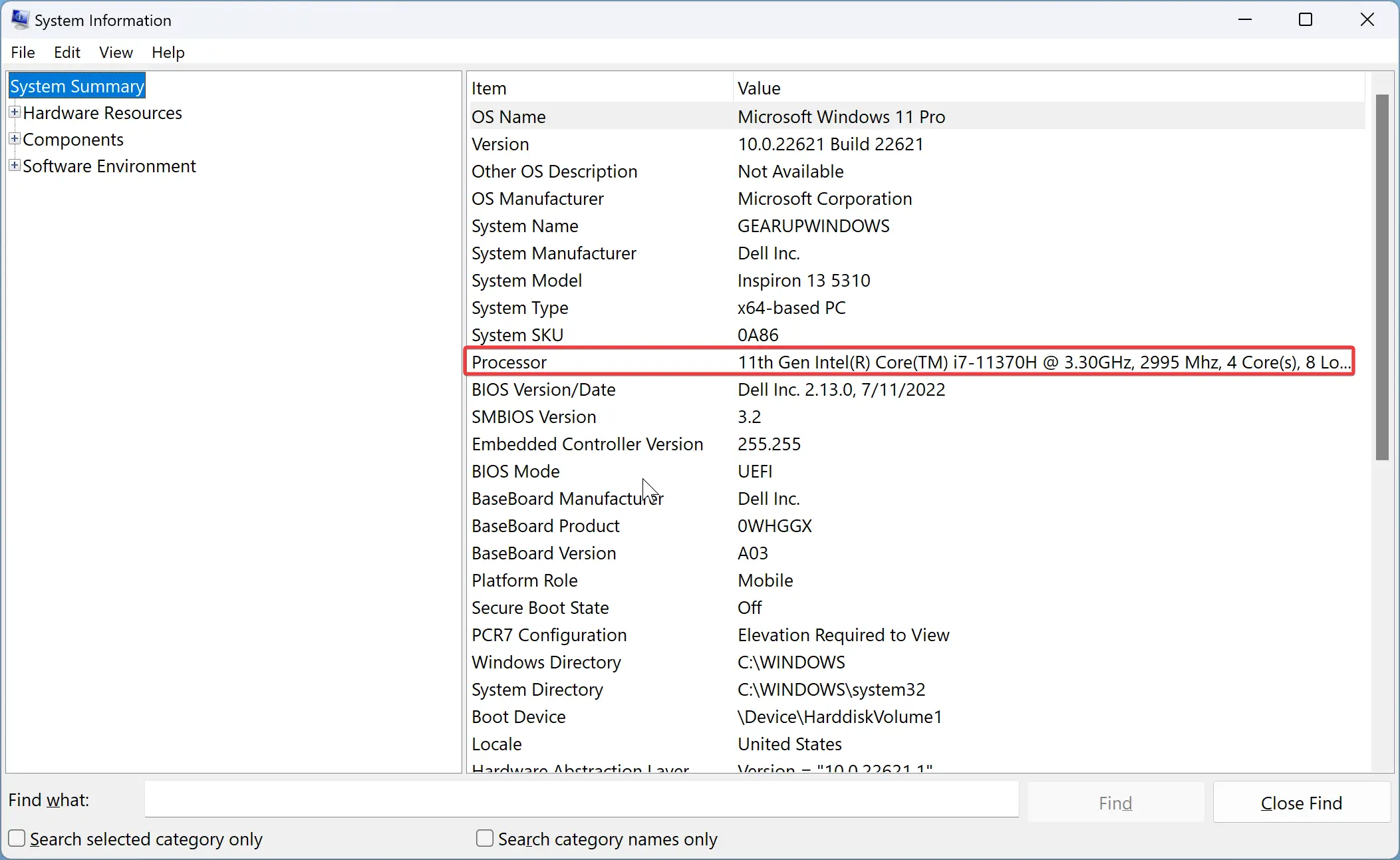
Step 1. Open System Information panel.
To do that, press Windows + R on the keyboard to open the Run dialog box. Type msinfo32 in the dialog box and press Enter.
Step 2. Select System Summary on the left sidebar, and next to Processor, you’ll find the CPU cores and threads (Logical Processor(s)).
Through Task Manager
Task Manager displays a variety of information about your computer, whether it’s about the hardware or the software. Here’s how to locate CPU cores and threads in Task Manager:-
Step 1. Open Task Manager on your computer.
Select Task Manager from the menu by right-clicking on the Start button. Or, a Task Manager window can also be accessed by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys.
Step 2. Then, click on Performance tab.
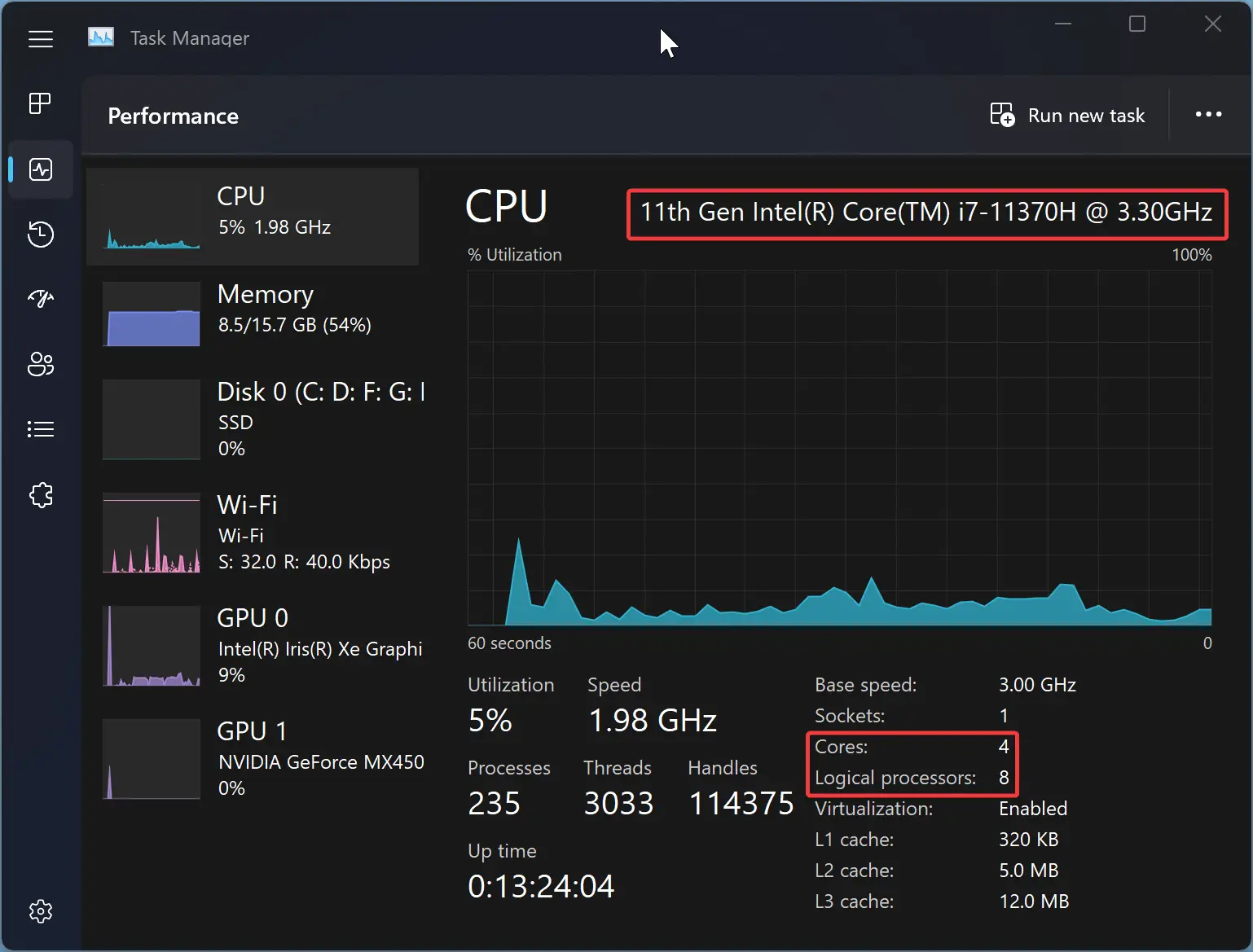
Step 3. At the top right of the window, you’ll see your processor’s name and the number of cores. You’ll also see a graph of your CPU’s usage in real time, along with more detailed information, like the base clock speed, the number of cores, and the number of logical processors (also known as threads).
By Windows PowerShell
This information is also available through Windows PowerShell. To get it, follow these steps:-
Step 1. Open Windows PowerShell as an administrator.
On the taskbar, click the Start button and enter Windows PowerShell. Right-click on the Windows PowerShell entry and select the Run as administrator option.
Step 2. Then, enter WMIC CPU Get NumberOfCores and hit Enter to determine the number of CPU cores.
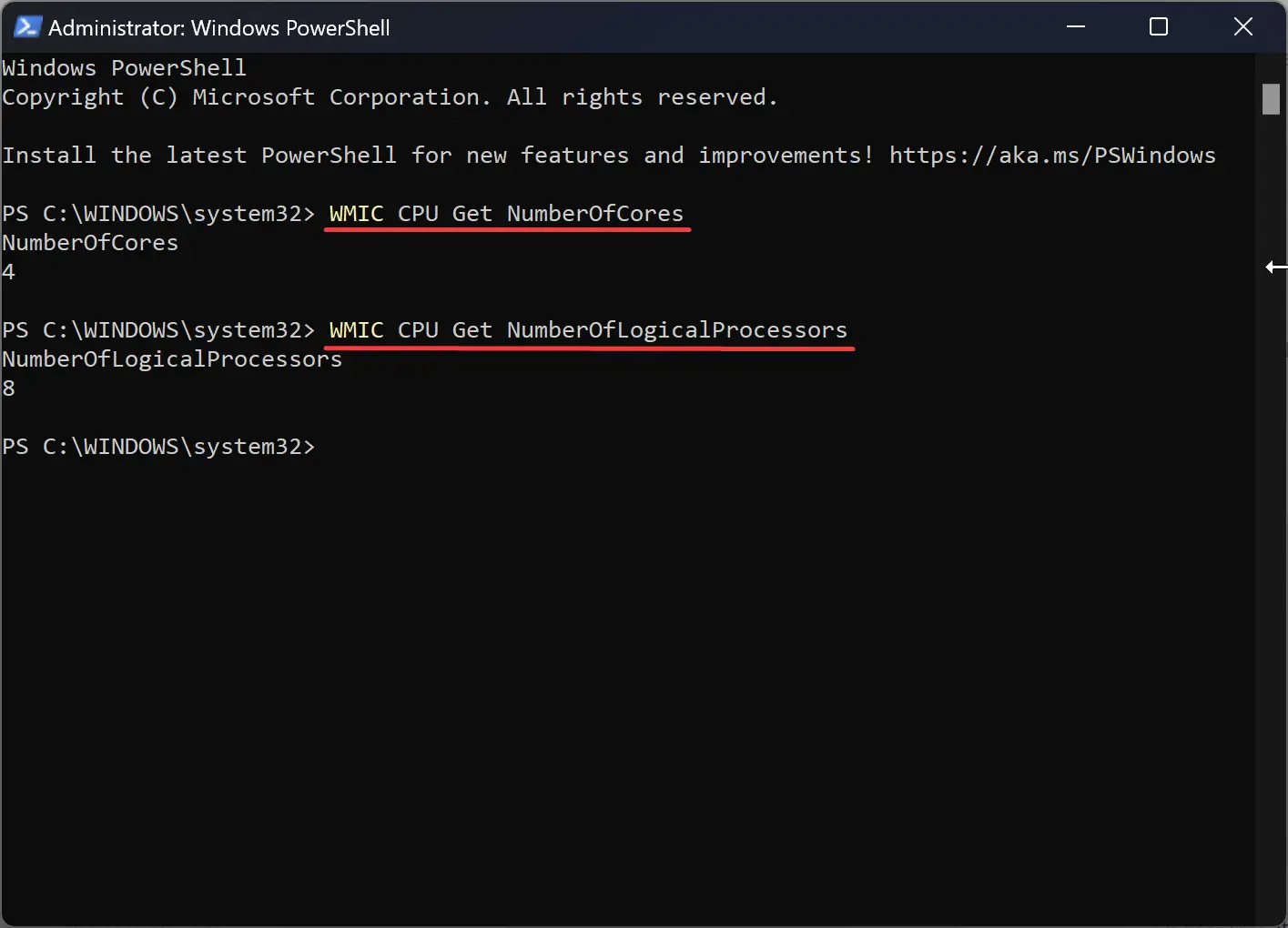
Step 3. Now, enter WMIC CPU Get NumberOfLogicalProcessors to determine the number of threads.
With Command Prompt
The same WMIC command that you used above in Windows PowerShell can also be used on the Command Prompt to find CPU information. The steps are as follows:-
Step 1. Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
On the taskbar, click the Start button and enter Command Prompt. Right-click on the Command Prompt entry and select the Run as administrator option.
Step 2. Then, enter WMIC CPU Get NumberOfCores and hit Enter to determine the number of CPU cores.
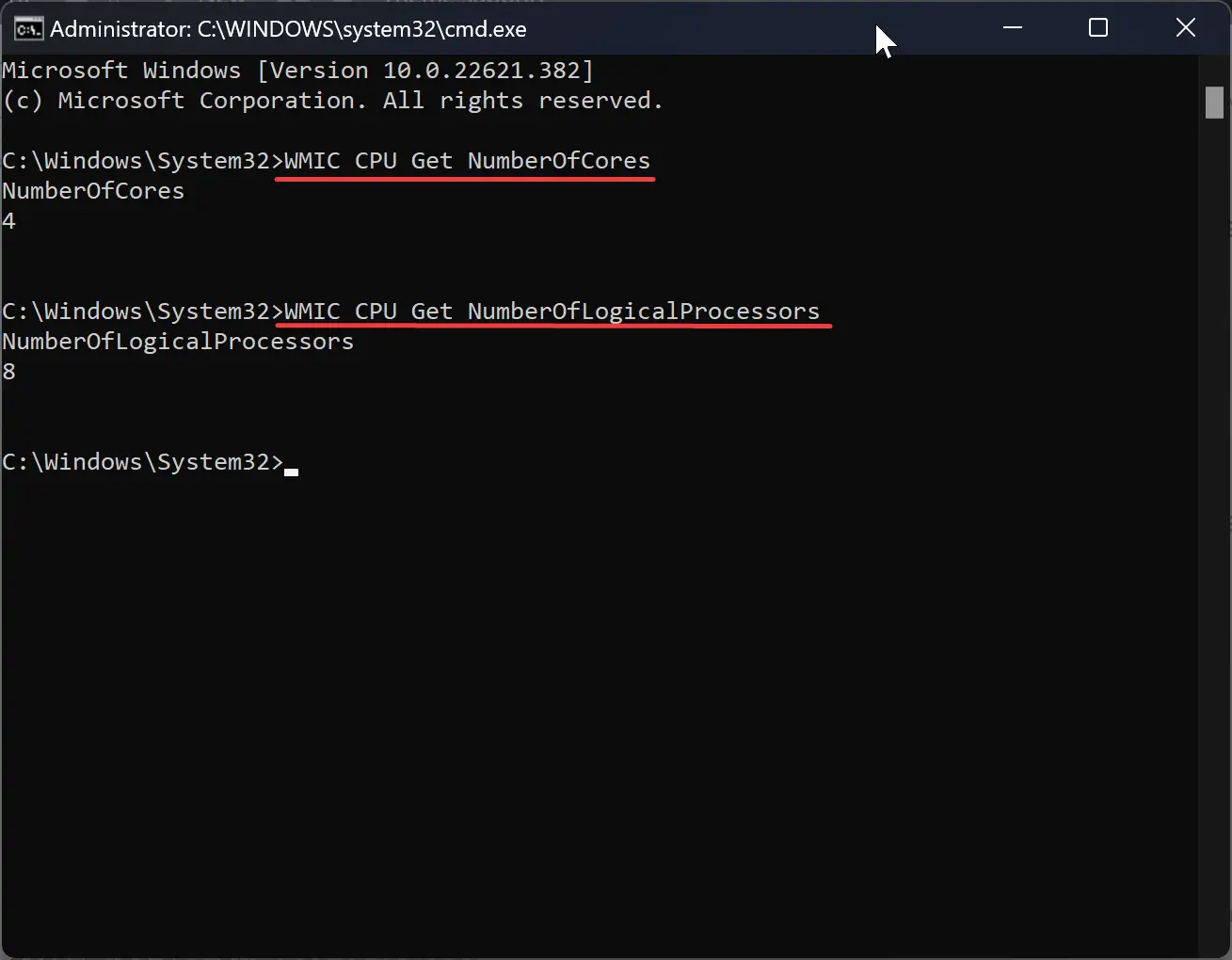
Step 3. Now, enter WMIC CPU Get NumberOfLogicalProcessors to determine the number of threads.
Using Third-Party Software
It is also possible to learn about the hardware of your PC, including the CPU, by using free third-party software like CPU-Z and HWiNFO. Although you do have to download and install these, they are some of the most comprehensive free tools out there if you want to learn every single detail about your system. In general, third-party software is dense with information and is used by professionals.
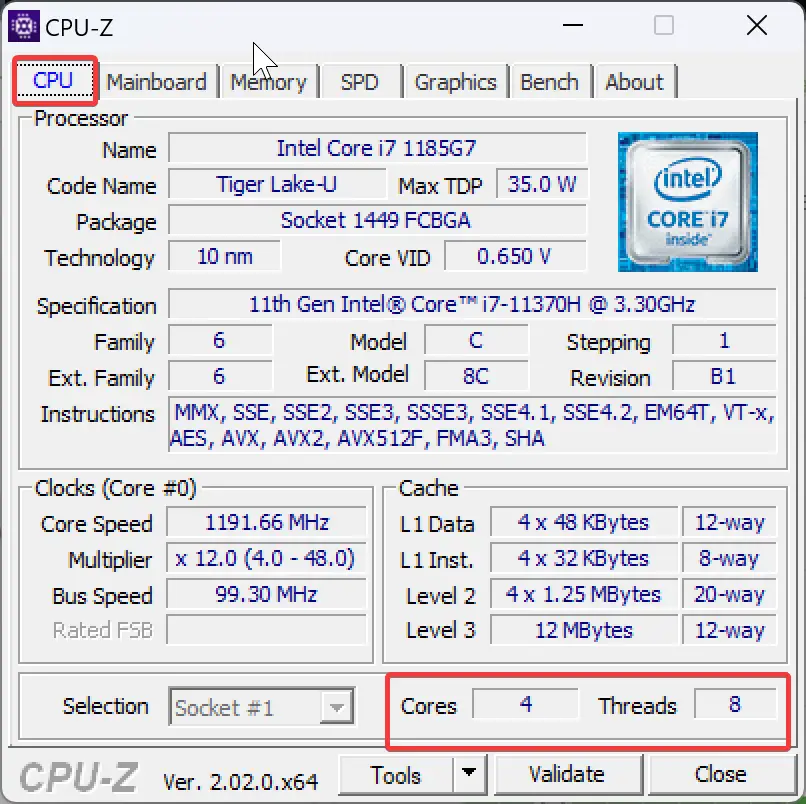
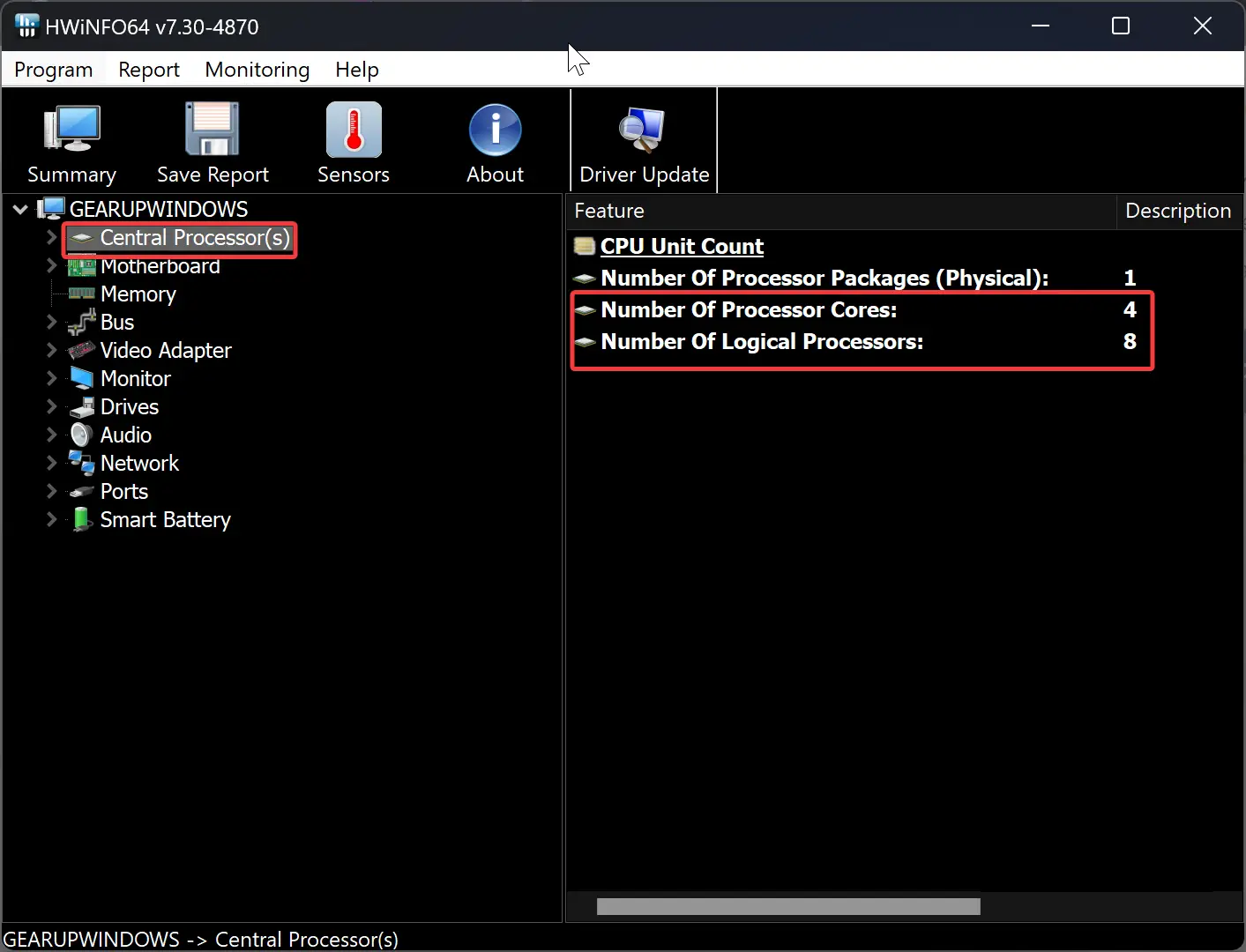
In the CPU-Z application, you can find cores and threads in the CPU tab. Whereas the HWiNFO tool displays information about cores and threats after selecting the “Central Processor(s)” option in the left sidebar.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knowing the number of CPU cores and threads is important for optimizing your computer’s performance, especially when multitasking, playing multithreaded games, or rendering videos. Fortunately, Windows 11 and 10 provide various ways to find this information. You can use the System Information panel, Task Manager, Windows PowerShell, or Command Prompt. Alternatively, third-party software like CPU-Z and HWiNFO can provide comprehensive details about your system’s hardware. By following these simple steps, you can quickly and easily find out how many CPU cores and threads your Windows 11 or 10 PC has.
- To determine a processor core count on Windows, open Task Manager’s Performance tab, click on “CPU,” and check the core number in the details.
- You can also use Command Prompt and PowerShell to find out this information.
UPDATED 1/28/2025: Windows 11 and 10 offer several ways to check how many cores your computer’s processor has. In this guide, I’ll outline three simple methods to find this information.
Most modern computers come with processors that have multiple physical cores, allowing them to process multiple instructions simultaneously. For example:
- A dual-core processor has “2” cores and can handle two sets of instructions at once.
- A quad-core processor has “4” cores and can process four sets of instructions simultaneously.
This scaling continues with processors featuring 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 18, 24, 28, or even 32 cores.
In addition to physical cores, many CPUs (Central Processing Units) support Hyper-Threading. This technology, available on Intel, Qualcomm, and AMD processors (AMD calls it “threads”), enables each core to handle two instructions simultaneously. If your processor supports this feature, it will also have logical processors, effectively doubling the number of available threads.
Knowing the number of cores and logical processors in the processor is useful in various scenarios, such as running virtual machines or optimizing performance for apps that benefit from multi-core processing.
Whatever the reason, Windows 11, as well as Windows 10, provide multiple built-in tools to check your processor’s core count. You can use Task Manager, Command Prompt, or PowerShell to find this information quickly.
In this guide, I will teach you how to determine the number of cores your Intel, AMD, or ARM processor has on Windows. (You can also use these instructions to find out if your computer has an NPU (Neural Processing Unit).)
- Check CPU core count from Task Manager
- Check CPU core count from Command Prompt
- Check CPU core count from PowerShell
Check CPU core count from Task Manager
To determine the number of cores your processor has on Windows 11 (and 10) through Task Manager, use these steps:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for Task Manager and click the top result to open the app.
-
Click the Performance tab.
-
Click on CPU from the left pane.
-
Check the core count at the bottom of the page.
Quick tip: If your processor has hyper-threading, you can also see the number of “Logical processors,” which is usually twice as many as the number of physical cores.
Once you complete the steps, you’ll understand your computer’s physical cores and logical processors.
Check CPU core count from Command Prompt
To check how many cores your CPU has through Command Prompt, use these steps:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for Command Prompt and click the top result to open the console.
-
Type the following command to find out how many cores your CPU has, and press Enter:
wmic cpu get NumberOfCores,NumberOfLogicalProcessors
-
Check the CPU core count and logical processors.
After you complete the steps, you’ll know the number of cores and logical processors on your machine.
Check CPU core count from PowerShell
To find out the processor core count through PowerShell, use these steps:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for PowerShell and click the top result to open the console.
-
Type the following command to find out how many cores your CPU has, and press Enter:
Get-WmiObject –class Win32_processor | ft NumberOfCores,NumberOfLogicalProcessors
- Check the processor core count and logical processors.
Once you complete the steps, the command will output the number of physical cores and logical processors on your computer (if it has hyperthreading).
Update January 28, 2025: This guide has been updated to ensure accuracy and reflect changes to the process.
Как узнать сколько ядер у процессора
Если по какой-то причине у вас возникли сомнения по поводу количества ядер CPU или просто одолело любопытство, в этой инструкции подробно о том, как узнать сколько ядер процессора на вашем компьютере несколькими способами.
Заранее отмечу, что не следует путать количество ядер (cores) и потоков или логических процессоров (threads): часть современных процессоров имеют по два потока (своего рода «виртуальных ядер») на одно физическое ядро и в итоге, заглянув в диспетчер задач вы можете увидеть диаграмму с 8-ю потоками для 4-х ядерного процессора, аналогичная картинка будет и в диспетчере устройств в разделе «Процессоры». См. также: Как узнать сокет процессора и материнской платы.
Способы узнать количество ядер процессора
Посмотреть, сколько физических ядер и сколько потоков у вашего процессора можно различными способами, все они достаточно простые:
- Во встроенной утилите Windows «Сведения о системе»
- С помощью командной строки Windows 10, 8.1 и Windows 7
- В диспетчере задач Windows 10 (в предыдущих версиях в диспетчере задач можно посмотреть лишь число «логических процессоров», т.е. потоков)
- На официальном сайте производителя процессора
- С помощью сторонних программ
Думаю, что это не полный список возможностей, но вероятнее всего их окажется достаточно. А теперь по порядку.
Сведения о системе
В Windows последних версий присутствует встроенная утилита для просмотра основных сведений о системе. Запустить её можно, нажав клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре и введя msinfo32 (затем нажать Enter).
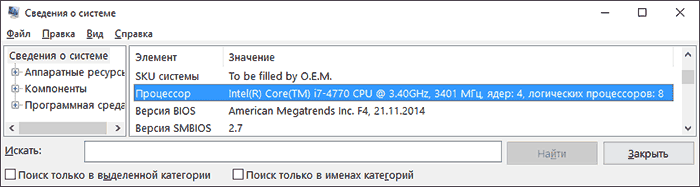
В разделе «Процессор» вы увидите модель вашего процессора, количество ядер (физических) и логических процессоров (потоков).
Узнаем, сколько ядер у CPU компьютера в командной строке
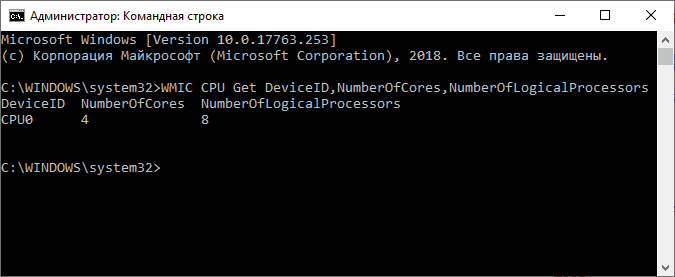
Не все знают, но посмотреть информацию о количестве ядер и потоков можно и с помощью командной строки: запустите её (не обязательно от имени Администратора) и введите команду
WMIC CPU Get DeviceID,NumberOfCores,NumberOfLogicalProcessors
В результате вы получите список процессоров на компьютере (обычно — один), количество физических ядер (NumberOfCores) и количество потоков (NumberOfLogicalProcessors).
В диспетчере задач
Диспетчер задач Windows 10 отображает информацию о количестве ядер и потоков процессора вашего компьютера:
- Запустите диспетчер задач (можно через меню, которое открывается по правому клику на кнопке «Пуск»).
- Перейдите на вкладку «Производительность».

На указанной вкладке в разделе «ЦП» (центральный процессор) вы увидите информацию о ядрах и логических процессорах вашего CPU.
На официальном сайте производителя процессора
Если вы знаете модель вашего процессора, которую можно увидеть в сведениях о системе или открыв свойства у значка «Мой компьютер» на рабочем столе, вы можете узнать его характеристики на официальном сайте производителя.
Обычно достаточно просто ввести модель процессора в любой поисковик и уже первый результат (если пропустить рекламные) будет вести на официальный сайт Intel или AMD, где можно получить технические характеристики вашего CPU.
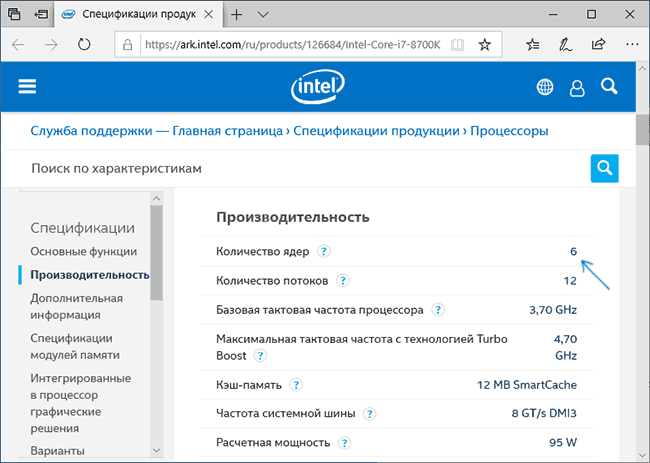
Технические характеристики включают в себя в том числе и информацию о количестве ядер и потоков процессора.
Информация о процессоре в сторонних программах
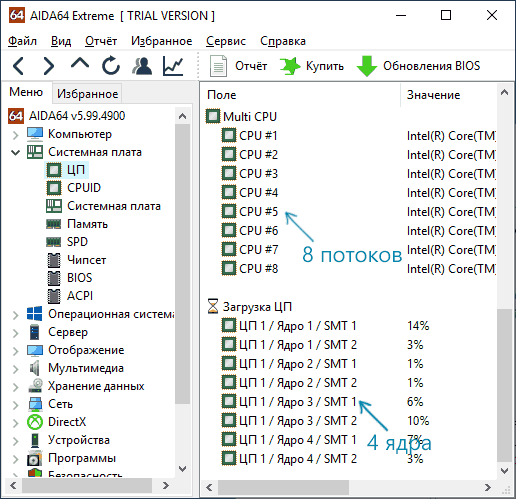
Большинство сторонних программ для просмотра аппаратных характеристик компьютера показывают, в том числе, и сколько ядер имеет процессор. Например, в бесплатной программе CPU-Z такая информация располагается на вкладке CPU (в поле Cores — количество ядер, в Threads — потоков).

В AIDA64 в разделе ЦП также можно получить информацию о количестве ядер и логических процессоров.
Подробнее о таких программах и где их скачать в отдельном обзоре Как узнать характеристики компьютера или ноутбука.



