Quick Links
-
Use Event Viewer to View BSOD Logs
-
Use Reliability Monitor to Access BSOD Logs
-
Make Windows 11 Display Error Details on the BSOD
Summary
To view Windows 11’s BSOD logs:
- Open Event Viewer.
- Click Action > Create Custom View.
- Change the «Logged» timeframe to one that includes when you saw the error.
- Check the «Error» box.
- Change Event Logs to «Windows Logs» and click OK.
- Enter a name for your view and select OK.
- Click each logged error to view its details.
Got a BSOD (Blue Screen of Death)? Checking Windows 11’s error logs could reveal what caused it. You can use either Event Viewer or Reliability Monitor, and you can also force the BSOD screen itself to display the error information in the future. Here’s how to do that.
Why Look at BSOD Logs?
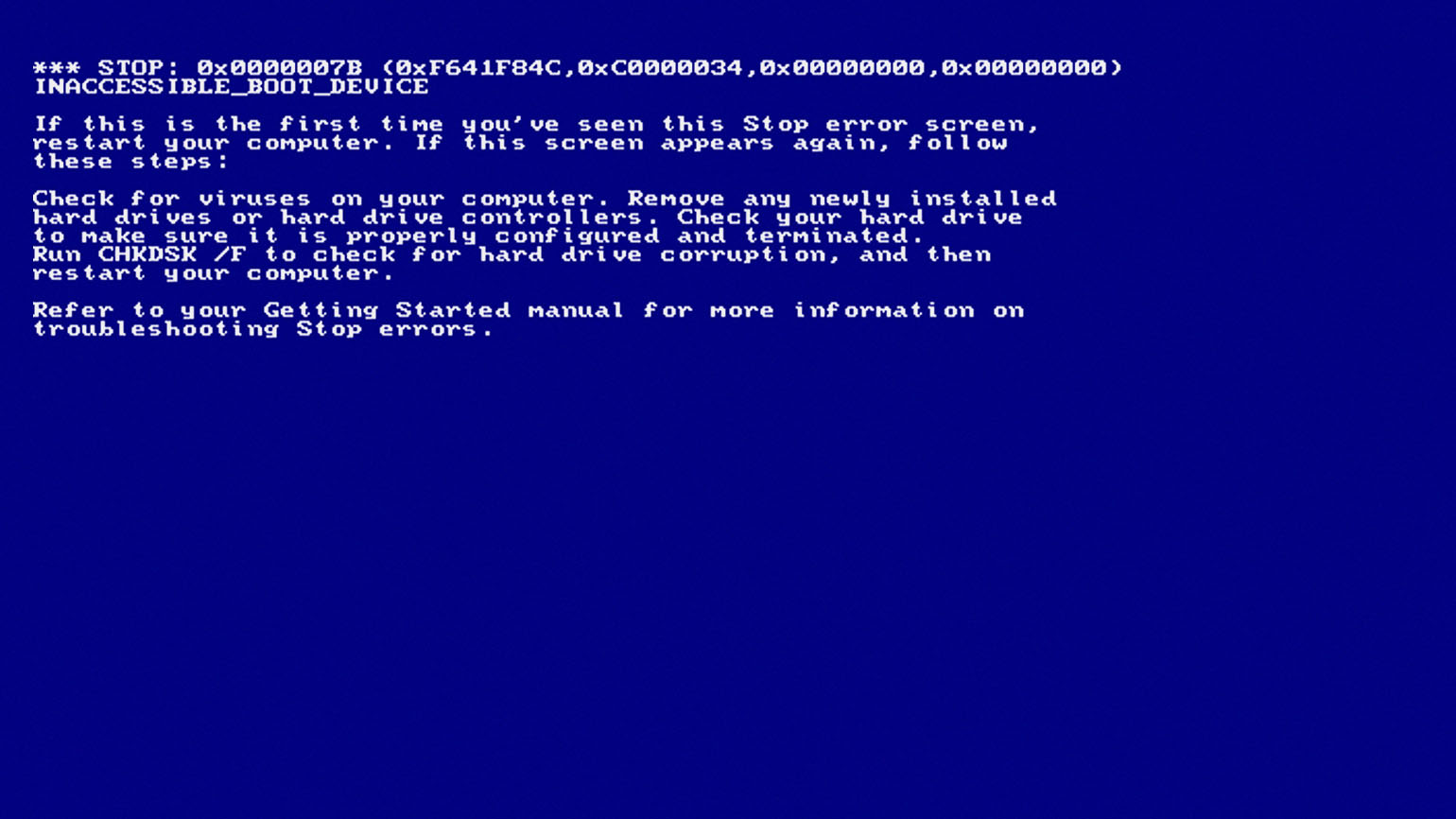
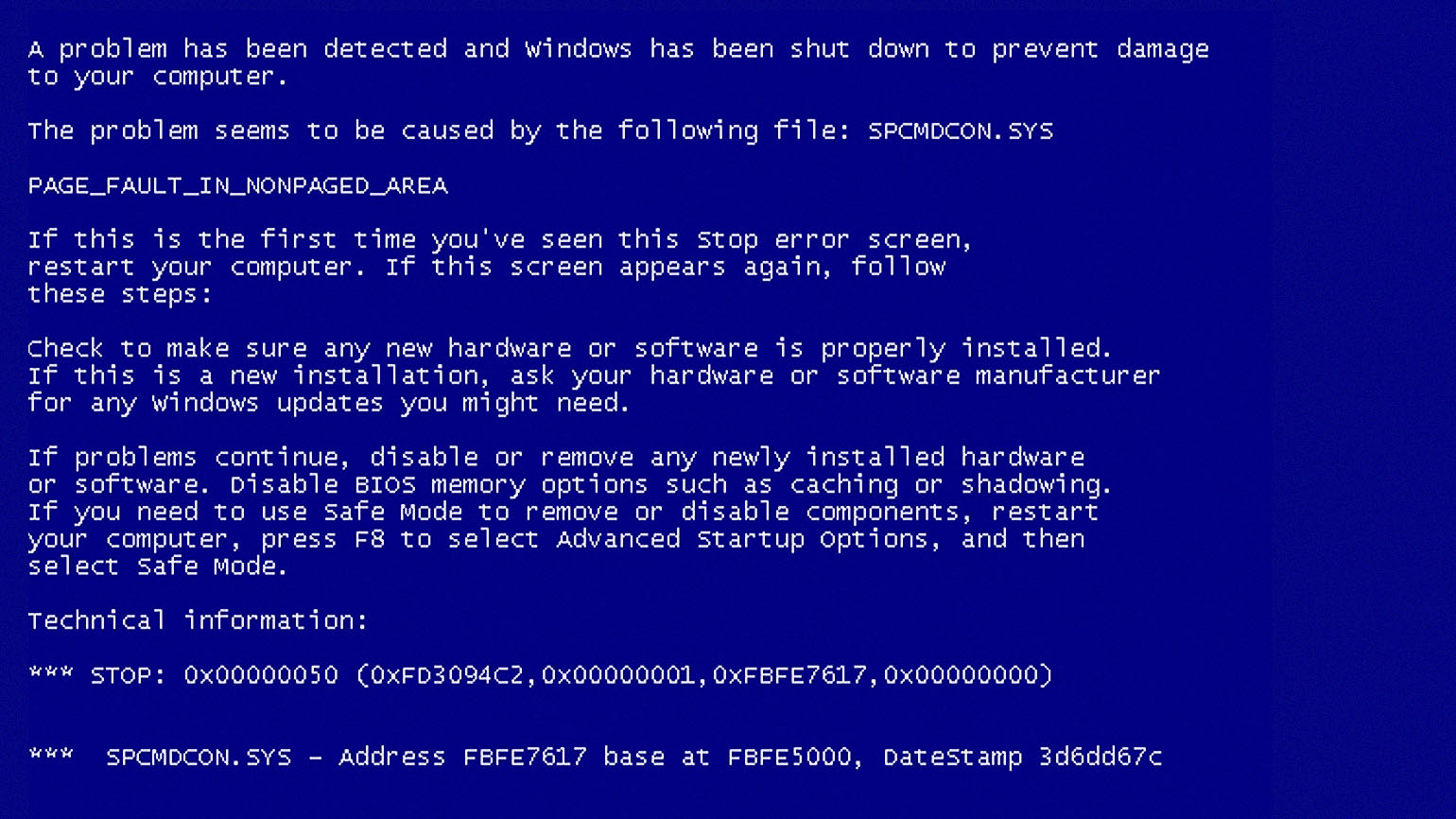
The main reason to find BSOD logs is to get to the root of the problem. You may have encountered a BSOD error, like the infamous Kmode exception not handled error, but you don’t know exactly what caused it and how it happened.
With BSOD logs, you get to see the program that caused the problem as well as other useful and related information to help you deal with the issue.
Once you’ve found your error log, you can analyze it, find the cause of the problem, and fix the underlying issue to prevent further BSOD errors.
Use Event Viewer to View BSOD Logs
A quick and easy way to access your BSOD logs is to use your PC’s built-in Event Viewer tool. This tool lets you create a custom report that contains the errors and logs from your specified timeframe. The process for this method involves more steps (at least the first time you do it) than using Reliability Monitor, but the data it gives you is more comprehensive.
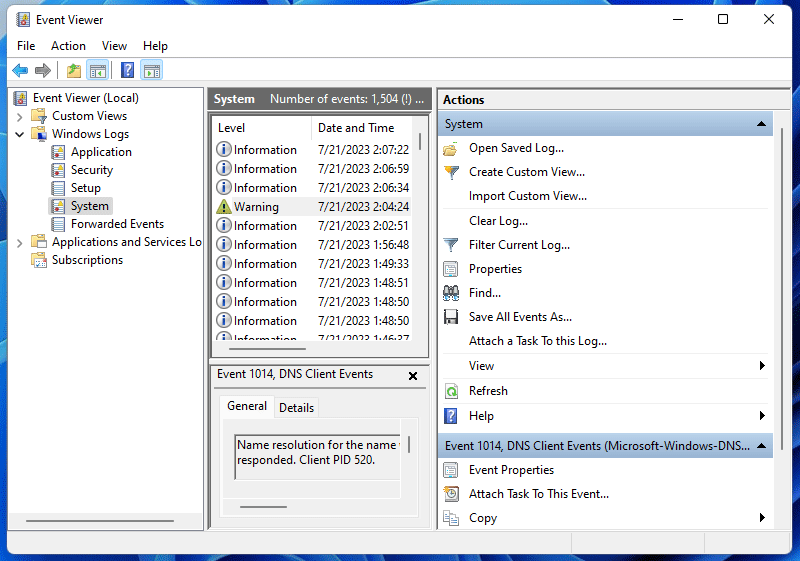
To do that, first, open Event Viewer by right-clicking your «Start» menu icon and choosing «Event Viewer.»
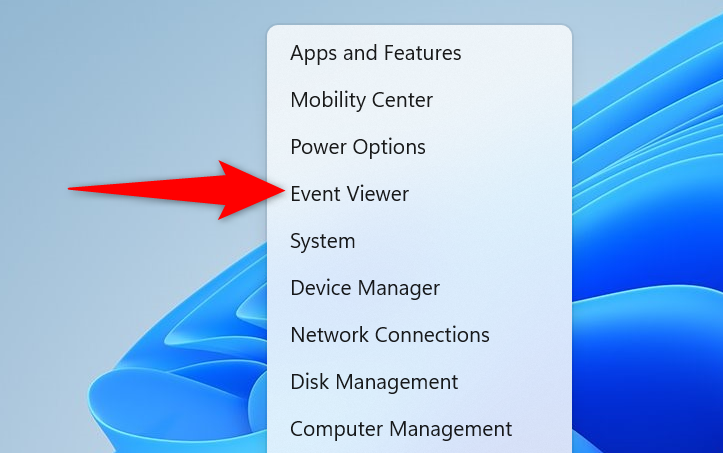
In Event Viewer, from the menu bar, select Action > Create Custom View.
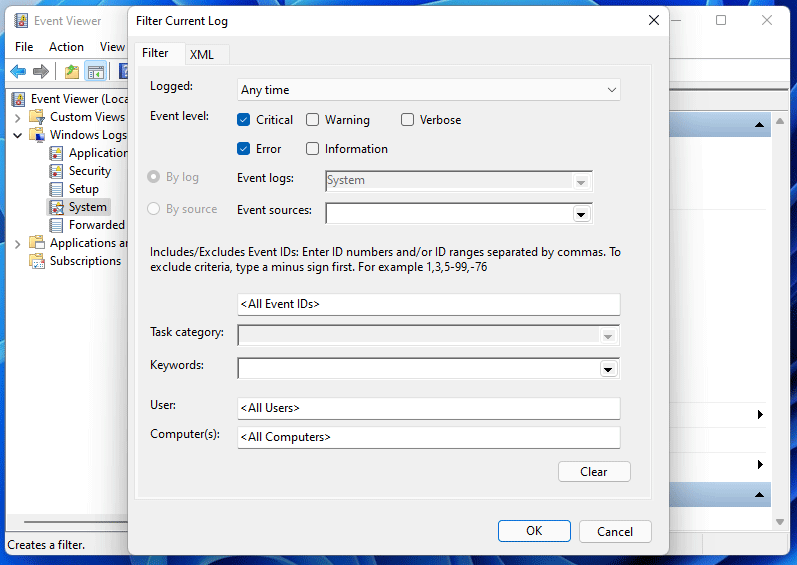
You’ll land on a «Create Custom View» page. Here, at the top, select the «Filter» tab. Then, click the «Logged» menu and choose the timeframe for which you want to see the logs. Make sure to select the timeframe when your BSOD error occurred.
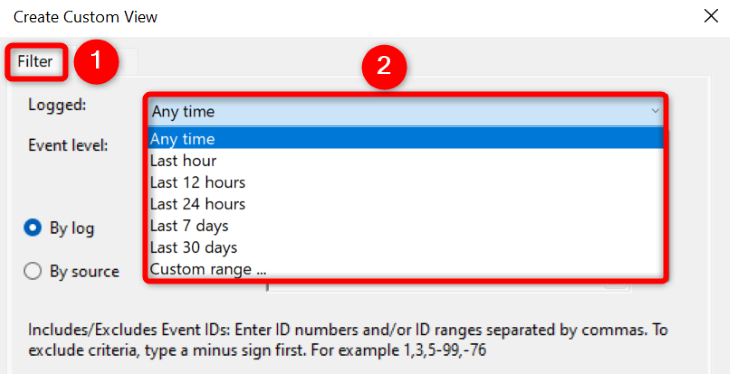
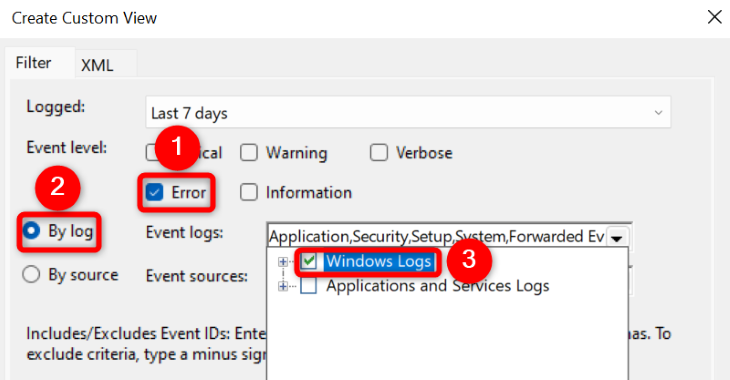
Next, in the «Event Level» section, choose «Error.» Turn on the «By Logs» option, click the «Event Logs» drop-down menu, and choose «Windows Logs.»
Then, confirm your selection by choosing «OK.»
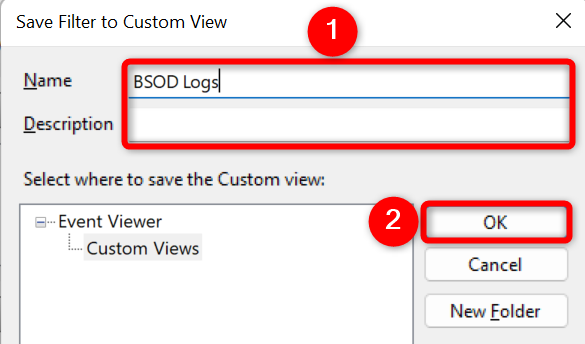
You’ll now save the custom view so that it’s easier to find these logs in the future. To do that, click the «Name» field and enter a name for your view. Enter a descriptive name (like BSOD Logs) so you can quickly find it again. Then, click «OK.»
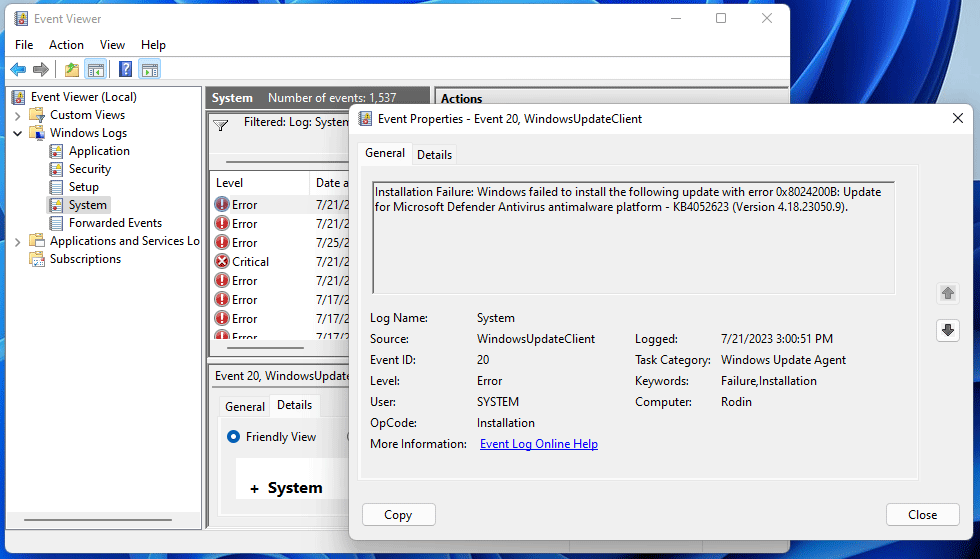
Your custom view is now ready to use. On your current screen, you’ll see all the errors that occurred in your specified timeframe on your PC. To get more details about an error, select it on the list. Then, beneath the error, you’ll see more information about it.
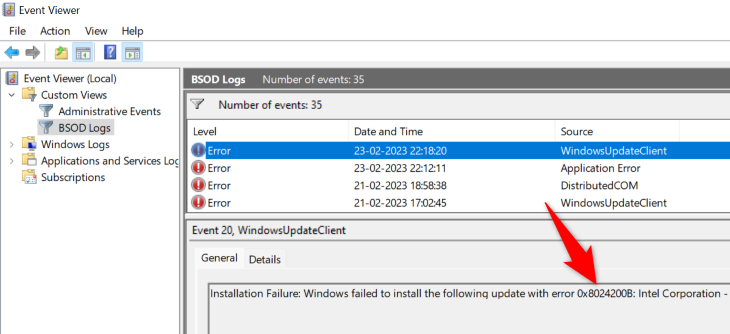
In the future, to access this custom log view, open Event Viewer, choose «Custom Views» on the left, and select the name of your custom view.
With the information available in these logs, you can take the appropriate steps and rectify your PC problems. Good luck!
Use Reliability Monitor to Access BSOD Logs
Another way to access error message logs in Windows 11 is to use Reliability Monitor. This tool monitors your PC’s usage over a period of time, allowing you to quickly get to any errors that have occurred on your machine. It may not give you quite as much data as Event Viewer does, but accessing Reliability Monitor is faster and it gives you a visual chart representing your PC’s overall stability.
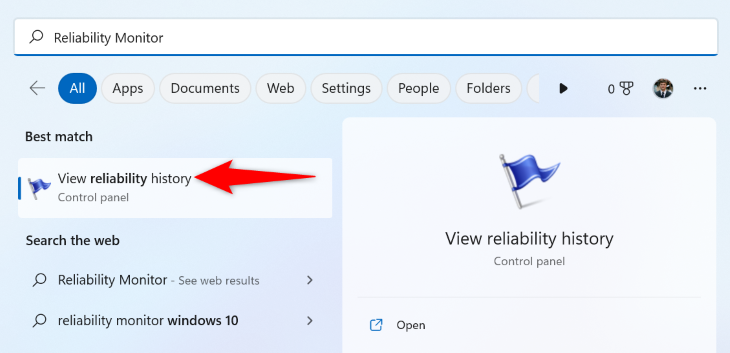
To access the tool, open the «Start» menu, search for «Reliability Monitor», and click «View Reliability History» in the search results.
On the screen that opens, you’ll see a graph showing your system’s status. Here, an error message is indicated with a red «X.» Click this icon for your error, and then in the pane at the bottom, double-click the error.
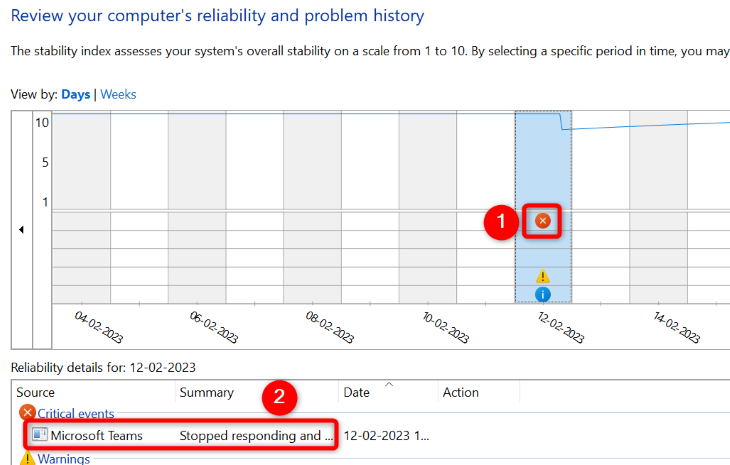
The screen that opens displays more information about your selected error. Here, the «Description» section will give you details about your issue.
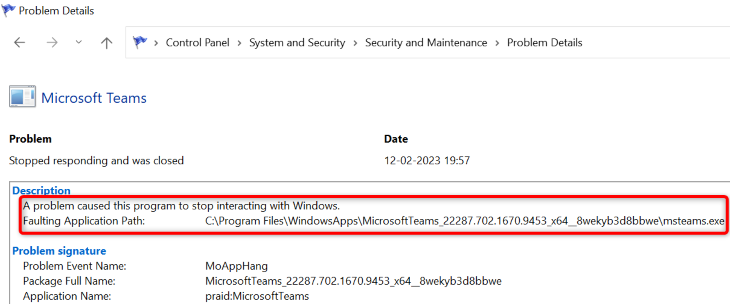
You now have some information about your BSOD error, and you can apply the possible fixes to resolve your problem.
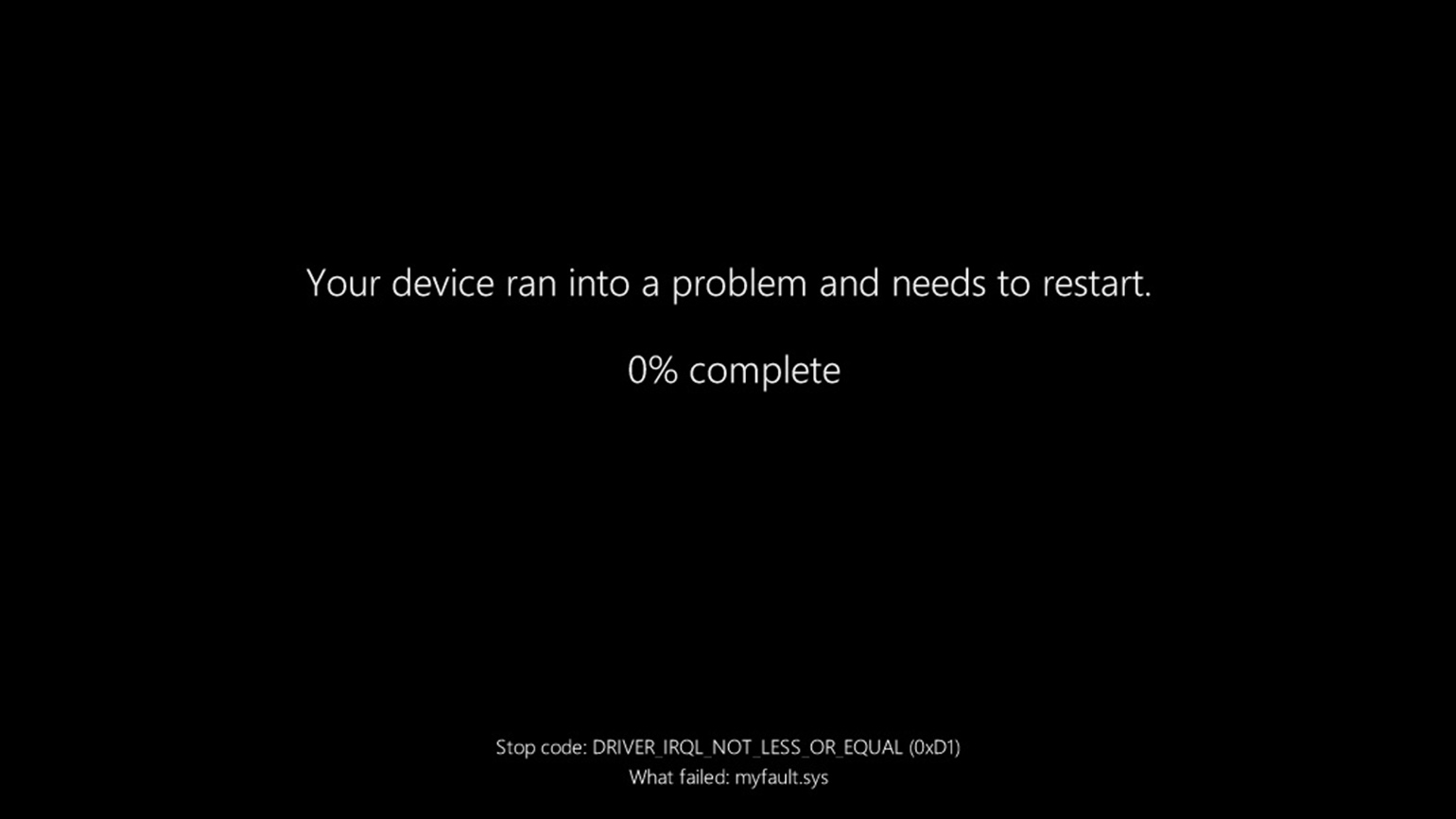
Make Windows 11 Display Error Details on the BSOD
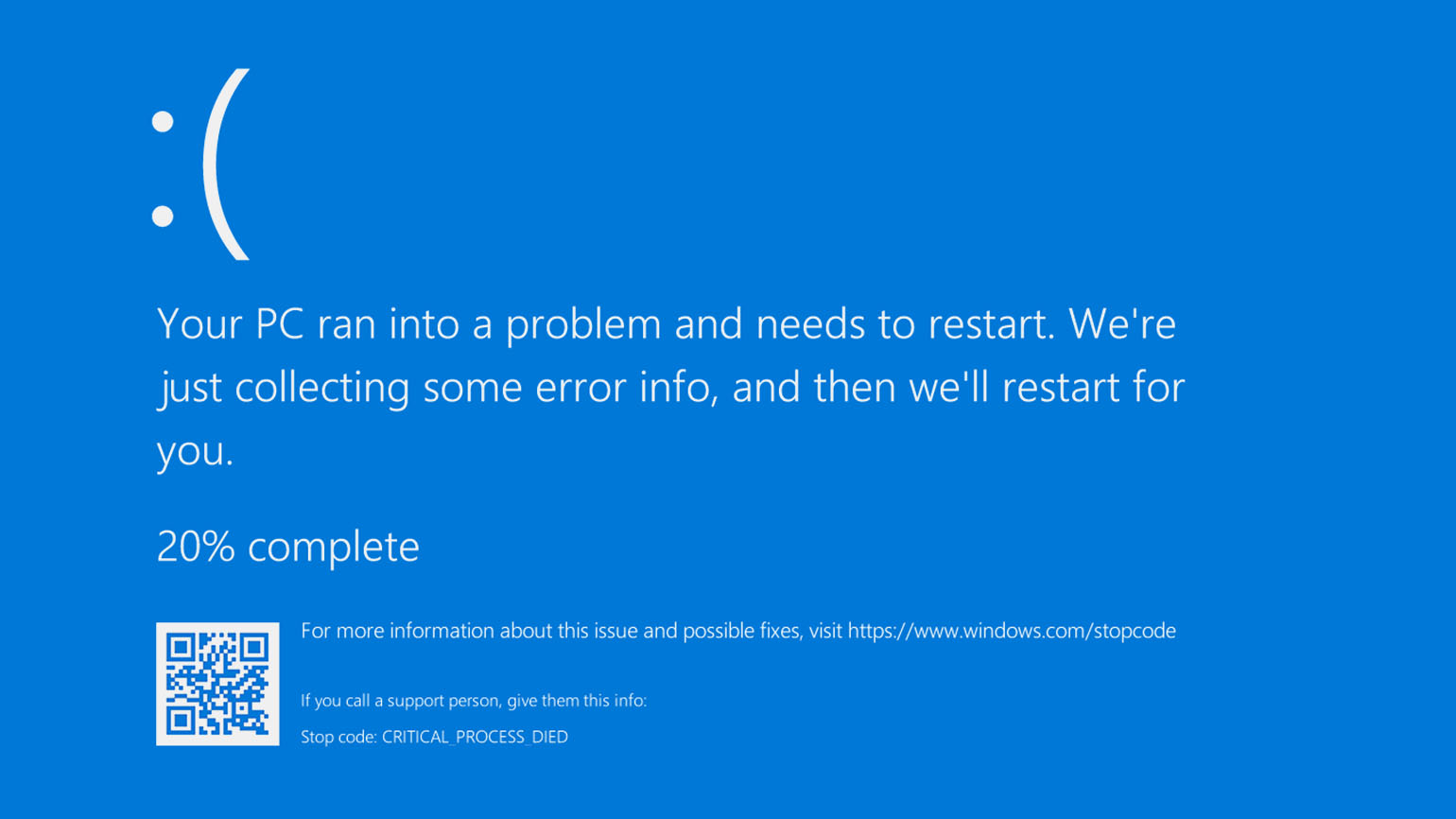
By default, Windows 11’s blue screen of death doesn’t display any information that can help you deal with the issue. It only shows a sad smiley and nothing much of value.
Luckily, you can change that and make the BSOD display more useful information. This information can help you find out the cause of the problem so you can fix it and get rid of BSOD.
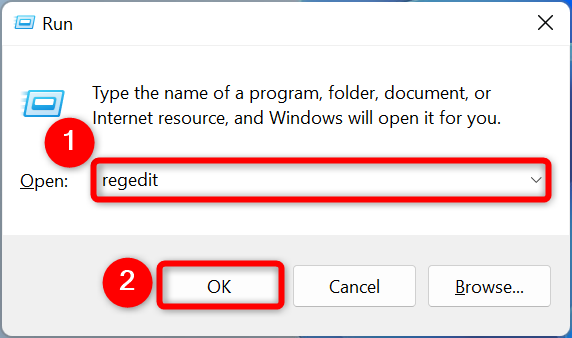
To get Windows 11 to show more details on the BSOD, add an entry to your PC’s registry. Start this process by opening the Run dialog box using Windows+R, typing the following in the box, and pressing Enter (or selecting «OK.»)
regedit
In the «User Account Control» prompt, select «Yes.»
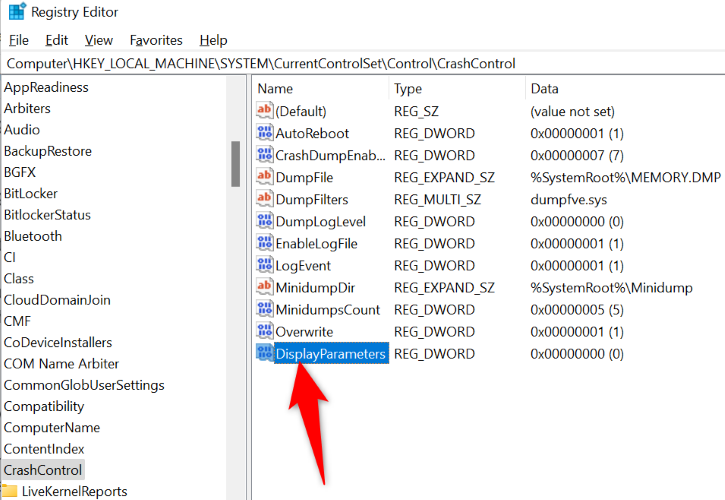
You’ll see a Registry Editor window. Here, navigate to the following path. Then, on the right pane, right-click anywhere blank and choose New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl
Enter DisplayParameters as the entry name and press the Enter key. Then, double-click this entry.
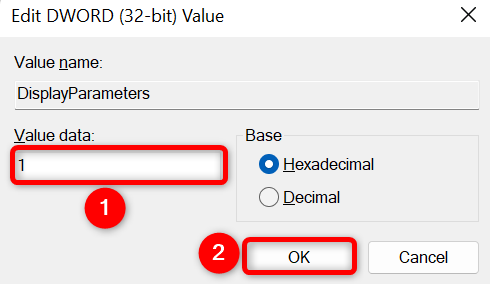
A small box will open. Here, click the «Value Data» field and enter 1 . Then, select «OK.»
You’ve successfully added the required entry to your registry. Now, reboot your PC to bring your changes into effect. From now on, when a BSOD error occurs, you’ll see the error details right on the BSOD itself.
And that’s how you access more details about your BSOD error on Windows 11. We hope these logs help you fix your PC problems.