Last Updated :
22 Apr, 2025
Learn how to manually run the Command Prompt in different versions of Windows — The Windows Command Prompt (CMD) is a powerful tool that allows users to execute commands, automate tasks, and troubleshoot system issues efficiently. Whether you’re a beginner looking to learn basic CMD commands or an advanced user wanting to optimize your workflow, mastering the Windows Command Line Interface (CLI) can significantly enhance your computing experience.
In this step-by-step Windows Command Prompt tutorial, we’ll cover everything from basic commands like cd, dir, and mkdir to advanced functions such as network troubleshooting, batch scripting, and system management. Learning CMD can help you navigate Windows faster, execute tasks more efficiently, and fix errors that may not be solvable via the graphical interface.
Follow this tutorial to unlock the full potential of Windows Command Prompt and take control of your system like a pro.

What is a Command Prompt?
The Command Prompt is a powerful tool for troubleshooting Windows and managing files. It provides a text-based interface where users can execute various system commands and configure their computer. The Command Prompt is for all levels of users who are looking to perform advanced Command Prompt techniques, CMD also opens a broad range of capabilities, from automating tasks to system diagnostics.
- What is a Command Prompt?
Getting Started with Command Prompt
Learn how to open the Windows Command Prompt and understand its basic functions. This foundational knwoledge is seesntial for navigating your system using simple command-line.
- How to Open Command Prompt in Windows 11, 10, 8, 7
- How to Open Command Prompt as Administrator?
- How to Open Command Prompt with Keyboard Shortcuts
Basic Command Prompt List
Master the essential CMD commands to manmage directories, list files and clear the screen. These commands are fundamental for effective system navigation.
- cd
- dir
- cls
Also read 39 Windows CMD Commands for Everyone
System Information
Utilize systeminfo and ipconfig commands to retrieve detailed information about your system’s configuration, including network settings and hardware specifications. This is crucial for troubleshooting and system optimization.
- System Info
- ipconfig
- ping
- tasklist
File and Directory
In this section, you’ll get to know how to list all files in directories, search files using CMD, and will also allow you to create, manage and delete files and folders.
- List all Files in a Directory
- Search files
- mkdir
- Rename (files and folders)
- del
- Hide
- Compress (files and folders)
- copy
- Xcopy
- move
Networking and Connectivity
Diagnose and configure network settings with netstat, ping and tracert commands. These tools help you to test network connections, check network routes, and troubleshoot connectivity issues in your Windows system.
- netstat
- Check Open Ports
- tracert
- ftp
- Telnet
- nslookup
System Utilities
Maintain and repair system files using sfc and chkdsk commands. These built-in prompts are essential to ensure that you can make the most out of it.
- Difference Between SFC, CHKDSK, and DISM
- Chkdsk
- Repair
- sfc
- Diskpart
Advanced Commands
In this section, you’ll get to know some of the advanced CMD commands and functionality to automate your system tasks so that you can manage and perform any complex tasks with ease.
- Powershell
- Abort Command Execution
- Regedit
- Shutdown
- CMD Commands to Gather Information of a System
Customization
Personalize your Command Prompt experience by changing its font, text, creating batch file, Wi-Fi Hotspot, and Install program. These commands will enhance and make your experience seamless.
- Color cmd command
- Change text colour
- How to Clear the Windows Command Prompt Screen
- Setting up custom batch file
- Create a Wi-Fi Hotspot
- Merge/Hide One File into Another
- Copy files from one Directory to another
- Personalize Environment
- Hide text behind text
- Install Program
- Install Chocolatey
- Install Specific Version using Chocolatey
- Uninstall Software
Common Troubleshooting
You can use CMD troubleshooting commands like bootrec, bcdedit and sfc to diagnose and fix boot issues, repair corrupt files, and resolve system errors.
- Scannow
- Bootrec
- Bcdedit
- Remove Virus
- Show Previously Connected Wi-Fi Devices
- How to Repair Windows Common Errors Only With CMD
Command Prompt Tips and Shortcuts
Enhance your productivity with CMD Keyboard Shortcuts such as Ctrl + C (to stop process), Ctrl + Z (undo), or F7 to check the command history. These shortcuts enahnce users to navigate moe efficiently.
- Keyboard shortcuts
- Change and Customize Keyboard Shortcuts
- Command Prompt Hacks
- Useful CMD Commands for Daily Usage
- 26 Useful CMD Commands for Everyone
- Remotely Start Windows
- How to Run an exe through CMD
Command Prompt Real-Life Use Cases
In this section, you’ll get to know about how CMD commands can work as a charm in real-life scenarios. Whether you are looking to automate any task, or schedule it for later, you can do it all by just using the Windows Command Prompt.
- Automate tasks using CMD
- Change Windows Password
- Manage Network configuration
- Basic Scripting with batch files
Do you know what Command Prompt Windows 10 is? Do you know how to open Command Prompt as administrator? Do you know how many Windows 10 Command Prompt commands? This post will explain these questions for you.
What Is Command Prompt
It is common that many users have little understanding of Command Prompt. One reason may go that this function isn’t put outside Windows interface so that users ignore it and haven’t discovered its usefulness yet.
Under this circumstance, knowing Command Prompt Windows 10 becomes necessary.
Command Prompt, also known as CMD, is the command-line interpreter in Windows operating system. You can input commands to your computer so as to tell your computer to take corresponding actions.
Commands vary in different operating systems. Command Line Program of Windows is shown as cmd.exe.
9 Ways to Open Command Prompt Windows 10
Before introducing the detailed Windows 10 Command Prompt commands, users have to know how to open it in Windows.
Generally speaking, two choices are available before running Command Prompt Windows 10: Command Prompt, Command Prompt (Admin).
The author in this part will cover 9 methods to open Command Prompt and you can choose whatever you prefer.
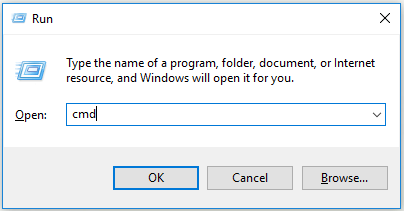
Open Command Prompt Windows 10 from Run Box
Option A: Press Windows + R simultaneously to open Run box. Then type down cmd and click OK to open it.
Option B: After opening Run box, type down cmd and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to run Command Prompt as administrator.
Open Command Prompt Windows 10 from the Start Menu Search
Option A: Click the start menu and type cmd in the search box. Click Command Prompt to run it.
Option B: After Command Prompt appears, you can right-click it to run as administrator.
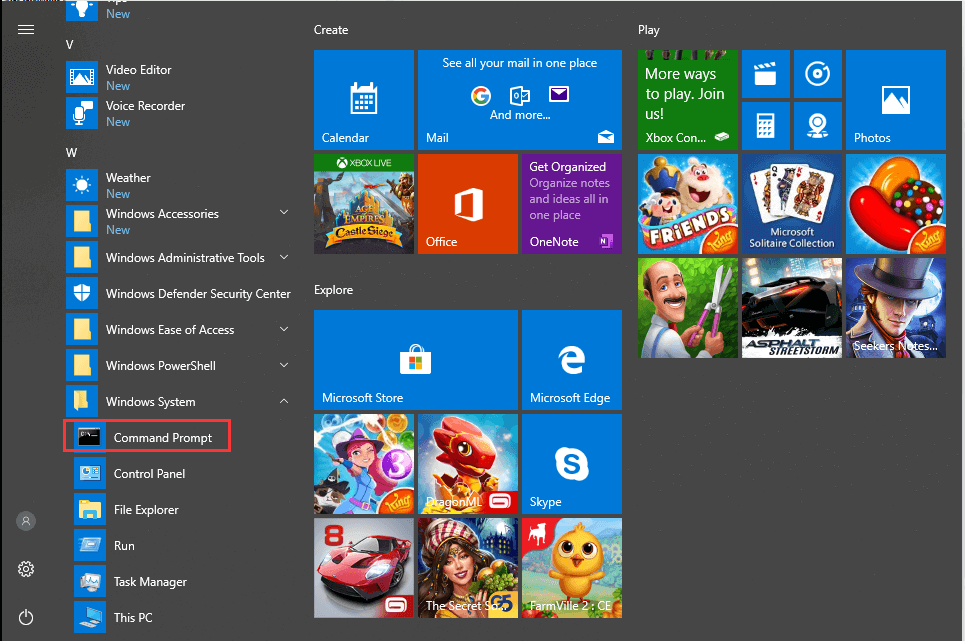
Open Command Prompt Windows 10 by Scrolling the Start Menu
- You can scroll the mouse to search for Command Prompt under the Windows System.
- Click it to run regularly or right-click it to choose as an administrator.
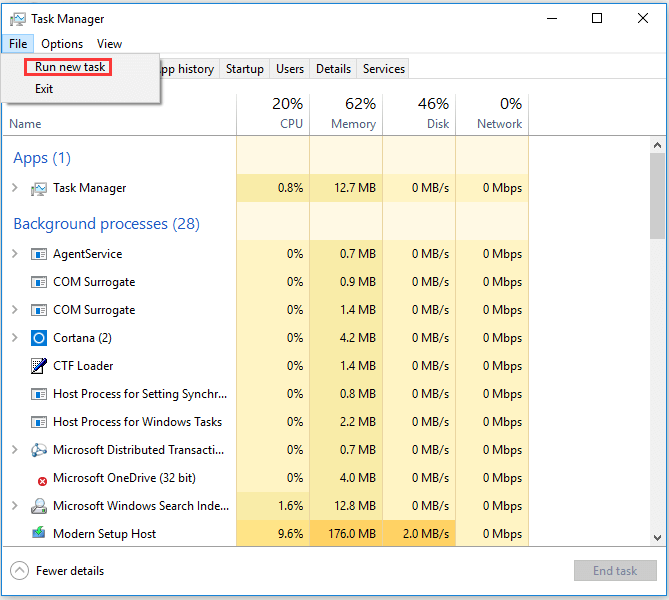
Open Command Prompt Windows 10 from Task Manager
- Type task manager in the search box to open Task Manager.
- Open Files tab and click Run new task and click OK to run Command Prompt regularly or check Create this task with administrative privileges to run as an administrator.
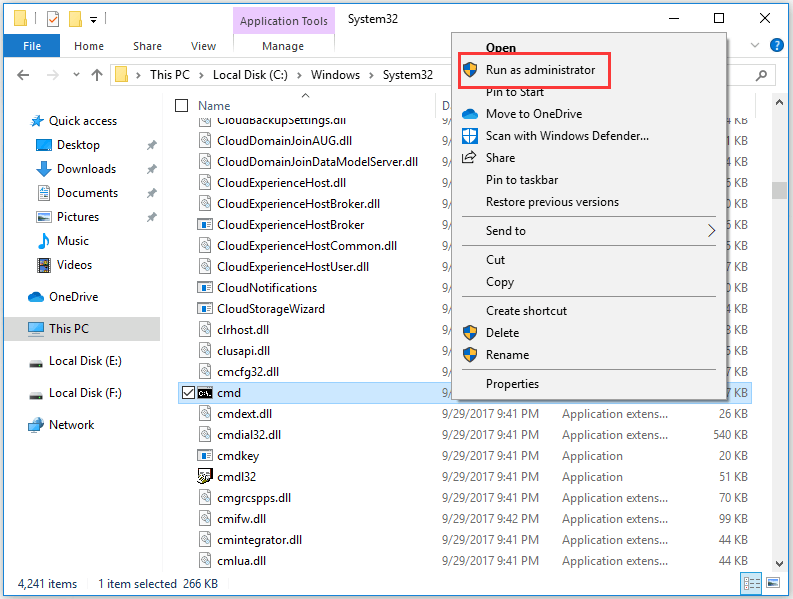
Open Command Prompt Windows 10 from File Explorer
- Open File Explore and navigate to C: drive > Windows > system32 > cmd.
- Right-click cmd to select Run as administrator.
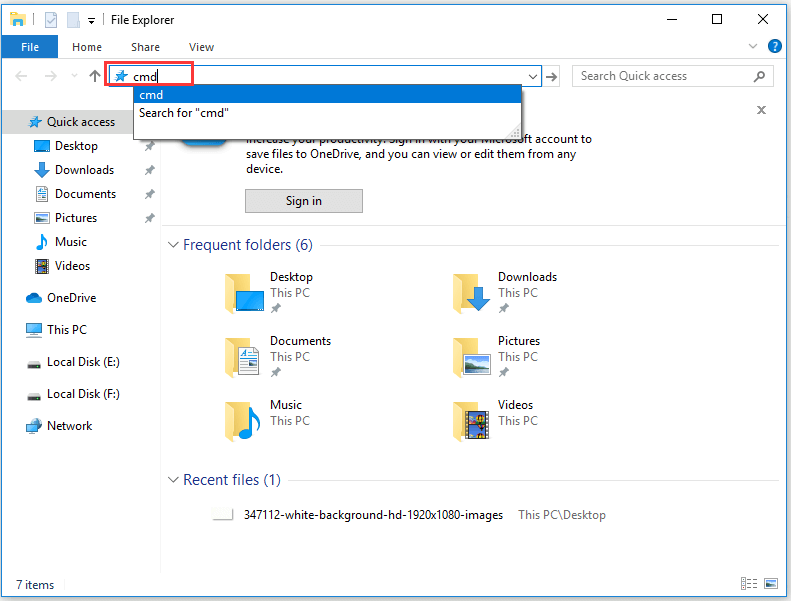
Open Command Prompt Windows 10 from File Explorer Address Bar
- Open File Explorer.
- Type cmd in its address bar and press Enter to run it as administrator.
Open Command Prompt Windows 10 from Win-X Menu
- Press Windows + X keys simultaneously to open Power User Menu.
- Click Command Prompt to run it regularly or click Command Prompt (Admin) to run it as administrator.
Open Command Prompt by Creating Command Prompt Shortcut
- Right-click the desktop to select New and create a shortcut.
- Type down cmd in the location of the item and name the shortcut as cmd.
- Double-click the shortcut or right-click the shortcut to run it as administrator.
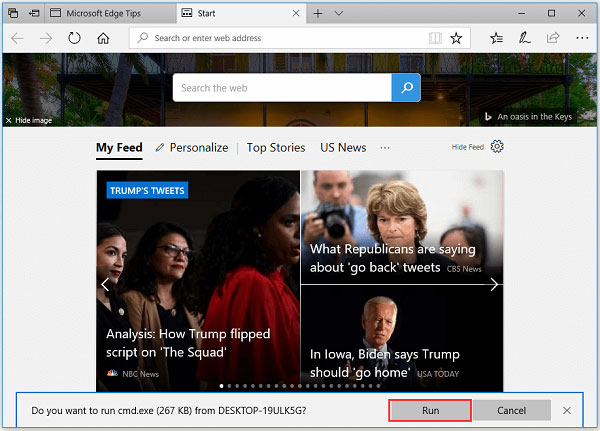
Open Command Prompt by Using Microsoft Edge
- Open Microsoft Edge.
- Type file://C:/Windows/System32/cmd.exe in its address bar and click Enter.
- Click Run to open Command Prompt.
Ten Practical Commands Windows 10 You Must Know
It is not difficult to find a complete computer commands list but it is not easy to master them all. Do you know how to use Command Prompt?
Based on actual situations, the following parts will list ten common commands. These are the most helpful commands and a good mastery of them helps you better control over your Windows PCs.
Tip: It is recommended to run Command Prompt as an administrator to get more privileges and you should press Enter after typing down each command.
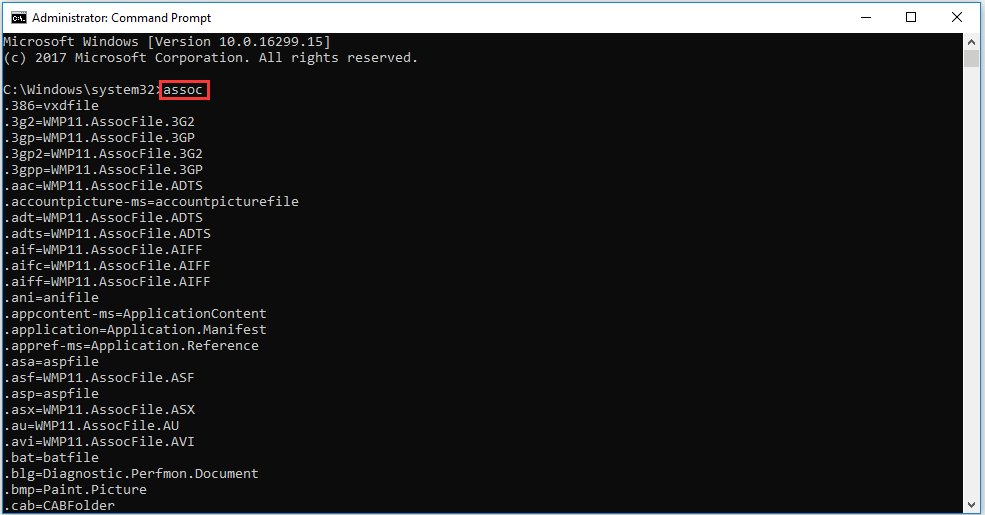
1.Assoc
Assoc plays an important role in Command Prompt Windows 10.
Lots of files are associated with a specific program and this program can open the file by default. However, it is sometimes hard to remember those associations. Therefore, if you type “assoc” on Command Prompt Windows 10, Command Prompt will list all filename extensions and program associations for you.
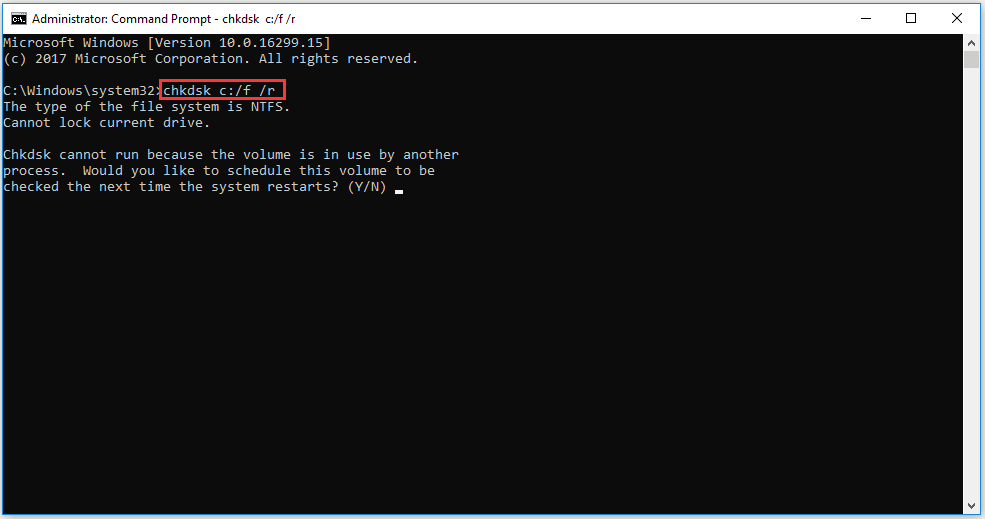
2. Chkdsk
Chkdsk command is mainly used to scan an entire disk. In this way, you can find whether there happens file fragmentation, disk errors or bad sectors on your disk. Apart from scanning, “chkdsk” command can repair your disk as well.
When you launch Command Prompt as an administrator in Windows, type down “chkdsk c:/f /r” (c refers to the letter of the drive you want to scan). This command will scan and repair your C drive during the time your computer restarts.
Tip: This command works only when you run Command Prompt as an administrator, or it will inform you that access is denied as you do not have sufficient privileges.
3. Cipher
Many users believe once they delete the files and empty the recycle bin, these files and data can never be found. However, it is not the case.
Although once you delete files, the space they occupy will be marked as free. They are still recoverable unless new data has been overwritten on it. Other people can use third-party data recovery software such as MiniTool Partition Wizard to get them back, which is not good for privacy.
So, what can you do to clean these data deleted once and for all? Cipher command is a good choice. It is originally used to encrypt files with EFS (Encrypting File System). However, it has another additional function – wipe free space of a hard disk so as to safely erase the deleted files of the free space.
After running Command Prompt, please type down “cipher”.
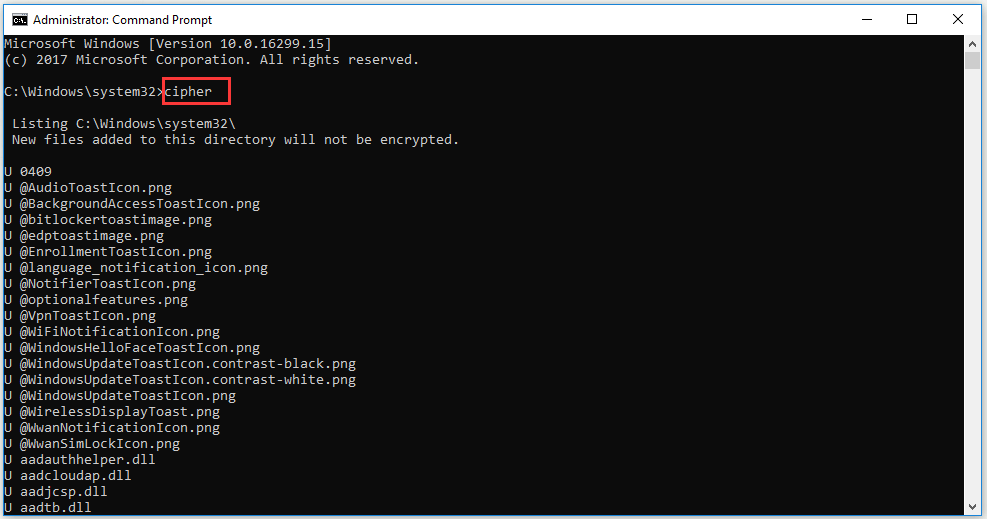
4. Diskpart
Diskpart command is specially designed to manage your partitions. It covers multiple operations about partitions such as creating, deleting, formatting and extending. To some extent, it is as powerful as some third-party partition managing software.
It even surpasses third-party software in some aspects. For example, it can manage dynamic disks and you don’t need to restart computer during this process. It even can convert basic disk to dynamic disk and dynamic disk to basic disk as well.
Common diskpart commands are presented as follows.
- List disk/volume: You can generally get the list of disks on your computer.
- List partition: You can get the list of partitions on the selected disk.
- Select disk/partition/volume: You can locate the disk/partition/volume you want.
- Detail disk/partition/volume: You can get the detailed information of selected disk/partition/volume.
- Delete disk/partition/volume: You can delete selected disk/partition/volume.
- Create partition primary/logical size = n: You can create a primary or logical partition on a disk and regulate its storage capacity in MB.
- Create volume stripe: You can create stripe volumes on a selected disk.
- Convert basic/dynamic: You can convert dynamic disk to basic disk or basic disk to dynamic disk.
- Convert MBR/GPT: You can convert GPT to MBR or MBR to GPT.
- Assign: You can assign a drive letter to the selected partition.
- Clean/clean all: The former command deletes files and these files can be recovered; the latter command deletes files and files can hardly be recovered.
- Format: You can format a partition and appoint file system to the partition.
- Active: You can set a partition as active.
But some third-party software has more powerful functions. For example, when suffering sudden system crash, apart from Command Prompt, you can also resort to a piece of professional partition manager – MiniTool Partition Wizard. Both its Copy Disk function and Migrate OS to SSD/HD function allow you to copy operating system to another disk. Once Windows fails to boot, you can insert the target disk and set it as the first boot disk to start your Windows.
MiniTool Partition Wizard also helps users manage partitions and disks. You can also recover lost/deleted files and clone entire disk and so on.
Apart from those above, it allows users to boot computer from bootable media created before when Windows fails to boot.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
5. File Compare
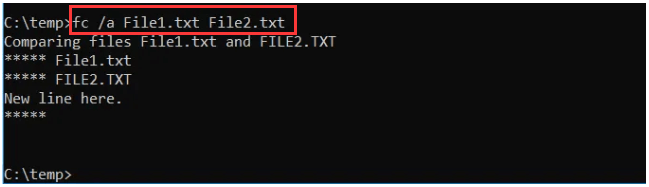
FC stands for File Compare. If you have two files with slight differences, this command can list all their differences for you.
FC command can compare text files as well as binary files and compare ASCII or Unicode text. Examples are listed as follows.
Fc /a File1.txt File2.txt will make a comparison between two ASCII files.
Fc /b Picture1.jpg Picture2.jpg will make a binary compare on two images.
6. Ipconfig
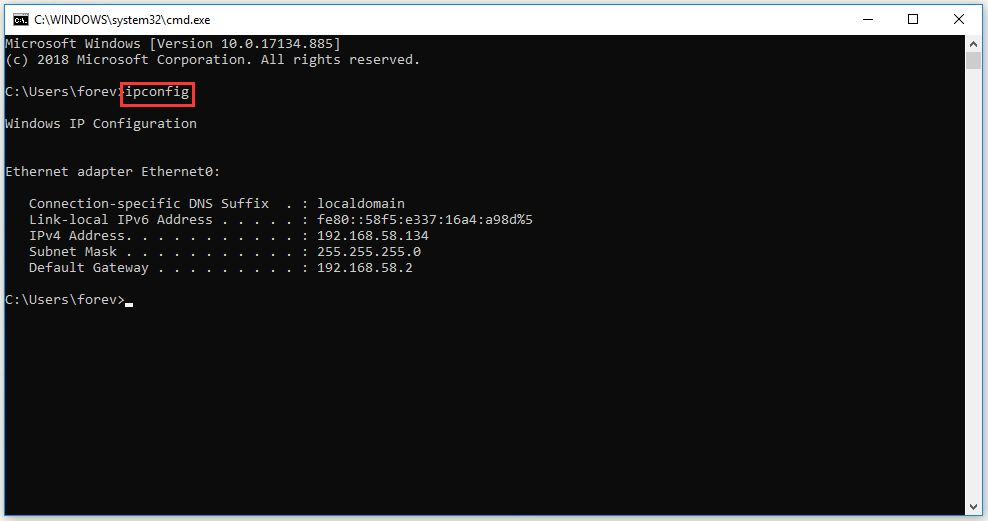
Sometimes your computer may meet network problems and do not know how to fix it. Command Prompt commands IP may be a useful tool.
Type “ipconfig” in Command Prompt Windows and you will get detailed information on current IP Address Subnet, Mask Default Gateway IP and current domain. This information can help you solve router issues and network connection problems.
7. Netstat
Netstat stands for network statistics. You are bound to suspect that some virus or malware connected to internet threat your computer. If you want to further check this problem, please type “netstat” on Command Prompt to see all active TCP connections.
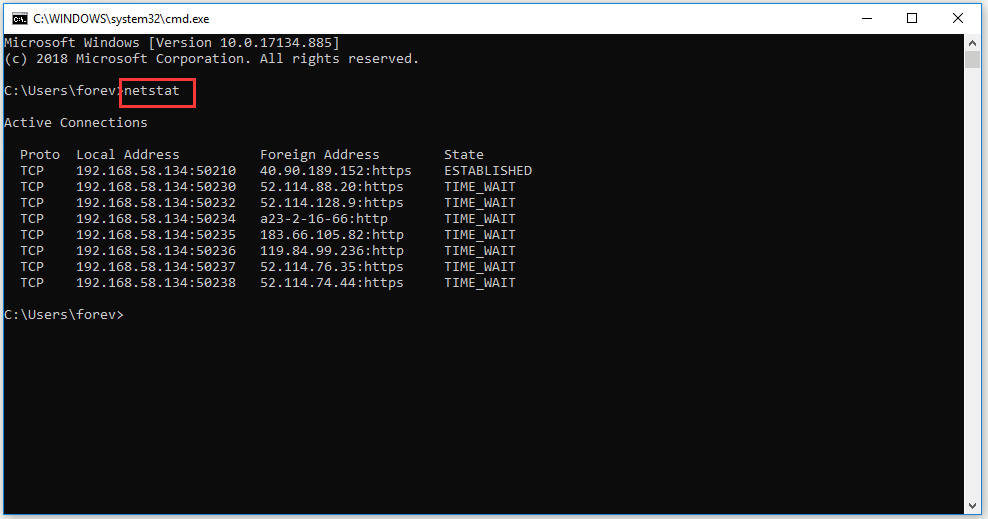
8. SFC
SFC stands for System File Checker. When you concern that virus or illegal software may threat your core file system, sfc /scannow command Windows 10 will scan these files and check their integrity.
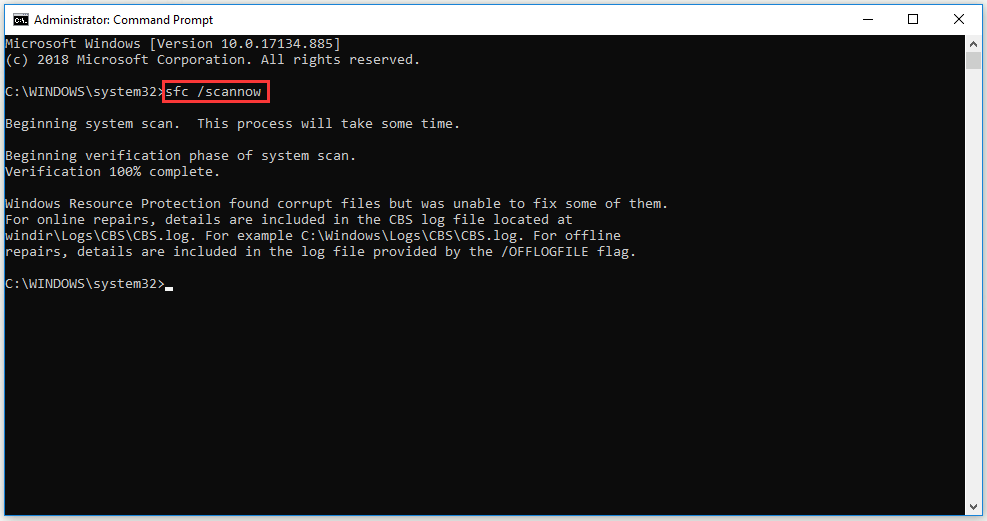
Tip: Remember to launch Command Prompt as an administrator.
Sfc /scannow will check the integrity of all protected system files and do repairs if system files have corrupted.
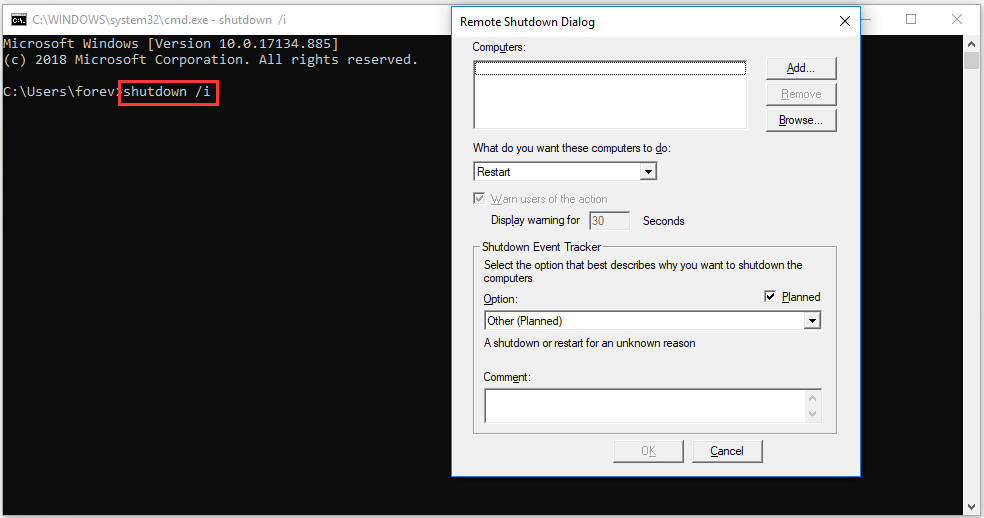
9. Shutdown
Shutdown command is different from the regular shutdown on start menu. You can set detailed parameters for your shutdown through the command.
Type down “shutdown /i” on Command Prompt and a remote shutdown dialog will pop up. You can manage the shutdown of remote computers, choose restart or shutdown and even select an option to describe why you want to shut down these computers.
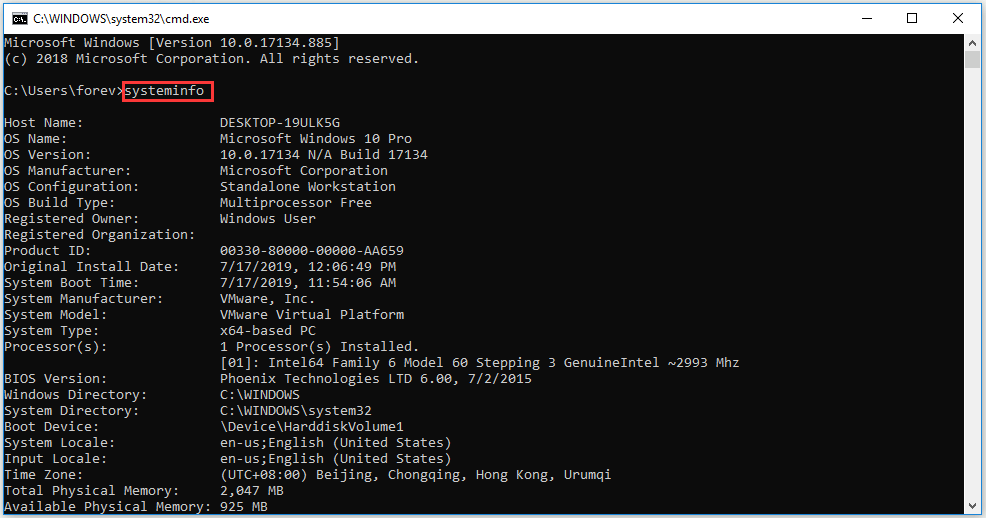
10. Systeminfo
How much do you know about your computer system? If you want to further know about it, you can use “systeminfo” command. This command will list plenty of information on your computer system, including its OS version, OS configuration, processor(s), BIOS version, boot device, network card(s) and so on.
Command Prompt Windows 10 allows you to discover more functions offered by your Windows. Mastering them helps you better make use of your computer and facilitate work and life.Click to Tweet
Conclusion
If you make yourself know more about Command Prompt Windows 10 and master the nine common commands above, you are bound to manage your computer issues better. And this post also has shown how to open run Command as administrator. You can try these methods.
If you have any question with MiniTool products, please contact us via [email protected] and we will reply to you as soon as possible.
Command Prompt Windows 10 FAQ
???? What are the commands in the Command Prompt?
There are various commands that can be done in the Command Prompt. In the Commnad Prompt, you can execute the comamnds to manage your disk, check file system, rebuild MBR and so on.
????How do I use Command Prompt?
The Command Prompt allows you to run programs, manupulate Windows settings, and access fils by typing in commands that you wish to execute. To use the Command Prompt, you can read the above content to learn how to open it in many different ways.
???? What is Windows Command Prompt?
Command Prompt is a command line interpreter application availabe in most Windows opearting system. It is used to execute entered commands.
???? What does CMD standard for?
CMD is the abbrevation for command. It is a Microsoft Windows command that opens the Windows command line window. Windows 95 and 98 users can only enter the command line by entering command, while all other users can enter by using either command or cmd.
В наших статьях про работу Windows 10 и других версий часто можно встретить упоминание командной строки. Все дело в том, что это удобный системный инструмент, который позволяет настраивать ОС под себя и управлять разными ее частями с помощью простых текстовых команд. Например, мгновенно запускать разные приложения или проводить проверку и сканирование файлов.
Для командной строки существует огромное количество различных кодов, которые мы можете использовать для того, чтобы упростить себе работу с системой и использовать ее функции по максимуму. Ниже разберемся, как открывается командная строка и какие команды можно в нее вводить.
Виды командной строки
Утилита для выполнения команд в Windows разделена на два интерфейса: непосредственно командную строку и оболочку PowerShell. Каждая из них — это консоль, которая напрямую соединяет вас с компонентами ОС или конкретными приложениями на вашем ПК.
Первой появилась командная строка. Ее встроили в систему для того, чтобы оптимизировать стандартные задачи, например, работу с учетными записями на ПК или создание резервных копий по ночам. Вы можете запускать и куда более сложные сценарии. Скрипты командной строки помогают вам облегчить и ускорить работу.
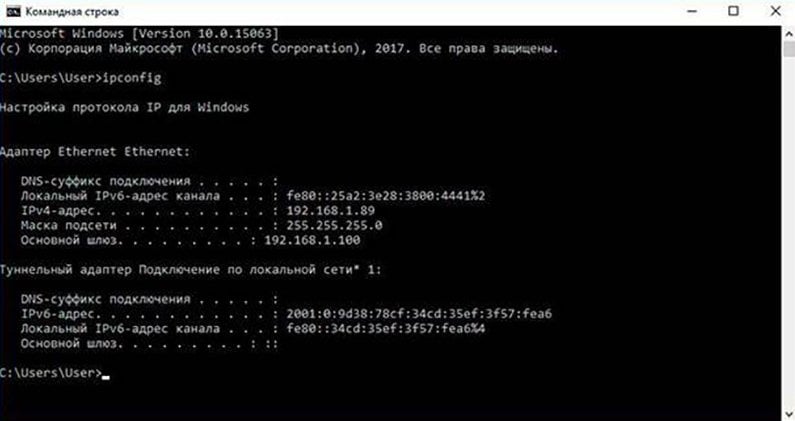
командная строка виндовс 10
PowerShell же создан как расширенная версия прошлой утилиты и использует собственные скрипты — командлеты. Они представляют собой язык сценариев, который можно расширять. По сути, вы можете использовать ту утилиту, которая удобнее вам, но помните, что командная строка не может использовать командлеты для PowerShell.
командная строка виндовс 10
Открываем командную строку
Проще всего запустить командную строку через системную утилиту «Выполнить». Ее можно вызвать с помощью комбинации клавиш Windows + R. В открывшемся окне введите cmd и подтвердите выполнение запроса.
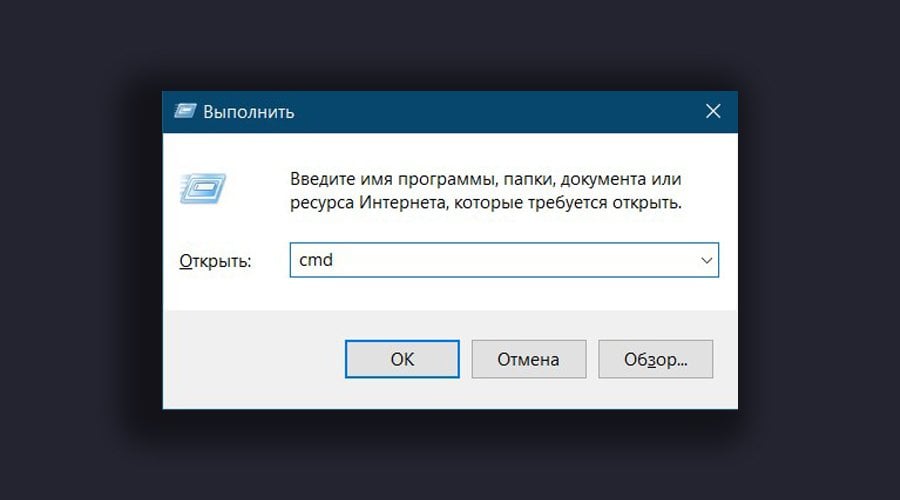
командная строка виндовс 10
Еще один вариант — запуск через меню «Пуск». Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по иконке меню и выберите «Командная строка» или «Windows PowerShell». Также вы таким образом можете запустить командную строку от имени администратора и получить максимальный ее функционал. Но помните, что этот способ сработает только если у вас не стоит модификации на меню «Пуск». В ином случае у вас откроется другое всплывающее окно.
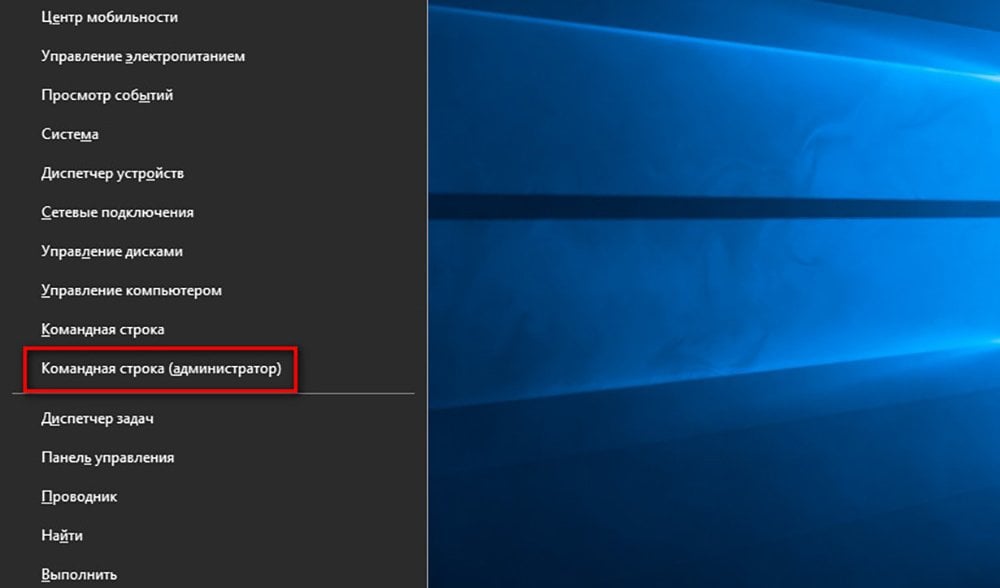
командная строка виндовс 10
Какой бы способ вы не выбрали — итог будет одинаковым. В результате откроется окно командной строки, в которое вы сразу же можете вводить нужные вам команды для системы и прочих файлов.
Список команд
Как мы уже отметили ранее, в командной строке есть очень много различных команд, но большинство из них настолько специфичны, что нужны только в редких случаях. В статье мы постарались собрать только основные команды, которые могут помочь вам быстро открывать системные утилиты и работать с папками на вашем ПК.
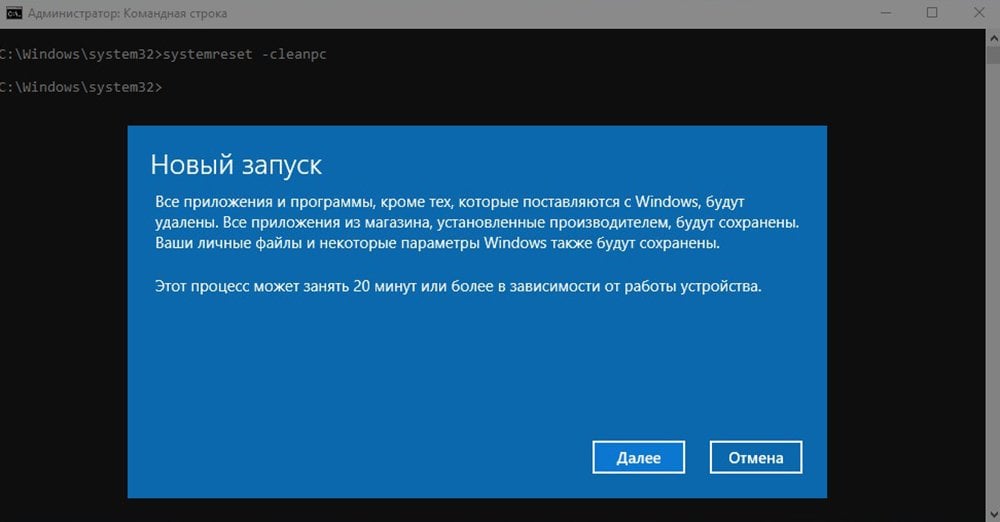
командная строка виндовс 10
Помните об осторожности при работе с системными файлами и инструментами, и не забывайте делать бэкапы файлов, если вам нужно что-то серьезно изменить.
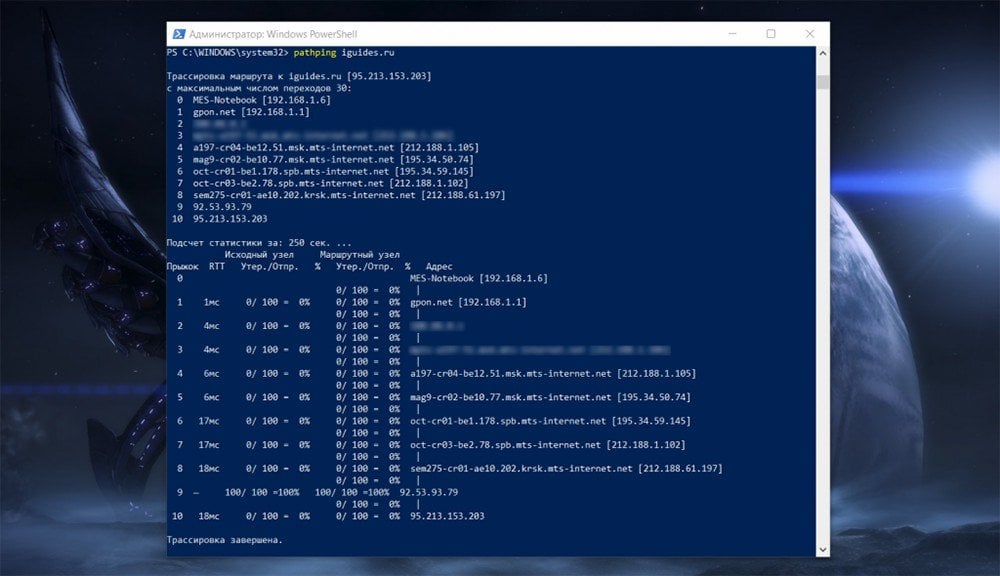
Программы и утилиты
Эти команды позволят вам моментально запускать программы и открывать разные системные утилиты. С их помощью вы можете быстро перемещаться по разным компонентам системы, без необходимости делать несколько шагов в меню пуск. А еще это позволяет запускать важные утилиты, для доступа к которым нужно лезть вглубь ПК.
- appwiz.cpl — программы и компоненты;
- certmgr.msc — меню управление системными сертификатами
- control — панель управления;
- control printers — меню управления подключенными устройствами и принтерами;
- control userpasswords2 — учетные записи на ПК;
- compmgmt.msc — управление параметрами ПК;
- devmgmt.msc — диспетчер устройств;
- dfrgui — меню оптимизации дискового пространства;
- diskmgmt.msc — управление дисками и пространством;
- dxdiag — средство диагностики DirectX.
командная строка виндовс 10
- hdwwiz.cpl — диспетчер устройств (другая команда);
- firewall.cpl — брандмауэр Защитника Windows;
- gpedit.msc — редактор локальной групповой политики;
- lusrmgr.msc — локальные пользователи и группы на вашем ПК;
- mblctr — центр мобильности;
- mmc — консоль управления системными оснастками;
- msconfig — системная конфигурация;
- odbcad32 — панель администрирования источника данных ODBC;
- perfmon.msc — системный монитор (можно смотреть изменения в производительности ПК и системы);
- presentationsettings — режим презентации;
- powershell — PowerShell (расширенная версия командной строки);
- powershell_ise — интегрированная среда сценариев для PowerShell;
- regedit — редактор реестра.
командная строка виндовс 10
- resmon — монитор ресурсов;
- rsop.msc — результирующая политика Windows;
- shrpubw — мастер создания общих ресурсов;
- secpol.msc — локальная политика безопасности;
- services.msc — средство управления службами операционной системы;
- taskmgr — диспетчер задач;
- taskschd.msc — планировщик заданий.
Приложения
Команд для работы с приложениями довольно мало. Они направлены в основном на уже открытые программы, которые выполняют определенные процессы на ПК.
- schtasks – отложенный запуск приложения через планировщик задач;
- shutdown – выключить или перезагрузить ПК;
- tasklist – список выполняемых задач на ПК;
- taskkill – остановить выполнение задачи и закрыть процесс (нужен PID, его вы можете узнать из прошлой команды);
- reg – редактор реестра;
- runas – запустить задачу от имени другого пользователя.
командная строка виндовс 10
Управление системой
С этим пунктом нужно обращаться осторожнее, ведь команды в нем связаны непосредственно с работой вашей системы. Конечно, если вы просто запустите утилиты с помощью этих запросов, и ничего не будете менять, все будет нормально. Но если вам нужно что-то изменить в системе — будьте крайне осторожны.
- computerdefaults — параметры программ по умолчанию;
- control admintools — папка со средствами администрирования;
- date — управление датой на ПК;
- displayswitch — управление подключенными экранами;
- dpiscaling — параметры дисплея;
- eventvwr.msc — журнал событий;
- fsmgmt.msc — средство работы с общими папками;
- fsquirt — работа с файлами по Bluetooth;
- intl.cpl — региональные настройки;
- joy.cpl — внешние игровые устройства;
- logoff — выход из системы.
командная строка виндовс 10
- lpksetup — управлениее языками интерфейса;
- mobsync — центр синхронизации Windows;
- msdt — средство диагностики службы поддержки Microsoft;
- msra — удаленный помощник Windows;
- msinfo32 — сведения о системе;
- mstsc — удаленный рабочий стол;
- napclcfg.msc — конфигурация операционной системы;
- netplwiz — управление учетными записями пользователей;
- optionalfeatures — управление стандартными компонентами операционной системы;
- shutdown — завершение работы компьютера;
- sigverif — средство проверки подлинности файлов;
- sndvol — запуск микшера громкости;
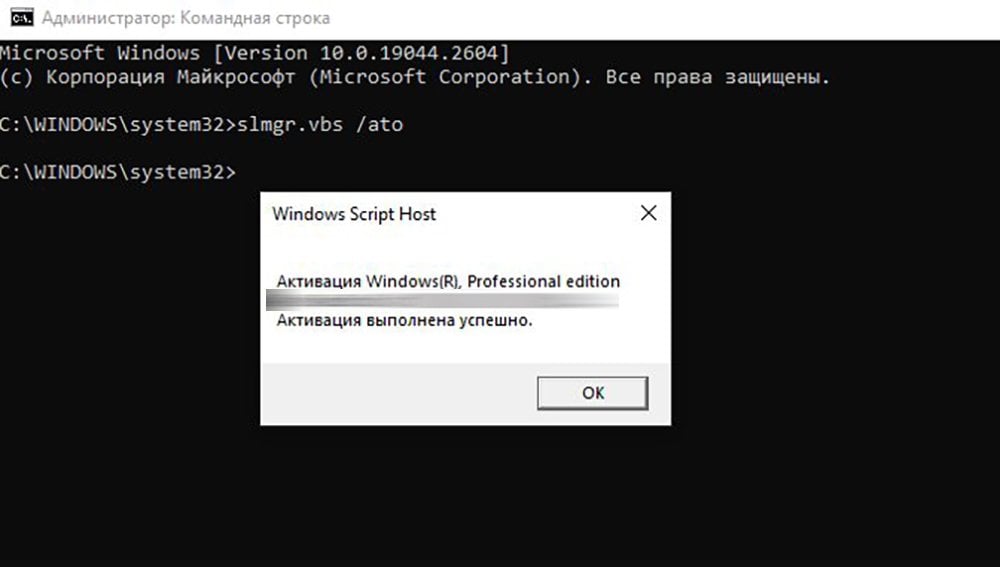
- slui — активация лицензии Windows;
- sysdm.cpl — свойства системы;
- systempropertiesperformance — параметры быстродействия;
- systempropertiesdataexecutionprevention — запуск службы DEP параметров быстродействия.
командная строка виндовс 10
- timedate.cpl — дата и время ПК;
- tpm.msc — управление доверенным платформенным модулем TPM на локальном компьютере;
- useraccountcontrolsettings — параметры управления учетными записями пользователей;
- utilman — специальные возможности;
- ver — сведения о текущей версии Windows;
- wf.msc — режим повышенной безопасности брандмауэра;
- winver —общие сведения о Windows;
- WMIwscui.cpl — центр поддержки Windows;
- wscript — параметры сервера сценария;
- wusa — автономный установщик обновлений Windows.
Сеть и интернет
С помощью этих команды вы можете проверить работоспособность вашего интернета и изменить настройки. Также вам будет доступна информация о сетевых устройствах и интерфейсах.
- control netconnections — просмотр и настройка сетевых подключений;
- inetcpl.cpl — свойства интернета;
- NAPncpa.cpl — аналог первой команды;
- telephon.cpl — настройка модемного подключения к интернету;
- ipconfig – информация о сетевых интерфейсах;
- ping – отправляет ICMP-запросы на целевой хост, проверяет его доступность.
командная строка виндовс 10
- tracert – путь пакетов в сети;
- nslookup – поиск IP-адреса по имени ресурса;
- route – таблицы сетевых маршрутов;
- arp – таблицу с IP-адресами, преобразованными в физические адреса;
- netsh – программа управления сетевыми настройками;
- getmac – MAC-адрес сетевого адаптера;
- tftp – запускает TFTP-клиент в консоли.
Периферия
Команды для управления оборудованием, подключенным к вашему ПК тоже есть. Их немного и они вызывают в основном окна настройки разных устройств, от мышки для принтера и графического планшета.
- main.cpl — панель настройки мыши;
- mmsys.cpl — панель настройки звука;
- printui — пользовательский интерфейс принтера;
- printbrmui — средство переноса принтера, с возможностью экспорта и импорта программ и драйверов;
- printmanagement.msc — управление параметрами печати.
командная строка виндовс 10
- sysedit — редактирование системных файлов с расширениями .ini и .sys;
- tabcal — средство калибровки дигитайзера;
- tabletpc.cpl — свойства планшета и пера;
- verifier — диспетчер проверки драйверов;
- wfs — факсы и сканирование;
- wmimgmt.msc — элемента управления WMI стандартной консоли.
Файлы и диски
Здесь мы рассмотрим команды для работы с дисками, папками и хранящимися в них файлами. Некоторые из них будут работать только если вы уже вызвали какую-то утилиту или запустили программу. А если вы запутаетесь, то всегда можно воспользоваться командой help, чтобы получить справку по командной строке.
- assoc — связь между расширениями имени и типа пакетного файла;
- attrib — редактирование атрибутов файла или папки;
- bcdboot — создание/восстановление системного раздела;
- cd — смена диска или просмотр выбранного;
- chdir — просмотр папки или переход к другой;
- chkdisk — проверка дисков и внешних накопителей;
- cleanmgr — очистка диска.
командная строка виндовс 10
- convert — смена файловой системы тома;
- copy — копирование файлов (с выбором конечного каталога);
- del — удаление выделенных файлов;
- dir — просмотр файлов и папок по выбранному пути;
- diskcopm — сравнить содержимое двух дисков;
- dickcopy — скопировать содержимое одного диска на любой другой;
- diskpart — утилита для работы с дисками (открывается в отдельном окне командной строки);
- erase — удаление одного или нескольких файлов;
- fc — сравнение файлов и поиск различий;
- format — форматирование дисков Windows;
- label — изменение меток тома для дисков;
- md — новая папка;
- mdsched — проверка оперативной памяти;
- move — перемещение файлов по указанному пути.
командная строка виндовс 10
- ntmsmgr.msc — средство работы с внешними накопителями;
- recdisc — создание диска восстановления операционной системы (только оптические накопители);
- recover — восстановление данных;
- rekeywiz — шифрующая файловая система (EFS);
- RSoPrstrui — восстановление системы;
- sdclt — резервное копирование и восстановление;
- sfc /scannow — проверка целостности системных файлов;
- tree — графическое отображение структуры каталогов;
- verify — анализ правильности записи файлов на диск;
- vol — метка и серийный номер тома диска.
Настройка командной строки
Командную строку также можно кастомизировать под себя. Изменить ее цвет, установить приветствие, очистить содержимое, если кода стало слишком много. Словом, всячески управлять ей.
- cls — очистить экран командной строки;
- color — изменить цвет фона (нужен идентификатор цвета);
- exit — закрыть утилиту;
- help — полный список команд;
- prompt — изменяет слева название.
командная строка виндовс 10
В статье мы собрали самые полезные команды для командной строки. Пользуйтесь ими при необходимости, но не забывайте об осторожности. Все действия с системными файлами и утилитами вы выполняете на свой страх и риск.
Заглавное изображение: wall.alphacoders.com
Everyone who uses Windows on a daily basis has definitely bumped into the command prompt every once in a while. It’s one of those things that you know exists, but most likely have no idea how to use or what it’s for. Most advanced users know a few basic commands, but very few know how to fully take advantage of the Windows Command Prompt.
That’s why it’s a damn good thing you are here. You are about to learn everything there is to know about the Command Prompt, also known as cmd or console. We will start off with the basics, like different ways to open it, as well as basic navigation and file modification. After that, we will move on to more complex commands and features.
No matter if you’ve never touched the command prompt before or you are an expert at it, you will definitely find tons of useful information in this guide.
If a video format is more your style, you can check out this guide on our YouTube channel. It won’t be as in-depth, but contains all the main commands and features you need to learn.
What is the Command Prompt?
Command Prompt or CMD is a command line interpreter, in which the user interacts with the the command prompt through its command-line interface. It can be used to interact with the Windows operating system through various built-in commands. It is not a cross-platform application, as it is native to Windows, unlike it’s big brother, PowerShell which works on many other operating systems.
The command prompt was most popular in its early days, as the user interfaces were a lot more limited back then. Navigating through the files on a computer was simple when using only the keyboard. Nowadays most people don’t know how to use cmd because there is often no real need for it.
Many of the basic functions in command prompt can be done easily with basic mouse operations and menus, so most end-users will never need to use CMD. However, even in the age of mouse dominated PC operations, there are tons of useful things you can only accomplish through the command prompt on Windows and that’s what we’re here to find out.
Let’s start off with the basics first, then move on to some more complicated examples and commands.
Quick Ways to Launch Command Prompt
The best thing about command prompt on windows besides its many uses; is how fast you can get it going. The easiest way to open it up is to just open up your start menu and look for the Command Prompt within it, but there are a few faster alternatives.
The easiest and probably fastest way to launch CMD on Windows operating systems is by pressing the Windows Key and typing in ‘cmd‘. You should then see the command prompt icon appear and then you can open it up by clicking on it. This is the way I tend to open it up, as I don’t use the command prompt more than a few times a week.
If you find yourself using the command prompt on a daily basis, it might be a better idea to pin the command prompt to your taskbar. This way it’s just one click away at all times.
In order to pin command prompt to your taskbar, first you need to find it in the start menu with the method showcased above. Then all you need to do is right-click on the app icon and select the ‘Pin to taskbar‘ option. Now you should see the CMD icon on your Windows taskbar at all times.
Run Command Prompt as Administrator
Sometimes you need to let Windows know that you have enough permissions to access certain directories and files. This includes other users folders and sensitive files within folders like System32, which might cause issues when tampered with. Also if you are going to be running batch scripts or using advanced commands, you need elevated permissions.
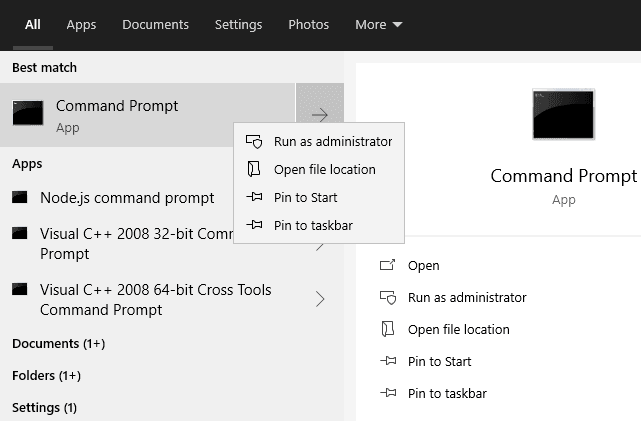
The easiest way to run command prompt as administrator is by finding it in the start menu as shown above, then right-clicking it and selecting the ‘Run as administrator‘ option from the drop-down menu. However, there is an even easier way to accomplish this if you pinned the app to your taskbar.
If you wish to automatically run cmd as admin every time you open it, just follow these simple steps. First, right-click the icon in your taskbar and then right-click the ‘Command Prompt’ selection from that pop-up menu as well. Once you see the menu, you could just run it as administrator from there, but select the ‘Properties‘ tab instead.
When you have opened up the ‘Properties‘ window, look for the tab labelled ‘Shortcut‘ and select it. Once you’re there, click on the ‘Advanced…‘ button to open up the advanced properties of the CMD shortcut. Finally, the last thing you need to do is tick the ‘Run as administrator’ checkbox. Now just click OK on both menus and you’re done.
After this step is done, every time you click on the command prompt icon in your taskbar, it will launch as admin automatically. This will save you a few clicks and you don’t ever have to remember to do it again. In order to make sure that you are running the cmd as an admin, you should see the text ‘Administrator: Command Prompt‘ at the top toolbar of the window.
Command Prompt vs Windows PowerShell
You might have already heard about PowerShell, but might not know what it is or how it differs from the normal command prompt. In a nutshell, PowerShell is a more complex and powerful alternative to cmd, a Command Prompt on steroids. You can do everything with PowerShell that you can do with cmd and much more.
The reason why most people have never used PowerShell, is because it hasn’t been integrated with Windows operating systems until Windows 7. Ever since then, it comes pre-installed and you can find it in the same manner as the cmd through your start menu. You can also pin it to the taskbar and run as admin the same way.
You can launch PowerShell just as you would CMD, but there is also a new quick method to do this in Windows 10. The best way to quickly open PowerShell on Windows by pressing the Windows key + X to open up a hidden menu. From that menu you can find ‘Windows PowerShell (Admin)‘ from which you can instantly open PowerShell as an administrator.
In the end it’s completely up to you if you wish to use the default Command Prompt or PowerShell, but here are some benefits of using PowerShell:
- PowerShell uses the .NET framework allowing users to use actual programming libraries and allowing for the creation of custom commands.
- It’s cross platform so you can use your newly learned skills on Windows, Linux and MacOS while the normal Command Prompt is only usable on Windows.
- PowerShell uses a lot of easier-to-understand commands and tons of documentation about all commands through the
Get-Helpcommand. - It has a higher learning curve as there’s a lot more things to learn about, almost like learning a new language. This means there’s more potential as well.
- Most end users will only ever need the CMD, which is why we will stick to it in this guide, but if you’re feeling up for it, we recommend you start with PowerShell as it will be more beneficial for you in the long run.
If you would like a guide similar to this one about Windows PowerShell, let us know in the YouTube video comments or through our About Us page.
You can find more information and documentation about the app on the official PowerShell Microsoft Documentation page.
Few Important Base Commands to Learn in CMD
To start your CMD journey, there are a few basic commands that are going to help you on your way.
As with all new software and applications, it’s great to have instructions or a user manual. Although this guide should have you covered, it’s nice to know how to find help within command prompt itself.
In order to find a neat list of all the basic commands within CMD, all you need to do is type in help and press enter.
The list above is a great refresher on the available commands, but they don’t explain much usage wise. That’s why there is a different documentation command which provides more in-depth information for each command.
In order to see the guide for a specific command, you can type help COMMAND or COMMAND /? both of which will show the same information.
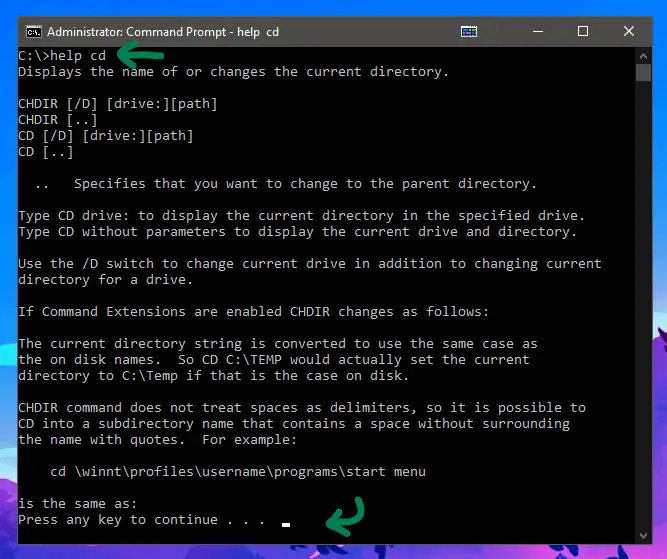
Now that you have a huge wall of text in your command prompt, you might be wondering how to get rid of it. Thankfully there’s a command for that instead of just scrolling down constantly.
In order to empty out the cmd of all text, you need to type in cls which stands for Clear Screen. It’s extremely useful once your prompt starts to get cluttered.
Another quick useful tip is that you can paste whatever text is on your clipboard by simply right-clicking anywhere on the command prompt window.
In order to copy whatever your command outputs, you can simply add | copy after the command. This will copy any results onto your clipboard.
It is good to note that all commands within the cmd are NOT case sensitive, so you can write in upper- or lower-case letters as you please. For example, help and HELP are the same command and work just fine. I prefer writing everything in lower case, as it seems faster.
Finally, if you don’t like to move your mouse to exit the command prompt, you can simply type exit in order to close down the cmd instantly.
System & Folder Navigation
Now we’re ready to get into the thick of things. These commands are the first thing you need to learn in order to navigate through your system within command prompt. They consist of changing folders and directories as well as switching between drives.
Change Directory (cd)
This is usually the first command you learn when starting out with cmd. When starting up the command prompt as administrator, you start out in the C:\WINDOWS\system32 folder.
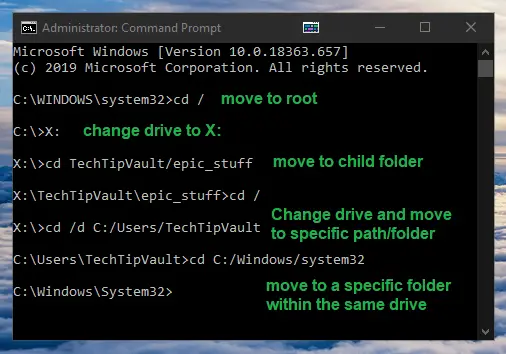
In order to move up one level in the folder hierarchy, you need to type cd .. so if you execute this command twice, you will be in the root of your C:\ drive. In addition, to go directly to the root level, in this case the C drive base, you can simply type cd / with or without the white-space.
cd is not necessary for the command to work.If you want to change the drive you are working in, all you need to do is type in the drive letter followed by a colon. For example, if you would like to change from C:\WINDOWDS\system32 to X:\ just type in X: and you’re done.
If you want to move to a specific folder within the current directory you can type in cd DIRECTORYNAME which is one of the most used commands. You can also press TAB while writing the folder name to auto-fill it. It will speed up your process and navigation a lot.
In order to move to specific path on the current drive, you can type the entire path after cd to jump there. For example if you’re located in C:\, you can type cd Windows/System32 to move up directly to the System32 folder.
If you want to jump to a different hierarchy on the same drive you need to start off with the drive letter. For example you can type in cd C:/Users/TechTipVault to move directly to that folder, no matter where you are currently.
Similarly if you want to jump to a path on a different drive, you need to add in cd /d and then the full path. For example if you want to move from C:/Users to X:/Users, you need to type in cd /d X:/Users and voilà.
Finally, it’s good to note that it is good practice to surround any folder names with quotes if they contain white-space. It is not required in all cases, but it is good to get used to. For example, you should type a path like this: cd C:/"Program Files (x86)"/"Tech Tip Vault"/dot_com
List Files and Directories (dir)
When you’re navigating through your system with cmd, you often want to know what your options are in the active directory. Thankfully there is a very versatile command that allows you to see all the files, directories and sub-directories in the current folder.
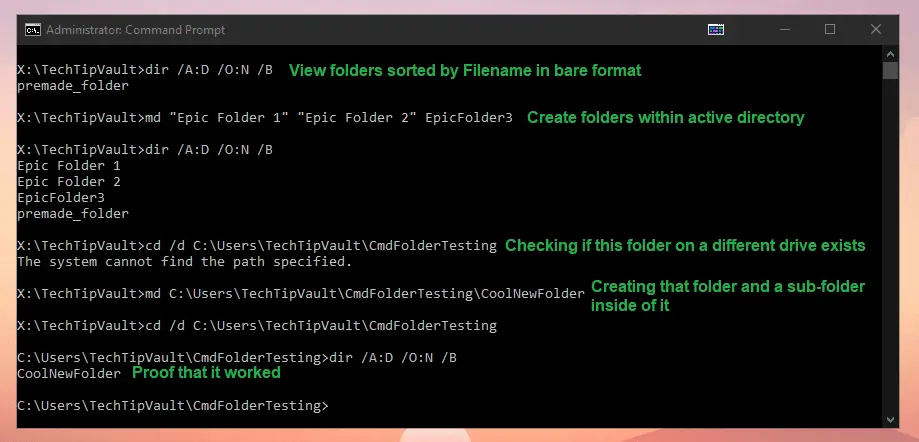
In order to see basic information about every file and folder in the current directory, type dir in the command prompt.
If you want to view the contents of a folder you’re not currently in, you can also use dir for that. The catch is, you need to use back-slashes or quotes for the file-path as otherwise the path won’t be recognized. This is due to the additional parameters that can be used. For example, if you want to see the contents of the Users folder, you can either type dir C:\Users or dir "C:/Users" as both options work the same. It just really depends on if you hate typing back-slashes as much as I do.
This command has tons of optional parameters that decide the amount of details and items to show. You can view all of them using the help command by typing dir /? but we will explain some of them here for clarity.
| Parameter | Example | Explanation |
/A:ATTRIBUTE or /A:-ATRRIBUTE |
dir /A:Ddir /A:Rdir /A:Hdir /A:-Ddir /A:-D-H |
Show all folders Show Read-Only files Show Hidden files Do NOT show folders Do NOT show folders or Hidden Files |
/O:SORTINGORDER or /O:-SORTINGORDER |
dir /O:Ndir /O:Sdir /O:Ddir /O:Edir /O:D-N |
Sort by filename Sort by file size Sort by Date & Time Sort by File Extension Sort by Date & Descending Filename |
/T:TIMEMODE |
dir /T:Cdir /T:Adir /T:W |
Sort or view by Creation time Sort or view by Last Access time Sort or view by Last Written time |
/S |
dir /S |
Include all sub-folders |
/B |
dir /B |
Bare format (no header, size, or summary) |
/L |
dir /L |
Use lowercase letters |
/Q |
dir /Q |
Show the owner of the file |
/N |
dir /N |
Long format with filenames on the right |
/X |
dir /X |
Long format with short filenames |
/C or /-C |
dir /C |
Include/Hide thousand separator in file size |
Launch and Application or Program
The last thing that you should know when navigation through your system in command prompt is how to start an app through it. Thankfully it’s as simple as navigating to the correct folder and typing the name of the executable.
For example, if for whatever twisted reason you wanted to start up another command prompt instance from within the command prompt, you can do that. First you need to navigate to System 32 folder with cd /d C:/Windows/System32 and then type in start cmd to launch a new instance of cmd.
You can also start an app simply through the full file-path. For example, to launch MS Paint you can type in C:/Windows/System32/mspaint.exe and the software will start up instantly.
File & Folder Editing
File and folder editing is the bread and butter of the command prompt. These are the main commands you will be taking advantage of when using cmd. Once you get the hang of the navigation first, you will be ready to get going with the editing itself.
Make Directory (md)
The first command will let you create a new folder or directory. The md command is an alias for the longer version mkdir which both do the same thing. As long as you remember one of them, you’re good to go.
In order to create a new folder in the current working directory, type md FOLDERNAME. You can also create multiple nested folders by just adding them in with slashes. For example, if you want to create folders and sub-folders at once, type in md TechTipVault/SubFolderName/EvenDeeperFolder and now you have a triple layered folder hierarchy.
If you want to create multiple folders within the same directory, you need to separate the folder names with white-space. For example, in order to create 3 folders within the active directory, type up md Folder1 Folder2 Folder3 and now you have three new folders to work with.
It is good to note that white-space or special characters like commas, equals or semicolons will separate multiple folders. This means if you want to add special characters or spaces within the folder names, you need to add the folder name between quotation marks. For example, to create two folders with spaces in the names, you can type md "Folder 1" "Folder 2 = Folder 2". Now you will have 2 new folders, one called Folder 1 and the other one called Folder 2 = Folder 2.
Finally, you can create a folder with the above commands directly into any location by writing the entire path after the command. For example, if you are currently in C:/Users folder, you can type md X:\TechTipVault\EpicFolder to create a new folder on a different drive. Make sure to use back-slashes for the path or it won’t work.
Rename Files & Folders (ren)
The rename command is one of the most useful commands cmd has to offer. It allows you to rename any files and even change their extensions, transforming the file into a different type.
Simply renaming a file can be done by typing ren tipvaulttech.txt TechTipVault.txt in order to name the file into the latter format. You can also use this same syntax to rename a folder.
As you might expect, you can use the same logic to change the extension of a file. By typing ren TechTipVault.txt TechTipVault.html you will change your text file into an html file.
The best part about the renaming syntax in the command prompt is the ability to use wildcards. You can use * and ? characters to make complicated naming scenarios very easily.
Below is an interesting example utilizing the forward slash, which is not really documented anywhere, but a fun use-case can be seen utilized to remove parts of the filename.
ren "Artist - " "/////////.*"(Add same amount of slashes as characters found on the left side) |
The * symbol basically means every character before the character that follows it. For example, if you wanted to transform every text file in a folder into log files, you could accomplish this by typing ren *.txt *.log noting the space(s) in between. The first “*” takes the original name and the second “*” replaces any character after (and including) the dot with .log.
The ? symbol finds the next character after it and appends it to the target name (as long as the next character is not a .). If the next character is a . then no character will be added in to the result.
For example, if you add 5 question-marks, it will replace 5 (or less) characters before a dot. See the examples in the table below.
If both are combined *?, they will append all remaining text from the source name to the target name and vice versa.
| Initial Files | Command | Final Files |
| ttv.txt TechTipVault.html file1.xyz.log |
1. ren *.* *.2. ren * *_NEW.log |
ttv_NEW.log TechTipVault_NEW.log file1.xyz_NEW.log |
| abc.abc 12345.12345 ABC123.docx TechTipVault.Backup.log |
ren * ????.???? (4 times ? on each side) |
abc.abc 1234.1234 ABC1.docx Tech.Back |
| ttv.txt TechTipVault.xxx.dat a.b.c_d |
ren * *?.bak |
ttv.txt.bak TechTipVault.xxx.dat.bak a.b.c_d.bak |
Copy Files & Folders (copy |xcopy)
When looking to copy things, it’s good to note that there are two separate commands you need to use. You have to use the copy command in order to copy files and the xcopy command to copy folders and their contents. Both of these commands also have their own parameters and options to give you more options.
Copy Files (copy)
Let’s first go in-depth with copying files using command prompt. The simple and easy basic functionality of this command is copy filename.ext newfilename.ext which will copy the file with a new name in the active directory.
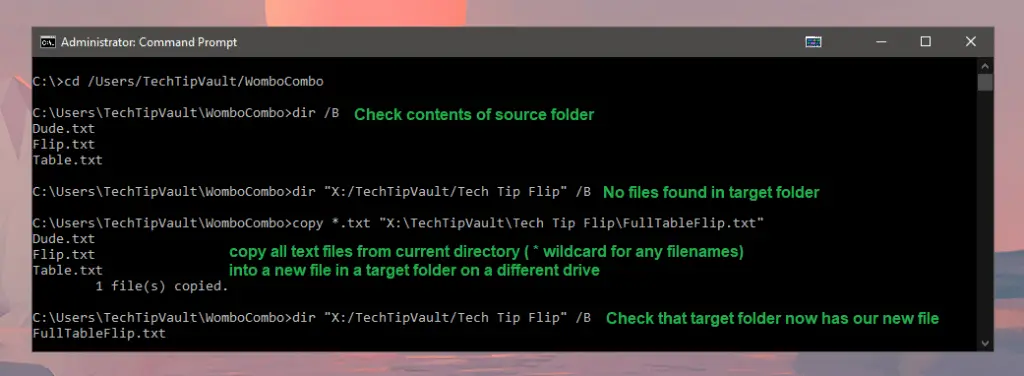
Similar to most of the other commands, you can copy files from the active directory to a different folder or drive by adding their separate paths. For example, copy "C:/Users/TechTipVault/Epic Text File.txt" "X:/TechTipVault/CopiedVersion.txt" will copy a file (even with white-space in the name) from the C-drive to the X-drive.
A unique feature with this command is the possibility to merge text files into a single new text file. For example, if you want to merge every text file in a folder into a single one, you can use copy *.txt "\TargetDirectory\CombinedFileName.txt" and you now have a nice wombo-combo. Check the example below.
Copy Files and Folders (xcopy)
Now let’s dive into the xcopy command. It is very similar to the normal copy command but provides more parameters and switches to take advantage of.
The basic syntax for copying files with xcopy is the same as with the normal copy command, which is why you should use that one instead. The main reason for this is because when using xcopy, you can’t tell if the target should be a file or a folder. If you do this, you will be prompted to enter either ‘F’ for file or ‘D’ for directory into the command prompt. In order to ignore this prompt and default as a file, you can add a wildcard (*) to the end of the target as such xcopy source.txt target.txt*
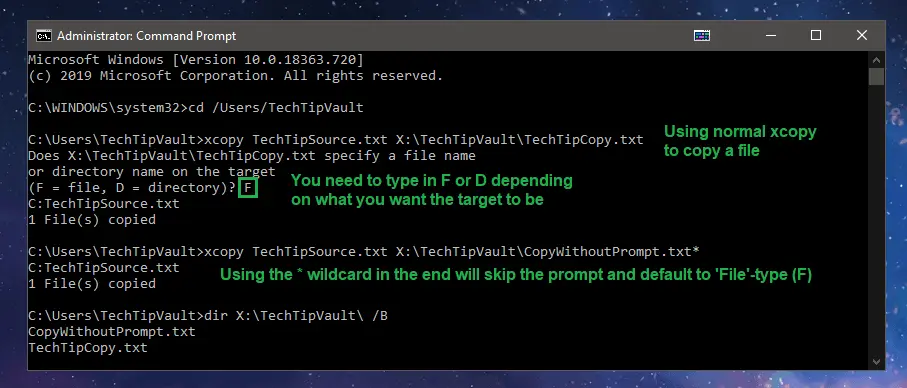
Finally, there are a few parameters you should be aware of with xcopy, although most of them are not very useful. You can type xcopy C:\Users\TechTipVault\FolderWithStuff X:\TechTipVault /S /I in order to copy every file, subfolder and files in the subfolders to the target folder. Here you can see the most important parameters that can be combined with the xcopy command.
| Parameter (Usage: xcopy source target parameter) |
Explanation |
/S |
Copy folders and sub-folders (including files within them) (excluding empty folders) |
/E |
Copy folders and sub-folders (including files within them) (including empty folders) |
/I |
Assume the target is a Folder (type) |
/Y |
Suppress the prompt for overwriting files. (Overwrites duplicates without warnings) |
/T |
Copy entire folder structure, but ignore any files. (/T /E combo will also include empty folders and subfolders) |
/K |
Copy attributes (otherwise things like read-only attributes will be reset) |
Modify File Attributes (attrib)
The attribute command is quite a simple but useful affair. It allows you to display a files attributes or change them to your liking. Attributes mean features like being Read-only or hidden files.
With this command you can add an attribute with a + symbol and disable an attribute with the - symbol. The two basic attributes you will be using are R for Read-only and H for Hidden. The Hidden parameter also works for folders, but the Read-only attribute can only be applied to files. There are also A for Archive and S for System attributes, but they are rarely used.
You can also use the /S modifier to apply the attributes to all files within sub-folders as well and /D to apply the changes to selected folders too. As with most file editing commands, you can also use wildcards with the attrib command to easily modify a group of files instead of just one.
The basic syntax to make a file hidden and remove its read-only property can be done as follows: attrib +h -r SuperSecretPasswords.txt
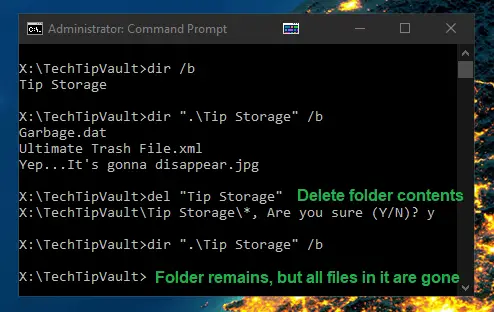
Delete Files (del)
The delete command is unsurprisingly quite self-explanatory. It can be used to delete files. However, it is not possible to remove folders with it, as that’s what the remove directory command is for, discussed below.
Thankfully, to make the del command a little more useful, it includes plenty of parameters for more specific deletions alongside the ability to use wildcards for filenames. As for basic usability, you can type one or multiple filenames after the command as such: del file1.docx "Tech Tip File.log" "X:\TechTipVault\File.txt"
A cool feature of the del command is if you use it on a folder, all the files within the folder will be deleted but the folder itself will remain intact.
Now let’s get to the parameters you can use alongside the delete command. Here’s a quick list of the useful ones:
| Parameter (Usage: del parameters /A:attributes filesToDelete) |
Explanation |
/F |
Ignore read-only settings and force-delete the file |
/Q |
Don’t show Yes/No prompt when deleting file |
/A |
Use this before adding file attributes (/A:format) |
/A:R or /A:-R |
Delete files that are Read-only or not Read-only |
/A:H or /A:-H |
Delete files that are Hidden or not Hidden |
You can combine multiple attributes by adding multiple of the parameters after the /A: syntax. There are a few more attributes, but rarely used in default cases. If you would like to learn more about them, check the documentation for the command with del /? syntax.
Remove Directory (rd)
The remove directory command is a very simple alternative to the delete command, but it allows the deletion of folders. The rd command doesn’t allow for the use of wildcards and only has 2 parameters, which makes it a lot easier to remember.
The usage of this command is simple, you can delete any amount of folders and their contents by simply typing rd FolderPath but without parameters, it will only delete an empty folder.
The parameters include: /S which deletes all files and sub-folders alongside the folder itself and /Q which will remove the Yes/No prompt on deletion. For example, rd /S /Q "X:\TechTipVault\GarbageFolder\" will delete the whole GarbageFolder and all of its contents without asking for confirmation for the deletion.
Advanced Command Prompt Commands
This is going to be the most exciting section of the entire command prompt ultimate guide. We will feature all the awesome commands you can use to find tons of useful information about your system and do things like repair corrupt files. These are the commands you will find yourself using over and over again and will want to tell your friends about.
Check All File Associations (assoc)
This command allows you to view or change what a file extension stands for. The basic usage is as simple as assoc .txt to find out what program the .txt extension is associated with.
If you want to add or change an association to a file extension, you can use similar syntax as to what you receive as a result from the base command. For example, if you want to associate the .log extension as a text file, you can type assoc .log=txtfile.
Similarly, if you would like to remove a file association, you can just type assoc .log= and execute the command.
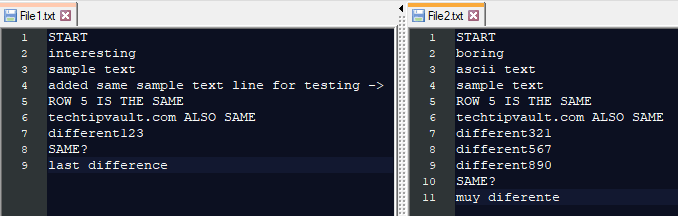
File Comparison (fc)
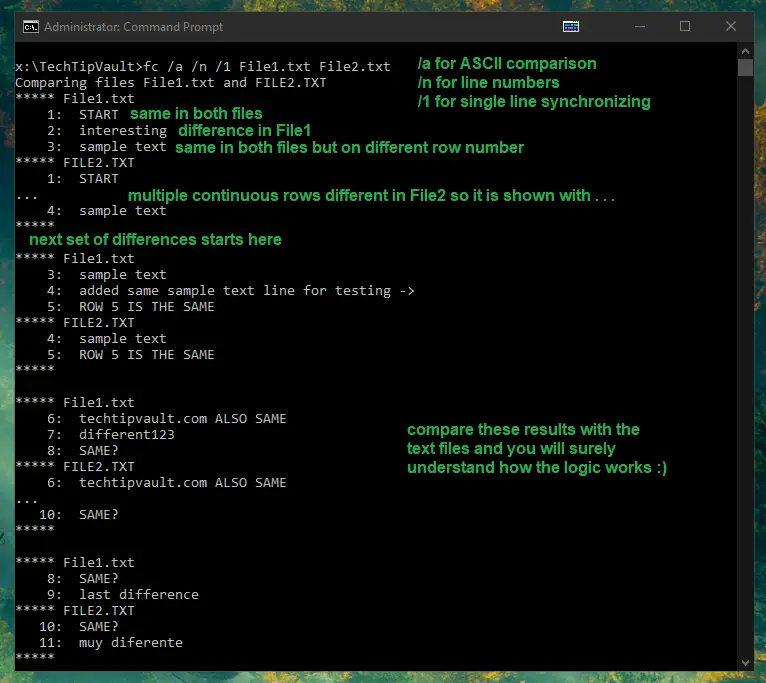
The file comparison is another interesting command. You can use it to find differences in files using binary or ASCII format. If you want to compare files with an ASCII format comparison, you need to add /a after the command and in case of binary comparison, add /b after the command. Then just enter the filenames or paths to compare.
You can also add /number like /1 which is the number of lines that need to match for the file to be considered synchronized. It is quite difficult to explain clearly, which is why I highly recommend you do some testing on your own to really notice how the differences are laid out (we also added some pictures below to explain this further). Another very useful parameter is /n which will show the line numbers next to the text lines within the command prompt.
The basic formatting of the differences in the command prompt results are as follows:
- Name of the first file
- First row that matches
- Differences
- Second row that matches after the differences
- Name of the second file
- Same as steps 2-4 but for the second file
- Rinse and repeat
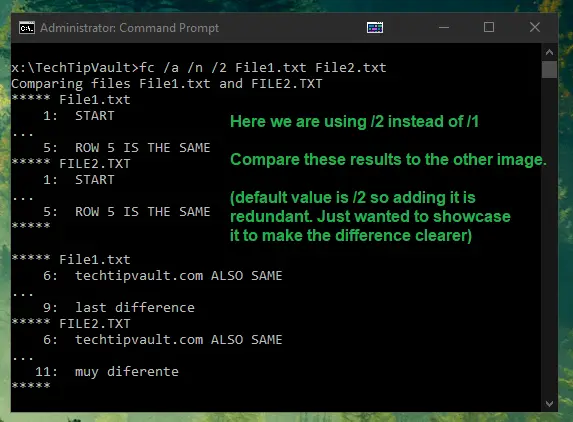
The use-cases for binary comparison (/b) are a lot more limited, as most end-users won’t have need for it. It’s best used when trying to find out if two non-text files are duplicates. This can be useful when looking for duplicate images with different names, for example, as the binary differences will show up.
Check IP-Address & Network Information (ipconfig)
This is without a doubt the most well-known command out of anything we list here. Everyone who has done any gaming or connection related things, has probably used ipconfig to find out their IP-address.
There’s not much to explain about ipconfig as what you see is what you get with the results. However, the command has a few cool parameters you can take advantage of to see more information and perform a few unique functions as well.
Probably the most useful parameter for this command is the /all command which shows the full TCP/IP configuration for all your network adapters. This way you will see all the information you need and there’s really no reason not run the command with this parameter every time.
Another very useful option to use with ipconfig is the /flushdns parameter. You can use it to clear your DNS cache. On the same note, you can also view your DNS cache with /displaydns to see if you should be clearing it up with the previous parameter.
For clarification, a DNS or a domain name server basically converts a domain name or URL (for example techtipvault.com) into an IP-address that the computer can understand and connect to. You system hold a record of these conversions to speed up repeated requests to same addresses and that record is called the DNS cache.
The reason why you might want to flush your DNS cache is because sometimes there’s out-dated conversions if a website has moved to a different server for example. You can flush your DNS cache to update those records on the next connection attempt.
See All Your Active Connections (netstat)
You can use the Network Status or netstat command to view all the connections going out and coming in to your machine. This command is mostly popular among Indian tech support scammers as they attempt to convince their victims there are hackers connected to the PC by typing in this command.
This command also a has a few parameters to increase its functionality. For example, you can use -a to display all connections and listening ports. You can also check out your Routing table by adding in the -r parameter.
Probably the most useful parameter that can be used with netstat is -b which will display the executable names with which each connection is associated with. This means you can easily see which connections are attached to your web browser or any other process.
Finally, you can add a number to the end of the command after all the parameters to indicate how fast you would like to automatically repeat the command (in seconds). If you don’t add a number, the command will only execute once. Typing netstat -b 10 would show the executable above each connection and command would repeat once every 10 seconds. In order to stop the repetition, you need to press Ctrl + C.
Show Optimal Route to Target Address (tracert)
The Trace Route or tracert command will tell you the optimal route from your system to the target IP-address or URL. It will also show that exact route step-by-step and tell you how long it took between each step or hop. It is fantastic for troubleshooting issues within large networks as many different paths can be acquired to arrive to a target machine.
The command has a default limit of 30 hops which means it will attempt to find the fastest route within 30 jumps from one router to the next. You can use the -h parameter to change the max hops, so tracert -h 10 techtipvault.com would use a maximum of 10 hops to reach the target.
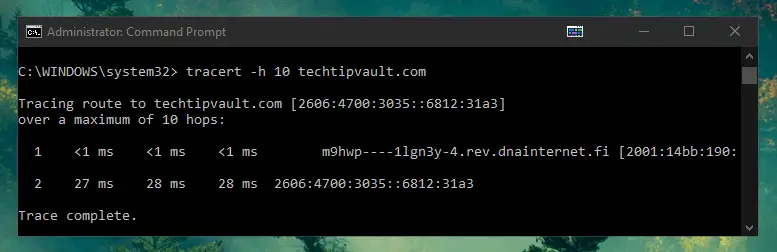
Conveniently, you can also see the IP address if you type in a URL. This can also be accomplished without the hops using the ping command, explained below.
It is also good to note that trace route shows the most optimal route, not always the ACTUAL route it takes.
Send Test Packet & Check Connection to Target Address (ping)
The ping command is used to test or ping the target IP-address to see if there’s any issues in the connectivity. It is very similar to the tracert command, but pinging is quicker as it just tells you if a specified target can be reached and how long it takes to send and receive packets to that target server.
It is as quick and simple to use as typing ping techtipvault.com to see the target IP-address as well as response times.
The ping command has a lot of optional parameters to use, but most of them are not useful for most users so if you’re interested, you should check out the information page by typing ping /? into the command prompt. The most useful one is probably -n number to specific the amount of ping attempts and -w number to specify how long to wait for each reply from the server in milliseconds.
Lookup the IP-Addresses on a Nameserver (nslookup)
The name-server lookup command in its simplest form is a way to find what IP addresses belong to a target address. This can be done simply by typing nslookup techtipvault.com to find the connection details.
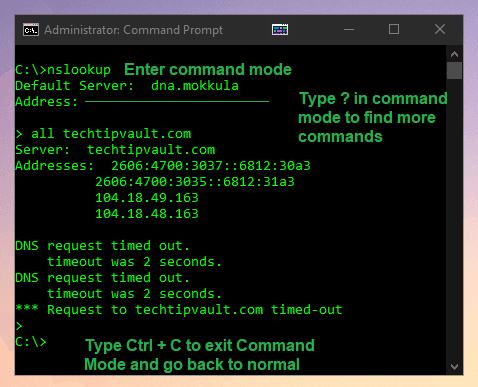
This command has a special Command Mode which can be accessed by typing the command without any parameters. Doing this will activate a mode where you can execute a bunch of unique commands to do name-server testing. You should check the command prompt info page (nslookup /?) for the special commands, as there are too many of them to explain here.
If you wish to exit the Command Mode, you can simply use the Ctrl + C keyboard shortcut.
Check Your System Specifications & Drivers (systeminfo | driverquery)
The System Info command is a great tool to quickly check your operating system information and other info like how much RAM you have installed. It is organized in a neat list so it’s easy to read and even copy if needed.
You can also see your network card information as well as Hyper-V requirements which are needed by some monitors and features like Miracast. It is possible to check remote system info as well by typing systeminfo /S targetSystem /U username /P password, noting you don’t need to use the username and password parameters if nothing is set-up for them.
To see a comprehensive list of all the drivers operating on your system, you can use the driverquery command. It uses the same syntax for remote connecting username and password wise as seen above.
Get a Power Efficiency Report of Your System (powercfg)
This is an interesting utility which allows you to see all kinds of information about your power usage. There are tons of parameters to take advantage of to view and modify your power schemes among other things.
The most useful one is powercfg /energy which will run a 60 second test of your computers power efficiency. The command will save a full report as an html file in your active directory so you can see any potential issues in full detail.
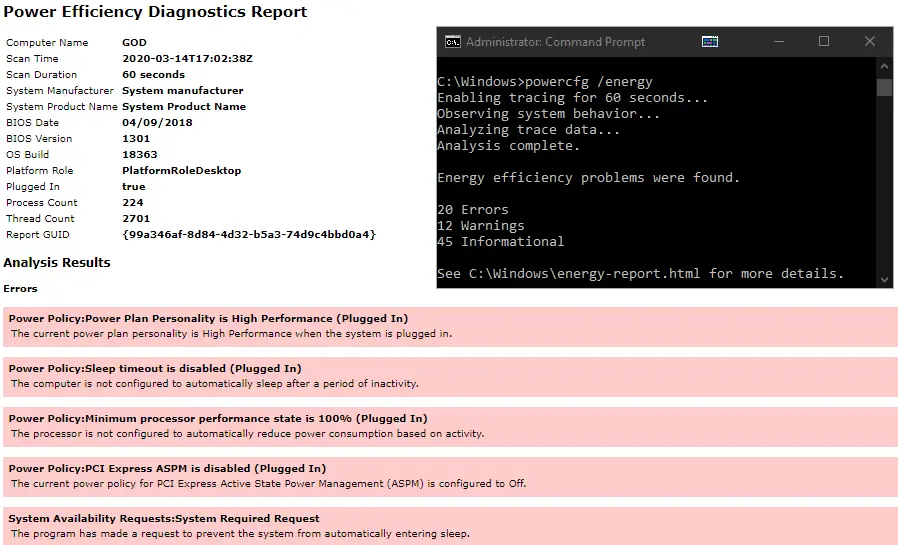
To check the other commands, again, type in powercfg /? to see what parameters are available for use.
Note that you need to run the command prompt as administrator to use this command.
Check the Integrity of Your Files and Fix Them (sfc)
The System File Scan is a great utility to make sure you don’t have any corrupted system files on your machine. The command will basically scan all of your protected system files and check their integrity.
The most useful and popular command is the /scannow parameter, which scans all the files and replaces any faulty ones with the official Microsoft files. Sometimes it might require the official installer files to replace them, so you need to follow any instructions given if this is the case.
The simpler version of this parameter is /verifyonly which does the same scan telling you of any problems, but it won’t do any repairs unlike the prior command.
Similarly, you can use /scanfile to check and repair a specific file or /verifyfile to check the integrity of a file, but no automatic repairs are done. With these parameters, you need to add the full path to the target file after an equals sign like so: sfc /scanfile=C:\Windows\System32\kernel32.dll
Scan Entire Drive or Disk for Issues (chkdsk)
The Check Disk command is a more impressive version of the Scan Disk command. With this command you can scan an entire disk for issues and repair them automatically.
The base use of the Check Disk command is chkdsk C: /F which stands for fix any corrupted files. It is important to note that when you run this scan, it will count any currently opened files as errors as well. This means it’s best to check the disk when booting up the PC with nothing open yet.
You should be aware that checking the disk can last a very long time depending on the number of files and your processing power. It’s also good to note that you can’t do anything or modify files on the disk being scanned, so it’s best to let then scan run and not touch the system while it’s running.
Here are some of the more useful parameters that can be used with the chkdsk command:
| Parameter (Usage: chkdsk /parameter) |
Explanation |
/F |
Fix any errors on the disk |
/R |
Recover any bad sectors and recover readable information |
/X |
Makes the specified disk dismount first, closing all open files and processes running from it |
/C |
Skip checking for corrupt folders, only check files |
/scan |
Run a scan online, checking for fixes on issues from the internet |
/scan /perf |
The perf parameter can only be used alongside scan to perform the scan a lot faster.This can slow down all other processes on the system during the scan. |
/sdcleanup |
Cleans up unnecessary security descriptor data from storage |
Find and Kill Any Running Task (tasklist | taskkill)
You can use the tasklist command to see all currently running tasks on your system, similar to the Task Manager. It might be somewhat redundant due to the simplicity of the Task Manager, but it can show some tasks that are not otherwise visible as well as the memory usage in a cleaner format, within command prompt.
If you wish to force-close a process, you should first take note of the name or process ID (PID) from the task list. Once you have decided on one, you can type either taskkill /im AppName to close an application by name or by typing taskkill /pid processID to kill it by its ID.
In some cases, this can be useful, for example if you want to make a batch script to close certain processes automatically when you start playing a game or boot up your machine. There are also plenty of additional parameters to be used with tasklist to sort it in a fashion you prefer.
Command Prompt Shortcut Keys
Here are the best and most useful keyboard shortcuts for command prompt. These will definitely speed up your performance with the command prompt and you can always return to this table for a quick refresher.
| Shortcut | Explanation |
Up/Down arrow key |
Select the previous/next commands you’ve previously executed. |
Right arrow key |
Repeat the previous command you’ve executed one character at a time. |
Ctrl + Right/Left arrow key |
Move the marker before the first character of the next or previous word. |
Ctrl + Up/Down arrow key |
Scroll up or down on the command prompt without moving the marker. |
Ctrl + A |
Select all written text on the current row and press the combination again to select everything within the cmd. |
Shift + Right/Left/Up/Down arrow key |
Increase the amount of text currently selected by one character left/right, or a full row up/down. |
Ctrl + C / Ctrl + V |
Copy / Paste text to and from the command prompt. Copying requires text to be selected first. |
Ctrl + Backspace |
Delete the word left of the marker. |
Escape (Esc) |
Delete the entire row of text. |
F1 |
Repeat the previous command you’ve executed one character at a time. |
F2 |
Repeat a portion of the previous command up to a specified number (or all of it). |
F3 |
Repeats the entire previous command. |
F4 |
Deletes a command up to a specified number (or all of it). |
F5 |
Repeats the last command without cycling more previous commands. |
F6 |
Pastes “^Z” to the current row. |
F7 |
Gives you a list of previously executed commands. |
F8 |
Repeats previously executed commands in a cycle (keep pressing for more). |
F9 |
Allows you to paste a previously executed command from the list (list obtained from F7). |
Edit the Look & Colors of Command Prompt
Now that you know all the good stuff there is to know about the Windows cmd, it’s time to customize it a little bit. There are a few commands available for customization. You can do things like change the font or background colors, title of the command prompt window and change the font itself.
Changing the title of the command prompt is quite a useless command unless you are creating scripts and want to showcase your name or company in it. The command doesn’t save the title after the prompt is closed. However, you can change it to whatever you want by simply typing title TechTipVault.com Command Prompt or whatever name you wish.
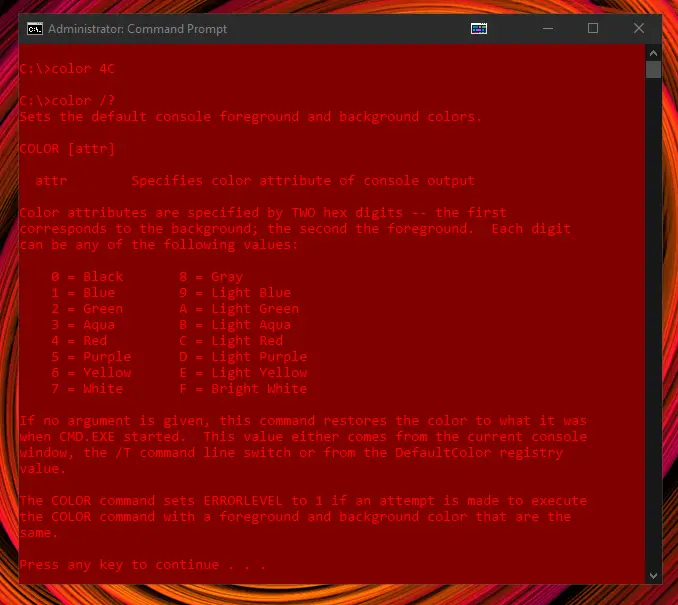
Change Background & Font Color
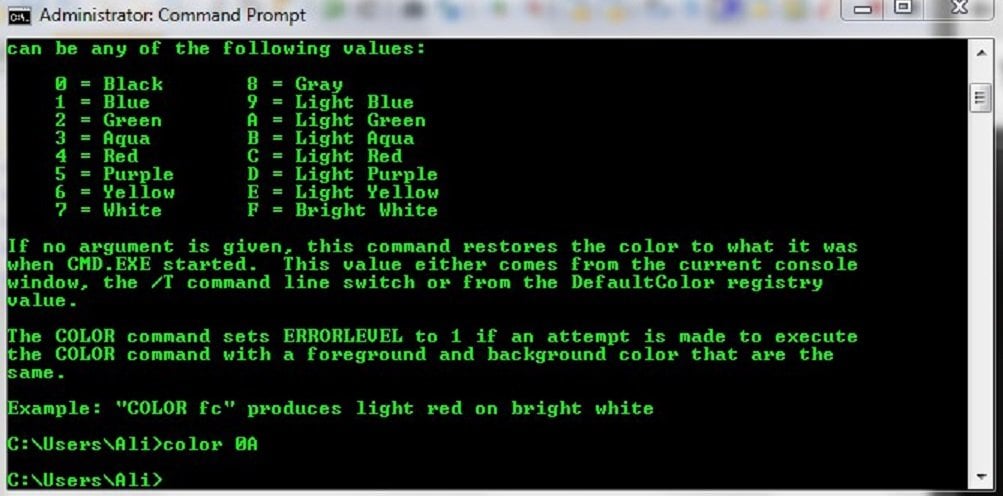
First and foremost, let’s figure out how to change the font and background colors. Thankfully it’s extremely simple as all you need to do is type color and 1 or 2 color codes.
The first character in the parameter is the background color and the second character is the font color. If you only enter one character, it will change the font color and the background will default to black.
So, if you wanted a red font and a bright white background, you could type color F4. To change the color scheme back to the default options, type in color without any parameters.
|
Change the Font Style
In order to change the font used in cmd, you need to first access the properties of the window. You can do this by right-clicking on the title bar of the command prompt and selecting Properties.
Once opened, you might notice you can also change the above colors there as well, but the most useful tab is the Font tab. The options there are very self-explanatory. At the top you can choose your font-size and below it you can pick a font family of your choosing.
You can also tick the Bold fonts checkbox to bold all fonts and you can see the preview of what your selection will look like at the bottom.
Now that you’ve read through the entire guide, you should have a firm grasp on the functionality of the Command Prompt. There’s tons of parameters and commands not covered in this guide, as it would become way too cluttered and hard to read. We highly recommend you go through all the command manuals within cmd and try as many of them out yourself to understand how they work in-depth.
If you noticed any issues with the contents or think we should add some clarifications, don’t hesitate to contact us. You can find our contact details on our About Us page.
Our every time rescuer, Command Prompt as we all know is a command line interpreter. It is famously called as cmd.exe or sometimes only cmd. You all might have liked the look of Windows 10 and its’ easy user interface.
Well, like others I also like bright colors, beautiful images, interesting interface, and lots of nice things that Windows 10 is providing. But the only thing that upsets me and many users is the Command Prompt. Don’t you think that it is very dull and looks lifeless? Though I will admit that in many situations it provides life to the computer but it is very dull. Well, my dear readers and friends, there is good news regarding the boring Command Prompt on Windows 10. You can customize it, fill it with colors, and change its fonts, cursor size, and many more things to do.
What is Command Prompt on Windows 10?
The main definition of Command Prompt has already been explained above. It is a line interpreter on Windows 10 and also of the previous versions of Windows. When you open Command Prompt, you type the commands to execute certain functions or work on your computer. And it carries out the task without making you use any graphical interface. The Command Prompt window is an access point for entering the computer commands. But if you have taken a trip to the Windows 10 Command Prompt you may have found out the new features that were never seen before in any versions of the Windows.
How to Launch and Use Command Prompt on Windows 10
1. Launching Processes
The different methods to launch the Command Prompt on Windows 10 screen are mentioned below –
a. Through Taskbar Search
- Open the Search field of Start Menu and type Command Prompt. You will see it being displayed in the results list.
b. Through Start Menu
- Open your Windows 10 Start Menu. Scroll down till your reach Windows System.
- Open it and see Command Prompt under Windows System.
c. Via Run
- Bring the Run window by pressing Windows and R keys on your keyboard. Type the command cmd or cmd.exe in the area provided. Click Ok to see Command Prompt on Windows 10 screen.
d. Via Power User Menu
- When you right click on the Start Menu icon of your Taskbar, the options available are called Power User Menu. Command Prompt is listed in them. Click on it to make it appear on your screen. Note – To enable this feature, go to Settings > Personalization > Taskbar and use switch toggle turn on “Replace Command prompt With Windows PowerShell in the menu when I right click the Start button or press Windows + X”.
You Might also like to read:
- How to Access Elevated Command Prompt on Windows 10
- How to Launch Command Prompt at Boot in Windows 10
- 4 Ways To Launch Command Prompt with Administrator Privileges In Windows 8
2. Getting Windows 10 Command Prompt Properties
To make changes in the Command Prompt window, you have to first access its Properties section from where you can carry out the customization process.
- You have learned to launch the Command Prompt window on your screen. So first of all, make it appear on your screen. Now, on top of the Command Prompt window, make a right click and choose the Properties option.
- The Command Prompt Properties window will now appear on the screen exhibiting you four different tabs for your customization – Options, Font, Layout, Colors, and Experimental.
The details of all the four tabs are explained below:
3. Customizing Cursor Size, Command History and Edit Option in Command Prompt on Windows 10
As you can see the first tab of the Command Properties window is of the Options. The Options tab has three sections into it – Cursor Size, Command History, and Edit Options.
a. Cursor Size
The Cursor Size options provide you three sizes for the cursor. The Small is selected by default which is used by almost all the users. When you wish to change the size of the cursor select either Medium or Large size as per your requirement.
b. Command History
The Command History has three options listed in it. The first one is the Buffer Size. The number seen beside the Buffer Size option represents you the track record of the commands been carried by you. You can use the drop-down menu of it and change the number of records. By default, the number is set to 50. You can take it up to 999 also.
The second option of Command History is the Number of Buffers. The number displayed with this option says the number of simultaneous occurrence of the Command Prompt being used by you, each with distinct buffers. Suppose, after changing its value to 5, you can open up five Command Prompts simultaneously, all with its own buffers, different from each other.
The third option is of Discard Old Duplicates. If you select this option, Windows will delete the duplicate command records from the buffer.
c. Edit Options
The Edit Options section also holds two options in it – QuickEdit Mode and Insert Mode.
The QuickEdit Mode permits you to copy content from Command Prompt window and paste it in the same using a mouse.
The next option Insert Mode gives you a permission to insert content at the position of the cursor. If this option is unchecked, you will notice the characters striking to each other.
4. Modifying Fonts on Command Prompt on Windows 10
The Font tab holds the second position in the Command Prompt Properties window. This tab gives you opportunities to change the size of the characters and also to change the font of the characters.
If seen carefully, the Size option provides you many sizes and its preview can be seen in the Window Preview. Choose the size which suits you.
Then on the middle part of the Font tab, you will see Font option. The Size option changes according to the selection of the Font. If you choose Consolas as your Font, you will see that the size list will display you different options. The look of the selected Font is displayed on the Selected Font section.
5. Changing the Layout of Command Prompt on Windows 10
The Layout is the third tab in the Command Prompt Properties window. This tab gives you three options in three different sections to work out – Screen Buffer Size, Window Size, and Window Position.
a. Screen Buffer Size
By changing the Width value, you can change the number of characters to be displayed on a line in the Command Prompt. And the numbers of lines saved in the memory are modified by utilizing the Height value.
b. Window Size
You can adjust the Width and Height of the Command Prompt window.
c. Window Position
You can set the distance of Command Prompt’s window from the upper and left corners of your screen. But to set the Width and Height, you need to select the Let system position window option.
Let system position window: if you select this option, you will be enabled to modify the Window Position. In case, it is not selected, using the mouse you can drag and drop and also can change the size of the Command Prompt window.
6. Setting Colors in Command Prompt on Windows 10
The fourth tab represents the Color section for editing. You will be provided with four different options: Screen Text, Screen Background, Popup Text, Popup Background. Let us know see what does the option gives you.
Screen Text: Select this option to choose the color for your text that will be displayed in the Command Prompt window.
Screen Background: You can even use your favorite color as the background. This option serves background color.
Popup Text: Utilize this option to adjust the color of the text that will be exhibited in the pop-up windows provoked by the Command Prompt.
Popup Background: The color for the background of the popup windows will be set that are provoked by the Command Prompt.
7. Using Experimental Tab of Command Prompt Properties on Windows 10
This tab is an addition to the Windows 10. It was not there previously in any versions of Windows. This Experimental tab has some options which will make work easier. There are seven different items to experiment with. Let us see them in detail.
The first option is Enable experimental console features (applies globally). You will see that by default this box is been selected. If you uncheck this option you will not be able to use the rest of the options of the Experimental tab, they all will be grayed out. So in order to do the experiment, keep the checkbox selected.
The next half of the tab is of Experimental Console Settings. And under this section, you will have seven options.
Enable line wrapping selection: This option upgrades how you choose and copy the text to the text editor. Here you don’t have to perfect the course of the text after you pasted the copied items to another application.
Filter clipboard contents on paste: This option eliminates the tabs and converts the smart quotes into the regular of that text which is copied from the clipboard and pasted into the Command Prompt.
Wrap text output on resize: The contents of the Command Prompt will be resized with the resizing the Command Prompt window by automatically fitting the width of the window.
Enable new Ctrl key shortcuts: It allows you to use the shortcuts which include the following –
- Ctrl + C: This will copy the selected text to the clipboard
- Ctrl + V: Use it to paste the text into the command line.
- Ctrl + Home: Will takes the cursor to the beginning of the buffer.
- Ctrl + End: Will take the cursor to the end of the buffer.
- Ctrl + M: Mark Mode to move the cursor within the window.
- Ctrl + F: This will open the Find dialog.
- Ctrl + Up Arrow: Moves the cursor upwards.
- Ctrl + Down Arrow: Moves the cursor downwards.
- Ctrl + Page Up: It will move up one page in the output history.
- Ctrl + Page Down: It will move down one page in the output history.
- Alt +F4: Closes the Command Prompt
Extended Edit keys: This enables the enhanced keyboard editing on the command line.
Trim leading zeros on selection: When you double click to choose a text, ignore leading zeros unless text begins with 0x or 0n.
Opacity: The Command Prompt window can be semi-transparent now. Use the slider and give the window a glassy look. You can bring down the transparency level to 30% also. These are keyboard shortcuts to adjust the opacity –
- Ctrl + Shit + Plus (+): This combination will increase the transparency.
- Ctrl + Shift + Minus (-): It will reduce the transparency level.
- Ctrl + Shift + Scroll up (Mouse): Increase the opacity level.
- Ctrl + Shift + Scroll down (Mouse): This will decrease the transparency level of the Command Prompt
