Introduction
While there are various methods available for file transfers from a Windows system to a Linux system, using the Command lines provides a straightforward and reliable approach. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the step-by-step process, highlighting the necessary commands and techniques to seamlessly transfer your files from Windows to Linux.
Prerequisites
Verify Your Remote Linux Server is Ready
If you have ordered one from Database Mart, you will receive an email containing the information of your VPS, including server IP and login credentials. You can also obtain the information on the overview page in the control panel. Please refer to this guide on how to get server credentials if you need assistance.
Steps to Transfer Files from Windows to Linux Using Command Prompt
Step 1. Open the Command Prompt in Local Windows
Search cmd in the search bar, and double-click the Command Prompt to open it. Or press the Windows key + R, then type cmd or cmd.exe in the Run command box, and press Enter.
Then, you should see the command prompt interface as below.
Step 2. Transfer Files between Local Windows and Remote Linux
Before the transfer, we will explain some terms used in the command. When using the command, you should replace these terms with the actual value.
filename.extension: it’s the name of a file and file extension that’s to be transferred. In this case, we may use mydata.txt and website.txt.
folderName: it’s the name of a folder that’s to be transferred. In this case, we may use the Website folder.
customPort: it’s the custom port you use to connect to your remote Linux server.
localFilePath: it’s the path on your local Windows PC.
username: it’s the username used to log into the remote Linux server.
remoteServerAddress: it’s the server IP of the remote Linux server.
remoteFilePath: it’s the path on the remote Linux server. In this case, we use /home/administrator.
2.1 Transfer a File from Local to Remote Server
For demonstration purposes, we have created a file in the desktop>website named «mydata.txt». First, we need to go to the file’s directory by inputting cd, followed by the file path on our local Windows. In this case, the file is located at desktop\website. Therefore, we enter the following command.
After that, you can see that we navigate to the folder where the file is located.
Then, we use the following command to transfer the «mydata.text» from local Window to the remote Linux server.
scp filename.extension username@remoteServerAddress:remoteFilePath
After entering the command, you will be prompted for the password for connecting to the remote server. Input the password and hit the Enter button, the file will be transferred. In this case, we have transferred the local file mydata.txt (located at desktop/website) to the /home/administrator directory on the remote Linux server.
2.2 Transfer a File from Remote Server to Local
You can run the following command to copy a file from the remote server to your local Windows PC.
scp username@remoteServerAddress:remoteFilePath/filename.extension localFilePath
In this case, we have transferred the mydata.txt (located at home/administrator on the remote server) to the desktop directory on the local server.
2.3 Transfer Multiple Files from Local to Remote Server
The SCP command also allows you to transfer multiple files in a single command. Navigate to the file folder and run the following command.
scp localFilePath/filename1.extension localFilePath/filename2.extension username@remoteServerAddress:remoteFilePath
In this case, we have transferred two local files mydata.txt (located at desktop) and mywebsite.txt (located at desktop/website) to the /home/administrator directory on the remote Linux server.
2.4 Transfer a Folder from Local to Remote Server
Besides files, the SCP command also allows you to securely copy folders between the local and remote server. Use the following command to copy a folder from local to the remote server.
scp -r localFilePath/folderName username@remoteServerAddress:remoteFilePath
In this case, we have transferred the local Website folder, which contains two files mydata.txt and mywebsite.txt, to the /home/administrator directory on the remote Linux server.
2.5 Transfer a File Faster
Adding the -c option after the scp command will compress the file while it’s being transferred. Once the file reaches its destination, it returns to its normal size.
scp -c localFilePath/filename.extension username@remoteServerAddress:remoteFilePath
In this case, we have transferred the local Website folder, which contains two files mydata.txt and mywebsite.txt, to the /home/administrator directory on the remote Linux server.
2.6 Transfer a File Using a Custom Port
The scp command uses the 22 port by default. If you have changed to a custom port, please run the following command to transfer a file. Make sure to capitalize the P.
scp -P customPort localFilePath/filename.extension username@remoteServerAddress:remoteFilePath
In this case, we have transferred the local file mydata.txt to the /home/administrator directory on the remote Linux server using a custom port.
Step 3. Verify the File has been Transferred
Then, Use a preferred editor to open the file. Here, we use the «Nano editor.» In this example, the remoteFilePath is /home/administrator, and the filename.extention can be mydata.txt, mywebsite.txt, and myweb.txt.
nano remoteFilePath/filename.extention
We can also check if the folder has been copied to the remote server. Go to the /home/administrator directory and check if the Website folder is there.
cd /home/administrator ll
Conclusion
In conclusion, transferring files from a local Windows machine to a remote Linux server using the command prompt (CMD) is a powerful and efficient method for managing data. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this blog, you can establish a secure connection, utilize the SCP (Secure Copy Protocol) command, and successfully transfer files between these two platforms.
Other Methods to Transfer Files between Windows and Linux Server

This guide has everything you need to successfully transfer files from Windows to Linux with Rsync and SSH. Rsync is a reliable tool for file synchronization, and when combined with SSH, it ensures secure file transfers between systems. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll show you how to set up Rsync and SSH on your Windows computer and Linux server, making file transfers effortless.
Setting up SSH on both Windows and Linux systems
Let’s start by setting up SSH on both your Windows and Linux environments.
For Windows, you can use the built-in OpenSSH client, which was introduced in Windows 10 version 1809 and later. To enable the OpenSSH client, open the Windows PowerShell or Command Prompt and run the following command:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object {$_.Name -like 'OpenSSH.Client*'} | Add-WindowsCapability -OnlineThis command will install the OpenSSH client on your Windows system.

Once the installation is complete, you can test the SSH connection by running the following command:
ssh user@remote_linux_serverReplace user with the username you use to log in to your Linux server, and remote_linux_server with the IP address or hostname of your Linux server.

On the Linux side, SSH is typically pre-installed, but you may need to ensure that the SSH server (sshd) is running. Open a terminal on your Linux system and run the following command to check SSH is available or not:
ssh -VIf this command shows an output, it means the SSH is installed on the machine. If not install OpenSSH and also make sure to check the status of the SSH on your machine before going to the next steps.
Refer to this article: How to install and use SSH on Linux for OpenSSH installation and checking status of it.

Now that you have SSH set up on both your Windows and Linux systems, you’re ready to move on to the next step.
Installing and configuring Rsync on Windows and Linux
Rsync is a powerful file synchronization tool that can be used in combination with SSH to efficiently transfer files between Windows and Linux systems. Let’s start by installing Rsync on your Windows computer.
For Windows, you can download and install the Cygwin tool, which includes the Rsync utility. Visit the Cygwin website (https://www.cygwin.com/) and download the Cygwin installer. During the installation process, make sure to select the “Rsync” package from the list of available packages.

Alternatively, you can use the WinSCP application, which includes a built-in Rsync implementation. Visit the WinSCP website (https://winscp.net/eng/index.php) and download the latest version of the software.
On the Linux side, Rsync is typically pre-installed, but you can install it using your distribution’s package manager. For example, on Ubuntu or Debian-based systems, you can run the following command:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install rsyncOnce Rsync is installed on both your Windows and Linux systems, you can configure it to work seamlessly with SSH.
Also, you’ll need to ensure that the SSH server is set up to allow Rsync connections in the Linux machine. You can do this by editing the SSH server configuration file, typically located at /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Look for the line that says Subsystem sftp /usr/lib/openssh/sftp-server and uncomment it (remove the “ at the beginning of the line).
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_configSave the configuration file and restart the SSH service using the following command:
sudo systemctl restart sshThe command to restart the SSH service can differ based on the Linux distribution you’re using. It’s essential to use the appropriate command that corresponds to the OpenSSH version installed on your machine to ensure a smooth and successful restart.

With Rsync and SSH set up on both your Windows and Linux systems, you’re now ready to start transferring files between the two environments.
Experience the Power of Veeble VPS Hosting
Experience the power of Veeble VPS hosting. Our plans are affordable, reliable, and packed with features that will help you take your business to the next level.
Choose Your Plan
Transferring files from Windows to Linux using Rsync and SSH
Now that you have Rsync and SSH configured on both your Windows and Linux systems, let’s explore how to use them to transfer files from your Windows computer to your Linux server.
Open a Command Prompt or PowerShell window on your Windows computer and navigate to the directory containing the files you want to transfer. Then, use the following Rsync command to copy the files to your Linux server:
rsync -avzc --delete -e "ssh" /path/to/local/files user@remote_linux_server:/path/to/remote/destination
When using rsync in Cygwin, you need to reference Windows directories through the /cygdrive mount point. For example, if your folder to sync is located in the Downloads directory of your user profile, the path would be something like /cygdrive/c/Users/your_username/Downloads/<your folder>.
Here’s what each part of the command does:
rsync: Invokes the Rsync utility.-avzc: Enables the following options:-a: Preserves file attributes and permissions.-v: Enables verbose mode, providing more detailed output.-z: Compresses the data during transfer to reduce the amount of data sent.-c: Checks the file checksums to ensure data integrity.--delete: Deletes any files on the remote server that are not present in the local directory.-e "ssh": Specifies that the transfer should be done over an SSH connection./path/to/local/files: The path to the local files or directory you want to transfer.user@remote_linux_server:/path/to/remote/destination: The SSH username and the path to the remote destination on your Linux server.
Replace the placeholders in the command with the appropriate values for your setup.
The first time you run this command, it will prompt you to accept the host key of the remote Linux server. Once you’ve accepted the host key, the transfer will begin, and you’ll see the progress displayed in the console.
If you need to transfer files regularly, you can create a batch file or a PowerShell script to automate the process. This will save you time and ensure that the file transfers are consistent and reliable.
Troubleshooting common issues during file transfer
While Rsync and SSH generally provide a seamless file transfer experience, you may occasionally encounter some issues. Let’s explore some common problems and their solutions.
- SSH connection refused: If you encounter an error message indicating that the SSH connection was refused, it’s likely that the SSH server on your Linux system is not running or is not accessible. Please refer to the article: Troubleshooting “SSH Connection Refused” Error and Regaining Access to resolve it.
- Permission denied: If you receive a “Permission denied” error during the file transfer, it means that the user account you’re using on the Linux server does not have the necessary permissions to access the destination directory. You can either log in as a user with higher privileges or change the permissions of the destination directory using the
sudo chmodcommand.
Reference: Managing File Ownership and Group Ownership in Linux - Checksum mismatch: Rsync uses checksums to ensure data integrity during the transfer process. If you encounter a checksum mismatch error, it could be due to a network issue or a problem with the source files. Try running the Rsync command with the
--checksumoption to perform a more thorough checksum verification. - Insufficient disk space: If the transfer fails due to insufficient disk space on the remote Linux server, you’ll need to free up some space or transfer the files to a different location with more available storage.
- Firewall or network issues: If the transfer is slow or intermittent, it could be due to firewall or network-related issues. Ensure that the necessary ports (typically 22 for SSH) are open and accessible between your Windows computer and the Linux server.
To troubleshoot these issues, you can try the following steps:
- Check the SSH server logs on the Linux system for any error messages.
- Verify the user permissions and directory access on the Linux server.
- Run the Rsync command with additional verbose options (
-vvv) to get more detailed output. - Test the network connectivity between your Windows computer and the Linux server using tools like
pingortelnet. - Temporarily disable any firewalls or antivirus software that might be interfering with the file transfer.
By addressing these common issues, you can ensure a smooth and reliable file transfer process between your Windows and Linux systems.
Best practices for efficient file transfer between Windows and Linux
To get the most out of your file transfers using Rsync and SSH, consider the following best practices:
- Use compression: Enabling the
-zoption in the Rsync command compresses the data during the transfer process, which can significantly reduce the amount of data sent over the network, especially for large files or directories. - Exclude unnecessary files: Use the
--excludeoption in the Rsync command to exclude files or directories that you don’t need to transfer, such as temporary files, log files, or hidden system files. This can help speed up the transfer process and reduce the amount of data transferred.
Refer: Optimizing Rsync: Ignore Unwanted Files and Directories - Maintain a consistent file structure: Try to keep the file structure and directory hierarchy the same on both the Windows and Linux systems. This will make it easier to manage and locate files after the transfer is complete.
- Use relative paths: When specifying the source and destination paths in the Rsync command, use relative paths instead of absolute paths. This will make the command more portable and easier to use in different scenarios.
- Automate the transfer process: Create a batch file or a PowerShell script to automate the Rsync command, making it easy to run the file transfer regularly or as needed.
- Monitor the transfer progress: Use the verbose options (
-vvv) in the Rsync command to get detailed output on the transfer progress, file sizes, and any errors that may occur. This will help you troubleshoot issues more effectively. - Leverage incremental backups: Rsync is particularly useful for performing incremental backups, where it only transfers the files that have changed since the last backup. This can save a significant amount of time and bandwidth, especially for large data sets.
- Consider using a graphical tool: While the command-line Rsync approach is powerful, you may also want to explore graphical tools like WinSCP or FileZilla, which provide a user-friendly interface for managing file transfers between Windows and Linux.
- Secure the SSH connection: Ensure that the SSH connection is secure by using strong passwords or SSH keys for authentication. Avoid using weak or default passwords, and consider implementing two-factor authentication for added security.
- Monitor disk space on the Linux server: Keep an eye on the available disk space on the Linux server to ensure that there is enough room to accommodate the transferred files. Set up alerts or monitoring tools to notify you when disk space is running low.
By following these best practices, you can streamline the file transfer process, improve efficiency, and maintain the security and integrity of your data during the transfer between your Windows and Linux systems.
Alternatives to Rsync and SSH for file transfer
While Rsync and SSH are a powerful combination for transferring files between Windows and Linux, there are alternative tools and methods you can consider:
- FTP/FTPS/SFTP: File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and its secure variants, FTPS (FTP over SSL/TLS) and SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol), are widely used for file transfers. These protocols can be used with various FTP client applications, such as FileZilla or WinSCP, to transfer files between Windows and Linux systems.
- Cloud storage services: Services like Dropbox, Google Drive, or Microsoft OneDrive provide a convenient way to transfer files between Windows and Linux systems. Simply upload the files to the cloud storage, and then download them on the other system.
- Network file sharing: You can set up network file sharing between your Windows and Linux systems using protocols like SMB (Server Message Block) or NFS (Network File System). This allows you to access and transfer files directly between the two systems over the network.
- Web-based file transfer tools: There are various web-based file transfer tools, such as WeTransfer or Sendspace, that you can use to transfer files between your Windows and Linux systems. These tools typically provide a simple and user-friendly interface for uploading and downloading files.
- Portable storage devices: If you have a portable storage device, such as a USB flash drive or an external hard drive, you can use it to physically transfer files between your Windows and Linux systems.
Each of these alternatives has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice will depend on your specific requirements, such as the size of the files, the frequency of transfers, and the level of security needed.
For example, FTP/FTPS/SFTP may be a good option if you need to transfer files regularly, but they may not provide the same level of security as Rsync and SSH. Cloud storage services can be convenient, but they may not be suitable for transferring sensitive or large files. Network file sharing can be efficient, but it may require additional configuration and setup.
When choosing an alternative method, consider factors such as ease of use, transfer speed, security, and compatibility with your Windows and Linux systems. Evaluate the trade-offs and select the solution that best fits your needs.
By following these guidelines, you’ll be able to seamlessly transfer files between your Windows computer and Linux server, whether you need to perform regular backups, share important documents, or synchronize project files. The combination of Rsync and SSH provides a robust and secure solution for your file transfer needs.
Scale Without Limits
Adapt to changing demands with flexible and scalable solutions. Grow your business seamlessly.
Choose Your Plan
Copying files from Windows to Linux can be accomplished using various methods, making it a seamless process for users. One way is to use SSH (Secure Shell) to transfer files via the command line. To do this, the Linux OS should be updated and the OpenSSH server installed. An SSH client like PuTTY can be utilized on Windows, along with the PSCP tool. Another method is using FTP (File Transfer Protocol) with SFTP support. This involves installing an SFTP-supported app like FileZilla on Windows and ensuring the Linux server is running. Sync software like Resilio or SyncThing can also be used to manage the connection between the two operating systems. Lastly, if running Linux in a virtual machine, files can be transferred by creating a virtual shared directory using software like VirtualBox. It’s important to have the Guest Additions installed on the virtual machine for this method. Overall, there are multiple options available for easily copying files from Windows to Linux.
Key Takeaways:
- Copying files from Windows to Linux can be done using SSH, FTP with SFTP support, sync software, or in a virtual machine.
- For SSH file transfer, update the Linux OS, install OpenSSH server, and use an SSH client like PuTTY.
- FTP with SFTP support requires installing a compatible app like FileZilla and ensuring the Linux server is running.
- Sync software like Resilio or SyncThing can facilitate a synchronized connection between Windows and Linux.
- In a virtual machine, create a virtual shared directory using software like VirtualBox and install Guest Additions in the virtual machine.
Using SSH for File Transfer
One method to copy files from Windows to Linux is by utilizing SSH (Secure Shell) for secure and efficient file transfer. SSH allows for remote access to a Linux server and provides a secure connection for file transfer. Here are the steps to transfer files using SSH:
- Ensure that your Linux operating system is updated and has the OpenSSH server installed.
- On your Windows machine, download and install an SSH client like PuTTY.
- Open PuTTY and enter the IP address or hostname of the Linux server.
- Enter your login credentials for the Linux server.
- Once connected, navigate to the directory where your files are located on the Windows machine.
- Use the PSCP (PuTTY Secure Copy) tool to copy the files from the Windows machine to the Linux server. The command syntax is as follows:
1
pscp [source file path] [destination file path]
.
- Wait for the file transfer to complete, and you’re done!
Using SSH for file transfer provides a secure and efficient way to copy files from Windows to Linux. It is a widely used method and allows for easy integration between the two operating systems.
Note: Make sure to replace [source file path] and [destination file path] with the actual paths to your files on the Windows and Linux machines, respectively.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| – Secure file transfer – Remote access to Linux server – Efficient and reliable |
– Requires installation and configuration of SSH server on Linux – Command-line interface may be intimidating for some users |
Using FTP with SFTP support
Another option for transferring files from Windows to Linux is by using FTP with SFTP support, providing a straightforward method for file transfer. FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a widely used protocol for transferring files between systems, and by adding SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) support, the process becomes even more secure.
To get started, you will need to install an SFTP-supported application on your Windows machine. One popular choice is FileZilla, which is free and easy to use. Once installed, open FileZilla and enter the IP address or hostname of your Linux server, along with your username and password.
Tip: Ensure that the Linux server has the necessary SSH server software installed.
Once connected, you can browse your local files on the left side of the FileZilla interface and the remote files on the right side. Simply navigate to the file you want to transfer from Windows to Linux, right-click on it, and choose “Upload” or drag and drop it to the desired location on the Linux server.
Benefits of using FTP with SFTP support:
- Secure file transfer: SFTP adds encryption to the FTP protocol, ensuring that your files are protected during the transfer.
- Easy-to-use interface: FileZilla provides a user-friendly interface for managing your file transfers and navigating between your local and remote files.
- Flexibility: FTP with SFTP support allows you to transfer files of any size and type, making it suitable for various file transfer needs.
Overall, using FTP with SFTP support offers a reliable and efficient method for copying files from Windows to Linux. Whether you are transferring a single file or multiple files, this approach provides a secure and user-friendly solution.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Secure file transfer | Requires installation of an SFTP-supported application |
| Easy-to-use interface | May require some initial setup and configuration |
| Flexibility for transferring files of any size and type | FTP/SFTP may not be suitable for extremely large file transfers |
Using Sync Software for File Management
Sync software offers a convenient solution for managing file transfers between Windows and Linux, providing a synchronized connection for seamless file sharing. With tools like Resilio or SyncThing, users can easily keep their files up to date across both operating systems.
Resilio, formerly known as BitTorrent Sync, offers a reliable and secure way to sync files between Windows and Linux. It utilizes peer-to-peer technology, ensuring fast and efficient transfers. Users can create shared folders and specify which files or directories to sync. The software also supports selective sync, allowing users to decide which files to download and sync to their devices.
Similarly, SyncThing is an open-source sync software that enables file synchronization between multiple devices, including Windows and Linux systems. It offers a decentralized approach, where data is stored locally instead of relying on a central server. Users can set up folders to sync and specify the devices they want to sync with. SyncThing also provides advanced features like versioning and conflict resolution to ensure data integrity.
| Sync Software | Features |
|---|---|
| Resilio | Peer-to-peer technology, selective sync |
| SyncThing | Decentralized approach, versioning, conflict resolution |
Using sync software eliminates the need for manual file transfers and reduces the risk of data loss or inconsistency. It provides a user-friendly interface that allows users to monitor the status of their sync operations and easily manage their files. Whether you’re a business professional working with different operating systems or a tech-savvy individual looking to streamline your file management, sync software is an excellent choice for transferring files between Windows and Linux.
Transferring Files in a Virtual Machine
If you’re running Linux in a virtual machine, transferring files from Windows is possible by creating a virtual shared directory. This allows for seamless file transfer between the two operating systems without the need for external storage devices or cloud services.
To get started, make sure you have a virtualization software like VirtualBox installed on your Windows machine. Once you have your Linux virtual machine set up, ensure that the Guest Additions are installed. These additions provide additional functionality and improved compatibility between the two systems.
Next, open the settings for your Linux virtual machine and navigate to the “Shared Folders” section. Here, you can add a new shared folder by specifying the folder path on your Windows host machine. Choose a folder that contains the files you want to transfer.
Once the shared folder is set up, you can access it from within your Linux virtual machine. Simply navigate to the specified mount point, usually found in the /media/ directory, and you will see the shared folder listed. From there, you can copy files from your Windows machine into the shared folder, and they will be instantly available in your Linux virtual machine.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple and straightforward setup | Requires a virtualization software |
| No need for external storage devices | Dependent on the host machine’s performance |
| Enables seamless file transfer | May require additional configuration in some cases |
Transferring files in a virtual machine provides a convenient way to share files between Windows and Linux without the need for complicated network configurations or external devices. By creating a virtual shared directory, you can easily move files between the two operating systems and work seamlessly across platforms.
Alternative Methods for File Transfer
In addition to the mentioned methods, there are alternative ways to copy files from Windows to Linux, offering flexibility based on individual preferences. These alternative methods include:
- Cloud Storage Services: Uploading files to cloud storage platforms like Google Drive or Dropbox allows for easy access and download from any device with an internet connection. Users can then download the files from the cloud storage to their Linux system.
- Email Attachments: Another option is to send the files as email attachments. Users can compose an email on their Windows machine, attach the desired files, and send them to their own email address. Then, they can access their email on the Linux system and download the attachments.
- External Storage Devices: For large file transfers, using external storage devices like USB flash drives or external hard drives can be a convenient option. Users can simply copy the files to the external device on their Windows computer and then connect the device to their Linux system for file transfer.
Each of these alternative methods offers its own advantages and can be utilized depending on the user’s needs and preferences. Whether it’s the convenience of cloud storage, the simplicity of email attachments, or the reliability of external storage devices, there is a solution for everyone.
Comparison of Alternative Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Storage Services | Easy access from any location, file synchronization, scalable storage options | Dependent on internet connection, limited free storage capacity |
| Email Attachments | Simple and familiar method, no additional software required | File size limitations, reliant on email service provider |
| External Storage Devices | No internet connection required, large storage capacity, portable | Physical device required, additional manual steps for file transfer |
It’s important for users to consider their specific needs, such as file size, accessibility, and convenience, when choosing the most suitable method for transferring files from Windows to Linux. Whether opting for the traditional methods mentioned earlier or exploring these alternative approaches, users can find a solution that meets their requirements.
Best Practices for File Transfer
To ensure a smooth and error-free file transfer from Windows to Linux, following these best practices can be immensely helpful.
- Organize your files: Before transferring files, make sure they are properly organized in a logical structure. This will save you time and effort when searching for specific files on the Linux system.
- Choose compatible file formats: Consider the compatibility between Windows and Linux when selecting file formats. Avoid proprietary file formats that may not be supported on the Linux system.
- Use secure transfer methods: Whenever possible, opt for secure file transfer methods such as SSH or SFTP. These protocols encrypt the data during transfer, ensuring the security and integrity of your files.
- Double-check file permissions: Before transferring files, make sure the necessary permissions are set correctly on the Linux system. This will help avoid any issues with accessing or modifying the transferred files.
- Test the transfer: To ensure a successful transfer, it’s always a good idea to test the process with a small set of files before transferring a large amount of data. This way, you can identify and resolve any potential issues early on.
By following these best practices, you can streamline the file transfer process and minimize the chances of encountering any problems or errors.
| Best Practice | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Organize your files | Easy access and management of files on the Linux system |
| Choose compatible file formats | Ensure seamless compatibility between Windows and Linux |
| Use secure transfer methods | Protect your files during transfer from potential threats |
| Double-check file permissions | Avoid permission-related issues when accessing or modifying files |
| Test the transfer | Identify and resolve any issues before transferring a large amount of data |
Conclusion
Copying files from Windows to Linux is a straightforward process with multiple options available, allowing for seamless and efficient file transfers. One way to transfer files is by using SSH (Secure Shell) through the command line. To do this, make sure the Linux operating system is updated and the OpenSSH server is installed. On Windows, an SSH client like PuTTY and the PSCP tool can be used for this method.
Another method is using FTP (File Transfer Protocol) with SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) support. Install an SFTP-supported app like FileZilla on Windows and ensure that the Linux server is running. Sync software such as Resilio or SyncThing can also be utilized to manage the connection between the two operating systems, providing a synchronized file transfer experience.
If you are running Linux in a virtual machine, you can transfer files by creating a virtual shared directory using software like VirtualBox. It is important to have the Guest Additions installed on the virtual machine to enable this method.
Overall, there are multiple options available for easily copying files from Windows to Linux. Whether you prefer using SSH, FTP with SFTP, sync software, or a virtual machine, these methods ensure a seamless and efficient file transfer process.
FAQ
How can I copy files from Windows to Linux?
There are multiple methods available for copying files from Windows to Linux. You can use SSH (Secure Shell) to transfer files via the command line, or utilize FTP (File Transfer Protocol) with SFTP support. Sync software like Resilio or SyncThing can also be used, as well as creating a virtual shared directory in a Linux virtual machine. There are various options to choose from based on your specific needs.
What is SSH and how can I use it for file transfer?
SSH (Secure Shell) is a network protocol that allows secure communication between two computers. To use SSH for file transfer from Windows to Linux, you need to update the Linux OS and install the OpenSSH server. On Windows, you can use an SSH client like PuTTY along with the PSCP tool to transfer files via the command line.
How can I use FTP with SFTP support to transfer files between Windows and Linux?
To use FTP with SFTP support, you need to install an SFTP-supported app like FileZilla on Windows. Make sure the Linux server is running and configure the necessary settings in the FTP client. This will enable you to transfer files securely between Windows and Linux using the FTP protocol.
Can I use sync software to manage file transfers between Windows and Linux?
Yes, you can use sync software like Resilio or SyncThing to manage file transfers between Windows and Linux. These tools allow you to establish a synchronized connection between the two operating systems, ensuring that any changes made to files on one system are automatically reflected on the other.
How can I transfer files from Windows to Linux in a virtual machine?
If you are running Linux in a virtual machine, you can transfer files by creating a virtual shared directory. This can be done using software like VirtualBox. Make sure to install the Guest Additions on the virtual machine, as they provide additional functionality and support for file sharing between the host and guest systems.
Are there any alternative methods for copying files from Windows to Linux?
Yes, there are alternative methods for copying files from Windows to Linux. Some options include using cloud storage services, sending files as email attachments, or using external storage devices like USB drives or external hard drives. Choose the method that best suits your requirements and preferences.
What are some best practices for seamless file transfer from Windows to Linux?
To ensure seamless file transfer from Windows to Linux, it is recommended to organize your files in a logical manner, use appropriate file formats that are compatible with both operating systems, and double-check file permissions and access rights. It is also advisable to maintain regular backups of important files to prevent data loss.
Can you summarize the key points discussed in this article?
This article has highlighted various methods for copying files from Windows to Linux, including using SSH, FTP with SFTP support, sync software, and virtual shared directories in a virtual machine. It has also mentioned alternative methods and provided best practices for smooth file transfer. Overall, there are multiple options available, and you can choose the one that best suits your needs and preferences.
- About the Author
- Latest Posts
Mark is a senior content editor at Text-Center.com and has more than 20 years of experience with linux and windows operating systems. He also writes for Biteno.com
Are you looking for a way to quickly transfer files from your Windows computer to your Linux computer and back again? The open source PSCP utility makes it easy to transfer files and folders, and of course it’s open source.
Setting your PATH in Windows
Knowing how to set your command path in Windows makes it easier to use a handy utility like PSCP. If you’re unfamiliar with that process, read how to set a PATH on Windows.
Using PSCP
PSCP (PuTTY Secure Copy Protocol) is a command-line tool for transferring files and folders from a Windows computer to a Linux computer.
-
Download
pscp.exefrom its website. -
Move
pscp.exeto a folder in your PATH (for example,Desktop\Appif you followed the PATH tutorial here on Opensource.com). If you haven’t set a PATH variable for yourself, you can alternately movepscp.exeto the folder holding the files you’re going to transfer. -
Open Powershell on your Windows computer using the search bar in the Windows taskbar (type ‘powershell` into the search bar.)
-
Type
pscp –versionto confirm that your computer can find the command.
IP address
Before you can make the transfer, you must know the IP address or fully-qualified domain name of the destination computer. Assuming it’s a computer on your same network, and that you’re not running a DNS server to resolve computer names, you can find the destination IP address using the ip command on the Linux machine:
[linux]$ ip addr show | grep 'inet '
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
inet 192.168.1.23/24 brd 10.0.1.255 scope global noprefixroute eth0In all cases, 127.0.0.1 is a loopback address that the computer uses only to talk to itself, so in this example the correct address is 192.168.1.23. On your system, the IP address is likely to be different. If you’re not sure which is which, you can try each one in succession until you get the right one (and then write it down somewhere!)
Alternately, you can look in the settings of your router, which lists all addresses assigned over DHCP.
Firewalls and servers
The pscp command uses the OpenSSH protocol, so your Linux computer must be running the OpenSSH server software, and its firewall must allow SSH traffic.
If you’re not sure whether your Linux machine is running SSH, then run this command on the Linux machine:
[linux]$ sudo systemctl enable --now sshd
To ensure your firewall allows SSH traffic, run this command:
[linux]$ sudo firewall-cmd --add-service ssh --permanent
For more information on firewalls on Linux, read Make Linux stronger with firewalls.
Transfer the file
In this example, I have a file called pscp-test.txt that I want to transfer from C:\Users\paul\Documents on my Windows computer to my destination Linux computer home directory /_home_/paul.
Now that you have the pscp command and the destination address, you’re ready to transfer the test file pscp-test.txt. Open Powershell and use the dir command to change to the Documents folder, where the sample file is located:
PS> dir %USERPROFILE%\Documents\
Now execute the transfer:
PS> pscp pscp-test.txt paul@192.168.1.23:/home/paul
| Password:
End of keyboard-interactive prompts from server
pscp-test.txt | 0 kb | 0.0 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100%Here’s the syntax, word for word:
-
pscp: The command used to transfer the file. -
pscp-test.txtis the name of the file you want to transfer from Windows. -
paul@192.168.1.23is my username on the Linux computer, and the IP address of the Linux computer. You must replace this with your own user and destination information. Notice thatpscprequires a destination path on the target computer, and:/home/paulat the end of the IP address specifies that I want the file copied to my home folder.
After you authenticate to the Linux computer, the pscp-test.txt file is transferred to the Linux computer.
[ Related read Share files between Linux and Windows computers ]
Verifying the transferred
On your Linux computer, open a terminal and use the ls command to verify that the file pscp-test.txt appears in your home directory.
[linux]$ ls
Documents
Downloads
Music
Pictures
pscp-test.txtCopying a file off of a Linux system
You aren’t limited to just copying files to your Linux system. With pscp, you can also copy a file from Linux onto Windows. The syntax is the same, only in reverse:
PS> pscp paul@192.168.1.23:/home/paul/pscp-test.txt %USERPROFILE%\Documents\pscp-win.txtHere’s the syntax:
-
pscp: The command used to transfer the file. -
paul@192.168.1.23:/home/paul/pscp-test.txtis my username on the Linux computer, the IP address of the Linux computer, and the path to the file I want to copy. -
%USERPROFILE%\Documentsis the location on my Windows computer where I want to save the file. Notice that in copying the file back to my Windows computer, I can give it a new name, such aspscp-win.txt, to differentiate it from the original. You don’t have to rename the file, of course, but for this demonstration it’s a useful shortcut.
Open your file manager to verify that the pscp-win.txt file was copied to the Windows C:\Users\paul\Documents path from the Linux computer.
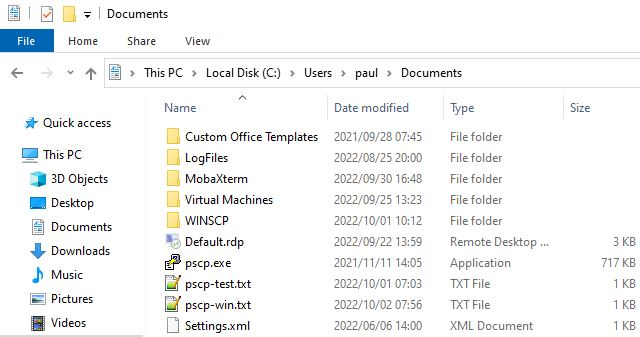
Image by:
(Paul Laubscher, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Remote copying
With the power of the open source pscp command, you have access to any computer in your house, and servers you have accounts on, and even mobile and edge devices.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License.
