on August 15, 2010
We normally use Services.msc to start or stop or disable or enable any service. We can do the same from windows command line also using net and sc utilities. Below are commands for controlling the operation of a service.
Command to stop a service:
net stop servicename
To start a service:
net start servicename
You need to have administrator privileges to run net start/stop commands. If you are just a normal user on the computer, you would get an error like below.
C:\>net start webclient System error 5 has occurred. Access is denied. C:\>
To disable a service:
sc config servicename start= disabled
To enable a service:
sc config servicename start= demand
To make a service start automatically with system boot:
sc config servicename start= auto
Note: Space is mandatory after ‘=’ in the above sc commands.
This SC command works on a Windows 7 machine and also on the down-level editions of Windows i.e Windows XP/2003 and Windows Vista. Again, if you do not have administrator previliges you would get the below error.
C:\>sc config webclient start= auto [SC] OpenService FAILED 5: Access is denied.
Note that the service name is not the display name of a service. Each service is given a unique identification name which can be used with net or sc commands. For example, Remote procedure call (RPC) is the display name of the service. But the service name we need to use in the above commands is RpcSs.
So to start Remote procedure call service the command is:
net start RpcSsTo stop Remote procedure call service
net stop RpcSs
These service names are listed below for each service. The first column shows the display name of a service and the second column shows the service name that should be used in net start or net stop or sc config commands.
| Display Name of the service | ServiceName which should be used with ‘net’ and ‘sc config’ commands. |
| Alerter | Alerter |
| Application Layer Gateway Service | ALG |
| Application Management | AppMgmt |
| ASP.NET State Service | aspnet_state |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service | BITS |
| Computer Browser | Browser |
| Bluetooth Support Service | BthServ |
| Bluetooth Service | btwdins |
| SMS Agent Host | CcmExec |
| Indexing Service | CiSvc |
| ClipBook | ClipSrv |
| .NET Runtime Optimization Service v2.0.50727_X86 | clr_optimization_v2.0.50727_32 |
| COM+ System Application | COMSysApp |
| Cryptographic Services | CryptSvc |
| Cisco Systems, Inc. VPN Service | CVPND |
| DCOM Server Process Launcher | DcomLaunch |
| DHCP Client | Dhcp |
| Logical Disk Manager Administrative Service | dmadmin |
| Logical Disk Manager | dmserver |
| DNS Client | Dnscache |
| Lenovo Doze Mode Service | DozeSvc |
| Error Reporting Service | ERSvc |
| Event Log | Eventlog |
| COM+ Event System | EventSystem |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Event Log | EvtEng |
| Fast User Switching Compatibility | FastUserSwitchingCompatibility |
| Windows Presentation Foundation Font Cache 3.0.0.0 | FontCache3.0.0.0 |
| Group Policy Monitor | GPMON_SRV |
| Help and Support | helpsvc |
| HID Input Service | HidServ |
| HTTP SSL | HTTPFilter |
| ThinkPad PM Service | IBMPMSVC |
| Windows CardSpace | idsvc |
| IMAPI CD-Burning COM Service | ImapiService |
| iPassConnectEngine | iPassConnectEngine |
| iPassPeriodicUpdateApp | iPassPeriodicUpdateApp |
| iPassPeriodicUpdateService | iPassPeriodicUpdateService |
| IviRegMgr | IviRegMgr |
| Server | lanmanserver |
| Workstation | lanmanworkstation |
| Lenovo Camera Mute | LENOVO.CAMMUTE |
| Lenovo Microphone Mute | Lenovo.micmute |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts |
| Intel(R) Management and Security Application Local Management Service | LMS |
| McAfee Framework Service | McAfeeFramework |
| McAfee McShield | McShield |
| McAfee Task Manager | McTaskManager |
| Machine Debug Manager | MDM |
| Messenger | Messenger |
| NetMeeting Remote Desktop Sharing | mnmsrvc |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator | MSDTC |
| Windows Installer | MSIServer |
| Net Driver HPZ12 | Net Driver HPZ12 |
| Network DDE | NetDDE |
| Network DDE DSDM | NetDDEdsdm |
| Net Logon | Netlogon |
| Network Connections | Netman |
| Net.Tcp Port Sharing Service | NetTcpPortSharing |
| Network Location Awareness (NLA) | Nla |
| NT LM Security Support Provider | NtLmSsp |
| Removable Storage | NtmsSvc |
| Microsoft Office Diagnostics Service | odserv |
| Office Source Engine | ose |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay |
| Pml Driver HPZ12 | Pml Driver HPZ12 |
| IPSEC Services | PolicyAgent |
| Power Manager DBC Service | Power Manager DBC Service |
| Protected Storage | ProtectedStorage |
| Remote Access Auto Connection Manager | RasAuto |
| Remote Access Connection Manager | RasMan |
| Remote Desktop Help Session Manager | RDSessMgr |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Registry Service | RegSrvc |
| Routing and Remote Access | RemoteAccess |
| Remote Registry | RemoteRegistry |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Locator | RpcLocator |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs |
| QoS RSVP | RSVP |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless WiFi Service | S24EventMonitor |
| Security Accounts Manager | SamSs |
| Smart Card | SCardSvr |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule |
| Secondary Logon | seclogon |
| System Event Notification | SENS |
| Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess |
| Shell Hardware Detection | ShellHWDetection |
| Print Spooler | Spooler |
| System Restore Service | srservice |
| SSDP Discovery Service | SSDPSRV |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | stisvc |
| System Update | SUService |
| MS Software Shadow Copy Provider | SwPrv |
| Performance Logs and Alerts | SysmonLog |
| Telephony | TapiSrv |
| Terminal Services | TermService |
| Themes | Themes |
| ThinkVantage Registry Monitor Service | ThinkVantage Registry Monitor Service |
| Telnet | TlntSvr |
| On Screen Display | TPHKSVC |
| Distributed Link Tracking Client | TrkWks |
| TVT Scheduler | TVT Scheduler |
| Windows User Mode Driver Framework | UMWdf |
| Intel(R) Management & Security Application User Notification Service | UNS |
| Universal Plug and Play Device Host | upnphost |
| Uninterruptible Power Supply | UPS |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS |
| Windows Time | W32Time |
| WebClient | WebClient |
| Windows Management Instrumentation | winmgmt |
| Portable Media Serial Number Service | WmdmPmSN |
| Windows Management Instrumentation Driver Extensions | Wmi |
| WMI Performance Adapter | WmiApSrv |
| Security Center | wscsvc |
| Automatic Updates | wuauserv |
| SMS Remote Control Agent | Wuser32 |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSVC |
| Network Provisioning Service | xmlprov |
Как завершить процесс службы Windows, которая зависла в статусе stopping (остановка) или starting (запуск)? Большинство администраторов Windows встречалось с ситуациями, когда при попытке остановить (перезапустить) службу из графического интерфейса консоли управления службами (
Services.msc
), служба зависает намертво и висит в статусе Stopping (или Starting). При этом все кнопки управления службой в консоли (Start, Stop, Restart) становятся недоступными (серыми). Самый простой способ – перезагрузить сервер, но это не всегда допустимо. Рассмотрим альтернативные способы, позволяющие принудительно завершить зависшую службу или процесс без необходимости перезагрузки Windows.
Если в течении 30 секунд после попытки остановки службы, она не останавливается, Windows выводит сообщение:
Не удалось остановить службу xxxxxxx Windows на локальном компьютере. Ошибка 1053. Служба не ответила на запрос своевременно.
Windows Could not stop the xxxxxx service on Local Computer Error 1053: The service did not respond in a timely fashion.
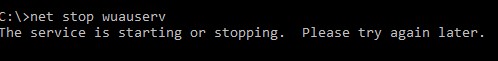
При попытке остановить такую службу командой:
net stop wuauserv
, появляется сообщение:
The service is starting or stopping. Please try again later.
Или:
[SC] ControlService: ошибка: 1061: Служба в настоящее время не может принимать команды.
Windows could not stop the Service on Local Computer. Error 1061: The service cannot accept control messages at this time.
Содержание:
- Как остановить зависшую службу Windows из командной строки?
- Принудительное завершение зависшей службы в PowerShell
- Анализ цепочки ожидания зависшего приложения с помощью ResMon
- Process Explorer: Завершение зависшего процесса из-под SYSTEM
Как остановить зависшую службу Windows из командной строки?
Самый простой способ завершить зависшую служу – воспользоваться утилитой taskkill. В первую очередь нужно определить PID (идентификатор процесса) нашей службы. В качестве примера возьмем службу Windows Update. Ее системное имя wuauserv (имя можно посмотреть в свойствах службы в консоли
services.msc
).
Важно. Будьте внимательными. Принудительная отставка процесса критичной службы Windows может привести к BSOD или перезагрузке операционной системы.
Отройте командную строку с правами правами администратора (иначе будет ошибка access denied) и выполите команду:
sc queryex wuauserv
В данном случае PID процесса —
9186
.
Чтобы принудительно завершить зависший процесс с PID 9186 воспользуйтесь утилитой taskkill:
taskkill /PID 9168 /F
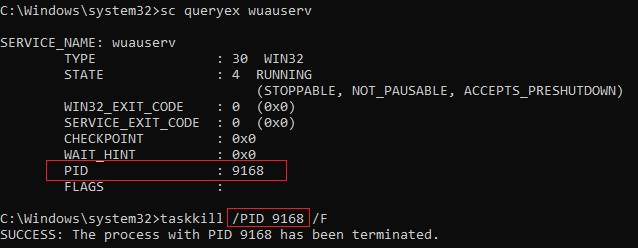
SUCCESS: The process with PID 9168 has been terminated.
Данная команда принудительно завершит процесс службы. Теперь вы можете запустите службу командой sc start servicename или через консоль управления службами (или совсем удалить эту службу, если она не нужна).
«Выстрел в голову» зависшей службы можно выполнить и более элегантно, не выполняя ручное определение PID процесса. У утилиты taskkill есть параметр /FI, позволяющий использовать фильтр для выбора необходимых служб или процессов. Вы можете остановить конкретную службу командой:
TASKKILL /F /FI “SERVICES eq wuauserv”
Или можно вообще не указывать имя, службы, завершив все сервисы в зависшем состоянии с помощью команды:
taskkill /F /FI “status eq not responding”
После этого служба, зависшая в статусе Stopping должна остановиться.
Также вы можете использовать утилиту taskkill для принудительной остановки зависших служб на удаленном компьютере:
TASKKILL /S CORPFS01 /F /FI “SERVICES eq wuauserv”
Принудительное завершение зависшей службы в PowerShell
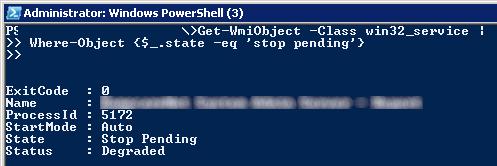
Также вы можете использовать PowerShell для принудительной остановки службы. С помощью следующей команды можно получить список служб, находящихся в состоянии Stopping:
Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service | Where-Object {$_.state -eq 'stop pending'}
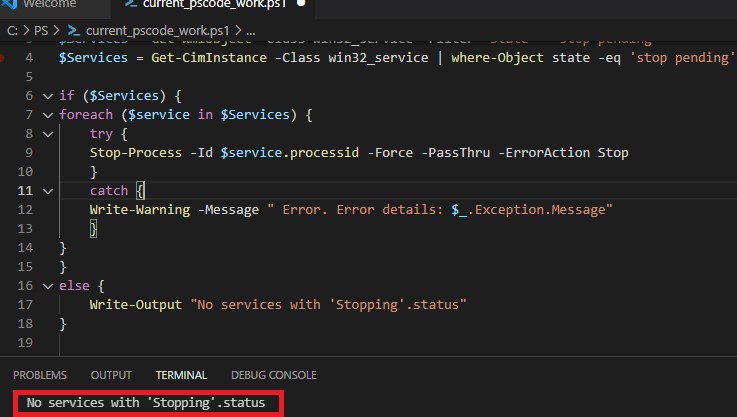
Завершить процесс для всех найденных служб поможет командлет Stop-Process. Следующий PowerShell скрипт завершит все процессы зависших служб в Windows:
$Services = Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service -Filter "state = 'stop pending'"
if ($Services) {
foreach ($service in $Services) {
try {
Stop-Process -Id $service.processid -Force -PassThru -ErrorAction Stop
}
catch {
Write-Warning -Message " Error. Error details: $_.Exception.Message"
}
}
}
else {
Write-Output "No services with 'Stopping'.status"
}
В новом PowerShell Core 6.x/7.x вместо командлета Get-WmiObject нужно использовать Get-CimInstance. Замените первую команду скрипта на:
$Services = Get-CimInstance -Class win32_service | where-Object state -eq 'stop pending'
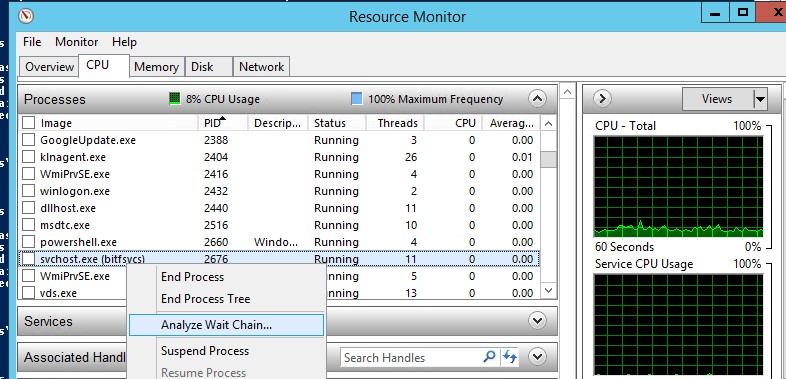
Анализ цепочки ожидания зависшего приложения с помощью ResMon
Вы можете определить процесс, из-за которого зависла служба с помощью монитора ресурсов (
resmon.exe
).
- В окне Монитора ресурсов перейдите на вкладку ЦП (CPU) и найдите процесс зависшей службы;
- Выберите пункт Анализ цепочки ожидания (Analyze Wait Chain);
- В новом окне скорее всего вы увидите, что вам процесс ожидает другой процесс. Завершите его. Если выполняется ожидание системного процесса svchost.exe, завершать его не нужно. Попробуйте проанализировать цепочку ожидания для этого процесса. Найдите PID процесса, которого ожидает ваш svchost.exe и завершите его
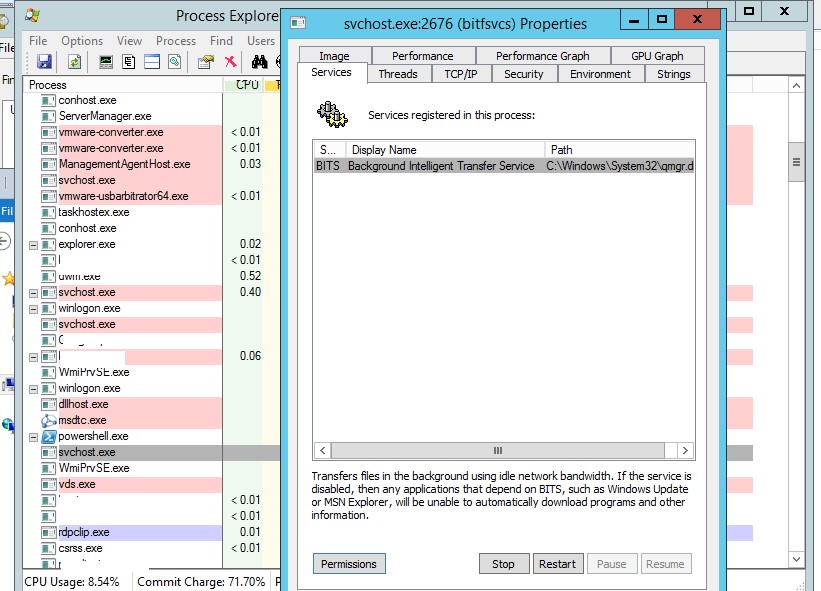
Process Explorer: Завершение зависшего процесса из-под SYSTEM
Некоторые процессы, запущенные из-под SYSTEM, не может завершить даже локальный администратора сервера. Дело в том, что у него просто может не быть прав на некоторые процессы или службы. Чтобы завершить такие процесс (службы), вам необходимо предоставить локальной группе Administrators права на службу (процесс), а потом завершить их. Для этого нам понадобятся две утилиты: psexec.exe и ProcessExplorer (доступны на сайте Microsoft).
- Чтобы запустить утилиту ProcessExplorer с правами системы (SYSTEM), выполните команду:
PSExec -s -i ProcExp.exe - В списке процессов Process Explorer найдите процесс зависшей службы и откройте ее свойства;
- Перейдите на вкладку Services, найдите свою службу и нажмите кнопку Permissions;
- В разрешения службы предоставьте права Full Control для группы администраторов (Administrators). Сохраните изменения;
- Теперь попробуйте завершить процесс службы.
Обратите внимание, что права на службу и ее процесс выдались временно, до ее перезапуска. Для предоставления постоянных прав на службы познакомьтесь со статьей Права на службы в Windows.
Таймаут, в течении которого Service Control Manager ждет ожидания запуска или остановки службы можно изменить через параметр реестра ServicesPipeTimeout. Если служба не запускается в течении указанного таймаута, Windows записывает ошибку в Event Log (Event ID: 7000, 7009, 7011, A timeout was reached 30000 milliseconds). Вы можете увеличить этот таймаут, например до 60 секунд:
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control /v ServicesPipeTimeout /t REG_SZ /d 600000 /f
Это бывает полезным при запуске/остановки тяжелых служб, которые не успевают завершить все процессы быстро (например, MS SQL Server).
How can I start, stop, or pause Windows Services from the command line? This Tech-Recipes tutorial describes how to perform these functions in all versions of Windows including XP and Windows 7.
First, we will need to open a command prompt terminal.
Go to the Start menu, and open a Command Prompt. With early versions of Windows, go to RUN, type CMD, and click on Enter. With later versions, just search for Command Prompt in the Start menu.
Command Examples
Here are the common methods of controlling the services through a command line. You can run these solo, scripted, or placed in batch files. The typical pattern is “net command servicename” where “command” is the actual command and “servicename” is the actual service you are manipulating.
Here are common examples, using the Telnet service as an example.
Net Start servicename to Start a Service
net start telnet
Net Stop servicename to Stop a Service
net stop telnet
Net Pause servicename to Pause a Service
net pause telnet
Net Continue servicename to Continue a Service
net continue telnet
In later versions of Windows, people frequently encounter the following error:
System error 5 has occurred.
Access is denied.
This error typically occurs when the user does not have administrative access. Try the command again after completing the following steps: right-click on Command Prompt, select Run as administrator, and confirm when the UAC prompt appears.
David Kirk
David Kirk is one of the original founders of tech-recipes and is currently serving as editor-in-chief. Not only has he been crafting tutorials for over ten years, but in his other life he also enjoys taking care of critically ill patients as an ICU physician.
The Task Manager lets you quit apps and stop and start a Windows service. It’s an easy, graphical way to stop a service if you ever need to but you can also stop and start a Windows service from the command prompt. The process is easy enough though it goes without saying that you need administrative rights to stop or start a service on Windows.
SPOILER ALERT: Scroll down and watch the video tutorial at the end of this article.
Open command prompt by entering Command Prompt in Windows Search. Right-click it and select ‘Run as administrator’ from the context menu. Alternatively, you can open Command Prompt with admin rights from the Run box by typing cmd, and hitting Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
Scan For Running Services
If you’re looking to stop and start a Windows service from the Command Prompt, chances are you may not know what a service is called. The task manager lists them so it’s easier but you can also scan for and list all running Windows services. Enter the following command to list all services that are currently running.
net start
You can stop any one of the services with the following commands. If the service name has spaces, you should enclose it in double quotes.
Syntax
NET STOP service name
Example
NET STOP "Apple Mobile Device Service"
Start Service
You can start a service with the following command. If the service name has spaces, make sure you enclose it in double quotes.
Syntax
NET START service name
Example
NET START "Apple Mobile Device Service"
If you want to stop and start a Windows service from the Command Line in one go, you can combine the above two commands as follows;
Syntax
net stop service name && net start service name
Example
net stop "Apple Mobile Device Service" && net start "Apple Mobile Device Service"
Service Status
The Command Prompt has a built-in tool that can perform other operations on a Windows service. For example, if you need to know whether a service is running or not, you can use this tool to query the status. It’s called sc, and again you need admin rights to use all its commands. You can view a complete list of the commands it supports on the official documentation page maintained by Microsoft. To simply check the status of a service, you can use the following command.
Syntax
sc command service name
Example
sc query “Apple Mobile Device Service”
Be careful which services you choose to stop or start. If you accidentally stop a critical service, your system might crash. Some services may be prone to starting up again automatically once they’re stopped.

Fatima Wahab
Fatima has been writing for AddictiveTips for six years. She began as a junior writer and has been working as the Editor in Chief since 2014.
Fatima gets an adrenaline rush from figuring out how technology works, and how to manipulate it. A well-designed app, something that solves a common everyday problem and looks
The services in Windows can be started using the Service Manager tool.
To start the Service Manager GUI, press ⊞ Win keybutton to open the start menu, type in services to search for the Service Manager and press Enter to launch it.
The services can also be started using the command-line prompt (CMD) or the PowerShell.
In this note i am showing how to start, stop or check the status of a service in Windows using the command-line prompt (CMD) or the PowerShell.
Cool Tip: List services in Windows from the CMD & PowerShell! Read more →
Start Service Using Command Line (CMD)
To avoid “Access is denied” errors, start CMD as an administrator: press ⊞ Win keybutton to open the start menu, type in cmd to search for the command prompt and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to launch it as administrator.
Use the following commands to start, stop or check the status of a service in Windows on the command-line prompt (CMD).
Start a service:
C:\> net start serviceName
Get a service status:
C:\> sc query serviceName
Stop a service:
C:\> net stop serviceName
Cool Tip: Kill a hanging process in Windows from the CMD! Read more →
To avoid “Access is denied” errors, start PowerShell as an administrator: press ⊞ Win keybutton to open the start menu, type in powershell to search for the PowerShell and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to launch it as administrator.
Use the following commands to start, stop or check the status of a service in Windows using the PowerShell.
Start a service:
PS C:\> Start-Service serviceName
Get a service status:
PS C:\> Get-Service serviceName
Stop a service:
PS C:\> Stop-Service serviceName
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!