Quick commands to install/update wget
wget http://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/wget/wget-1.19.tar.gz tar -xzf wget-1.19.tar.gz cd wget-1.19 yum install gcc-c++.x86_64 yum install gnutls-c++.x86_64 yum install gnutls-devel.x86_64 ./configure make && make install # logout and login again in order to test wget --version
More info on each command
For some reason many linux distributions don’t contain latest version of wget and even searching with yum search wget or apt-cache search wget will not show you latest version.
Some useful options of wget like --timeout can fail silently in version like 1.14 and this can cause bugs in more complex scripts or programs. You need to manually update wget in order to make sure latest options work.
First check your current version:
wget --version GNU Wget 1.14 built on linux-gnu.
Download latest wget from http://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/wget/, e.g wget-1.19.tar.gz
You can put the .tar.gz file on your server by FTP or download it with your existent wget:
wget http://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/wget/wget-1.19.tar.gz
Extract and go to directory
tar -xzf wget-1.19.tar.gz cd wget-1.19
install these dependencies that are required when compiling:
yum install gcc-c++.x86_64 yum install gnutls-c++.x86_64 yum install gnutls-devel.x86_64
Configure and install wget
./configure make && make install
!!! You need to re-login to ssh or do a server rstart in order to show new version
test your current version with:
wget --version GNU Wget 1.19 built on linux-gnu.
Windows binaries of GNU Wget 1.21.4
This is a command-line tool that can be used to retrieve files via the HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP protocols.
GNU Wget is a free software package that allows users to retrieve files through the most commonly used Internet protocols,
including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and FTPS. As a non-interactive command-line tool,
it can be easily integrated into scripts, cron jobs, and terminals.
How to use wget
To learn how to use Wget, please refer to the official GNU Wget manual by clicking the link below.
https://www.gnu.org/software/wget/manual/wget.html
Build Environment
Wget has been built using GitHub Actions and cross-compiled with mingw64 on Ubuntu, using GNU/gcc 9.3.
It is completely safe to use and free from viruses.
All the necessary libraries have been statically linked, so there is no need to use any third-party DLL.
Wget features
The Windows version of Wget includes all features of Wget except for NLS (the multi-language version).
GnuTLS version:
+cares +digest +gpgme +https +ipv6 +iri +large-file +metalink -nls +ntlm +opie +psl +ssl/gnutls
OpenSSL version:
+cares +digest +gpgme +https +ipv6 +iri +large-file +metalink -nls +ntlm +opie +psl +ssl/openssl
Local Build
To build Wget for Windows on WSL 1 or 2 (Debian/Ubuntu), please follow these steps.
sudo apt-get install -y mingw-w64 mingw-w64-tools mingw-w64-i686-dev gcc sudo apt-get install -y make m4 pkg-config automake gettext cd /tmp git clone https://github.com/webfolderio/wget-windows.git cd wget-windows ./build.sh
Update: With the recent release of Wget2 2.0.1, there’s now an official Windows release. You can download it from here.
Wget2 is the next-generation non-interactive command-line content downloader. It will be the successor of Wget.
It comes with new features, such as file compression and multi threaded downloads. You can view the full comparison table in this link.
Originally, Wget2 was designed and compiled for Linux-based systems, but I have successfully compiled it for Windows (using i686-w64-mingw32).
Also, it includes libwget, so you will be able to develop applications using Wget2 (very unstable).
If you are interested, you can download Wget2 for windows through the button below.
View documentation (very buggy)
Please read before using Wget2 and libwget:
Wget2 is currently under development and it isn’t specifically designed for Windows, so it may be very unstable. Please do not use it for serious things. Also, there are currently some functions that doesn’t work as intended on Windows, such as:
- –progress bar
- -r (https://gitlab.com/gnuwget/wget2/-/issues/592)
However, it is very useful to quickly download files from the internet.
Wget is a free, open-source, command-line download manager that enables users to retrieve files from the internet using HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP protocols. Developed by the GNU Project, Wget is a powerful tool that allows users to download files, web pages, and entire websites with ease. Its primary function is to facilitate the non-interactive download of files, making it an essential utility for web developers, system administrators, and power users.
Wget’s primary advantage lies in its ability to resume broken downloads, which is particularly useful for large file transfers. It also supports HTTP cookies, proxy servers, and authentication, making it a versatile tool for downloading content from various sources. Additionally, Wget’s command-line interface allows for automation and scripting, making it a favorite among developers and system administrators.
Although Wget is primarily designed for Linux and Unix-like operating systems, its functionality and flexibility have made it a sought-after tool for Windows users as well. However, due to the differences in operating systems, installing Wget on Windows requires additional steps. Fortunately, with the right guidance, Windows users can also harness the power of Wget to manage their downloads efficiently. In this article, we will walk you through the process of installing Wget on Windows, making it accessible to users who want to take advantage of its features.
Installing Wget on Windows
Installing Wget on Windows is a straightforward process that requires downloading the GNU Wget package and placing it in the correct directory. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Download GNU Wget for Windows
To begin, navigate to the official GNU Wget download page. This website provides pre-compiled binaries of Wget for Windows, making it easy to install and use.
Step 2: Select the Latest Version
On the download page, you’ll find multiple versions of GNU Wget for Windows. Look for the latest version and click on the corresponding `.exe` file to download it. The file name should be in the format `wget-<version>.exe`, where `<version>` is the version number. For example, if the latest version is 1.21.3, the file name would be wget64-1.21.3.exe:
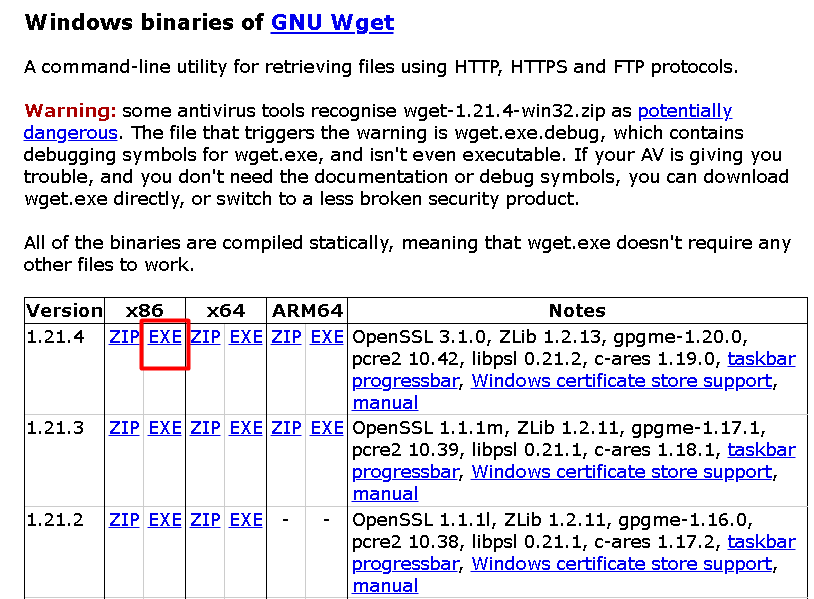
Step 3: Place Wget in the System32 Folder
Once the download is complete, navigate to the folder where the .exe file is saved and copy it. Then, go to the C:\Windows\System32 folder (for 64-bit systems) or C:\Windows\SysWOW64 (for 32-bit systems) and paste the .exe file:
It’s essential to place the `wget.exe` file in the System32 folder because this directory is included in the system’s PATH environment variable. By placing the Wget Windows tutorial in this folder, you can execute it from anywhere in the Command Prompt or PowerShell without specifying the full path.
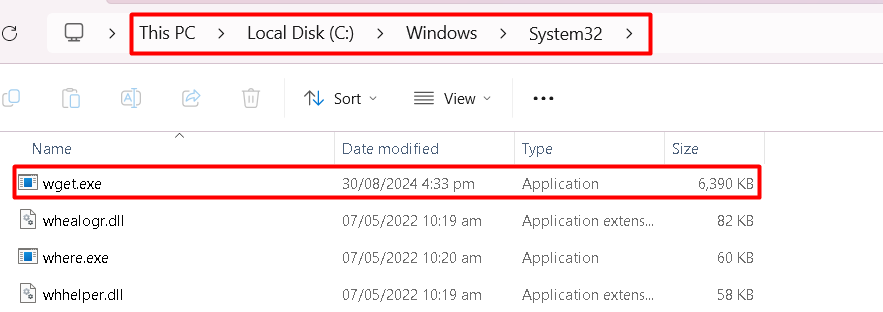
Step 4: Verify Wget Installation
To verify that Wget has been installed correctly, open the Command Prompt or PowerShell and type the following command:
wget -V
Press Enter to execute the command. If Wget has been installed successfully, you should see a message indicating the version number and a list of supported protocols, similar to this:
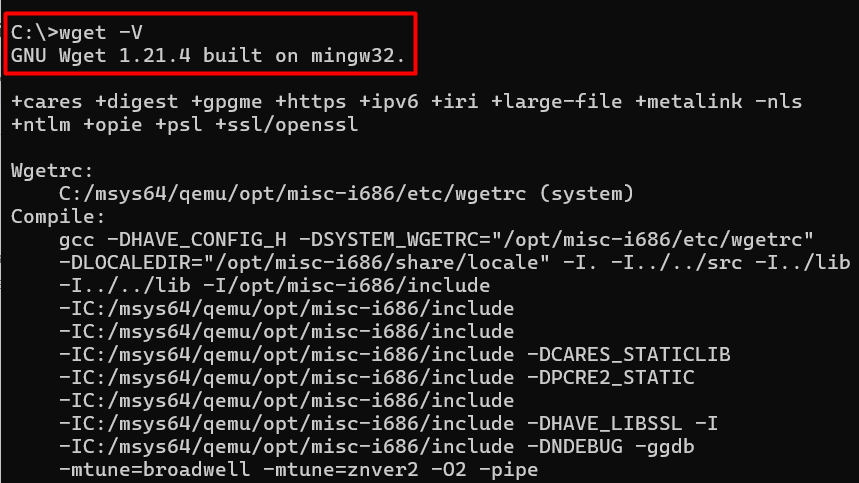
This confirms that Wget is installed and ready to use on your Windows system.
Explore the Blazing Fast Speed of Windows VPS!
Hosting a Windows VPS with Ultahost is now simpler and faster than ever. Experience ultra-fast SSD NVMe speeds with no interruptions or slowdowns.
Features of Wget
Wget’s primary advantage lies in its ability to resume broken downloads, which is particularly useful for large file transfers. It also supports HTTP cookies, proxy servers, and authentication, making it a versatile tool for downloading content from various sources. Additionally, Wget’s command-line interface allows for automation and scripting, making it a favorite among developers and system administrators.
Some of the key features of Wget include:
- Resuming broken downloads: Wget can resume downloads that were interrupted due to network issues or other errors.
- Support for HTTP cookies: Wget supports HTTP cookies, which allows it to download content from websites that require authentication.
- Proxy server support: Wget can use proxy servers to download content from the internet.
- Authentication support: Wget supports authentication protocols such as HTTP Basic and Digest.
- Command-line interface: Wget’s command-line interface allows for automation and scripting.
- Multi-threading: Wget can download multiple files simultaneously, making it faster than traditional download managers.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter any issues during the installation process, here are some common solutions:
- Wget not recognized: Make sure that the wget.exe file is in the
C:\Windows\System32folder (for 64-bit systems) orC:\Windows\SysWOW64(for 32-bit systems). - Error message “wget is not recognized as an internal or external command”: Make sure that the
C:\Windows\System32folder (for 64-bit systems) orC:\Windows\SysWOW64(for 32-bit systems) is in the system’s PATH environment variable. - Wget not downloading files: Make sure that the URL is correct and that the file is available for download.
Wget Options and Flags
Wget has a wide range of options and flags that can be used to customize its behavior. Here are some common options and flags:
- -a: Append to the output file instead of overwriting it.
- -b: Run in the background.
- -c: Continue downloading a file that was interrupted.
- -d: Set the debug level.
- -e: Execute the specified command after the download is complete.
- -i: Read URLs from the specified file.
- -l: Specify the maximum depth of recursive downloads.
- -m: Mirror the specified website.
- -n: Specify the number of tries to retry a download.
- -o: Output the downloaded file to the specified file.
- -q: Quiet mode, suppress output.
- -r: Recursive download, which downloads all files and subdirectories.
- -s: Specify the maximum size of the output file.
- -t: Specify the number of tries to retry a download wget on Windows.
- -u: Specify the username for authentication.
- -v: Verbose mode, display detailed output.
- -w: Specify the wait time between retries.
Conclusion
Installing Wget on Windows is a straightforward process that requires downloading the GNU Wget package and placing it in the correct directory. The installation process involves downloading the latest version of Wget, placing the wget.exe file in the C:\Windows\System32 folder (for 64-bit systems) or C:\Windows\SysWOW64 (for 32-bit systems), and verifying the installation by running the wget -V command. With these simple steps, users can easily install Wget on their Windows system and start using it to download files and web pages from the internet.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, users can overcome the limitations of traditional download managers and take advantage of Wget’s advanced features, such as resuming broken downloads, supporting HTTP cookies, and authenticating with proxy servers. With Wget installed on their Windows system, users can automate downloads, mirror websites, and perform other tasks with ease, making it an essential tool for web developers, system administrators, and power users.
After completing these steps, you’ve successfully installed Wget on your Windows system and are now ready to develop robust applications. For optimal performance and smooth development, remember to follow best practices. consider using Ultahost Windows hosting. You get reliable and high-speed hosting tailored to your needs.
FAQ
What is wget?
wget is a free utility that allows you to download files from the web using HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP protocols. It is often used for retrieving files from the internet or mirroring entire websites.
Why would I want to install wget on Windows?
While Windows has built-in tools like PowerShell and Command Prompt for downloading files, wget offers more advanced features and options. It is particularly useful for automating downloads, handling complex file retrieval tasks, and mirroring websites.
Where can I download wget for Windows?
You can download the Windows version of wget from the official GNU site or other reputable sources like Chocolatey or Git for Windows.
How do I install wget using the installer?
- Download the wget installer executable from the GNU site.
- Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
- By default, the installer should add wget to your system PATH. If not, you may need to do this manually (see below).
How do I verify that wget is installed correctly?
Open Command Prompt and type wget –version. You should see version information if wget is installed correctly. If you receive an error or command not found message, ensure wget is correctly installed and added to your PATH.
Are there alternatives to wget on Windows?
Yes, there are several alternatives including curl (which is built into Windows 10 and later), aria2, and tools provided by Git for Windows.
Where can I find additional documentation or help for wget?
The official wget manual and documentation can be found on the GNU website. Online forums and communities also offer valuable tips and troubleshooting help.
