Copilot is your AI companion
Always by your side, ready to support you whenever and wherever you need it.
Internet Information Services (IIS) 6.0 Resource Kit
Whether you manage a single Web server or many, the prescriptive, task-based, and scenario-based guidance in this book will help you effectively plan, deploy, operate, and troubleshoot your IIS 6.0 solution.
Important! Selecting a language below will dynamically change the complete page content to that language.
-
File Name:
11_APPENDIX_A_IIS_Deployment_Procedures.doc
14_CHAPTER_1_Introducing_IIS_6.0.doc
26_APPENDIX_B_Unattended_Setup.doc
17_CHAPTER_4_Working_with_the_Metabase.doc
27_APPENDIX_C_Using_FrontPage_2002_Server_Extensions_with_IIS_6.0.doc
22_CHAPTER_9_IIS_6.0_Administration_Scripts_Tips_and_Tricks.doc
05_CHAPTER_2_Deploying_ASP.NET_Applications_in_IIS_6.0.doc
08_CHAPTER_5_Upgrading_an_IIS_Server_to_IIS_6.0.doc
15_CHAPTER_2_IIS_6.0_Architecture.doc
20_CHAPTER_7_Web_Server_Scalability.doc
16_CHAPTER_3_Running_IIS_6.0_as_an_Application_Server.doc
13_Part_2_Internet_Information_Services_(IIS)_6.0_Resource_Guide.doc
21_CHAPTER_8_Configuring_Internet_Sites_and_Services.doc
09_CHAPTER_6_Migrating_IIS_Web_Sites_to_IIS_6.0.doc
10_CHAPTER_7_Migrating_Apache_Web_Sites_to_IIS_6.0.doc
04_CHAPTER_1_Overview_of_Deploying_IIS_6.0.doc
29_APPENDIX_E_IIS_6.0_Event_Messages.doc
24_CHAPTER_11_Troubleshooting_IIS_6.0.doc
03_Part_1_Deploying_Internet_Information_Services_(IIS)_6.0.doc
19_CHAPTER_6_Optimizing_IIS_6.0_Performance.doc
07_CHAPTER_4_Ensuring_Application_Availability.doc
01_Front.doc
25_APPENDIX_A_Common_Administrative_Tasks.doc
12_APPENDIX_B_Changes_to_Metabase_Properties_in_IIS_6.0.doc
IIS_6_RG.zip
06_CHAPTER_3_Securing_Web_Sites_and_Applications.doc
30_APPENDIX_F_Centralized_Binary_Log_File_Format.doc
02_Introduction.doc
23_CHAPTER_10_Analyzing_Log_Files.doc
32_Glossary.doc
18_CHAPTER_5_Managing_a_Secure_IIS_6.0_Solution.doc
33_Index.doc
31_APPENDIX_G_IPv6_and_IIS_6.0.doc
28_APPENDIX_D_IIS_6.0_Performance_Counters.doc
File Size:
2.5 MB
158.0 KB
206.0 KB
1.1 MB
235.5 KB
435.0 KB
980.0 KB
1.7 MB
1.3 MB
922.0 KB
1.1 MB
104.5 KB
686.5 KB
1.6 MB
1.5 MB
719.0 KB
460.5 KB
1.2 MB
578.5 KB
1.0 MB
958.5 KB
265.0 KB
1.0 MB
592.0 KB
14.0 MB
1.6 MB
315.0 KB
1.2 MB
425.0 KB
245.0 KB
1.6 MB
318.0 KB
295.5 KB
610.0 KB
Microsoft® Windows® Server 2003 and IIS 6.0 provide the services to support a secure, available, and scalable Web server on which to run your Web sites and applications. Whether you manage a single Web server or many, Internet Information Services (IIS) 6.0 Resource Kit will help you effectively plan, deploy, operate, and troubleshoot your IIS 6.0 solution. This comprehensive technical resource delivers an in-depth description of the new IIS 6.0 architecture, as well as reference information about IIS 6.0 features and services. It also includes practical information and tools to help you accomplish everyday administrative tasks.
Deployment scenarios in part one of this book include installing a new Web server, upgrading an existing Web server from an earlier version of IIS, and migrating existing Apache or IIS Web sites and applications to a newly installed Web server. Part two of this book includes information about running IIS 6.0 as a platform for Web applications, managing a secure IIS 6.0 solution, administering servers programmatically, and capitalizing on built-in scalability features to manage large-scale deployments. In addition, part two includes a thorough discussion of IIS 6.0 troubleshooting concepts, tools, and procedures.
This page contains the following files for download:
• Book Cover (front)
• Introduction
• Part I: Deploying Internet Information Services (IIS) 6.0
• Ch 1: Overview of Deploying IIS 6.0
• Ch 2: Deploying ASP.NET Applications in IIS 6.0
• Ch 3: Securing Web Sites and Applications
• Ch 4: Ensuring Application Availability
• Ch 5: Upgrading an IIS Server to IIS 6.0
• Ch 6: Migrating IIS Web Sites to IIS 6.0
• Ch 7: Migrating Apache Web Sites to IIS 6.0
• Appx A: IIS Deployment Procedures
• Appx B: Changes to Metabase Properties in IIS 6.0
• Part II: Internet Information Services (IIS) 6.0 Resource Guide
• Ch 1: Introducing IIS 6.0
• Ch 2: IIS 6.0 Architecture
• Ch 3: Running IIS 6.0 as an Application Server
• Ch 4: Working with the Metabase
• Ch 5: Managing a Secure IIS 6.0 Solution
• Ch 6: Optimizing IIS 6.0 Performance
• Ch 7: Web Server Scalability
• Ch 8: Configuring Internet Sites and Services
• Ch 9: IIS 6.0 Administration Scripts, Tips, and Tricks
• Ch 10: Analyzing Log Files
• Ch 11: Troubleshooting IIS 6.0
• Appx A: Common Administrative Tasks
• Appx B: Unattended Setup
• Appx C: Using FrontPage 2002 Server Extensions
• Appx D:IIS 6.0 Performance Counters
• Appx E: IIS 6.0 Event Messages
• Appx F: Centralized Binary Log File Format
• Appx G: IPv6 and IIS 6.0
• Glossary
• Index
• Entire book as a .zip fileWe want to provide high-quality, relevant content for IT Pros who plan, support, deploy, and operate Internet Information Services 6.0 in small, medium, and large organizations. In order for us to improve our content offerings, we want to hear from you. Please click here to send us your feedback on the usefulness and relevance of this content or any suggestions for content you would like to see.
-
Supported Operating Systems
Windows Server 2003, Windows XP
- Microsoft Word or Word Viewer
-
- In the Files in this Download list, click the file that you want to download, or scroll to the bottom of the list and click IIS_6_RG.zip to download all of the files in the IIS 6.0 Resource Kit.
- Do one of the following:
- To start the installation immediately, click Open or Run this program from its current location.
- To copy the download to your computer for installation at a later time, click Save or Save this program to disk.
-
The companion IIS 6.0 Resource Kit Tools are a collection of software tools that will help you complete the necessary tasks to deploy, migrate, administer, secure, and manage your IIS 6.0 solution.
Windows · September 28, 2024
Internet Information Services (IIS) is a flexible, secure, and manageable Web server for hosting anything on the Web. It is a popular choice for Windows Server environments, including Windows Server 2003. This tutorial will guide you through the installation process of IIS on Windows 2003, providing step-by-step instructions and illustrations to ensure a smooth setup.
Prerequisites
Before you begin the installation, ensure that you have the following:
- A computer running Windows Server 2003.
- Administrator access to the server.
- Installation media for Windows Server 2003 (if needed).
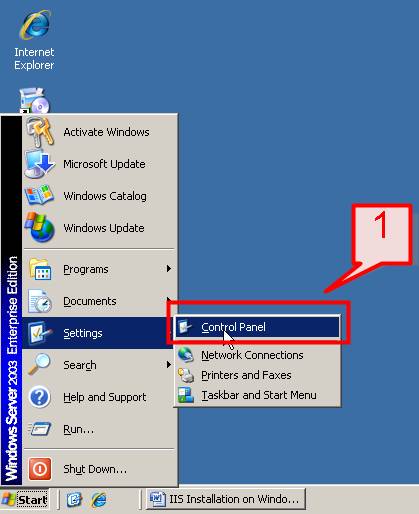
Step 1: Accessing the Add/Remove Programs
To start the installation of IIS, you need to access the Add/Remove Programs feature in the Control Panel.
- Click on the Start menu.
- Select Control Panel.
- Double-click on Add or Remove Programs.
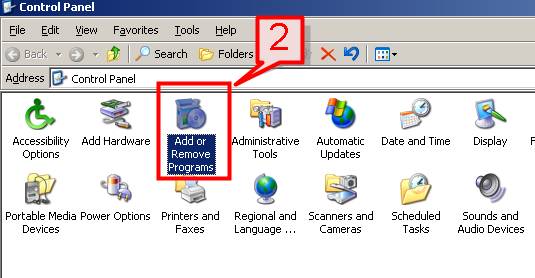
Step 2: Adding Windows Components
Once you are in the Add or Remove Programs window, you will need to add the IIS component.
- On the left side of the window, click on Add/Remove Windows Components.
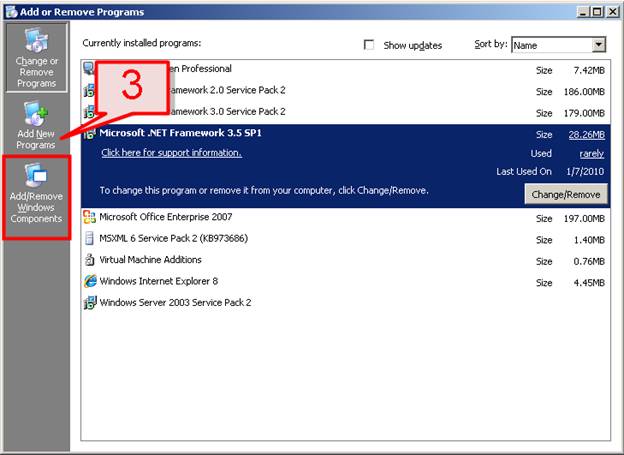
- This will open the Windows Components Wizard. Scroll down and find Application Server.
- Select Application Server and click on the Details button.
Step 3: Selecting IIS
In the Application Server details, you will find the option to install IIS.
- Check the box next to Internet Information Services (IIS).
- Click OK to return to the Windows Components Wizard.
- Click Next to proceed with the installation.
Step 4: Completing the Installation
The installation process will begin, and you may be prompted to insert the Windows Server 2003 installation media. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
# Example of a command to check IIS status
iisreset /status
Step 5: Verifying the Installation
After the installation is complete, you can verify that IIS is running correctly.
- Open a web browser.
- Type http://localhost in the address bar and press Enter.
- If IIS is installed correctly, you should see the default IIS welcome page.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter issues during the installation or after, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Ensure that you have administrative privileges on the server.
- Check for any pending Windows updates that may need to be installed.
- Review the Event Viewer for any error messages related to IIS.
Conclusion
Installing IIS on Windows Server 2003 is a straightforward process that can be completed in just a few steps. By following this illustrated tutorial, you should be able to set up IIS successfully and begin hosting your web applications. For those looking for reliable hosting solutions, consider exploring options like USA VPS Hosting for enhanced performance and security.
Используйте следующую процедуру для включения необходимых веб-расширений IIS и установки IIS, если не установлен.
Необходимое веб-расширение — ASP.
<Примечание> Необходимо вставить компакт-диск с Windows Server 2003 Enterprise x64 Edition CD-ROM для копирования файлов, необходимых для установки IIS.
Для установки IIS и необходимых веб-расширений на Windows Server 2003:
- Установите службы IIS.
- Перейдите к диалоговому окну Программы и функции (). Открывается диалоговое окно «Установка и удаление программ».
- На панели в левой части окна выберите . Открывается мастер компонентов Windows.
- Выберите .
<Примечание> Необходимо вставить компакт-диск с Windows Server 2003 Enterprise x64 Edition CD-ROM для копирования файлов, необходимых для установки IIS.
- Нажмите кнопку . Программа установки устанавливает IIS.
- Разрешите ASP в качестве расширений веб-службы.
- Перейдите к Диспетчеру служб IIS. (). Открывается Диспетчер служб IIS.
- Выберите в левой панели. В правой панели открывается диалоговое окно «Расширения веб-служб».
- Выберите , и нажмите . Расширения ASP разрешены.
- Закройте Диспетчер IIS. Теперь можно запускать программу установки WhatsUp Gold.
ServerWatch content and product recommendations are editorially independent. We may make money when you click on links to our partners. Learn More.
Welcome to the third installment of Internet Information Services 6.0 on Windows Server 2003. This series of articles discusses IIS 6.0 on Windows Server 2003 and is designed as both a refresher for the IT professional familiar with designing and administrating IIS 4.0 and IIS 5.0, and for newcomers looking to get their feet wet.
This installment in our IIS 6.0 series offers a comparative look at default installations for IIS 6.0 vs. IIS 4.0 and 5.0.
This installment continues our introduction to Internet Information Services 6.0 on Windows Server 2003 by providing an initial overview of the differences between the default installation state of IIS 6.0 vs. that of IIS 4.0 and IIS 5.0.
Those who have administered IIS in the past, either Internet Information Server 4.0 on the NT 4 platform or Internet Information Services 5.0 on the Windows 2000 platform, are well aware of the difficulty in securing the service from would-be attackers, as both versions installed with most of the services running by default. IIS 6.0 on Windows Server 2003 is a departure from this, as all of the services are disabled by default.
As a brief overview: Internet Information Server 4.0 on the NT 4 platform was not part of the Windows NT 4 Server operating system. Rather, it was an add-on made available through the Windows NT 4 Option Pack, and it included Internet Information Server 4.0, Microsoft Transaction Server 2.0, Microsoft Message Queue Server 1.0, and Internet Connection Services for Microsoft Remote Access Service (RAS).
The Windows NT 4 Option Pack also included the Personal Web Server (PWS) for Windows 95 and Windows NT Workstation. PWS 4.0 on an NT Workstation is more limited in functionality than its NT 4 Server cousin in that it has less available functionality. Index Server, Certificate Server, Multiple Web Hosting, ODBC logging, Internet Protocol restrictions, and Process Isolation cannot be used on PWS 4.0.
Another reduction in services on Windows NT Workstation comes from the fact that Windows NT Workstation can have only 10 simultaneous inbound connections at any given time, which would thus limit the number of Web connections the Web services installed on a Windows NT workstation could have.
Over the time and with use, many exploits were discovered within the program itself. They have been fixed with service packs and hot fixes for the Windows NT 4 operating system.
The main issue with IIS 4.0 on NT 4 is the amount of time it takes to secure the underlying NT 4 server operating system by installing service pack 6a and all of the subsequent hot fixes. In addition, the default installation of IIS 4.0 enables many options that are inherently insecure if not properly configured and oftentimes are not needed for a standard Web server used for little to no dynamic content.
The default installation of IIS 4.0 included FTP, SMTP, and Web server capabilities. The Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) is not installed during a default installation and must be chosen intentionally.
Internet Information Services 5.0 is installed on Windows 2000 Server by default when the operating system is loaded onto server hardware. Effectively, any Windows 2000 Server build that uses the default settings, be it a Web server, file server, print server, or domain controller, is going to have the IIS 5.0 services installed, running, and listening for calls on the network.
We assume the thought process behind having IIS 5.0 install by default was for ease of use. In reality, however, it provided nothing but hassles for system administrators who needed to secure their environments. There was always the option to script out the IIS 5.0 installation during an unattended install or via initial builds for imaging, but in situations where this wasn’t done, it was a larger problem.
There is also Web server functionality available for Windows 2000 Professional; however, unlike NT 4, where it is referred to as PWS 4.0 on the client, it is just called Internet Information Services 5.0 in both the Professional and Server editions.
Like on IIS 4.0, the default installation of IIS 5.0 on the Server and Professional platforms includes FTP, SMTP, and Web server functionality. NNTP is not installed during a default installation, however, and must be selected.
IIS 6.0 on Windows Server 2003 is not installed by default when the operating system is installed. When the application is installed, the default installation enables it to be a static content Web server only. ASP and ASP.NET must be explicitly installed by the administrator for dynamic content to be made available for use on the particular system. Additional functionality, such as FTP, SMTP, and NNTP, is available but must be explicitly installed.
In situations where Windows 2000 Server with IIS 5.0 installed is upgraded to Windows Server 2003, IIS 6.0 will be automatically installed as a simple static content Web server unless an administrator installed and ran the IIS Lockdown Tool or configured the RetainW3SVCStatus registry key to secure the Windows 2000 Server operating system and IIS 5.0 installation.
IIS Lockdown Tool version 2.1 turns off unnecessary features and services of IIS 4.0, 5.0, and 5.1 in an effort to reduce the available attack surface for would-be attackers.
The tool can be run to secure IIS 4.0 on Windows NT 4.0 Server systems as well as IIS 5.0, which, as noted above, is installed by default on Windows 2000 Server installations. IIS 5.1, which is found under the Windows XP family of operating systems (but not installed by default), can also be locked down via the tool.
Version 2.1 of the tool can use templates supplied for Microsoft Exchange 5.5 and 2000, Commerce Server, BizTalk, Small Business Server 4.5 and 2000, SharePoint Portal Server, FrontPage Server Extensions, and SharePoint Team Server in an effort to lock down these IIS-dependent applications when they are installed and using IIS.
In effect, the base installation of IIS 6.0 does not require the additional step of running the IIS Lockdown Tool, as the default installation of IIS 6.0 is already in a locked-down state.
Many additional steps must be taken to properly lock down IIS services on older platforms, including ensuring all of the latest service packs are installed and the most recent hot fixes downloaded.
Running URLscan 2.5 is yet another part of this overall effort. UrlScan blocks specific HTTP requests in an effort to restrict the types of calls that can be made to the IIS server. It runs on all versions of IIS — 4.0, 5.0, 5.1, and 6.0.
UrlScan provides some additional functionality to IIS 6.0 installations beyond the initial security provide by IIS 6.0. Future articles in this series will detail the differences between the features found in UrlScan 2.5 and those built into IIS 6.0.

Internet Information Services (IIS) is a powerful Web server on Windows Server 2003 that provides reliable, manageable and scalable Web applications.
Let’s check as how to install IIS on Windows Server 2003 system. We can install IIS on a Domain Controller (DC), a member server in an Active Directory (AD), or on a standalone server.
# 1. Click Start-> Choose Settings->Control Panel
#2. On the next screen Click Add or Remove Program
#3. Add or Remove Windows will appear, on the Left pane Click Add/Remove Windows Components
#4. On Windows Components Wizard, Select Application Server and Click Details
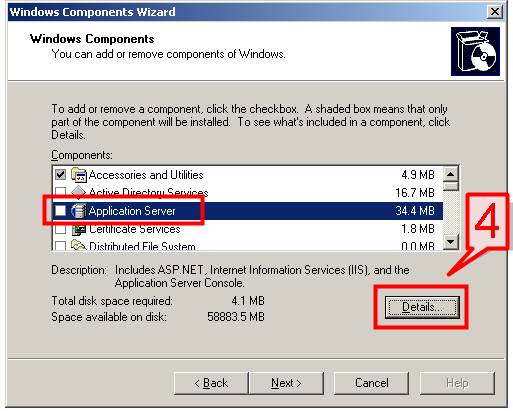
#5. On the Application Server page, Choose Internet Information Services (IIS) and Click on the Details button.
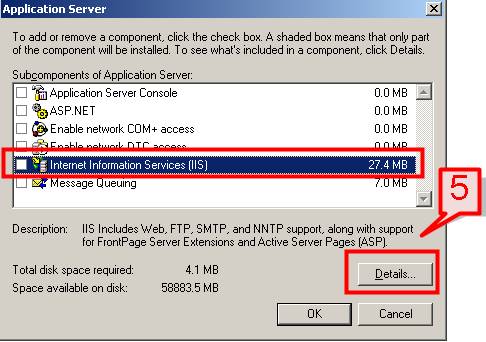
#6. On the Internet Information Services (IIS) dialog box, put a check mark on the lists of components that you want to install to support your Web server. Let’s select World Wide Web Services and other components.
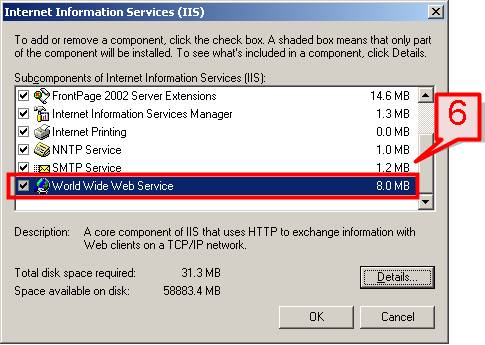
#7. You can also check the lists of components that will be installed on World Wide Web Service by clicking on Details button. Check the components and click OK,
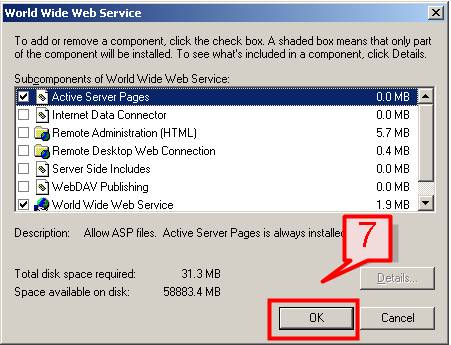
#8. Click OK on the Internet Information Services (IIS) dialog box.
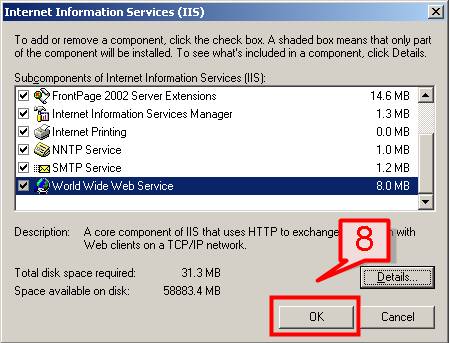
#9. Click OK on the Application Server dialog box.
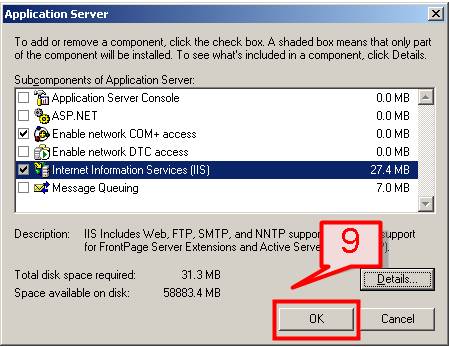
#10. On Windows Component Wizard page, Click Next
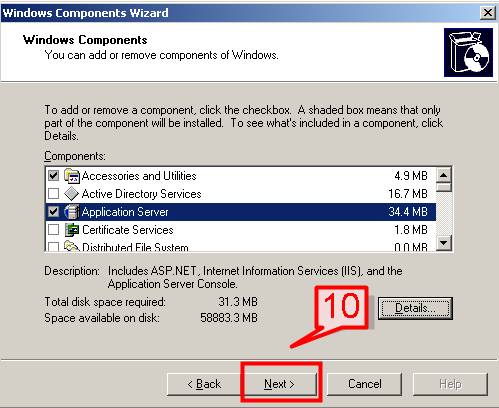
#11. Windows will start installing IIS Server.
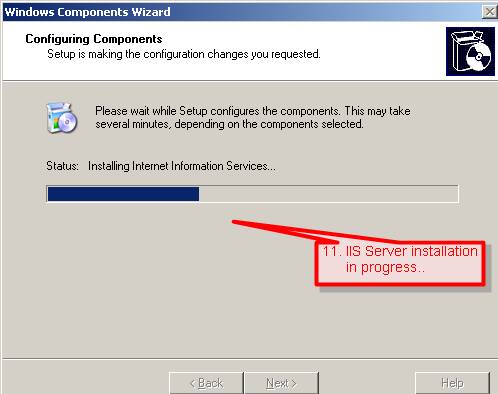
#12. Click Finish on Windows Component Wizard dialog box.
This finishes the installation of IIS. Now to check whether IIS installation is successful or not,
#13. Click on Start->Program->Administrative Tools->Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager link will appear.
#14. Click Start->Programs->Administrative Tools->Services, IIS Admin Service will be created and started.
Now let’s create a New Web site for IIS testing.
#15. Open IIS Manager from Start->Program->Administrative Tools->Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager link
#16. On left pane, Right click on Web Site->check New->Web Site.
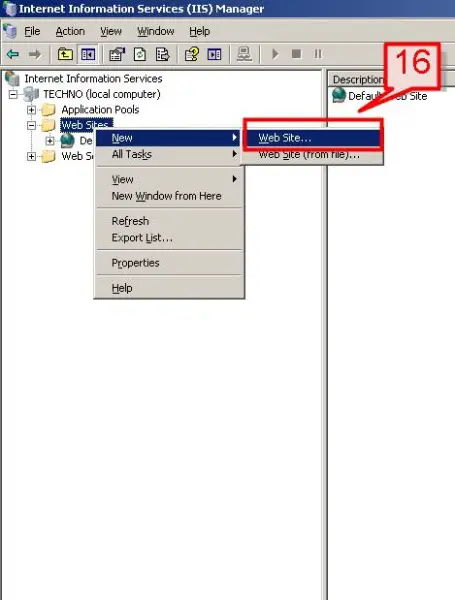
#17. On the Web Site Creation Wizard, click Next
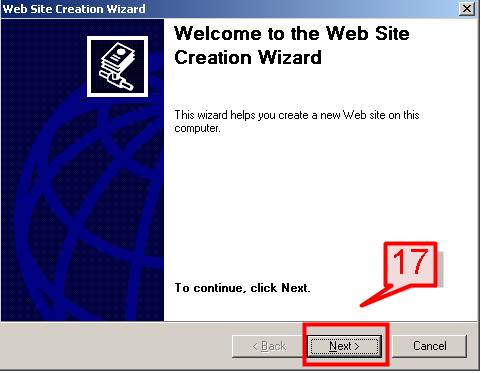
#18. On the Description field give a name to your Web site and click Next,
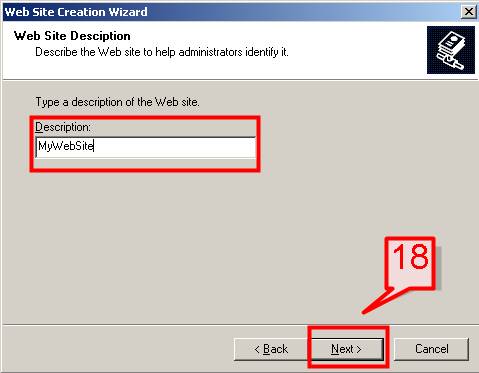
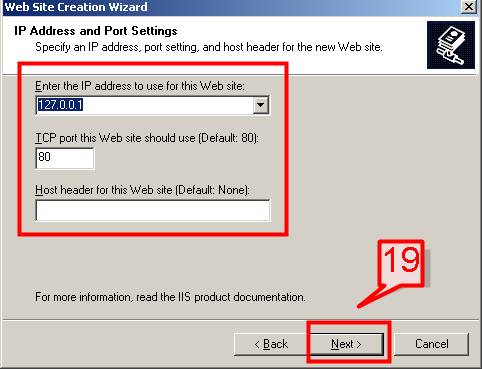
#19. On the next screen, Enter the IP address for your website, TCP port no (default is 80) and Host header name. The default IP address is your local machine IP. If the computer is configured on a Network Setup then it will get an IP from DHCP or a static IP.
Click Next
#20. On next screen, provide a path of your home directory where the Website files reside. The default location is C:Inetpubwwwroot location.
Click Next
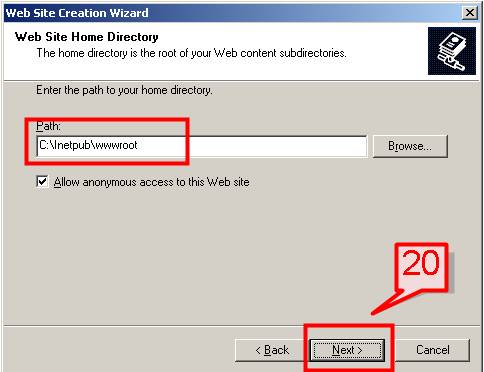
#21. Provide the type of access permissions for the web site and click Next,
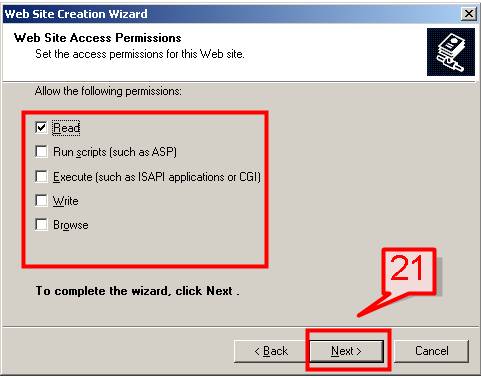
#22. The installation wizard will complete, click Finish.
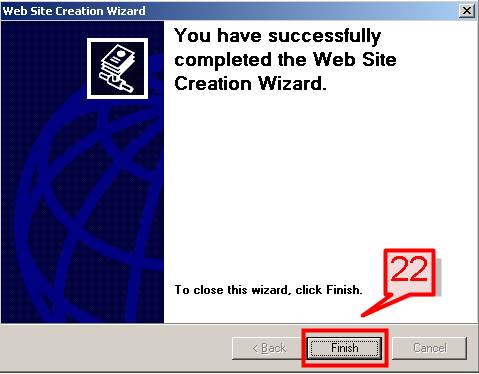
#23. Now let’s create a static html page that we will display as the welcome screen for the site.
Open Notepad and create an html file,
#24. Save the file as “index.htm” and save to C:Inetpubwwwroot folder.
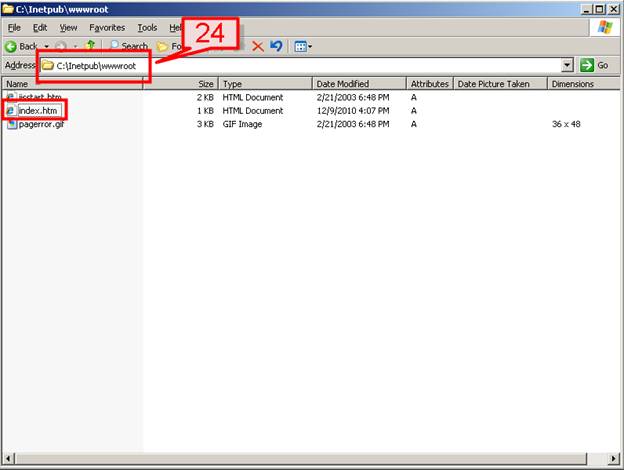
#25. Now open IIS manager, on your Website ->right click and go to properties
#26. On your website properties dialog box click on Documents tab, scroll up then choose index.htm file to the top of the page. Then click OK.
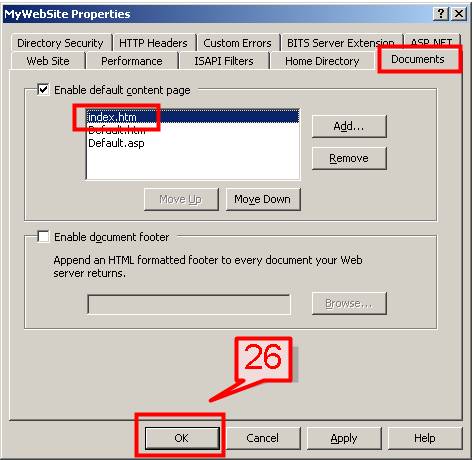
On the web site properties dialog box there are other options such as Directory security, ISAPI filters (to support ASP .NET) features that you can set to further customize your site.
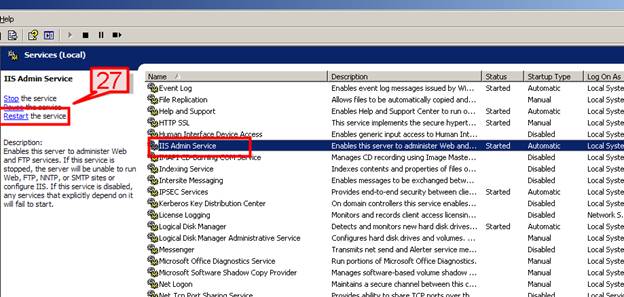
#27. We need to restart the IIS for the changes to take effect.
Go to Start->Programs->Administrative Tools->Services, select IIS Admin Service and click restart.
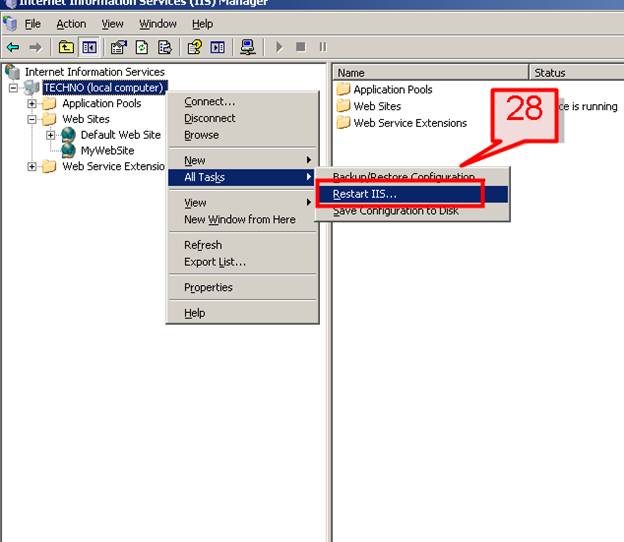
#28. Alternatively we can restart IIS from IIS Manager.
Go to IIS console select IIS server name->right click->All Tasks->Restart IIS
#29. Go to Internet Explorer and on the address bar type
http://localhost
The static index.html home page will appear if the IIS service is up and running.
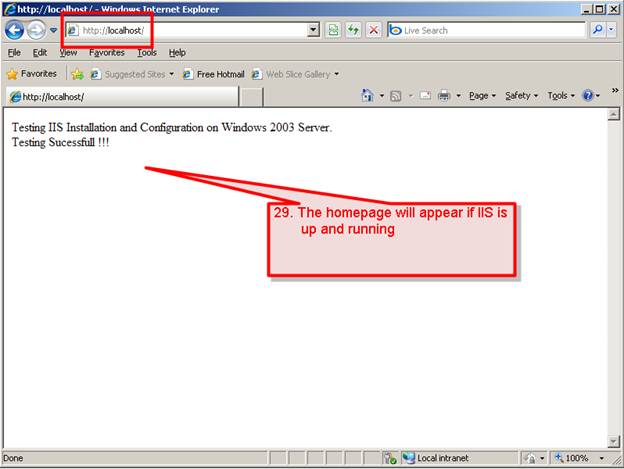
Now let’s check at some of new features of IIS
#30. New Authentication Method
IIS 6.0 includes a new authentication method called Advanced Digest Authentication. User credentials are stored in the Active Directory as an MD5 type of hash message digest which work on HTTP 1.1. So if the browser is not HTTP 1.1 compatible, the web pages can’t be displayed due to lack of Authentication. This provides better security.
To enable Advanced Digest Authentication, Open IIS console->select the website->right click->properties->select Directory Security tab.
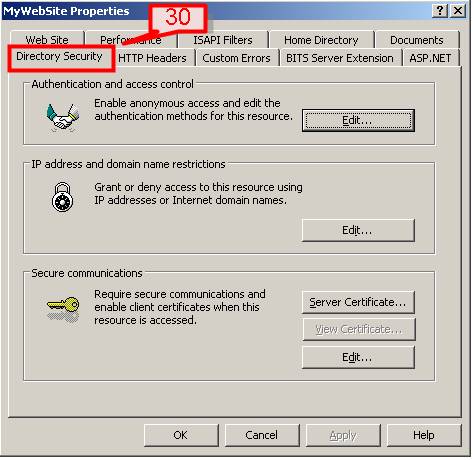
#31. Click Edit on the Authentication and access control tab.
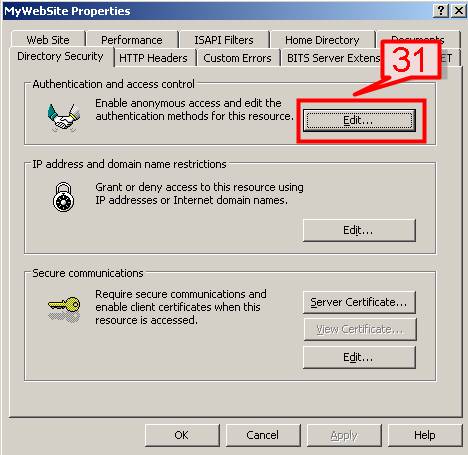
#32. In the Authentication Methods dialog box, check the Digest authentication for Windows domain servers checkbox.
A window message dialog will open to inform you that Digest authentication works with Active Directory domain accounts and asks if you wish to continue. Click Yes.
#33. In the Realm box, configure a realm name. Then click OK.
Realm is a security boundary which allows user authentication within that boundary. If the user moves to other realm boundary then they need to re-authenticate to access. Realm feature provides greater security to Web server.
#34. URL Authorization
This is a new security feature in IIS 6.0. Based on user’s role as defined in LDAP queries, Authorization Manager Scripts, and custom-created user roles, IIS provides authorization to a particular URL. You need to associate the URL with an Authorization Manager store in which the authorization policy for the URL is contained.
#35. Enabling and Disabling Dynamic Content
IIS 6.0 has the option to enable or disable dynamic content such as Active Server Pages (ASP), ASP.NET, Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV) and server-side includes (SSI). This provides highly secure or lockdown mode.
To enable dynamic content features
Go to IIS Manager Console->in the left pane of the IIS Manager->click Web Service Extensions
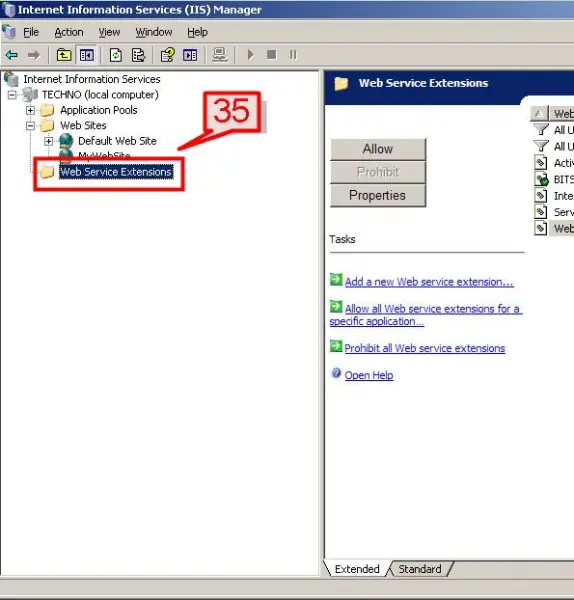
#36. On the right pane, a list of web service extensions and the status (Prohibited or Allowed) for each are shown.
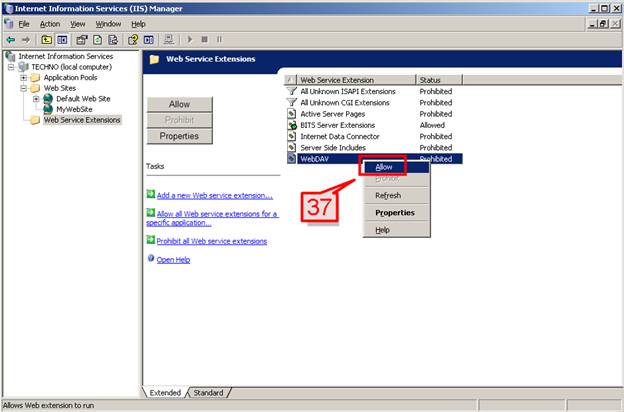
#37. Based on your requirement, select a Web Service Extension name which is Prohibited, right click and select Allow to enable.
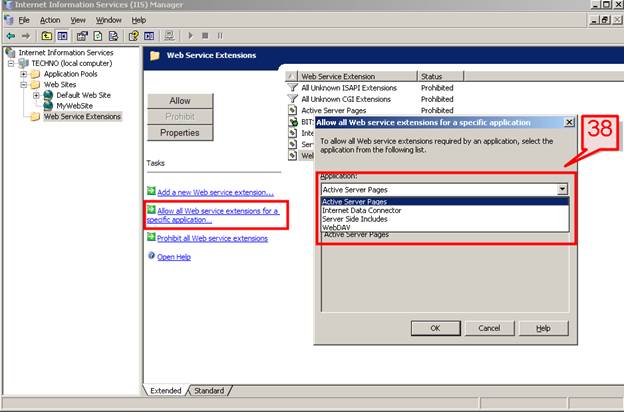
#38. We also have the option to allow all extensions for a specific application. Select the Allow all Web service extensions for a particular application icon in the Tasks section and then select the application from a dropdown box.
#39. Application Pools
Application Pools allow setting applications to run in their own pool or area or bucket so that they don’t interfere each other on the server.
#40. ASP .NET support
IIS 6.0 supports ASP .NET based applications which provide better customization, scalability and security run on .NET architecture mechanism.
