You are here:
Home » Windows 10 » How To Enable Hidden Administrator Account In Windows 10
As you know, towards the end of the Windows 10 installation or setup, the Windows setup prompts you to create a user account. Although Windows gives the Administrator user status to this user account, Windows 10 automatically generates another super or elevated Administrator account during the installation, and the account is hidden by default due to security reasons.
The built-in Administrator account is usually used to troubleshoot Windows. Unlike the standard Administrator account, this hidden by default or built-in Administrator account runs all programs and tools with admin rights by default, which means that the annoying UAC box will not appear when you attempt to run a program as administrator. This also means that all applications that are launched from this account are running without any restrictions.

There are three ways to enable the built-in or hidden administrator account in Windows 10. You can enable the same via Command Prompt, Local Users and Groups or Local Security Policy.
IMPORTANT: As the hidden Administrator launches applications and tools without any restrictions, it’s wise to enable and use the account only if you know how to use it. Also, we recommend you assign a password to the account as soon as you enable it.
Method 1 of 3
Step 1: Open elevated Command Prompt (Command Prompt with admin rights). To open Command Prompt as an administrator, you need to type CMD in Start search box and then simultaneously press Ctrl + Shift + Enter keys. Be sure to press all three keys simultaneously.
When you see the UAC prompt, click the Yes button.
Alternatively, you can type CMD in the Start/taskbar search box, right-click on Command Prompt entry, and then click Run as administrator option. Click the Yes button when you see the UAC box to open elevated Command Prompt.
When the elevated Command Prompt is launched, the “Administrator” word will appear on the toolbar of the Command Prompt (see below picture).

Step 2: In the elevated Command Prompt, type the following command and then press Enter key.
Net user administrator /active:yes

Step 3: Close the Command Prompt. That’s it!
The newly enabled built-in Administrator account can now be accessed by clicking your user account picture in the Start menu and then clicking the Administrator account. This hidden Administer will now also appear on the login screen of Windows 10.

Tip: To disable the built-in Administrator account, type Net user administrator /active:no in the elevated Command Prompt.
Method 2 of 3
Enable the hidden administrator account
Step 1: Open Run command box by simultaneously pressing Windows + R keys.
Tip: You can pin Run command to Start by following our how to pin Run to Start menu in Windows 10 guide.
Step 2: In the Run command box, type lusrmgr.msc and then press Enter key to open Local Users and Groups window.
Step 3: Here, in the left pane, click Users folder to see various account names in the middle pane.
Step 4: Now, double-click on the Administrator entry in the middle pane to open its properties dialog.

Step 5: Under the General tab, uncheck the option labeled Account is disabled, and then click the Apply button to enable the built-in admin account. That’s it!

Close the Local Users and Groups window. The enabled Administrator account should be visible on the login screen. Also, you can quickly switch to or sign in to the Administrator account by clicking the user account picture on the Start and then clicking the Administrator.
Method 3 of 3
Enable the hidden administrator account
In this method, we are going to enable the hidden Administrator account using Local Security Policy, and this feature (Local Security Policy) might not be available in all editions of Windows 10.
Step 1: Open the Run command box. To do so, as you likely know, you need to press Windows + R keys simultaneously.
Alternatively, you can type Run in the Start search box and then press Enter key to open Run command box.
Step 2: In the Run command box, type secpol.msc, and then click the OK button to open Local Security Policy.
Step 3: In the left pane of the Local Security Policy window, click Local Policies, and then click Security Settings.
Step 4: On the right-side, look for the policy entry named Accounts: Administrator account status, and then double-click on the same to open its Properties.

Step 5: Under the Local Security Setting tab of the opened Properties, select the option titled Enabled, and then click the Apply button to enable the hidden Administrator account.
That’s it! Good luck.
Our how-to delete an administrator account in Windows 10 guide might also interest you.
When you install Windows 10 anew on a PC, or run it for the first time if it comes pre-installed with the computer, you create the first user account during that process.
This is the main account on the system and configured to be an administrator account by default, but it is not the only one that is available out of the box.
Windows 10 creates two additional user accounts automatically which are both inactive by default. They are:
- Guest account
- Administrator account
The first is a guest account which Microsoft designed for users who access the device but don’t have a permanent account on it.
Guest accounts are severely limited as it is not possible to install software or hardware, or modify system settings.
Tip: run the command net user from the command prompt or PowerShell to get a list of all user accounts on the Windows 10 machine (inactive and active).
The administrator account
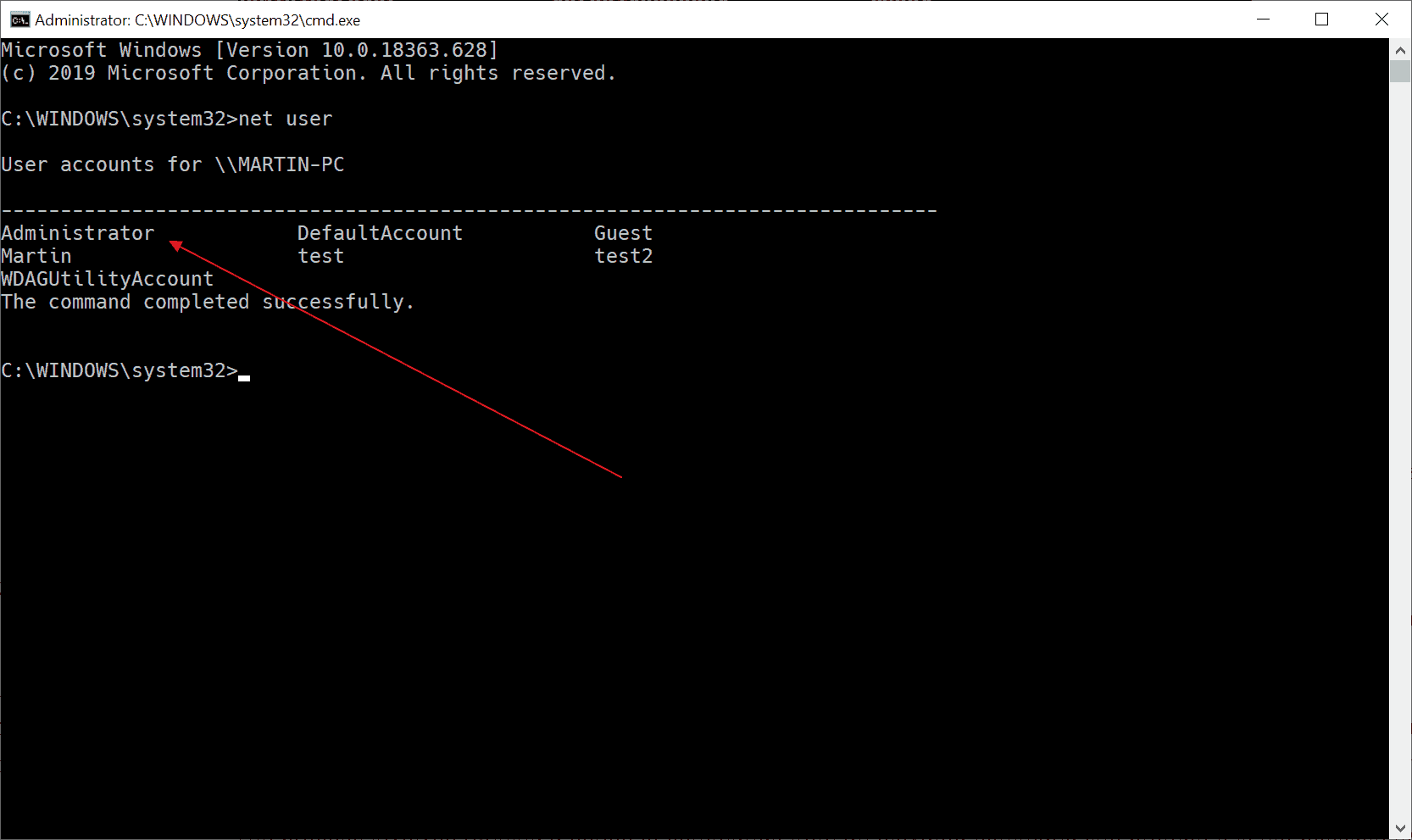
The second account that you find preinstalled on any Windows 10 device is the Administrator account.
It is also inactive by default and needs to be enabled before it can be used. While not required at all, it is often used for troubleshooting or administrative purposes when it is enabled.
A core difference between the administrator account of the user and the built-in administrator account is that the former receives UAC prompts while the latter does not. The first user account that is created by the actual user of the system on first start is an unelevated administrator account while the built-in Administrator account is an elevated account.
It is relatively easy to enable or disable accounts on Windows 10 devices provided that you have access to an admin account. You cannot make user account changes if you sign in with a regular account and don’t have access to an admin account on the system.
The process involves running a series of commands from an elevated command line prompt. It is not possible to activate the default Administrator account on Windows 10 devices using the account related options found in the Settings application as default accounts are not listed there at all.
Enable the Administrator account
To enable the Windows 10 administrator account do the following (note: this works in older versions of Windows as well):
- Tap on the Windows-key. This should open the start menu or bring you to the Start Screen interface depending on how Windows 10 is configured on the system.
- Type cmd and wait for the results to be displayed.
- Right-click on the Command Prompt result (cmd.exe)Â and select «run as administrator» from the context menu. Alternatively, hold down the Shift-key and the Ctrl-key before you start cmd.exe.
- Run the command net user to display a list of all user accounts on the system. You should see Administrator listed as one of the accounts.
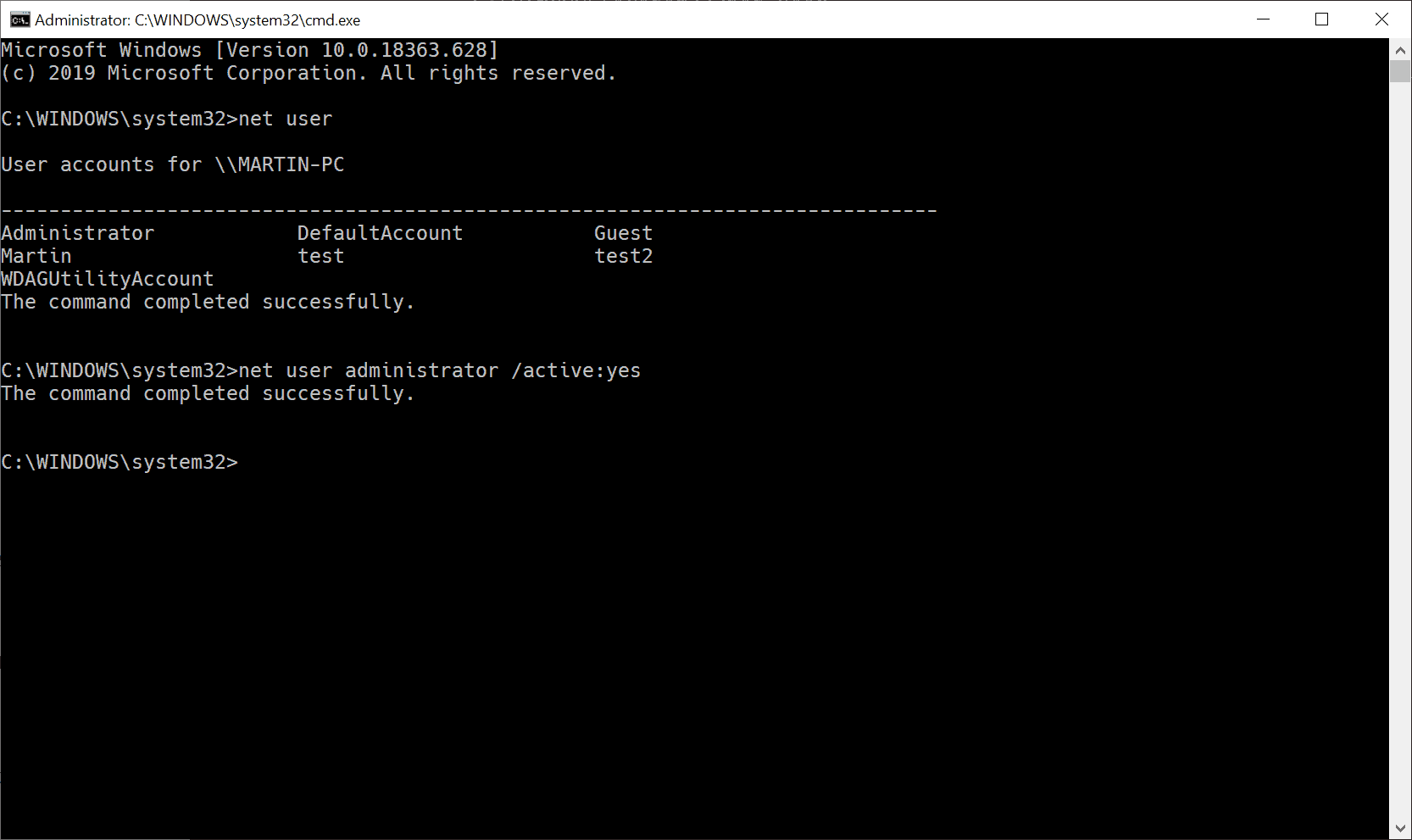
- To activate the inactive administrator account, run the command net user administrator /active:yes
- Windows returns «The command completed successfully» if the operation is successful. Check the spelling and that you are in an elevated command prompt interface if you get error messages.
- If you want to enable the guest account as well run the command net user guest /active:yes
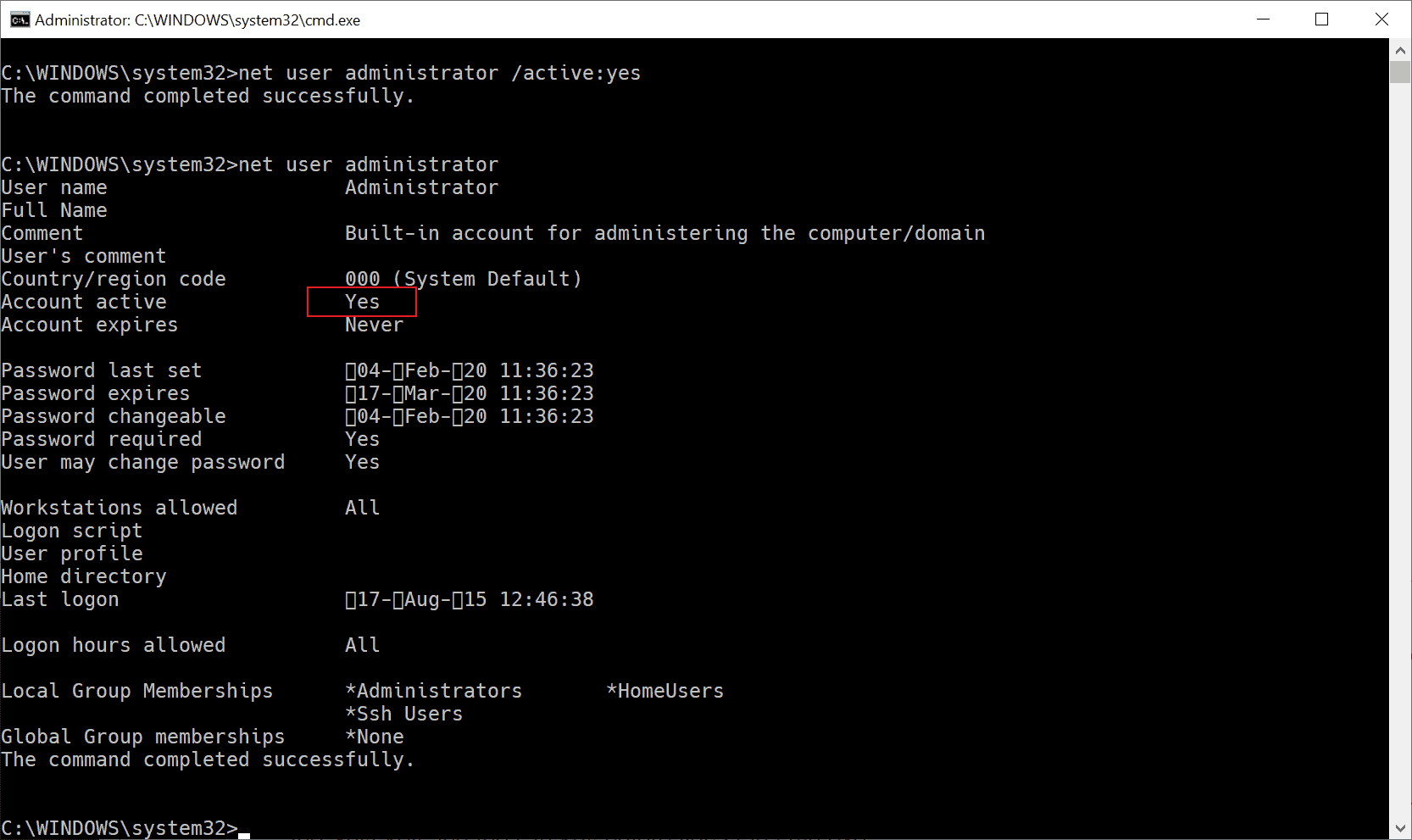
Verify that the account is activated by running net user administrator from the command line prompt. Check «account active» to verify the status of the account. Repeat the process for the guest account if you activated it as well.
Change the password of the admin account
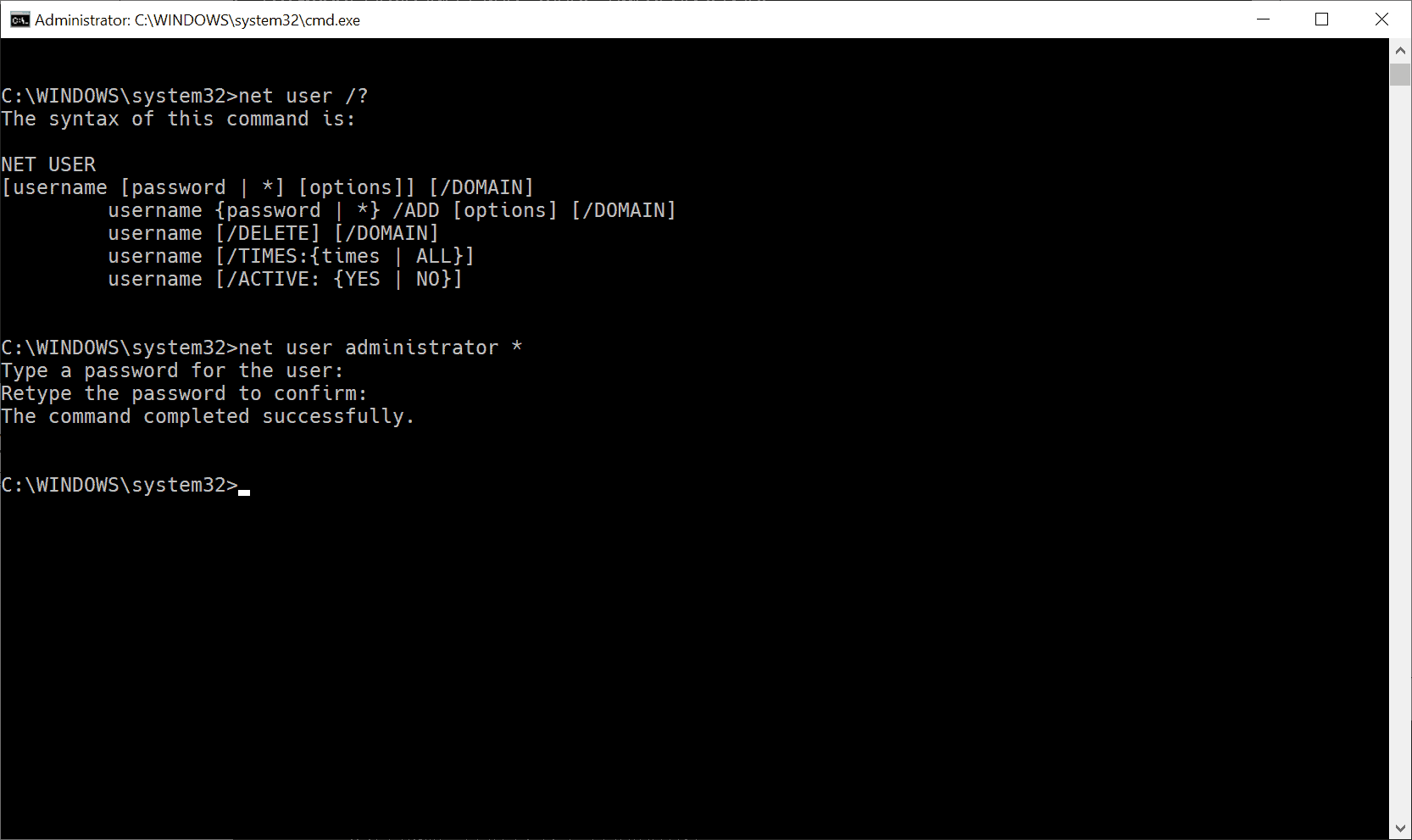
The administrator account is active after you run the commands mentioned above which means that you can sign in to the system using it. It is not password protected by default which means that anyone with local access to the system can use it to sign in. While that is comfortable, it may also be a security risk.
It is highly recommended to protect it with a password. This can also be done using the command line:
- Type net user administrator * and hit enter.
- You get a password prompt. Type the desired password and again when you are asked to type it a second time for confirmation. The password is not displayed at all as you type.
Disable the administrator account
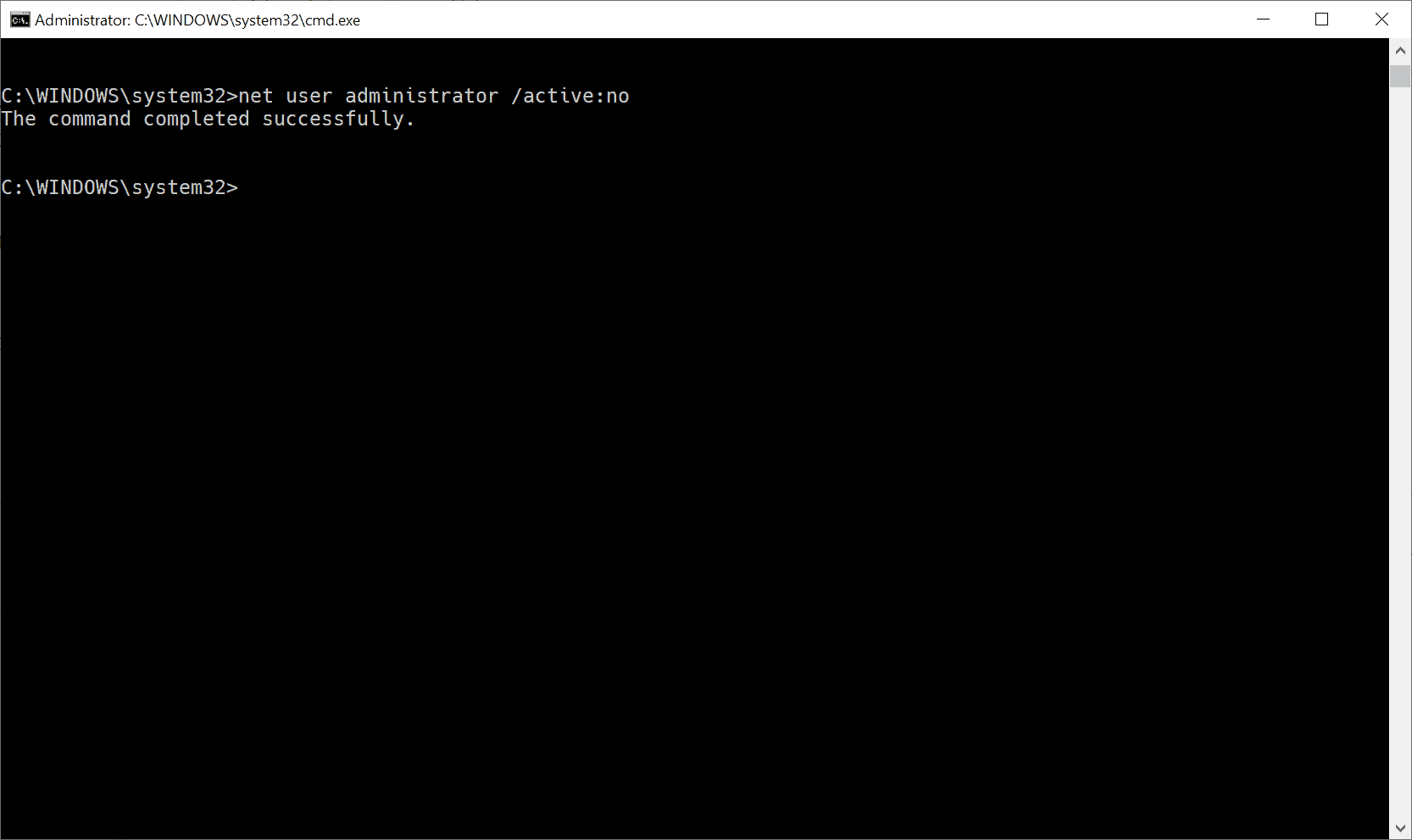
To disable accounts at any time, use the following command:
- On an elevated command prompt: net user administrator /active:no
You can verify that by running the command net user administrator again from the command line. The line «account active» should state «no».
Other commands of interest are:
- Net user administrator — Displays information about the user account on the command line.
- Net user username /delete — Deletes username on the system. This does not work with built-in accounts.
Tip: if you are running Windows 8, check out this guide which walks you through the procedure on this version of Windows.
Note: The following two methods work as well but they are only available on professional and Enterprise versions of the Windows 10 operating system.
Using Local Users and Groups
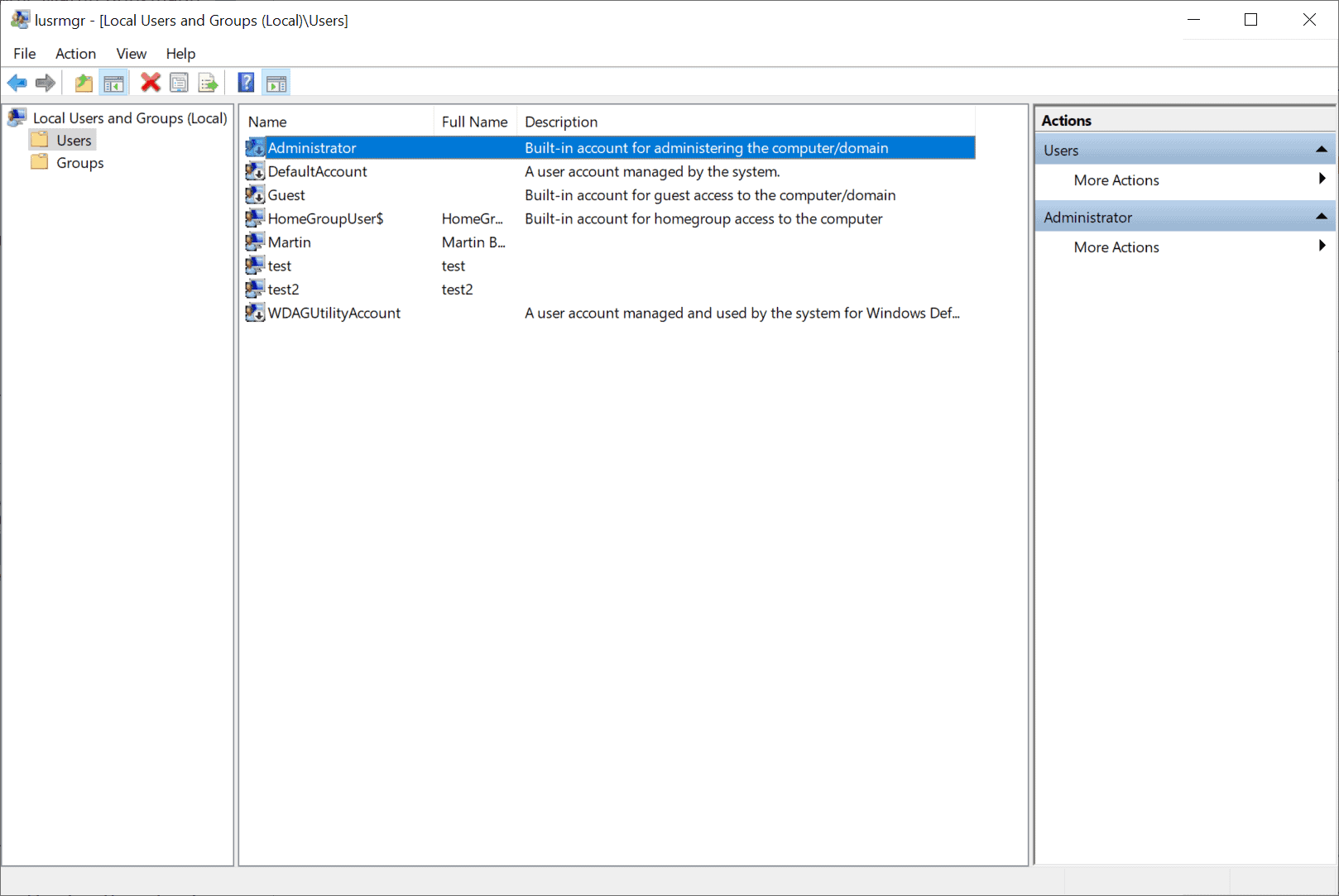
Windows users who prefer to work on user interfaces instead of the command prompt may use the built-in tool Local Users and Groups to manage accounts.
- Activate the Start menu on the system, e.g. with a click on Start or using the Windows-key.
- Type lusrmgr.msc and select the result that is returned to you.
- Left-click on Users in the left sidebar. You get a list of all accounts of the local system on the right.
- Right-click on Administrator and select Properties from the context menu.
- Remove the checkmark from «Account is disabled» on the Administrator Properties window and click apply, then ok.
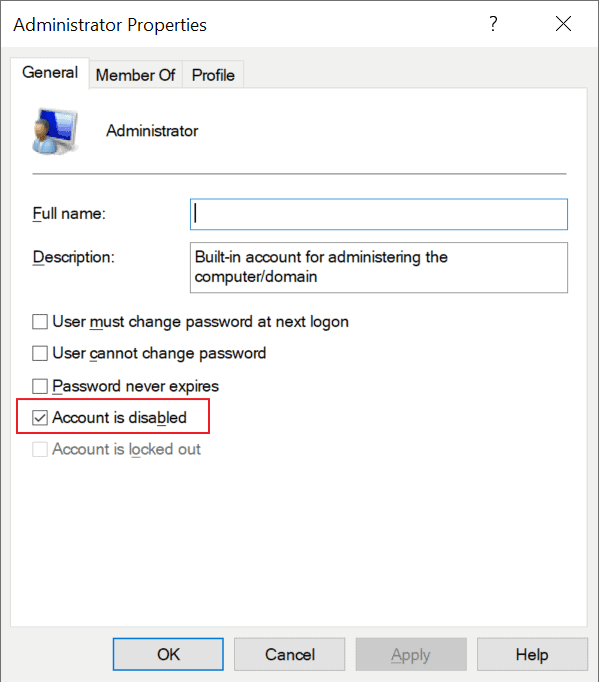
The method activates the Administrator account on the Windows 10 machine. To deactivate the account again, place a checkmark in the «account is disabled» checkbox and click on ok.
Using Security Policies
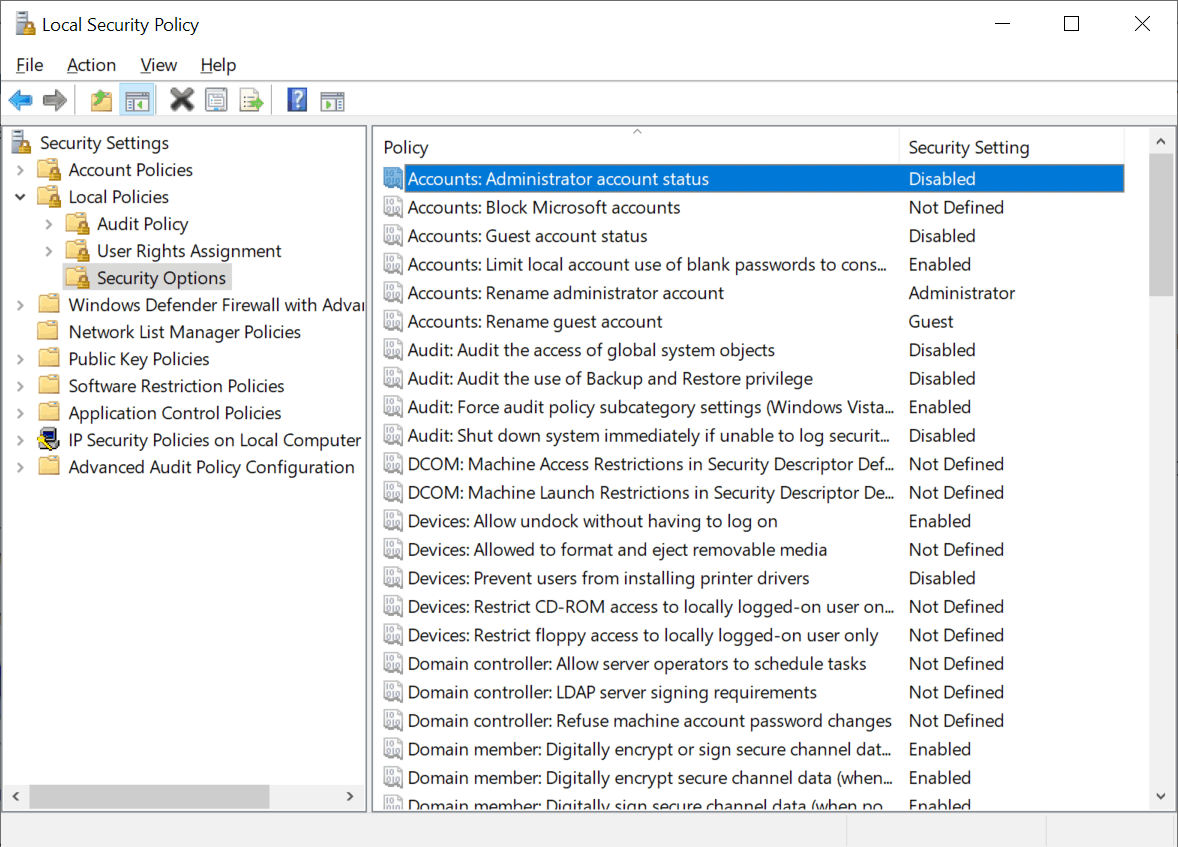
The second option to change the status of the built-in Administrator account on Windows 10 devices is to use Security Policies:
- Activate the Start Menu.
- Type secpol.msc and select the result to load the Local Security Policy.
- Go to Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options.
- The policy Accounts: Administrator account status determines whether the local Administrator account is enabled or not. Check the «Security Setting» to see if it is disabled or enabled.
- Double-click on the policy and select «Enabled» to enable the account.
- Select ok and close the Local Security Policy.
Summary
Article Name
How to enable the hidden Windows 10 administrator account
Description
The guide walks you through the steps of enabling the hidden administrator account in the Windows 10 operating system.
Author
Martin Brinkmann
Publisher
Ghacks Technology News
Logo
Advertisement
While installing Windows 10 at the end of the installation Windows setup prompts you to create a user account. This is the main account on the system and is configured to be an administrator account by default. Although Windows gives the Administrator user status to this user account, and it has almost all administrative privileges. But did you know by default Windows 10 automatically generates another super or elevated Administrator account during the installation? Yes, the Build in administrator account is hidden by default due to security reasons that usually used to troubleshoot Windows problems. While it’s not required at all, it is often used for troubleshooting or administrative purposes If you Require this account Here we have Different ways to Enable The Hidden Administrator Account On Windows 10, 8.1 and 7.
Contents
- 1 Built-in admin vs local admin
- 2 Enable Windows 10 administrator account
- 2.1 Using Local Users And Groups
- 2.2 Using Command prompt
- 2.3 Using Local Group Policy
Built-in admin vs local admin
The Built-in Windows 10 Administrator account is different from your current Administrator account. The main difference between the administrator account of the user and this built-in administrator account is that the former receives UAC prompts while the latter does not. The user account is an unelevated administrator account while the built-in administrator account for an elevated one. It gives you many more permissions to change things in the OS. It also gives you some extra privileges over the normal administrator account. The built-in Administrator account runs all programs and tools with admin rights by default. That means that all programs that are launched from this account are running without any restrictions.
Windows have different ways to enable this Hidden Administrator Account. You can enable the same through Local Users and Groups, Using the command prompt. Also, you can use the Local Security Policy ( Group Policy ) to Enable The Administrator Account as well.
Using Local Users And Groups
- Press Windows + R, type lusrmgr.msc click on Ok
- This will open Local Users and Groups windows,
- Here on the left-hand side click the Users folder,
- You see various account names in the middle pane
- And you will find the Administrator with an arrow mark. (That means The account is disabled)
- Now Right-click on Administrator and click properties
- Now under General Tab uncheck Account is disabled (refer to image Bellow)
- Now Click ok to make save changes and enable the administrator account.
- To set a password for this Administrator account
- Again right-click on administrator and select set password
- Type password for this Administrator account.
The newly enabled built-in Administrator account can now be accessed by clicking your user account name in the Start and then clicking the Administrator account. This hidden Administer will now also appear on the login screen of Windows 10.
Disable Windows 10 Administrator Account
If you have Enabled the Administrator Account only for Troubleshooting purposes or Run A program without any Restrictions. After Complete the task you can simply check the tick mark Account is disabled on the Administrator properties window.
Using Command prompt
Enable Administrator Account using Command Prompt is a very simple and easy task. You can do this by only type a command line.
- Open the command prompt as administrator,
- Type command net user administrator /active: yes and press enter key,
- This will prompt the command to complete successfully.
The newly enabled built-in Administrator account can now be accessed by clicking your user account name in the Start and then clicking the Administrator account. This hidden Administer will now also appear on the login screen of Windows 10.
To disable the built-in Administrator account Type Net user administrator /active:no and hit Enter key.
Using Local Group Policy
you can also use Local Security Policy (Group Policy) Editor to Enable the Hidden Administrator Account. Note Group policy Not Available on Windows Home And stater Editions.
Recommended: How To Enable Group policy For Home And Starter Users.
- Press Windows + R, type secpol.msc and click ok,
- This will open the Local Security Policy window,
- Now on the left pane expand Local Policies and click on Security Options.
- Here On the Middle pane Find and double-tap the policy called “Accounts: Administrator account status”.
- Right-click on it Select Enabled and click OK to enable it.
Click ok and apply To make save changes. That’s all Now you can log in with your Administrator Account.
To Disable The Administrator Account Follow The Same way. Open the Security policy Double click on Accounts: Administrator account status and select the Disable Radio button.
Also read:
- Different Ways To Enable Guest Account On Windows 10
- Windows 10 local account vs Microsoft account, which one is best for you?
- Windows 10 won’t shut down after the update? Here’s How To Fix It!
- Troubleshoot blue screen errors on Windows 10
- Solved: Windows 10 start menu search not working after update
Windows operating system comes with a built-in Hidden Admin Account, which is disabled by default on the computer for security purposes.
While the presence of Hidden Admin Account in Windows is not known to most users, system admins routinely make use of the Hidden Admin account to gain access to computers, troubleshoot problems and perform other functions.
The default option on a Windows computer is to activate the Hidden Admin Account with “Administrator” as its user name and require no password for login.
In general, the recommendation is to enable the Hidden Admin Account only when you are unable to login to the Local Admin Account on your computer.
Advertisement
This can happen, if the User Profile for the current Admin Account becomes corrupted or if you cannot remember the Admin password for your computer.
1. Enable Hidden Admin Account Using Command Prompt
The easiest way to Enable Hidden Admin Account on a Windows computer is by using Command Prompt.
1. Type Command Prompt in the Search bar > right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as Admin option.
2. On the Command Prompt screen, type net user administrator /active:yes and press the Enter Key.
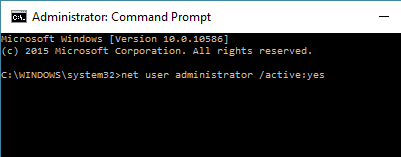
3. After this, restart the computer and you will be able to login to the Hidden Admin Account that you just activated.
Once you are done with the purpose of activating the Hidden Admin Account, you can disable or hide the Admin Account on your computer by using net user administrator /active:no command.
Important: Do not use net user administrator /active:no command, if the User Name for the original Admin Account on your computer was Admin or Administrator (this can lock you out from the computer).
2. Enable Hidden Admin Account Using PowerShell
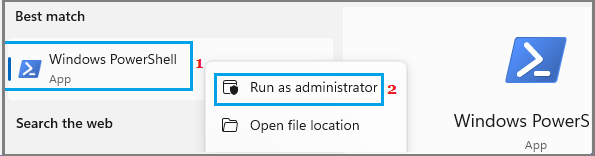
1. Type PowerShell in the Search bar > right-click on Windows PowerShell and select Run as Admin option.
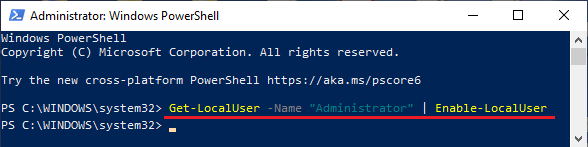
2. In PowerShell window, type Get-LocalUser -Name “Administrator | Enable-LocalUser and press the Enter key.
Advertisement
3. Restart the computer and you will be able to access the Hidden Admin account on the login screen.
At any time, you can disable the Hidden Admin Account on your computer by using Get-LocalUser -Name “Administrator | Disable-LocalUser.
3. Enable Hidden Admin Account Using Computer Management
1. Right-click on the Start button > select Computer Management in the right-click menu.
2. On Computer Management screen, go to Local Users and Groups > Users Folder in the left-pane. In the right-pane, right-click on Administrator and click on Properties.
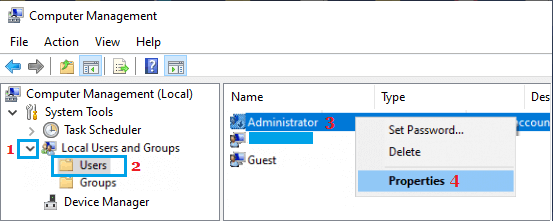
3. On Administrator Properties screen, uncheck Account is disabled entry.
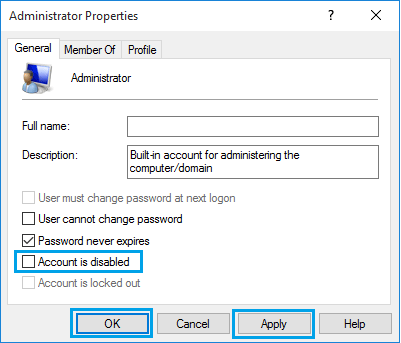
4. Click on Apply & OK to save this revised setting on your computer.
Now, when you restart the computer, you will be able to Access the Hidden Admin Account from the Login Screen.
Как вы знаете, при установке Windows 10, система просит создать учетную запись пользователя и предоставляет этой учетной записи права локального администратора. Однако, в процессе установки Windows создается еще один скрытый встроенный аккаунт Администратор (Administrator), который по соображениям безопасности отключен. В этой статье мы поговорим о встроенной записи администратора Windows 10, для чего она нужна, как ее включить, заблокировать и сбросить пароль.
Содержание:
- Встроенный аккаунт Administrator Windows
- Как включить встроенную учетную запись администратора в Windows 10?
- Пропали права администратора Windows
Встроенный аккаунт Administrator Windows
Аккаунт Administrator создается при установке Windows автоматически и используется для инициализации системы. Затем этот аккаунт отключается и пользователю предлагается создать собственную учетную запись, которая добавляется в локальную группу Administrators.
Учётная запись встроенного администратора имеет полные, не ограниченные права на компьютере. На эту учету не распространяется действие UAC (User Account Control), а все программы выполняются без запроса UAC (в этом ее важное отличие от пользовательских учетных записей с правами администратора). Встроенный Administrator в Windows в какой-то степени похож на root в Linux – у него есть максимальные права в системе (не System, конечно, но близкие).
Для встроенного администратора Windows можно включить UAC, для этого используйте параметр политик User Account Control: Admin Approval Mode for the Built-in Administrator account.
По умолчанию в Windows 10 и Windows Server 2016 встроенный Administrator отключен. Этот аккаунт нельзя удалить или исключить из группы Администраторы.
Если вы загружаете Windows в безопасном режиме или режиме восстановления, аккаунт администратора включается автоматически.
В целях безопасности желательно переименовать аккаунт встроенного администратора. Это можно сделать вручную, с помощью LAPS или параметра GPO Accounts: Rename administrator account в секции Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies -> Security Options.
Переименование аккаунта администратора несколько снижает риск его использования злоумышленниками или подбора пароля, но главная проблема в том, что его SID не меняется, что упрощает подбор. У встроенного аккаунта администратора всегда известный идентификатор безопасности SID S-1-5-domain-500.
Совет. По-умолчанию пароль Администратора не задан (пустой).
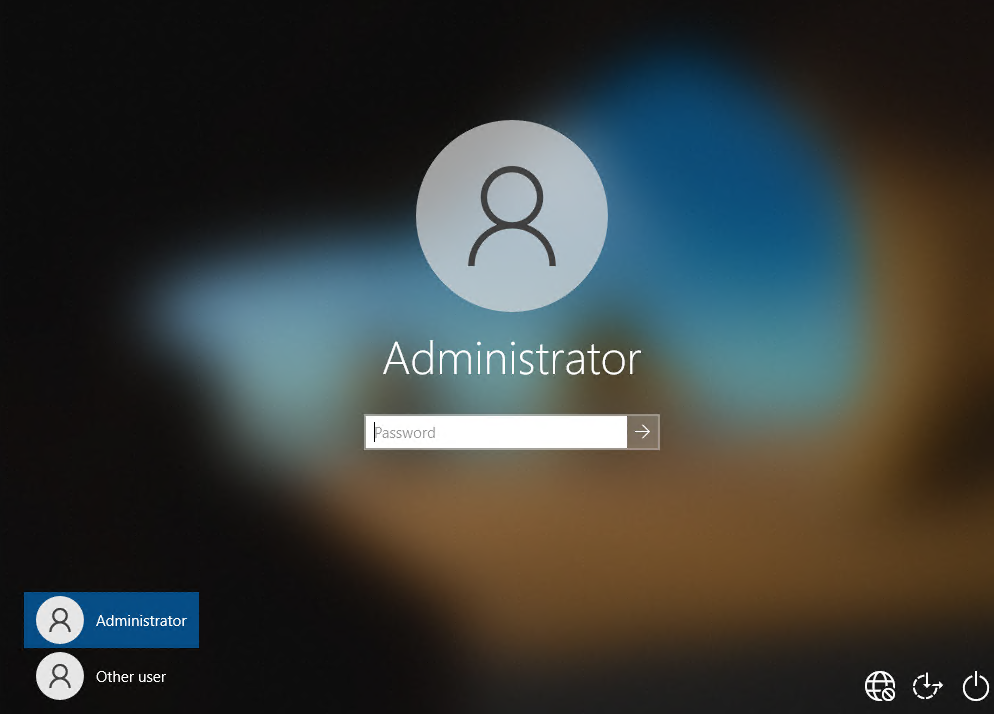
Важно. Microsoft не рекомендует держать учетную запись Administrator включенной (активной), а тем более работать из-под нее постоянно. Включать учетную запись “Администратор” нужно только в случае крайней необходимости для выполнения конкретной задачи или траблшутинга. Ни в коем случае не используйте его для автовхода в Windows.
Как включить встроенную учетную запись администратора в Windows 10?
Рассмотрим несколько простых способов включения встроенной учетной записи администратора в Windows 10.
Быстрее и проще всего активировать учетную запись администратора из командной строки (или консоли PowerShell), запущенной с повышенными привилегиями.
Для этого, выполните команду:
net user administrator /active:yes

The command completed successfully.
Как мы уже говорили ранее, в современных версиях Windows у аккаунта администратора не задан пароль. Если на компьютер действует доменная политика сложности паролей, при включении аккаунта администратора вы можете увидеть сообщение:
The password does not meet the password policy requirements. Check the minimum password length, password complexity and password history requirements.
В этом случае перед включением аккаунта администратора нужно установить для него пароль:
net user administrator *
Рекомендуем использовать достаточно сложный и надежный пароль, можете сгенерировать его (пароль нужно будет указать дважды).
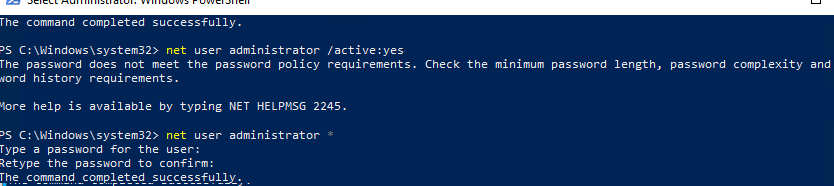
Если предыдущая команда пишет, что пользователь не найден “The user name could not be found”, скорее всего аккаунт администратора на компьютере переименован.
Вы можете определить, как на вашем компьютере называется аккаунт встроенного администратора по его известному SID (в конце он обязательно содержит -500). Воспользуйтесь командой:
wmic useraccount where "SID like 'S-1-5-%-500'" get name
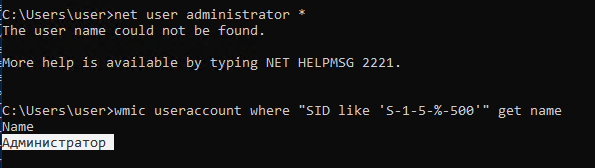
В этом примере используется русская версия Windows 10, поэтому встроенный аккаунт администратора называется “Администратор”.
Чтобы включить его, выполните:
net user Администратор/active:yes
Либо вы можете вывести список всех локальных учетных записей:
net user
Если при попытке включить встроенного администратора Windows вы получаете ошибку Отказ в доступе (
System error 5 has occurred. Access is denied
), убедитесь, что консоль cmd.exe или powershell.exe запущена с правами администратора. Также проверьте, что ваша учетная запись входит в группу локальных администраторов компьютера.
Выведите список групп, в которых состоит ваш аккаунт:
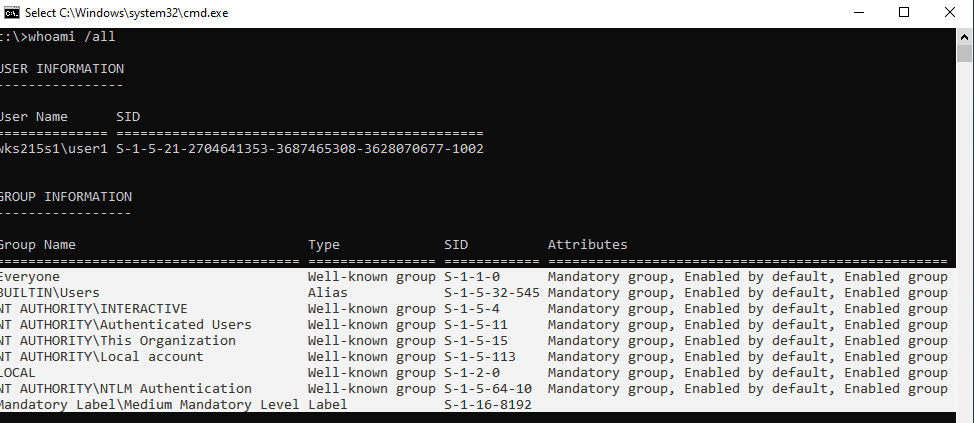
whoami /all
В этом примере пользователь user1 не состоит в локальной группе Administrators, поэтому у него нет прав на включение аккаунта администратора.
Вывести список пользователей в группе локальных администраторов в Windows можно так:
net localgroup administrators
или
net localgroup администраторы
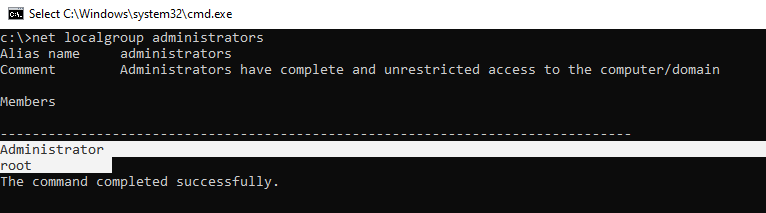
В данном примере в группу Administrators добавлены только два аккаунта. Если вы не знаете пароль ни для одного из них, значит у вас нет прав администратора на компьютере. Чтобы включить аккаунт встроенного администратора и предоставить своей учетной записи права локального админа, смотрите следующий раздел статьи.
Примечание. Рассмотренный способ активации встроенного администратора из командной строки будет работать во всех версиях Windows 10. Другие способы, описанные ниже, не применимы к домашним редакциям Win 10, в которых отсутствует оснастки управление компьютером и пользователями (
compmgmt.msc
и
lusrmgr.msc
) и редактор локальной групповой политики (gpedit.msc).
Откройте MMC оснастку Local Users and Groups, набрав в строке поиска или командой строке
lusrmgr.msc
. В окне консоли разверните раздел Users. Откройте свойства учетной записи с именем Администратор и снимите чекбокс Account is Disabled (Учетная запись отключена). Сохраните изменения.
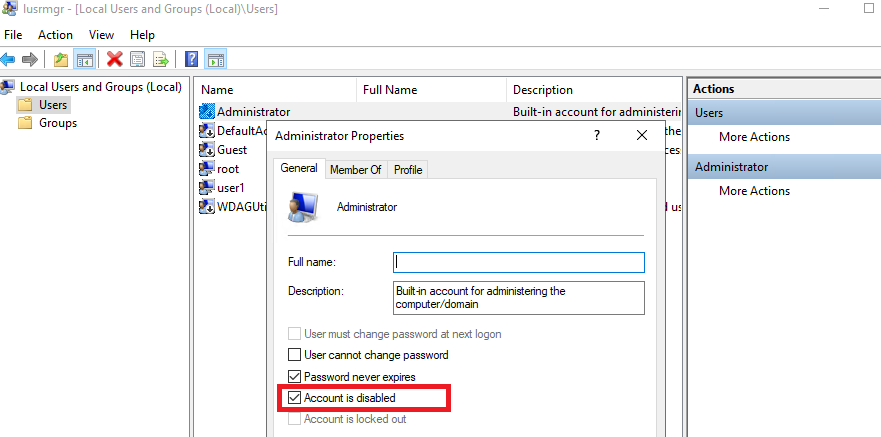
Учетная запись администратора теперь включена. В этой же консоли можно изменить его пароль, выбрав в контекстном меню Set Password.
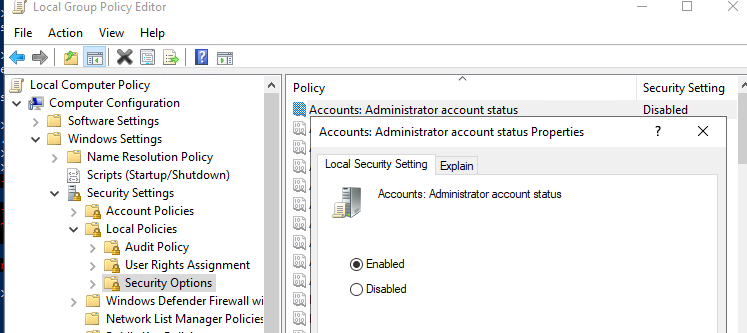
Можно включить встроенную учетную запись администратора через локальную GPO. Откройте редактор локальной групповой политики
gpedit.msc
(или редактор локальной политик безопасности —
secpol.msc
). Перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies -> Security Options. Найдите и отредактируйте политику Accounts: Administrator account status (Учетные записи. Состояние учетной записи ‘Администратор’), переведя ее в состояние Enable.
Обновите настройки групповых политик командой:
gpupdate /force
или просто перезагрузите компьютер.
После включения учетной записи администратора любым из рассмотренных способов, она будет отображаться на экране входа в систему Windows.
Чтобы отключить аккаунт встроенного администратора, воспользуйтесь командой строкой:
net user administrator /active:no
или так:
net user администратор /active:no
Если вы включили администратора через политику Accounts: Administrator account status, придется ее отключить (или полностью сбросить все настройки локальной GPO).
Пропали права администратора Windows
Бывают ситуации, когда вы случайно заблокировали свою учетную запись пользователя с правами администратора. Рассмотрим, как в этом случае включить встроенного администратора или добавить свой аккаунт в группу локальных админов, когда невозможно войти в Windows.
Вам нужно загрузить ваш компьютер с LiviCD (но не диска восстановления MSDaRT) или установочного диска с Windows 10. Проще всего создать загрузочную USB флешку с установочным образом Windows 10 с помощью Media Creation Tool.
На экране начала установки Windows нажмите
Shift + F10
. Откроется командная строка.
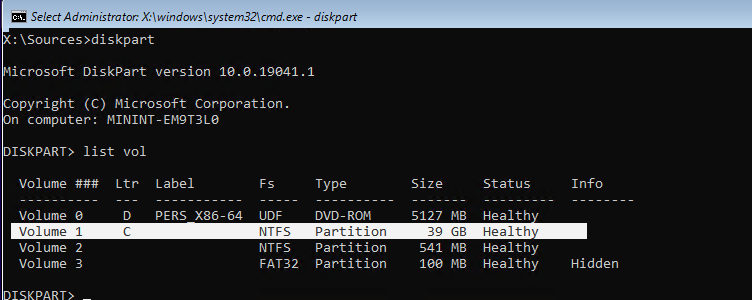
Теперь вам нужно определить на каком диске находится ваша Windows. Запустите
diskpart
и выполните
list vol
.
В моем примере видно, что Windows находится на диске C:. Именно эту букву диска я буду использовать в следующих командах. Чтобы завершить diskpart, наберите
exit
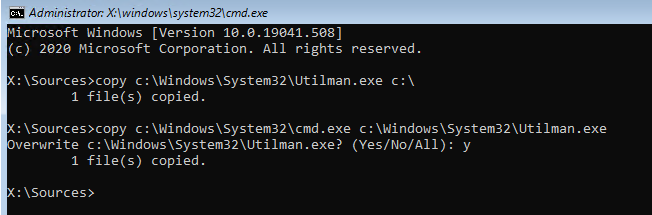
Выполните следующие команды, чтобы создать копию файла utilman.exe (апплет Центра специальных возможностей) и заменить его исполняемым файлом cmd.exe:
copy c:\windows\System32\utilman.exe c:\
copy c:\windows\System32\cmd.exe c:\windows\System32\utilman.exe
Перезагрузите компьютер:
wpeutil reboot
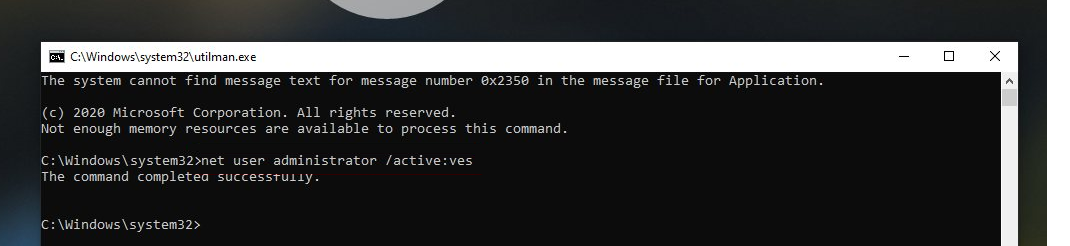
Выполните обычную загрузку Windows. На экране входа в систему (со списком учетных записей) нажмите сочетание Win+U.
Откроется окно командной строки с правами System. Чтобы добавить свою учетную запись в группу локальных администраторов, включить встроенного администратора Windows и сбросить его пароль, выполните команды:
net localgroup administrators user1 /add
net user Administrator /active:yes
net user administrator *
Теперь вы можете зайти на компьютер под Administrator или своим аккаунтом, которому назначены права локального админа.
Не забудьте вернуть оригинальный файл utilman.exe на место. Еще раз загрузитесь с установочного диска и выполните команду:
copy c:\utilman.exe c:\windows\System32\utilman.exe
