This tutorial intends to teach you how to Install Grafana on Windows Server 2022. Grafana is an open-source and amazing web-based analytics and visualization platform. It allows users to create customizable dashboards to visualize data from various sources such as databases, cloud services, and other monitoring tools.
You can download the latest version of Grafana from the official site and start the setup installation on Windows Server 2022. To do this, follow the rest of the article on the Orcacore website.
Table of Contents
To Install Grafana on Windows Server 2022, you must have access to your Windows Server and follow the steps below.
We will use the Grafana Installer to Install Grafana on Windows Server 2022.
Step 1 – Download Grafana Installer
At this point, you can visit the Grafana Downloads page and click on the Windows installer to get the latest version of the Grafana Enterprise edition on Windows Server 2022.
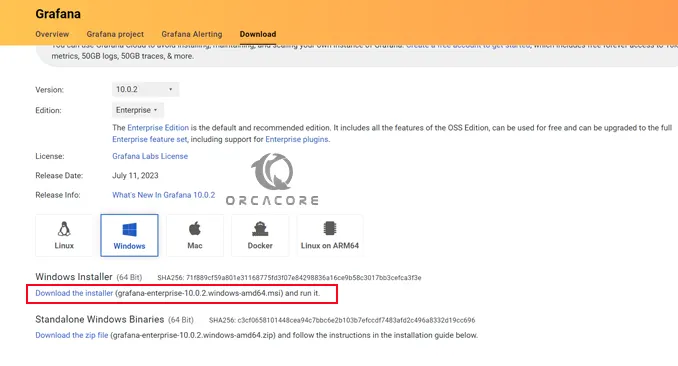
When your download is completed, click on your Grafana downloaded file to open the setup wizard.
Step 2 – Grafana Installation steps on Windows Server 2022
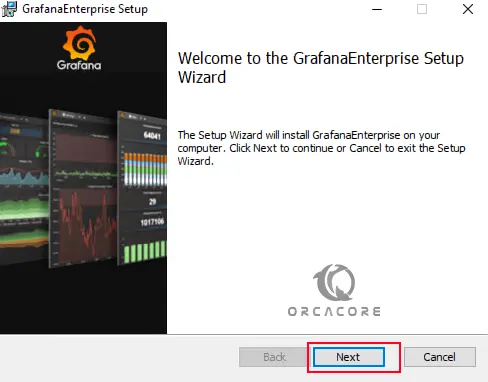
First, you will see the welcome screen. Simply click Next.
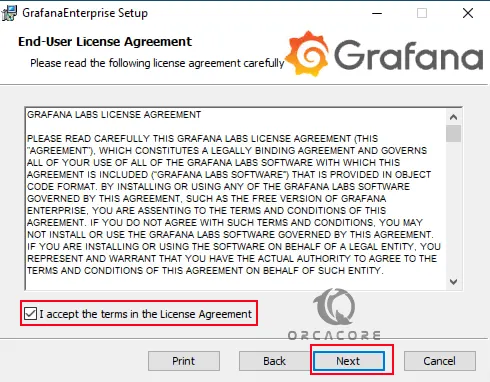
Next, accept the license agreement and click Next.
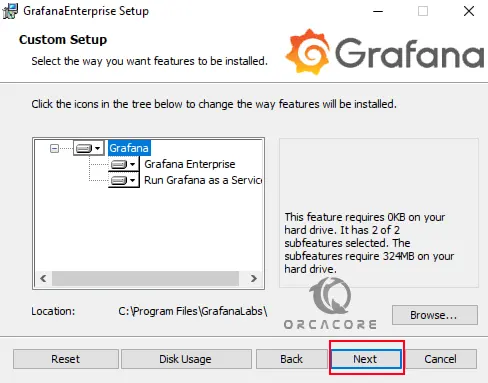
At this point, you must select the Grafana components. By default everything has been done, you can simply click Next. Or you can make your desired changes and click Next.
Now your Grafana app is ready to install. Click Install.
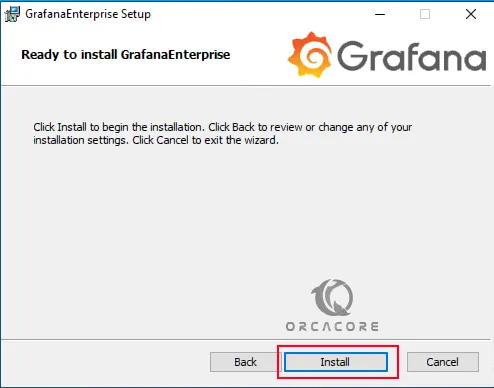
When your installation is completed, click Finish.

Step 3 – Access Grafana Dashbaord on Windows Server
At this point, you can easily access your Grafana dashboard from your web browser. In your web browser type:
http://localhost:3000/loginOr, if you wish to access Grafana from other computers on your network, you’ll need to use the local IP address of your Windows Server:
http://windows-server-ip-address:3000/loginYou should see the Grafana login screen. Enter admin as the username and password and click login.
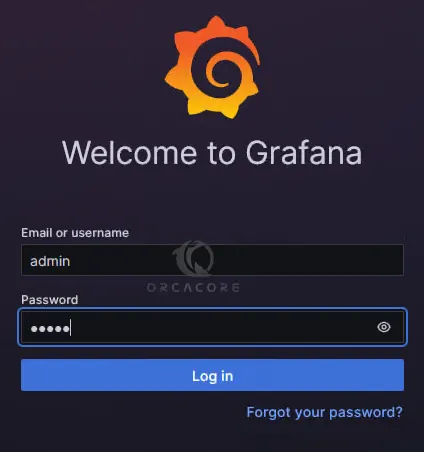
Then, you must change the admin password for security reasons and click Submit.

At this point, you should see your Grafana dashboard on your Windows server.
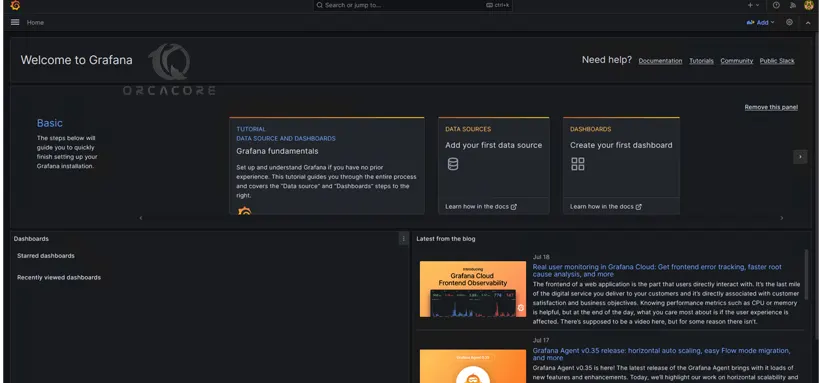
From here you can start to monitor your data. You can proceed to the next step to create your first dashboard with Grafana.
Step 4 – Start Using Grafana on Windows Server
At this point, you can easily create your first dashboard and start using Grafana on Windows Server 2022. To create your first dashboard, click Dashboards in the left-side menu.
Then, click New and select New Dashboard from the dropdown menu.
Next, click on + Add visualization.
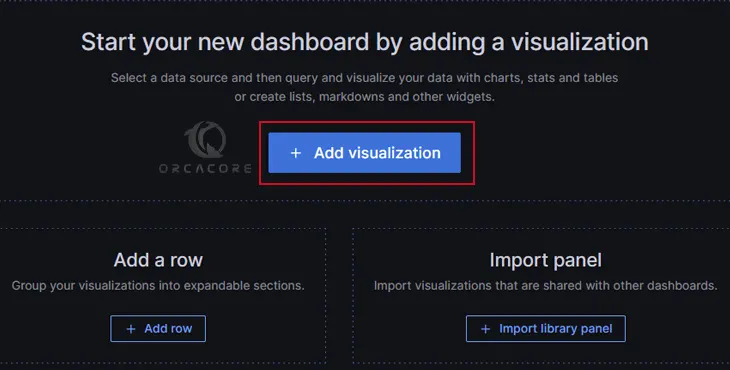
From the data source, click — Grafana —.
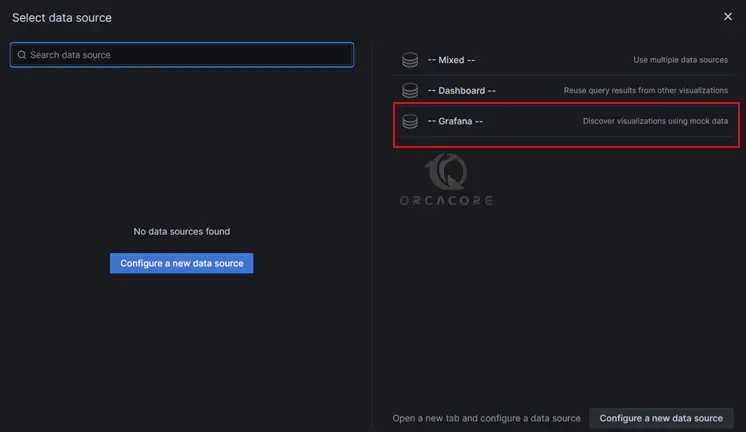
This configures your query and generates the Random Walk dashboard. Click the Refresh dashboard icon to query the data source. And click Save to save the dashboard.
Enter a name for your password and click save.
That’s it, you have created your first dashboard with Grafana.
For more information, you can visit the Grafana Documentation page.
Conclusion
Grafana is a powerful tool that is used for data visualization and monitoring. It is widely used in DevOps, IT operations, and engineering teams to get into their systems and applications. With Grafana, you can build interactive and dynamic dashboards with graphs, charts, tables, and alerts. They help you to effectively monitor the performance and health of systems, applications, networks, and infrastructure.
At this point, you have learned to Install Grafana on Windows Server 2022, Access it from a web browser, and create your first dashboard with Grafana on your server.
Hope you enjoy using it. You may be interested in these articles:
Install MSIX App on Windows Server 2022
Install OpenSSL on Windows Server 2022
Disable Ctrl+Alt+Delete logon on Windows Server
In this article we are going to cover Install Prometheus and Grafana on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS with Node Exporter and WMI Exporter | Windows and Linux Server Monitoring using Prometheus and Grafana
Table of Contents
What is prometheus?
- Prometheus is a open source Linux Server Monitoring tool mainly used for metrics monitoring, event monitoring, alert management, etc.
- Prometheus has changed the way of monitoring systems and that is why it has become the Top-Level project of Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF).
- Prometheus uses a powerful query language i.e. “PromQL”.
- In Prometheus tabs are on and handles hundreds of services and micro services.
- Prometheus use multiple modes used for graphing and dashboarding support.
Why we used prometheus?
- A multi-dimensional data model with time series data identified by metric name and key/value pairs
- PromQL, a flexible query language to leverage this dimensionality
- Pushing time series is supported via an intermediary gateway
- Multiple modes of graphing and dashboarding support
Prometheus Architecture
- As above we can see an architecture of Prometheus monitoring tool.
- We made a basic design to understand it easily for you people.
Now lets understand the Prometheus components one-by-one
Prometheus Components
- Prometheus server is a first component of Prometheus architecture.
- Prometheus server is a core of Prometheus architecture which is divided into several parts like Storage, PromQL, HTTP server, etc.
- In Prometheus server data is scraped from the target nodes and then stored in the database.
1.a. Storage
- Storage in Prometheus server has a local on disk storage.
- Prometheus has many interfaces that allow integrating with remote storage systems.
1.b. PromQL
- Prometheus uses its own query language i.e. PromQL which is a very powerful querying language.
- PromQL allows the user to select and aggregate the data.
2. Service Discovery
- Next and very important component of Prometheus Server is the Service Discovery.
- With the help of Service discovery the services are identified which need to be scraped.
- To Pull metrics, identification of services and finding the targets are compulsory needed.
- Through Service discovery we monitor the entities and can also locate its targets.
3. Scrape Target
- Once the services are identified and the targets are ready then we can pull metrics from it and can scrape the target.
- We can export the data of the end point using node exporters.
- Once the metrics or other data is pulled, Prometheus stores it in a local storage.
4. Alert Manager
- Alert Manager handles the alerts which may occurs during the session.
- Alert manager handles all the alerts which are sent by the Prometheus server.
- Alert manager is one of the very useful components of the Prometheus tool.
- If in case any big error or any issue occurs, alert manager manage those alerts and contact with human via E-mail, Text Messages, On-call, or any other chat application service.
5. User Interface
- User interface is also an important component as it builds a bridge between the user and the system.
- In Prometheus, user interfaces are note that much user friendly and can be used till graph queries.
- For good exclusive dashboards Prometheus works together with Grafana (visualization tool).
- Using Grafana over Prometheus to visualize properly we can use custom dashboards.
- Grafana dashboards display via pie charts, line charts, tables, good data graphs of CPU usage, RAM utilization, network load, etc with indicators.
- Grafana supports and run with Prometheus by querying language i.e. PromQL.
- To fetch data from Prometheus and to display the results on Grafana dashboards PromQL is used.
What is Grafana ?
- Grafana is a free and open source visualization tool mostly used with Prometheus to which monitor metrics.
- Grafana provides various dashboards, charts, graphs, alerts for the particular data source.
- Grafana allows us to query, visualize, explore metrics and set alerts for the data source which can be a system, server, nodes, cluster, etc.
- We can also create our own dynamic dashboard for visualization and monitoring.
- We can save the dashboard and can even share with our team members which is one of the main advantage of Grafana.
What is Node Exporter ?
- Node exporter is one of the Prometheus exporters which is used to expose servers or system OS metrics.
- With the help of Node exporter we can expose various resources of the system like RAM, CPU utilization, Memory Utilization, disk space.
- Node exporter runs as a system service which gathers the metrics of your system and that gathered metrics is displayed with the help of Grafana visualization tool.
What is WMI Exporter?
- It is same like Node Exporter but Node Exporter for Linux and WMI Exporter for Windows
- WMI Exporter is an exporter utilized for windows servers to collects metrics like CPU usage, memory, and Disk usage.
- It is open-source which can be installed on Windows servers using the .msi installer
Prerequisite:
Good internet connectivity
Security Groups Configured properly
Any web Browser
Security Groups Configured on EC2 Instances:
Port 9090 — Prometheus Server
Port 9100 — Prometheus Node Exporter
Port 9182—-WMI Exporter
Port 3000 — Grafana
We will update the system repository index by using the following command.
sudo apt update -yswitch to root user
sudo su -
#1. Creating Prometheus System Users and Directory
We will have to create a Prometheus user named Prometheus and a Prometheus directory named as Prometheus.
Using below commands we can create a user and directory.
sudo useradd --no-create-home --shell /bin/false prometheus
sudo useradd --no-create-home --shell /bin/false node_exporter
sudo mkdir /etc/prometheus
sudo mkdir /var/lib/prometheus
#2. Update Prometheus user
As user groups and directories are created successfully which store the Prometheus data and files.
Now we will have to update the group and user ownership on the newly created directories.
By using the below command we update the ownership.
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /var/lib/prometheus
#3. Download Prometheus Binary File on Ubuntu
Now we will download the latest version of Prometheus. We can copy the download link as per our Operating System from Prometheus download page
Using the below command we can download Prometheus, here we are downloading Prometheus 2.31.1 version, you use the above link to download specific version.
Navigate to /tmp directory
cd /tmp/
Download the Prometheus setup using wget
wget https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.31.1/prometheus-2.31.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
Now we have successfully downloaded the Prometheus file and now we will extract that file.
#4. Install Prometheus and Grafana on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
Extract the files using tar command :
tar -xvf prometheus-2.31.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
#5. Move the configuration file and set the owner to the prometheus user:
cd prometheus-2.31.1.linux-amd64
sudo mv console* /etc/prometheus
sudo mv prometheus.yml /etc/prometheus
sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus
#6. Update Prometheus user ownership on Binaries
Now we will update the user and group ownership on the binaries of Prometheus.
Using following commands we will update the user and group ownership.
sudo mv prometheus /usr/local/bin/
sudo chown prometheus:prometheus /usr/local/bin/prometheus
#7. Check Prometheus Version
Now the Prometheus is successfully installed on our system. We will check the version of Prometheus and to configure it.
Follow the commands to verify prometheus version.
prometheus --version

#8. Prometheus configuration file
We have already copied /tmp/prometheus-2.31.1.linux-amd64/prometheus.yml file /etc/prometheus directory, verify if it present and should look like below and modify it as per your requirement.
sudo nano /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
# my global config
global:
scrape_interval: 15s # Set the scrape interval to every 15 seconds. Default is every 1 minute.
evaluation_interval: 15s # Evaluate rules every 15 seconds. The default is every 1 minute.
# scrape_timeout is set to the global default (10s).
# Alertmanager configuration
alerting:
alertmanagers:
- static_configs:
- targets:
# - alertmanager:9093
# Load rules once and periodically evaluate them according to the global 'evaluation_interval'.
rule_files:
# - "first_rules.yml"
# - "second_rules.yml"
# A scrape configuration containing exactly one endpoint to scrape:
# Here it's Prometheus itself.
scrape_configs:
# The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config.
- job_name: "prometheus"
# metrics_path defaults to '/metrics'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9090"]
#9. Creating Prometheus Systemd file
Now we will create a system service file in /etc/systemd/system location.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/prometheus.service
After creating file successfully, copy the below files and it to the newly created file. /etc/systemd/system/prometheus.service
[Unit]
Description=Prometheus
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
[Service]
User=prometheus
Group=prometheus
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/prometheus \
--config.file /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \
--storage.tsdb.path /var/lib/prometheus/ \
--web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles \
--web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
After adding the program save the file with Ctrl+O and exit with Ctrl+X.
To use the newly created service we will have to reload the daemon services, Use the below command to reload daemon services.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
start and enable prometheus service using below commands
sudo systemctl start prometheus
sudo systemctl enable prometheus
We will check the Prometheus status weather it is running or not
sudo systemctl status prometheus

Prometheus installation and configuration is set up, We can see status Active: active(running)
#10. Accessing Prometheus on Browser
Now as Prometheus installation and configuration is set up and it is ready to use we can access its services via web interface.Also check weather port 9090 is UP in firewall.
Use below command to enable prometheus service in firewall
sudo ufw allow 9090/tcp
Now Prometheus service is ready to run and we can access it from any web browser.
http://server-IP-or-Hostname:9090.

As we can see the Prometheus dashboards, we can also check the target.As we can observe Current state is UP and we can also see the last scrape.

#11. Install Grafana on Ubuntu
Download the Grafana GPG key with wget, then pipe the output to apt-key. This will add the key to your APT installation’s list of trusted keys, which will allow you to download and verify the GPG-signed Grafana package:
wget -q -O - https://packages.grafana.com/gpg.key | sudo apt-key add -
In this command, the option -q turns off the status update message for wget, and -O outputs the file that you downloaded to the terminal. These two options ensure that only the contents of the downloaded file are pipelined to apt-key.
Next, add the Grafana repository to your APT sources:
sudo add-apt-repository "deb https://packages.grafana.com/oss/deb stable main"
Refresh your APT cache to update your package lists:
sudo apt update
You can now proceed with the installation:
sudo apt install grafana
Once Grafana is installed, use systemctl to start the Grafana server:
sudo systemctl start grafana-server
Next, verify that Grafana is running by checking the service’s status:
sudo systemctl status grafana-server
You will receive output similar to this:

Now finally enable the Grafana service which will automatically start the Grafana on boot
sudo systemctl enable grafana-server.service
To access Grafana Dashboard open your favorite browser, type server IP or Name followed by grafana default port 3000.
http://your_ip:3000
Here you can see Login page of Grafana now you will have to login with below Grafana default UserName and Password.
Username – admin
Password – admin

It is always a good practice to change your login credentials.

Provide your New Password and click on Change Password
Now here you can see Home Dashboard page of Grafana

#12. Configure Prometheus as Grafana Data Source
Once you logged into Grafana Now first Navigate to Settings Icon ->> Configuration ->> data sources

Now lets click on Add Data sources and select Prometheus

Now configure Prometheus data source by providing Prometheus URL

As per your requirement you can do other changes or you can also keep remaining configuration as default.
Now click on Save & test so it will prompt a message Data Source is working.

#13. Install Node Exporter on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
Node Exporter collects the metrics of your system such as Memory usage, CPU usage, RAM, disk space, etc.
To install Node Exporter first navigate to Prometheus official download page, Scroll down and you will get node_exporter section and then select Linux OS for amd64.
Now right click on node exporter and copy link address

Now lets run the copied URL with wget command
cd /tmp
wget https://github.com/prometheus/node_exporter/releases/download/v0.18.1/node_exporter-0.18.1.linux-amd64.tar.g
Unzip the downloaded the file using below command
tar xvfz node_exporter-*.*-amd64.tar.gz
Move the binary file of node exporter to /usr/local/bin location.
sudo mv node_exporter-*.*-amd64/node_exporter /usr/local/bin/
Create a node_exporter user to run the node exporter service.
sudo useradd -rs /bin/false node_exporter
#14. Create a node_exporter service file in the /etc/systemd/system directory
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/node_exporter.service
Paste the below content in your service file
[Unit]
Description=Node Exporter
After=network.target
[Service]
User=node_exporter
Group=node_exporter
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/node_exporter
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Now lets start and enable the node_exporter service using below commands
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable node_exporter
sudo systemctl start node_exporter
sudo systemctl status node_exporter
We have covered How to Install Prometheus and Grafana on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS with Node Exporter.

#15. Configure the Node Exporter as a Prometheus target
Now to scrape the node_exporter lets instruct the Prometheus by making a minor change in prometheus.yml file
sudo nano /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
-job_name: 'Node_Exporter'
scrape_interval: 5s
static_configs:
- targets: ['<Server_IP_of_Node_Exporter_Machine>:9100']
After changing in config file you need to restart to prometheus
Now restart the Prometheus Service
sudo systemctl restart prometheus
Hit the URL in your web browser to check weather our target is successfully scraped by Prometheus or not
https://localhost:9100/targets

#16. Creating Grafana Dashboard to Monitor Linux Server
Now lets build a dashboard in Grafana so then it will able to reflect the metrics of the Linux system.So we will use 14513 to import Grafana.com, Lets come to Grafana Home page and you can see a “+” icon. Click on that and select “Import”

Now provide the Grafana.com Dashboard ID which is 14513 and click on Load

Now provide the name and select the Prometheus Datasource and click on Import.

There you are done with the setup. Now your Dashboard is running up!.
#17. Install WMI Exporter on Windows
For Windows hosts, you are going to use the Windows exporter.
You can download the latest version of windows installer from here

When the download is done, simply click on the MSI file and start running the installer.

After Installation of WMI Exporter lets check its sucessfully installed or not
So go to services and search windows exporter.
Make sure windows exporter service is running.

Now that your exporter is running, it should start exposing metrics on
http://localhost:9182/metrics
So let’s check

#18. Configure the WMI Exporter as a Prometheus Target
Now run the below command to update config file
sudo nano /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
Update config file with below code:
- job_name: "WMI Exporter"
# metrics_path defaults to '/metrics'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
static_configs:
- targets: ["Host_ip:9182"]
Now save the file nd exit
After changing in config file you need to restart prometheus server with below commands:
sudo systemctl restart prometheus
sudo systemctl status prometheus
Hit the URL in your web browser to check weather our target is successfully scraped by Prometheus or not
https://localhost:9182/targets

#19. Creating Grafana Dashboard to monitor Windows server
Now lets build a dashboard in Grafana so then it will able to reflect the metrics of the Windows system.
So we will use 14510 to import Grafana.com, Lets come to Grafana Home page and you can see a “+” icon. Click on that and select “Import”

On the next window, simply enter the dashboard ID in the corresponding field

Now provide the name and select the Prometheus Datasource and click on Import.

There you are done with the setup. Now your Dashboard is running up!

Conclusion:
In this article we have covered Install Prometheus and Grafana on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS with Node Exporter and WMI Exporter | Windows and Linux Server Monitoring using Prometheus and Grafana.
Related Articles:
Kubernetes cluster Monitoring with Prometheus and Grafana
Reference:
Prometheus official site
Grafana official site
Уровень сложностиПростой
Время на прочтение5 мин
Количество просмотров42K
Немного расскажу про установку Grafana на windows и настройку базовых метрик системы.
Пару слов о самой Grafana и для чего она нужна.
Grafana – это платформа для мониторинга, анализа данных и визуализации собранных данных с открытым исходным кодом. По сути она используется для визуального представления собранных метрик для более комфортного слежения за состоянием системы.
В данной статье буду использовать:
-
Grafana
-
Prometheus
-
Windows_exporter
-
Blackbox_exporter
Для начала скачаем актуальный дистрибутив самой Grafana и установим его (Для скачивания, может потребоваться VPN).
Переходим по ссылке: https://grafana.com/grafana/download и выбираем необходимую версию для скачивания.

Затем скачаем и установим Prometheus.
Prometheus по сути является сборщиком метрик. Установив на один пк, который будет выступать в качестве сервера для Grafana, достаточно будет только запускать сбор метрик с других машин (вносить соответствующий блок в файл конфигурации Prometheus), а Prometheus в свою очередь подготовит метрики уже для самой Grafana.
Prometheus: https://prometheus.io/download
Для установки потребуется NSSM — это сервисный помощник, который помогает установить служебные вспомогательные программы.
Ссылка NSSM: https://www.nssm.cc/download
Приступим к установке Prometheus.
Переходим в CMD и вводим следующие команды (запускаем CMD от админа):
-
Переходим в директорию с пакетом NSSM:
cd C:\GrafanaSetup\nssm-2.24\win64 -
Выполняем установку сервиса Prometheus:
nssm.exe install prometheus C:\GrafanaSetup\prometheus-2.43.0.windows-amd64\prometheus.exe

На данном этапе служба Prometheus должны быть установлена, Далее установим службы для сбора метрик.
Установим Windows_exporter – сборщик метрик, который как раз собирает статистику с системы и составляет своего рода «логи».
Ссылка для скачивания Windows exporter: https://github.com/prometheus-community/windows_exporter/releases
Выбираем подходящую нам версию и устанавливаем

После установки, так же проверяем в службах, что установка прошла успешно и служба запущена (название службы по умолчанию windows_exporter).
Теперь можно проверить сбор метрик по ссылке к порту службы: http://localhost:9182/metrics

На данном этапе можем установить Blackbock exporter — используется для мониторинга статуса доступности URL-ов. Переходим по ссылка и скачиваем нужную нам версию Blackbox: https://prometheus.io/download/ и устанавливаем.

Теперь приступим к настройке установленных сервисов.
Начинаем с Grafana:
Переходим в папку C:\Program Files\GrafanaLabs\grafana\conf и открываем файл defaults.ini при помощи текстового редактора и меняем значение в блоке smtp в поле enabled на true и сохраняем изменения. Запускаем службу Grafana, если она уже запущена, просто делаем перезапуск для вступления изменений в силу.

Перейдя по ссылке: http://localhost:3000 увидим активный интерфейс Grafana. Для входа по умолчанию используется комбинация admin / admin, затем попопросит Вас изменить пароль и направит на домашнюю страницу управления Grafana.
Далее приступаем к настройке Prometheus:Нам необходимо внести изменения в конфигурацию, включив метрики в конфиг. Для этого переходим в каталог prometheus») и открываем файл prometheus.yml и вносим следующие изменения:
Добавляем блок для подключения windows_exporter:
- job_name: "Любое комфортное имя"
static_configs:
#IP-адрес и порт, где собираются метрики window_exporter\
- targets: ["localhost:9182”]При добавлении нескольких машин, можно добавить блок lables, который изменит отображаемый IP-адрес на свое описание:
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9182"]
labels:
instance: Server-1
- targets: ["192.168.0.254:9182"]
labels:
instance: Server-2Сразу добавим блок для blackbox_exporter:
- job_name: 'blackbox'
metrics_path: /probe
params:
module: [http_2xx] # Look for a HTTP 200 response.
static_configs:
- targets:
-https://youtube.com
-https://google.com
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- source_labels: [__param_target]
target_label: instance
- target_label: __address__
replacement: localhost:9115 # The blackbox exporter's real hostname:portВ блоке targets перечисляем необходимые URL-адреса.
Только обратите внимание, для того, что бы блок корректно заработал и не было ошибок при запуске службы, необходимо строго соблюдать табуляцию строк.
Добавив необходимые блоки можем запускать prometheus.
Затем убедитесь, что все службы запущены:
-
Grafana
-
Prometheus
-
Windows_ exporter
-
Blackbox_exporter
и теперь проверяем статус сервисов по ссылке: http://localhost:9090/targets

В целом мы настроили базовые метрики, осталось включить отображение метрик в Grafana.
Переходим на главную страницу grafana ( По умолчанию: http://localhost:3000 ).
Подключаем источник данных Prometheus:
На главной странице, переходим в меню Data sources
Выбираем наш Prometheus

И указываем наш URL. В нашем случае, всё находится на одной локальной машине и можем прописывать через формат: http://localhost:port/

И нажимаем кнопку: Save & test
Теперь необходимо настроить панели мониторинга для метрик windows exporter. Для настройки переходим на главную страницу и добавляем панель:

На момент написания статьи, нашёл два наиболее охватывающих Dashboard`а:
-
14510
-
14694
Можете использовать их или же настроить всё самостоятельно.
Для добавления Dashboard`а указываем в поле ID и нажимаем на кнопку Load.

Затем нас направляет на панель настроек, где мы указываем источник данных Prometheus и можем изменить имя самой панели. Затем жмём кнопку Import
И у нас уже готовая, настроенная панель мониторинга, которую уже можно добавлять необходимым функционалом. Не нужные графики можно удалить или расставить в нужном для себя порядке.

При добавлении новых пк для мониторинга, достаточно внести строки в конфигурационный файл Prometheus.yml и перезапустить службу Prometheus. Служба самостоятельно разберёт метрики и добавить новый пк к мониторингу на уже готовый dashboard, где уже не составит труда переключаться между пк.
Далее уже можно поиграть с конкретными метриками, и отображением конкретных служб с различных машин. К примеру: На главном экране нажимаем ADD > Visualization и попадаем в меню создания панели. В поле Metrics browser вносим выбранную метрику и указываем параметры, которые хотим получить (ну или отобразить). Сделаем на примере службы windows:
-
Name — имя службы
-
State — вид статуса, который относится к метрике windows_service_state
-
Instance — с какой конкретной машины брать метрику.
windows_service_state{name="нужная служба", state="running", instance="Server-1"}
и в правом верхнем углу выбираем нужный вид панели, в моем случае это Stat:

В параметрах панели в меню Value mappings и меняем цифровые значения метрик на удобные для восприятия слова, к примеру: Ok/Bad Up/Down.

Сохраняем и получаем такую панель :
Ну и настроим метрику для получения статусов HTTP:
Используем метрику: probe_http_status_code и настроим Value mapping:
probe_http_status_code{instance="https://youtube.com"}

И в итоге получаем такую панель:
Далее можно самостоятельно зайти в http://localhost:9090/targets выбрать нужные для своих задач метрики и настроить нужные под свои задачи.
Думаю, на этом можно закончить. Базовая настройка не так сложна, но когда ты сталкиваешься с этим в первый раз, могут возникнуть трудности, поэтому хотел поделиться пошаговой настройкой. Надеюсь, кому-то это поможет и сократить достаточно времени на поиске информации и первичной настройки.
Grafana is an advanced, web-based data analysis program for Windows, Linux, and other platforms. In this guide, we’ll show you how to install Grafana on your Windows Server system.
Downloading Grafana on Windows Server
To get started with Grafana on your Windows Server, you need first to download the software. To download it, head over to the official download page. Once there, find “Windows,” and select it with the mouse.
Upon selecting “Windows,” find “Windows Installer (64-bit)” and download it to your Windows Server. Alternatively, if you wish to use a standalone Grafana binary, you can download a ZIP file. However, the standalone binaries are not recommended if you are not an expert, and we will not be covering this method of Grafana on Windows Server in this guide.
Once you’ve downloaded the Grafana EXE file to your computer, open up Windows Explorer, and select the “Downloads” folder. Once there, find the Grafana MSI file and double-click on it to start up the installation wizard.
With the Grafana installation wizard open, you’ll see “Welcome to GrafanaEnterprise Setup Wizard.” Read the welcome message, and then select the “Next” button to move to the next page in the installation tool.
After selecting the “Next” button, you will be presented with the “End-User License Agreement.” This is a long legal agreement. Read it. When you’ve finished reading it, check the “I accept the terms in the License Agreement” box. Click the “Next” button to continue when done.
With the EULA accepted, you’ll be presented with the “Custom Setup” page. On this page, select the components of Granfana you wish to install on Windows Server. By default, everything is selected. Customize the installation to suit your needs. Click the “Next” button when done to continue.
On the next page, the installation tool says it is “Ready to install GrafanaEnterprise.” Find the “Install” button, and click on it with the mouse. When you select this button, it’ll start the installation process.
When you select the “Install” button, Grafana will install itself to your computer. This process should be quick. When the installation is finished, find the “Finish” button, and click it to close the installation tool.
Accessing Grafana
Now that the Grafana application is installed on your Windows Server device, you’ll need to access it. To access Grafana on your Windows Server, start by launching a web browser on the Windows Server desktop. Once it is open, navigate to the following URL in Microsoft Edge, or whichever web browser you prefer to use on the Windows Server Desktop Experience.
http://localhost:3000/login
Alternatively, if you wish to access Grafana from other computers on your network, you’ll need to use the local IP address of your Windows Server.
http://windows-server-ip-address:3000/login
If you do not know your Windows Server’s local IP address, you can open up a PowerShell window and enter the command below. Note that this command assumes your server’s network device is “Ethernet”. If it isn’t, you’ll need to replace it.
(Get-NetIPAddress -AddressFamily IPv4 -InterfaceAlias 'Ethernet' | Where-Object {$_.PrefixOrigin -eq 'DHCP'}).IPAddress
After accessing the Grafana URL in your browser, you’ll need to log in. By default, Grafana is set so that users log in with admin for a username and admin for the password. Enter this information to log into Grafana.
When you enter the default username and password, Grafana will immediately prompt you to change your password from the default. Enter a memorable, and secure password. If you’re having trouble thinking of a good password, try the BitWarden password generator.
Getting started with Grafana
Grafana is an incredibly complex data visualization app. As a result, it would take a lot of words to cover how to master it in this article. Thankfully, when you log into Grafana for the first time, you’ll be met with the “Basic” area.
In the “Basic” area, locate “TUTORIAL DATA SOURCE AND DASHBOARDS” and click on it using the mouse. This in-depth tutorial, provided by the developers of Grafana, can quickly get you up and running with the app, helping you set up dashboards, data sources, and more.
For more information on getting started with Grafana on your Windows Server, check out the official documentation. This documentation is in-depth and covers just about everything you need to know about it.

Resources, Security, Getting Started
15 min read
Last updated:
Grafana is a data analytics and monitoring software that is considered to be a transformative open-source tool that enables organizations to visualize and analyze data in real time. Grafana creates interactive and dynamic dashboards, which then allow users to gain significant business sense from the data they have retrieved making them informed in their decision-making process for effective operational efficiencies. Whether it is DevOps, business intelligence or system administration, Grafana stands out as the preferred open source solution because of its strong features and flexibility.
Various data sources are able to be used with Grafana due to its adaptability through which it has gained popularity across various different sectors. The user-friendly interface coupled with powerful functionalities of this software allows users to come up with custom dashboards not only showing critical metrics but also giving suggestions on what actions can be taken based on the insights.
In this article will give an insight into some of the best Grafana dashboards and visualizations that help make monitoring simpler and will help you to improve business outcomes.
Contents
- Grafana dashboards explained
- How to create a Grafana Dashboard
- How has Grafana grown in recent years?
- How can Grafana be used for Docker monitoring?
- How can Grafana be used for virtual machine monitoring?
- What information does the Grafana dashboard for Node exporter provide?
- Why were these specific Grafana examples chosen?
- 1. Server Monitoring
- 2. Lighthouse Metrics Report
- 3. Weather Forecast
- 4. Performance Testing
- 5. Monitoring Global ISP Latency
- 6. Windows Host Monitoring
- 7. OpenVPN Connection Monitoring
- 8. Tracking Udemy Progress
- 9. Fitbit Health Monitor
- 10. TrueNAS Dashboard
- 11. Homelab Monitoring & Cost Analysis
- 12. Forecasting Stocks
- 13. Docker Monitoring
- 14. SSL Expiry Tracker
- 15. AWS Billing Estimator
- 16. Kubernetes Cluster Monitoring
- 17. GitLab CI Pipeline Status
- 18. Kong Monitoring
- 19. Alertmanager Visualisation
- 20. Monitoring Spring Boot Microservices
- 21. Spark Streaming Monitoring
- 22. HDD Temperature Monitor
- 23. Nextcloud Audit Log Dashboard
- 24. Strava Monitoring Dashboard
- 25. Monitoring Linux Processes
- 26. Monitoring Redis
- 27. Graphite
- 28. Grafana Billing Dashboard
- 29. Kubernetes Integration Efficiency
- 30. Loki NGINX Logs
Grafana dashboards explained
Grafana dashboards are incredibly powerful for visualizing and analyzing data from a wide variety of sources. It acts as a single pane of glass, enabling users to view and interact with their metrics and log data through various visualizations. This is essential for monitoring system performance, detecting trends, troubleshooting issues in real-time and for providing an overarching view into the data being ingested.
There are many options for representing your data within a Grafana dashboard. For instance, tables present information in an easily comparable format while timelines show events over time so you can track changes or incidents occurring during that particular period. Time series charts plot out points against each other according to when they occurred which makes these a great option for keeping an eye on any metric that changes over time. Stat panels highlight important measurements by displaying them prominently. Bar charts compare different values side-by-side and pie charts break down one value based on their proportional size compared against other values being measured.
What sets Grafana dashboards apart as a visualisation tool is its flexibility and ability to be customized. Grafana dashboards can also connect to various data sources such as traditional databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL. It also supports time-series databases such as InfluxDB and Prometheus. Moreover its support for Elasticsearch makes log analysis possible while Grafana’s REST APIs integration allows working with custom source types to achieve holistic system visibility across multiple environments.
Alerting and notification capabilities are another area where Grafana really shines, as users have full control over configuring their alerts based on the data being collected. Users are able to define an alert rule upon which notifications should fire once certain condition has been met. Notifications themselves can be sent via email, Slack integration and/or PagerDuty.
To show you how much you can do with Grafana dashboards we’ve collected the top open-source Grafana visualisations and reports to inspire you to get started with this leading data visualisation tool.
How to create a Grafana Dashboard
Creating a dashboard in Grafana is particularly simple, the complexity tends to come from the initial configuration of Grafana. However, this can be completely removed by opting for a hosted solution such as hosted Grafana from Logit.io. With our solution, you gain all the best features of Grafana but without all the time-consuming and challenging configuration and maintenance, as this will be handled by us. If you’re interested in finding out more about hosted Grafana from Logit.io, don’t hesitate to reach out or begin exploring the platform for yourself with a 14-day free trial.
Below we’ve outlined how you to create a dashboard in Grafana. This method is also applicable for hosted Grafana from Logit.io, just select ‘launch’ next to Grafana from the dashboard and follow the instructions listed below.
-
Create a dashboard: Once logged in, click on the «Create» button in the left-hand sidebar to create a new dashboard.
-
Add panels: A Grafana dashboard consists of panels, which are individual visualizations or data displays. To add a panel, click the «Add new panel» button on the dashboard.
-
Configure panels: After adding a panel, you can configure it by clicking on its title or the gear icon in the top-right corner. Depending on the panel type (e.g., Graph, Singlestat, Table), you’ll have different configuration options.
-
Customise the dashboard: Customize your dashboard layout by clicking the «Settings» (gear icon) on the top-right corner of the dashboard. Here, you can set the dashboard title, define time ranges, apply themes, and adjust other dashboard-level settings.
-
Add rows and panels: You can organize your panels into rows to create a more structured layout. To add rows, click the «+» icon on the left sidebar and choose «Add Row.» You can then add panels to each row.
-
Configure data sources: Grafana connects to various data sources to fetch data for your panels. You need to configure data sources before creating panels. To configure data sources, click on the gear icon in the left sidebar, select «Data Sources,» and add the data source relevant to your use case.
How has Grafana grown in recent years?
Grafana has experienced significant growth in recent years, with its launch in 2014 marking the beginning of its success story. Over time, the platform has garnered increasing recognition and adoption, resulting in a remarkable expansion. This growth trajectory reached a significant milestone in 2021 when Grafana secured an impressive $220 million in funding during its latest funding round. The substantial investment highlights the thriving popularity of Grafana and emphasizes the increasing number of individuals who are recognizing and appreciating its value. The platform’s noteworthy journey demonstrates its continuous growth and the wide-scale appeal it has gained among users.
How can Grafana be used for Docker monitoring?
Grafana can be utilized effectively for Docker monitoring, providing a comprehensive solution for Docker users seeking to manage and monitor their deployments. By employing Grafana, users can keep tabs on crucial statistics such as CPU, memory, disk usage, and traffic. The monitoring dashboard specifically designed for Docker showcases insightful details such as average, maximum, and current values for each tracked metric.
One of the notable advantages of using Grafana for Docker monitoring is its user-friendly nature. With minimal configuration required, it seamlessly integrates into Docker environments. This means that users can start benefitting from the monitoring capabilities right out of the box, without the need for tedious and complex setup procedures.
The positive reviews and feedback received by Grafana’s Docker monitoring solution further attest to its efficiency. With this tool at hand, users gain a broad overview of their entire deployment, allowing them to quickly detect and address any issues that may arise. Grafana’s Docker monitoring offers an effortless way to stay informed about the performance and health of Docker containers, making it an ideal choice for Docker users who value efficiency and ease-of-use in their monitoring process.
How can Grafana be used for virtual machine monitoring?
Grafana can be effectively utilized for monitoring virtual machines. By utilizing Grafana, users can track crucial metrics such as CPU usage, memory usage, network activity, and filesystem usage of their virtual machines.
Notably, this tutorial incorporates an intelligent alerting system, which leverages Slack to promptly notify users if any of the monitored metrics surpass the defined thresholds. Additionally, this monitoring solution relies on Prometheus, along with node-exporter, to gather and visualize the metrics effectively on the Grafana dashboard. Overall, Grafana proves to be an excellent tool for efficient virtual machine monitoring, offering comprehensive insights and proactive alerting capabilities.
What information does the Grafana dashboard for Node exporter provide?
The Grafana dashboard for Node exporter provides a vast range of information, presenting almost every value exported by the Prometheus Node exporter. Users can explore an extensive selection of dials and graphs, which provide an in-depth understanding of the Node’s performance. Additionally, the dashboard offers expandable panels located at the bottom of the interface, which further enrich the available information. This comprehensive overview caters to the needs of Node developers, offering a wealth of data to satisfy their hunger for information. With this dashboard, users can effortlessly monitor and analyze various Node metrics, gaining valuable insights into Node’s activities.
Why were these specific Grafana examples chosen?
These specific Grafana examples were carefully selected based on various factors. Firstly, some of these dashboards were chosen for their technical excellence, demonstrating the powerful capabilities of the Grafana platform. These examples showcase how the platform can handle complex data visualizations and analytics, serving as an inspiration for users looking to explore its potential.
Furthermore, the selected dashboards are also remarkable for their interesting range of use cases presented, which highlight the versatility of the Grafana platform. These unique implementations demonstrate that Grafana can be utilized in diverse ways, encouraging new users to think outside the box and explore innovative possibilities for their future monitoring projects.
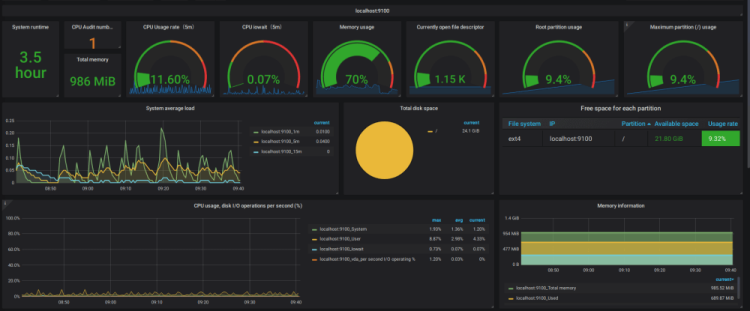
1. Server Monitoring
Credit: @Hector Smith
As the vast majority of Sysadmin’s realise, server monitoring is an essential part of monitoring the overall health of your environment.
This reporting dashboard uses a combination of Grafana, Prometheus & Node Exporter to allow you to pinpoint the root cause behind servers going down and enables you to take preemptive steps if you find you are running low on available disk space.
2. Lighthouse Metrics Report
Credit: @WikiMedia
Whilst many marketing specialists may not have much awareness of Grafana we think it is no excuse for not delving into its capabilities and experimenting, as this example above shows.
This dashboard displays all of the metrics that are included within Google’s own Lighthouse report and provides a way of being able to dive deeper into these metrics at any time without the need to perform a new audit from scratch.
Unlock complete visibility with hosted ELK, Grafana, and Prometheus-backed Observability
Start Free Trial
3. Weather Forecast
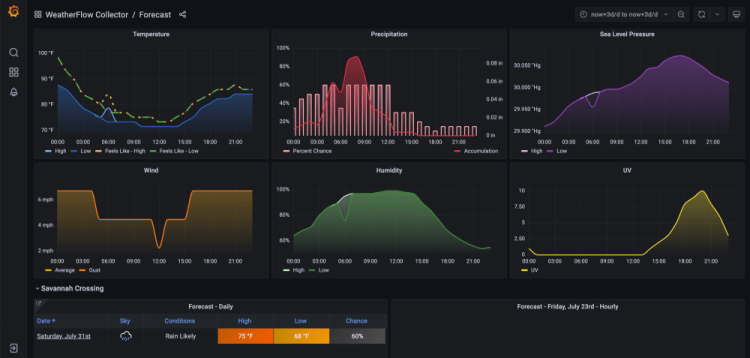
Credit: @WeatherflowCollector
This Grafana dashboard example can be used to view weather conditions, upcoming forecasts, overall temperature & precipitation.
As this dashboard is hosted by Grafana’s gallery you are free to experiment with the live dashboard within your browser, saving you from having to configure your own local setup to start improving your knowledge of this data visualisation tool.
Want to recreate this dashboard for yourself? Then check out the original creator’s Github repo.
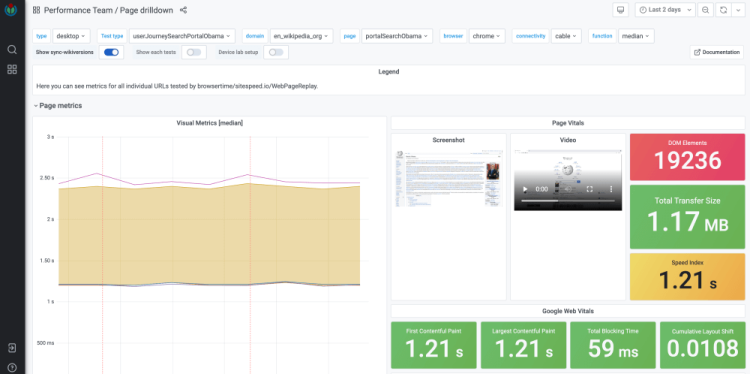
4. Performance Testing
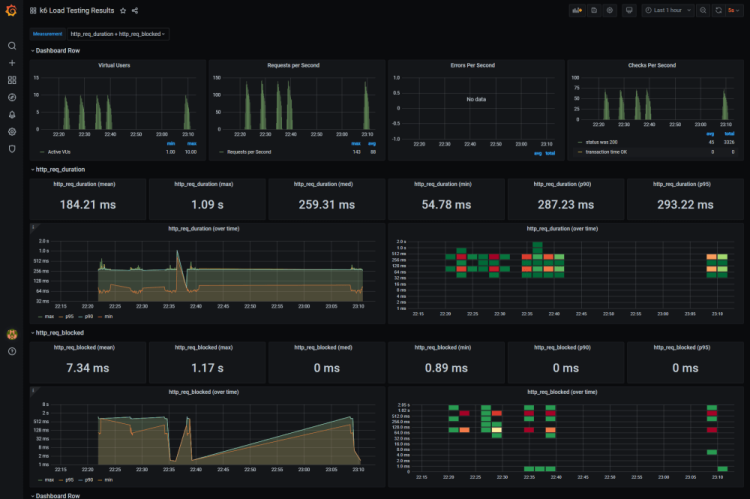
Credit: @Nigel Mulholland
Being able to conduct reliable performance testing is vital for assuring the quality of software that you are releasing to your users.
By putting workload and pressure against your system you can analyse if it behaves as expected or if you need to do further work to improve your code or scale up your operations to meet the demands of high traffic load
5. Monitoring Global ISP Latency
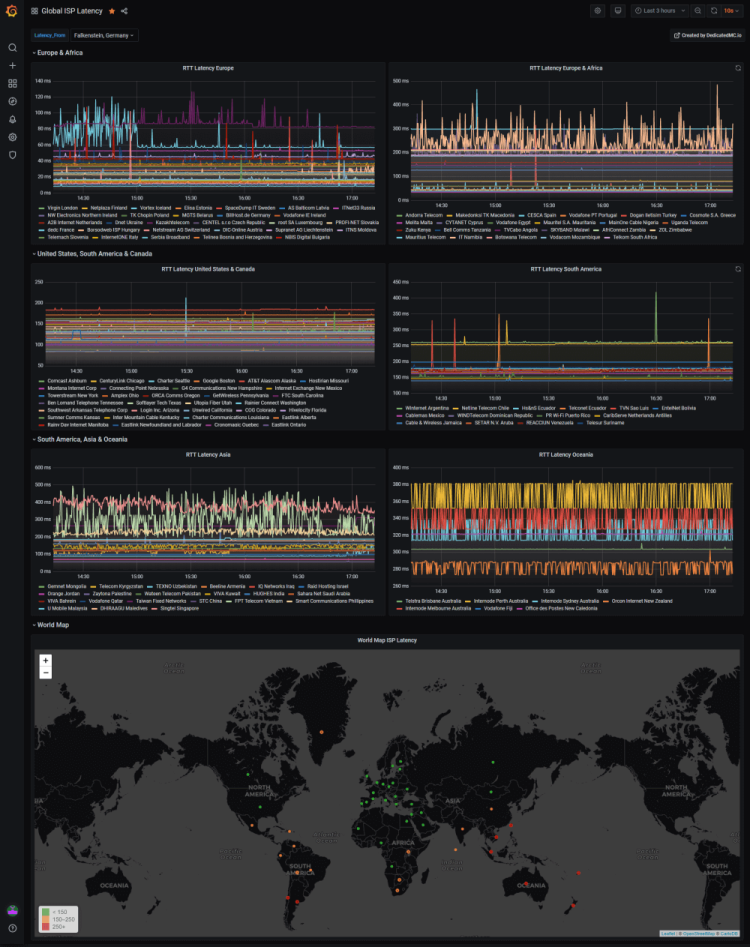
Credit: @Tehlo
This Grafana Dashboard uses InfluxDB and Telegraf to display the latency of over two hundred ISP endpoints from around the world.
The original creator of this intuitive dashboard created this as they host a gaming company and wanted to give their users the best possible experience by being able to explain that a
6. Windows Host Monitoring
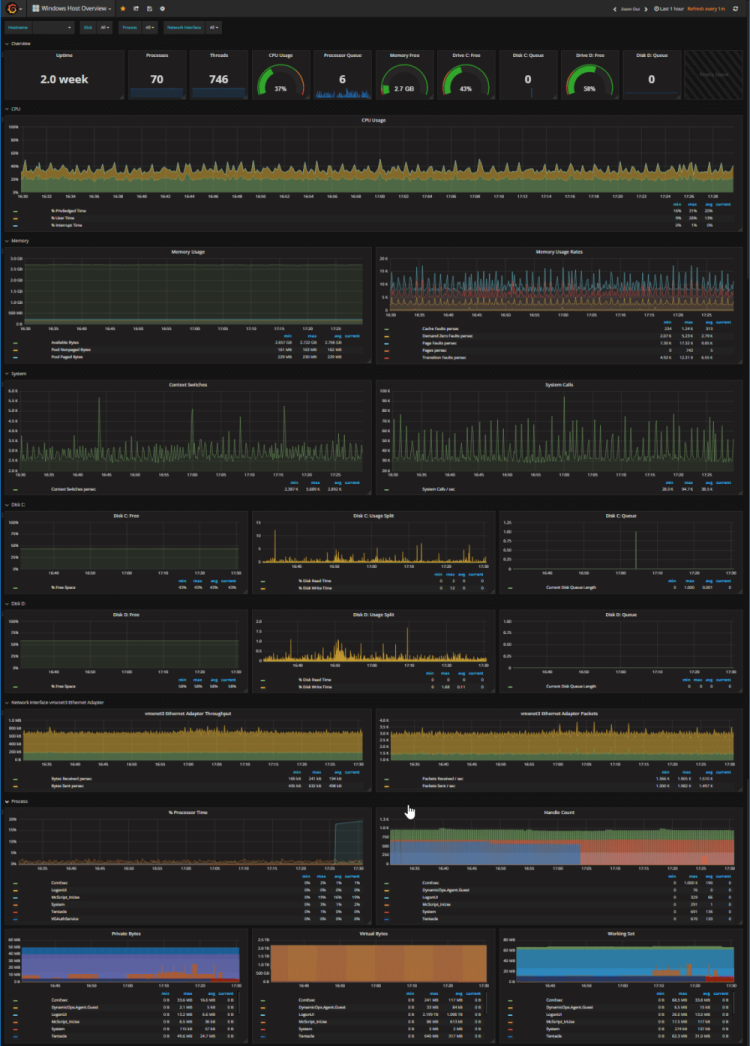
Credit: @David Stephens
If you want to see the memory usage, processes, threats and CPU usage of your Window’s hosts then you should consider using Grafana to create the dashboard above to give you full visibility into the performance of your Window’s host.
This dashboard requires integration with Telegraf and Influxdb, otherwise, there will be panels that are not populated with data as a result.
7. OpenVPN Connection Monitoring
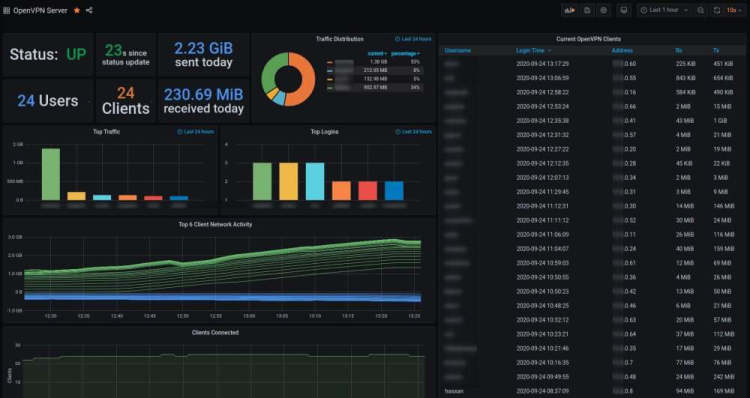
Credit: @Hassan Momin
As well as using Grafana, this dashboard also uses Prometheus to monitor OpenVPN connections. This report displays status, time since status update, data sent and received today alongside the number of users and clients.
If you want to have a go at creating your own monitoring service for OpenVPN then check out this guide.
8. Tracking Udemy Progress
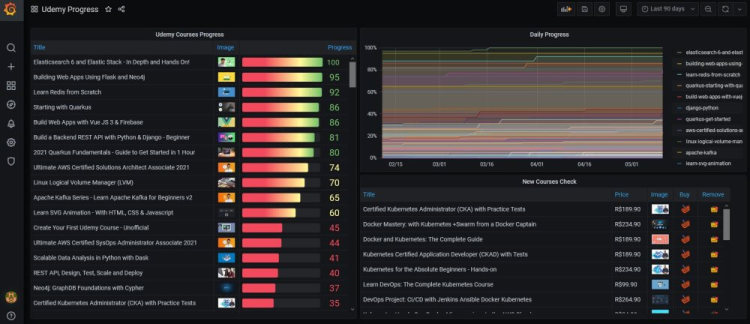
Credit: @crashlaker
This unique report uses Loki alongside Grafana for tracking the user’s progress on completing their Udemy courses by percentage and daily progress.
This dashboard took an admirable degree of manual work by the original creator (as they encountered limits when using Udemy’s official API for data scraping).
If you want to grab your own copy of this Grafana dashboard template then you may be waiting a while as the original creator hasn’t linked their guide yet. As soon as they have, you can be sure that we’ll add it to this post!
9. Fitbit Health Monitor
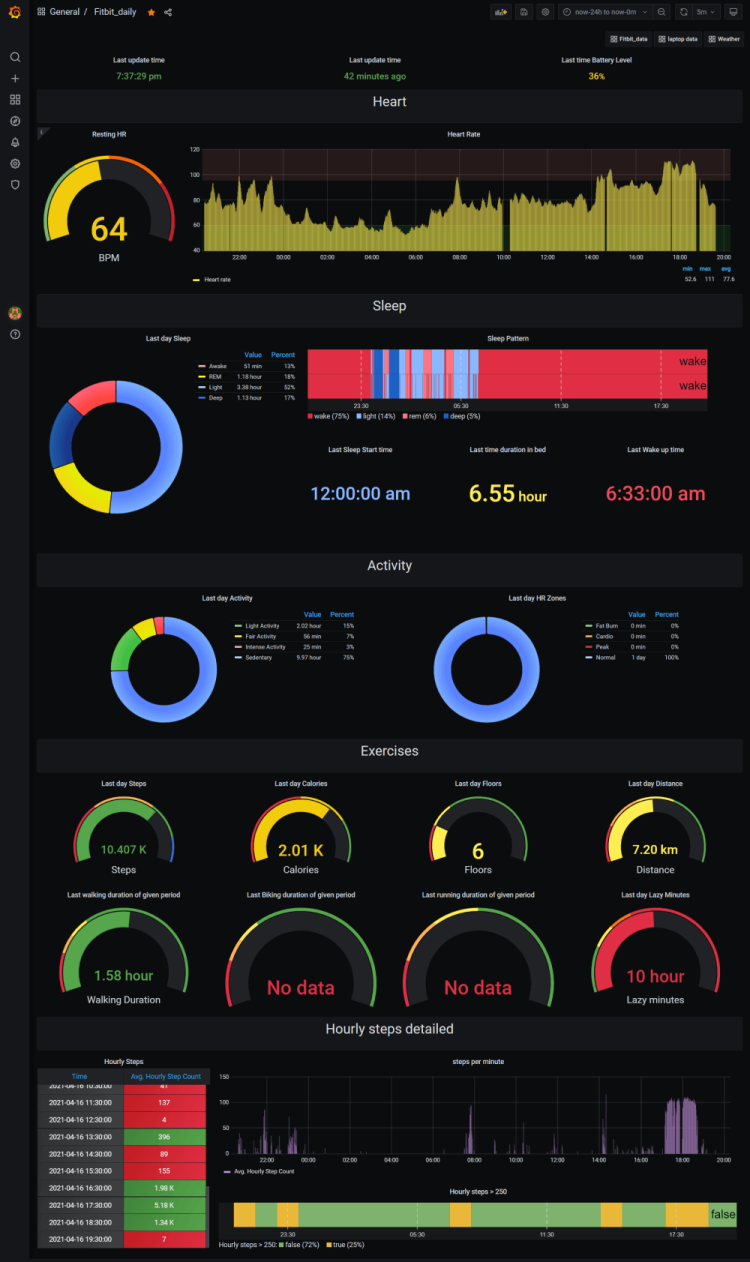
Credit: @Arpanghosh8453
The next dashboard in our list of the most ingenious ways to use Grafana uses the Fitbit API to pull together key metrics regarding heart health, activity, calories burnt and sleep quality of whoever is using the device being measured.
If you want to have a go at creating this dashboard for your own health and activity monitoring, then why not have a browse of the original Github repo?
10. TrueNAS Dashboard
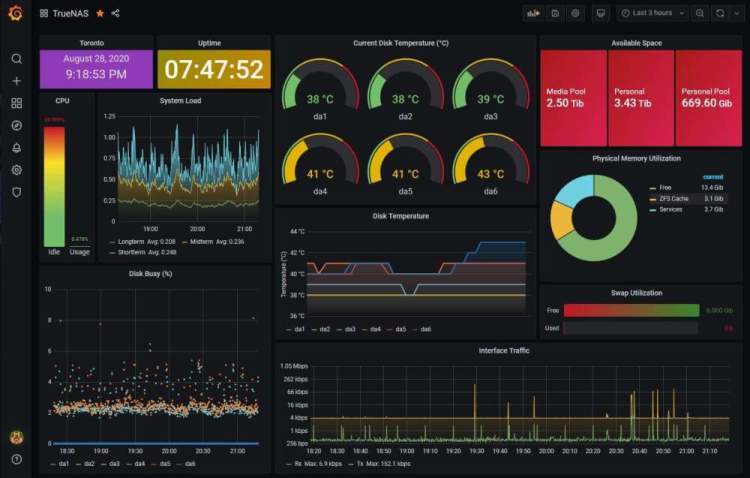
Credit: @thinhla
TrueNAS is a Network Attached Storage (NAS) software that shares and protects data from modern-day threats like ransomware and malware.
This report captures the full performance of your TrueNas devices and displays key metrics including: location, uptime, current disk temperature, available disk space, disk busy and interface traffic levels.
11. Homelab Monitoring & Cost Analysis
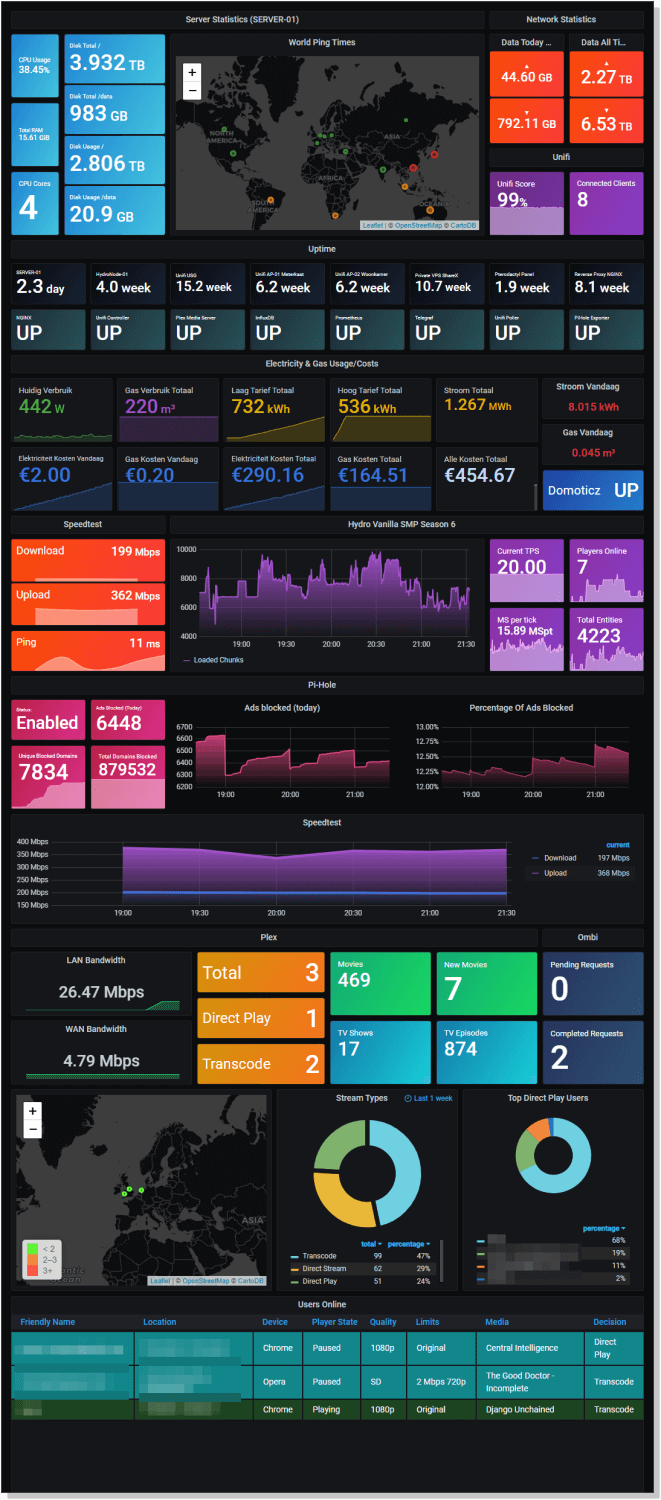
Credit: @Tehlo
This homelab dashboard is in a league of its own and was one of our favourite uses of Grafana out of the examples we considered for this roundup.
This highly detailed visualisation centralises not only server and network statistics but also displays the gas and electricity costs associated with this comprehensive homelab setup.
If you want to get your hands on the template to create this homelab monitor for yourself then you’ll need to head on over to the Github repo for the project.
12. Forecasting Stocks
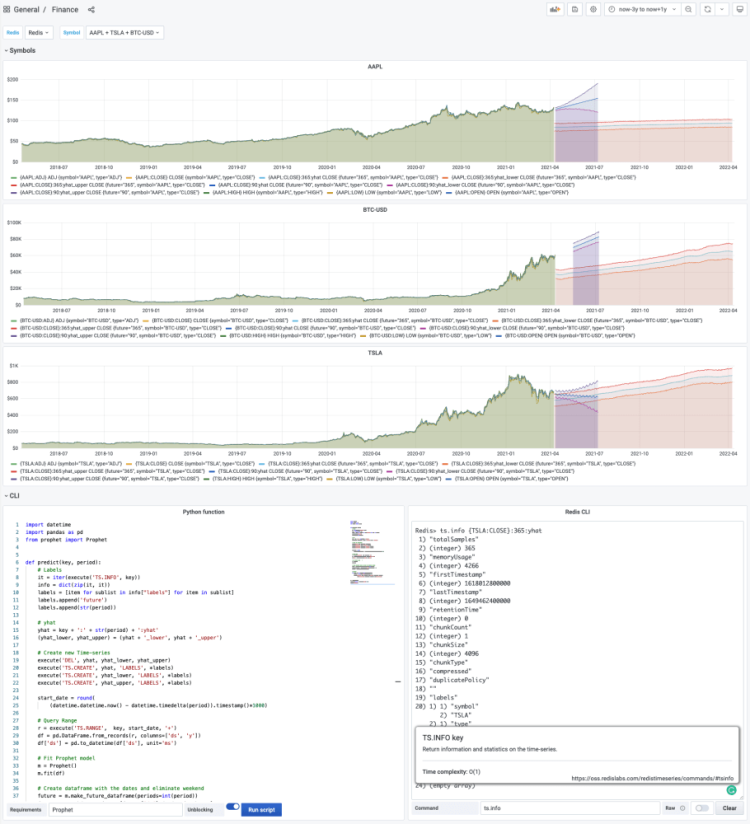
Credit: @Mikhail Volkov
This ingenious dashboard combines using the Redis Application plug-in with Grafana alongside Facebook’s Prophet model to predict prices of stocks and forecast future cryptocurrency prices.
13. Docker Monitoring

Credit: @Nazar
Another one of Grafana’s key use cases is its capability for container monitoring as shown in the example above regarding Docker monitoring.
The view configured above displays the following essential metrics with clarity: total running containers, total memory usage, total CPU usage, network RX & network TX.
When it comes to avoiding container bottlenecks, monitoring is the best safeguard you can have to ensure visibility of the performance of your containerised applications and overall infrastructure.
14. SSL Expiry Tracker
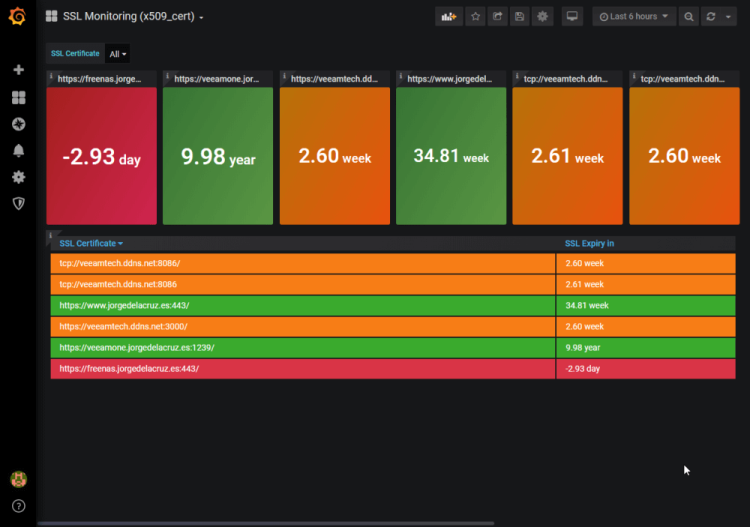
Credit: @Jorge de la Cruz
If you own numerous domains then you might quickly find that monitoring the validity of all of your SSL certificates to be quite tedious and you may require a dashboard to improve your visibility of when your certificates are due to expire.
This SSL monitoring dashboard uses Grafana & InfluxDB to show you which certificates are valid, which are expiring soon and which ones have already expired (and by how many days).
By proactively monitoring your SSL certificates you can take further steps to avoid outages and subsequent loss of revenue and damage to your brand’s reputation as a result of not being available to your customers.
15. AWS Billing Estimator
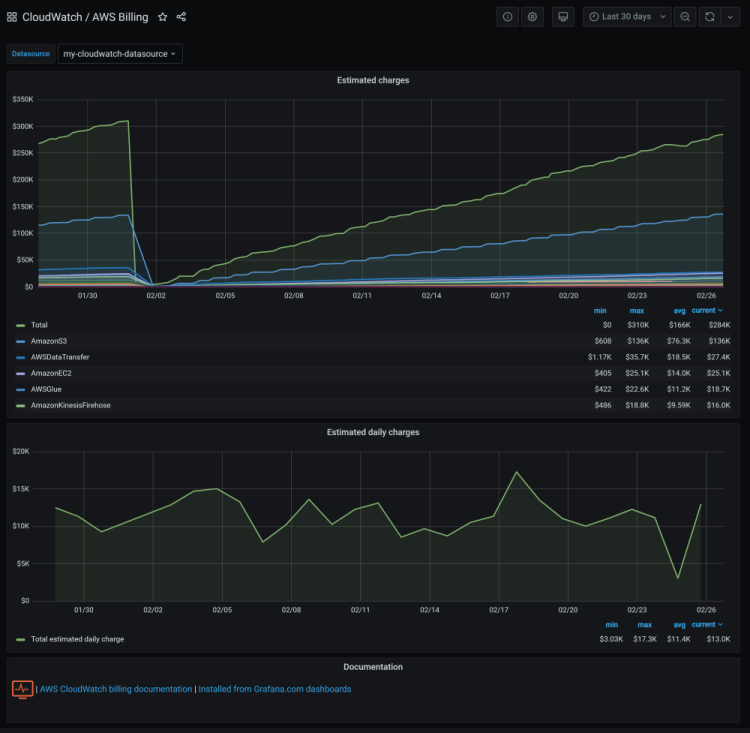
Credit: @Monitoring Artist
As AWS billing is often known for being quite hard to predict, we are sure that many AWS users will find the Grafana dashboard above to be a good workaround for estimating their monthly and daily charges.
This view also splits out individual AWS services by cost, allowing you to see charges for S3, EC2, Glue & Kinesis side by side.
16. Kubernetes Cluster Monitoring
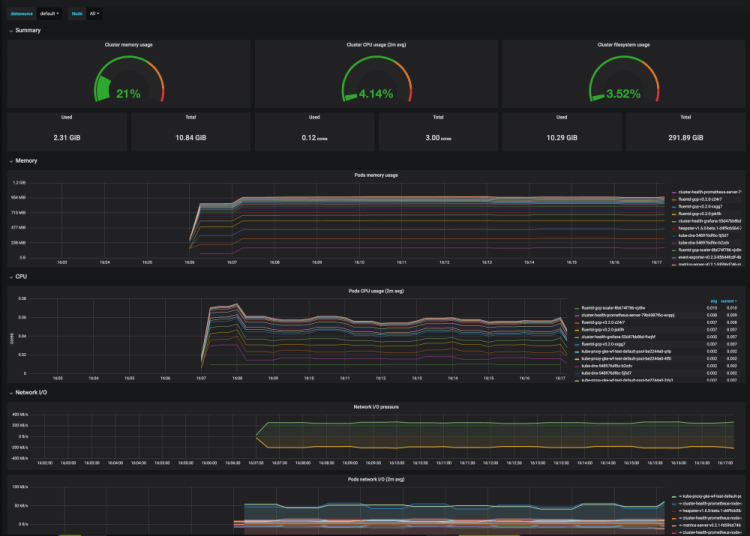
Credit: @Pivotal Observability
If you are a developer that already uses Kubernetes, then you’ll know firsthand just how important it is to actively monitor Kubernetes clusters to ensure that resources are being used efficiently.
For this use case, Grafana provides an alternative Kubernetes dashboard for analysing which nodes are contributing to workload bottlenecks and see metrics relating to pod CPU usage, network I/O pressure and memory usage split out by pod.
17. GitLab CI Pipeline Status
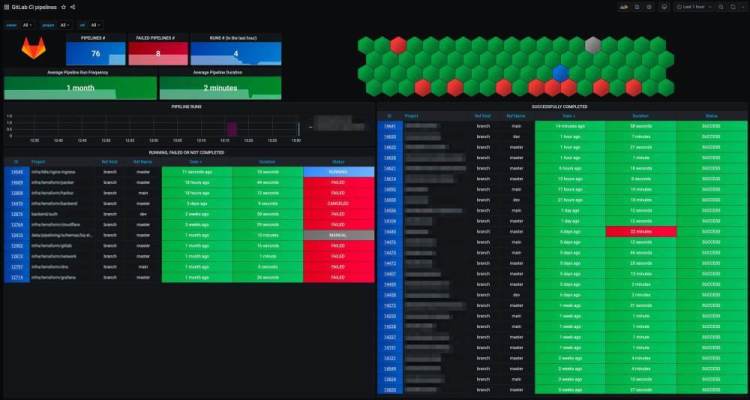
Credit: @Mvisonneau
In case you were not already familiar with all of GitLab’s key features then you might not know that they provide a continuous integration service that builds and tests code as you push it to the application.
If you already use GitLab CI or wish to get started with this feature then you may soon find the Grafana dashboard we’ve included above useful. This dashboard displays total pipelines, any failures, pipeline runs within the last hour, successfully completed jobs and the average pipeline runtime duration.
If you are new to using Gitlab or have only used Github in the past then why not check out our expert-led review comparing Github vs Gitlab?
18. Kong Monitoring
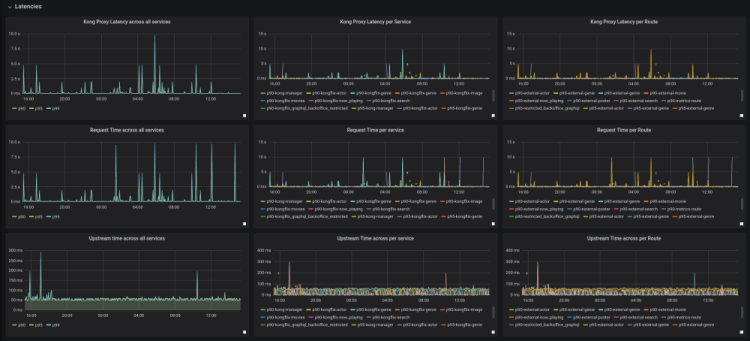
Credit: @KongHQ
Kong is a popular API gateway that serves as middleware and extends the capabilities of APIs through the use of additional plugins.
This dashboard example allows you to visualise total requests per second (RPS), requests per service, Kong memory usage by Node as well as Nginx connection states shown by time-series graph.
You can even find a similar and simpler dashboard and function in Google Apigee. However, you can compare Apigee vs Kong based on your requirements and decide which one works for you.
19. Alertmanager Visualisation
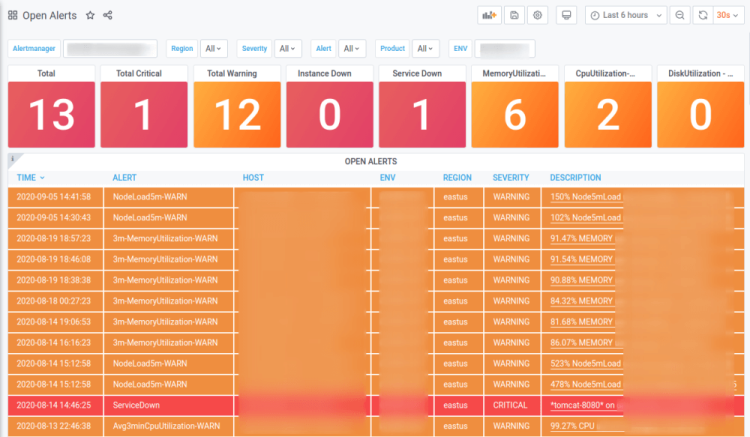
Credit: @Shubham Choudhary
When the creator of this dashboard was tired of manually searching for specific alerts through Slack, teams & emails they soon found out that there was a far better way of displaying this information concisely using Grafana and Prometheus.
By using Alertmanager’s API as a data source for Grafana the software engineer behind this tutorial was able to bypass using the default Alertmanager UI.
As a result of implementing this reporting dashboard, the cognitive load was reduced among the team and it also made prioritising highly important errors easier which assisting in reducing the organisation’s overall MTTR (mean time to recovery).
20. Monitoring Spring Boot Microservices
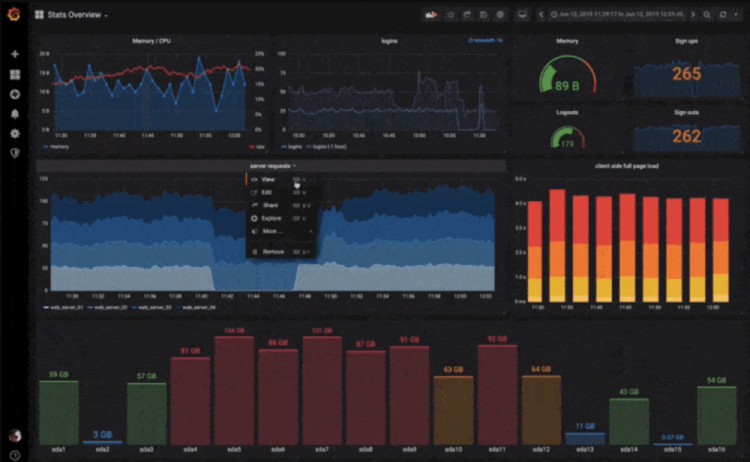
Credit: @Firas Messaoudi
In our next example of a dashboard that uses Grafana alongside Prometheus, we’ve found a great example of how you can get started with monitoring your Spring Boot microservices.
Spring Boot is a popular choice for developers that wish to create production-ready applications swiftly, so we are sure that many of our readers will find this animated tutorial helpful to your next microservice led project.
If you are new to the concept of microservices then why not check out our article on Microservices vs APIs?
21. Spark Streaming Monitoring

Credit: @Dima Statz
Software architects can use this Grafana dashboard alongside Prometheus to monitor streaming from Apache Spark on Kubernetes.
This dashboard can be used to provide a monitoring and alerting alternative to those who are used to using managed solutions such as AWS EMR or Azure Databricks but wish to build their own in-house reporting solution.
Want to get started with creating your own Grafana dashboards? Then sign up today for our managed Grafana platform and start creating dashboards within minutes with our 14-day free trial, no credit card required.
22. HDD Temperature Monitor
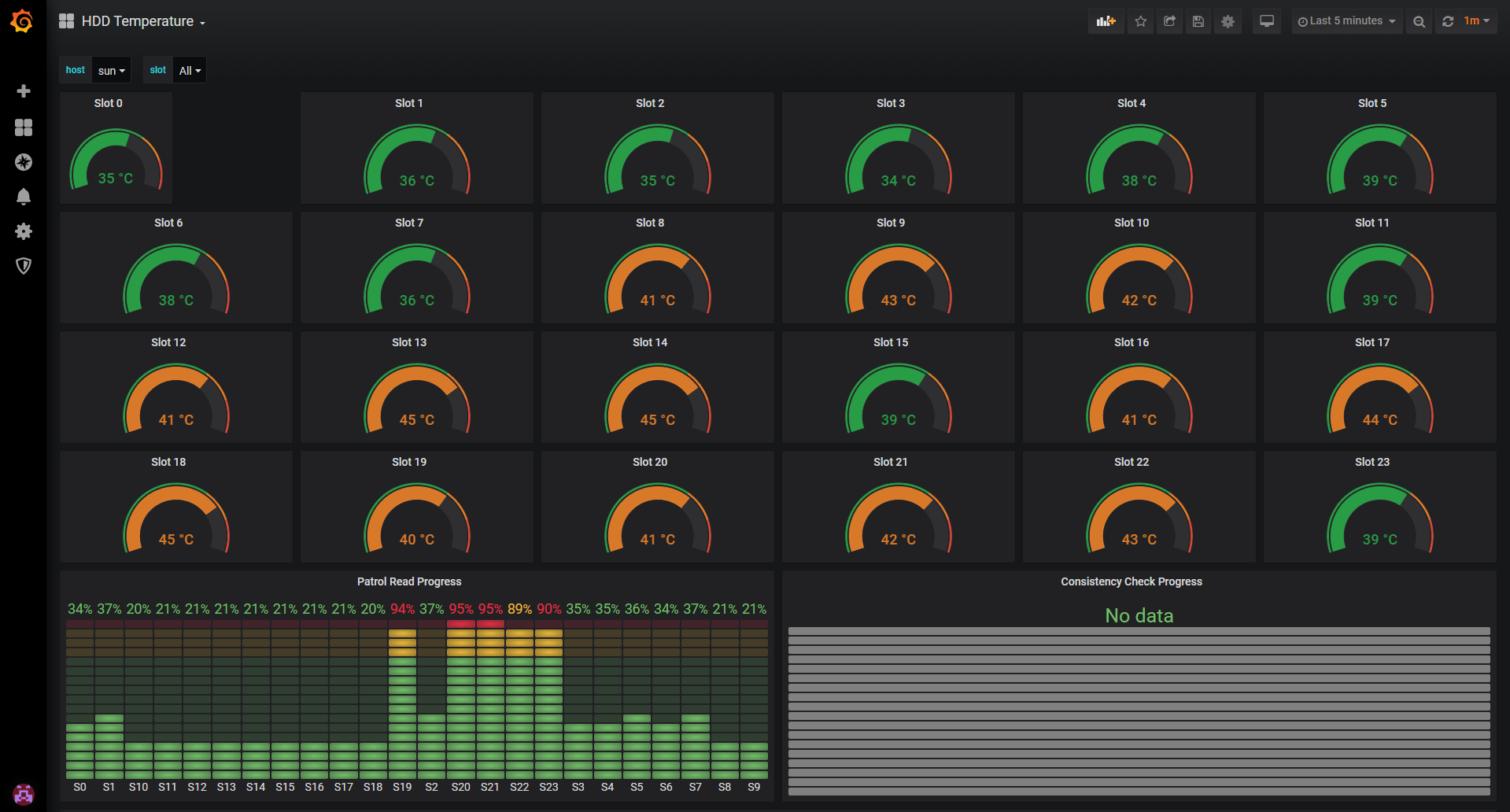
Credit: @anywhoever
Hardware specialists state that the average HDD temperature should be around 35 Celcius, so if your set-up is often far hotter than this you may wish to invest in a solution that offers hard drive cooling.
It is one thing knowing what temperature you should meet but dynamically monitoring all of your HDDs is another use case for monitoring entirely. This Grafana dashboard provides clarity and awareness to the user to let them know if they should be concerned with the current state of their hardware’s temperature.
23. Nextcloud Audit Log Dashboard
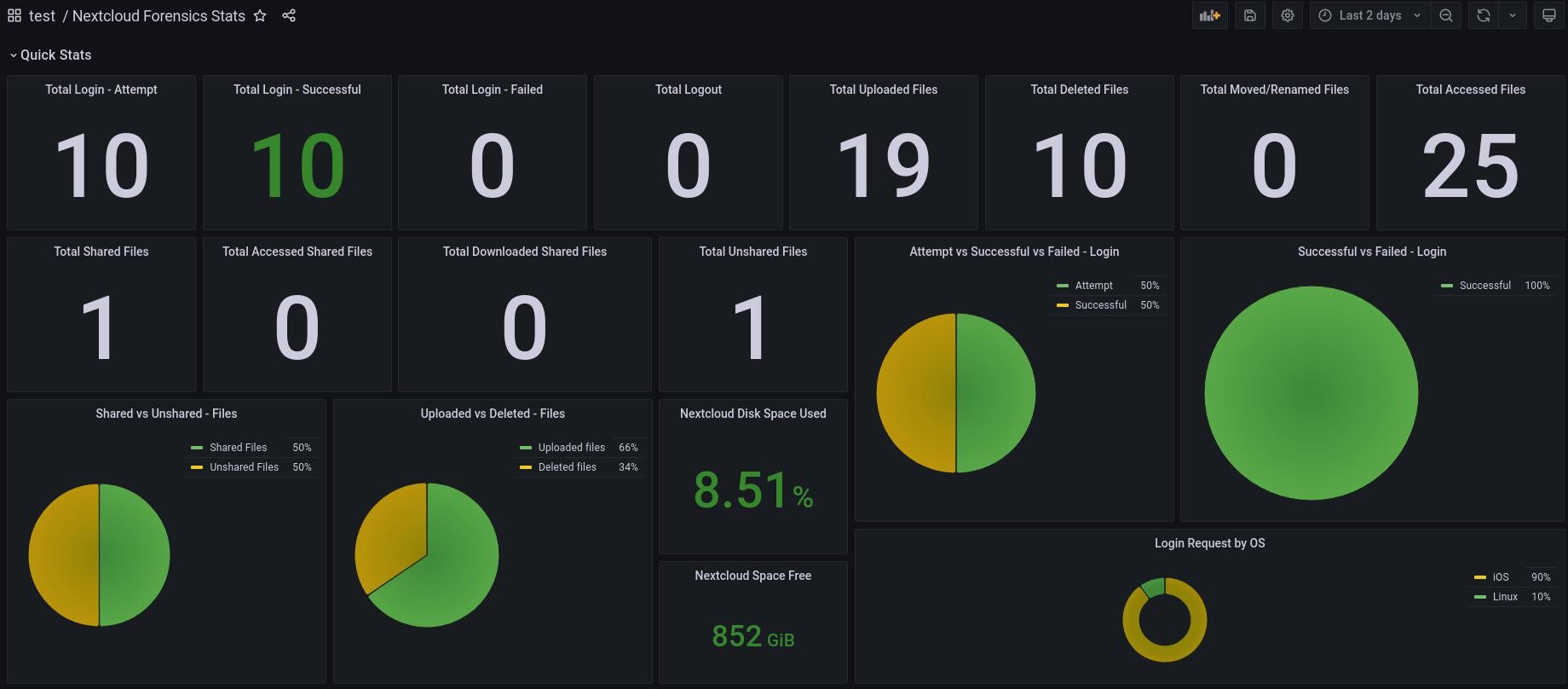
Credit: @tvojamatka
If you are looking to monitor the activity of your Nextcloud server, then hopefully our next Grafana dashboard will inspire you to get started with reporting on the metrics that matter to your system’s performance.
As you can see from the preview above, this forensic dashboard captures total logins, total uploaded files, total shared files, as well as total failed logins and total accessed files.
For this dashboard to work, this setup requires integration with Loki and Promtail, the latter of these integrations aids with the collection of logs, much like how Logstash works as part of the ELK Stack.
24. Strava Monitoring Dashboard
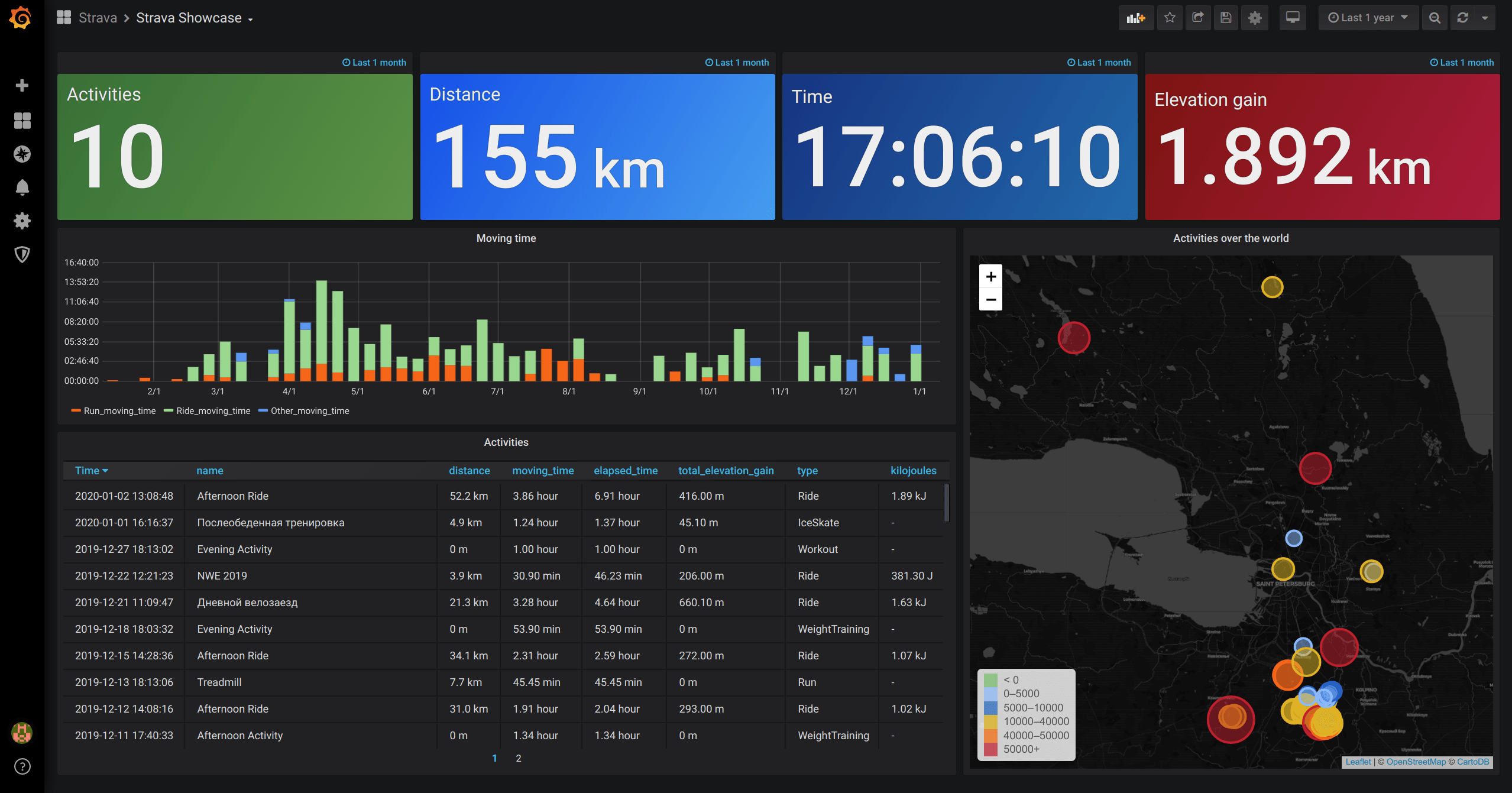
Credit: @Grafana Labs
For another health and wellness-themed addition to this list, we’ve found an example dashboard that displays usage metrics from the popular cycling and running platform Strava.
As this dashboard is yet another example dashboard that is hosted by Grafana’s gallery you are also free to download this visualisation to experiment with and configure for use on your own machine.
25. Monitoring Linux Processes
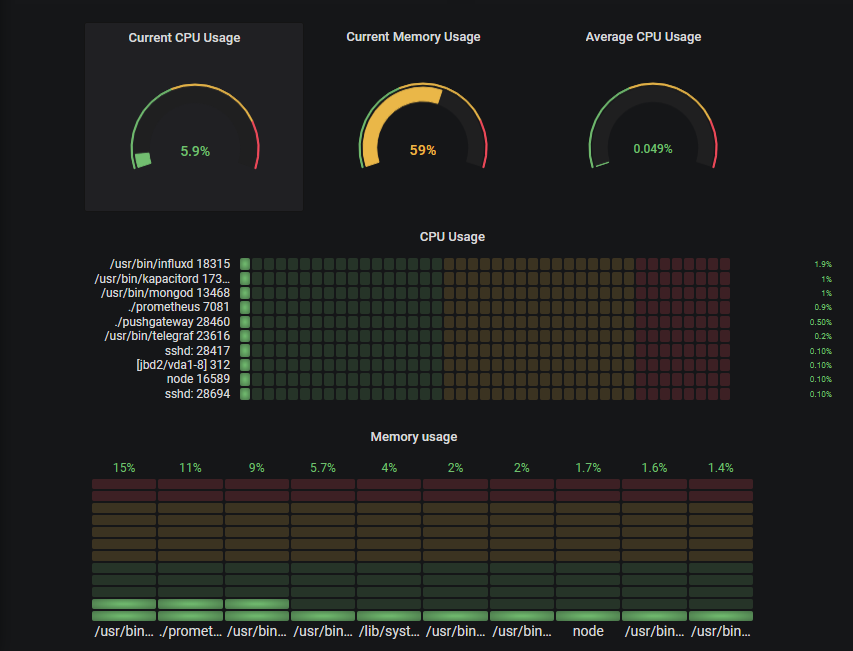
Credit: @SCHKN
This reporting dashboard uses Prometheus in addition to Grafana to monitor Linux machine processes. This monitoring dashboard is likely to be useful to both DevOps and Linux system administrators and anyone else whose role values tracking server performance metrics.
This report helps to highlight which of your instances are running too slowly, as well as also displaying unresponsive instances that have happened as a result of unresolved bottlenecks.
If you wish to attempt creating this dashboard for yourself then you may wish to follow the steps outlined in this tutorial.
26. Monitoring Redis
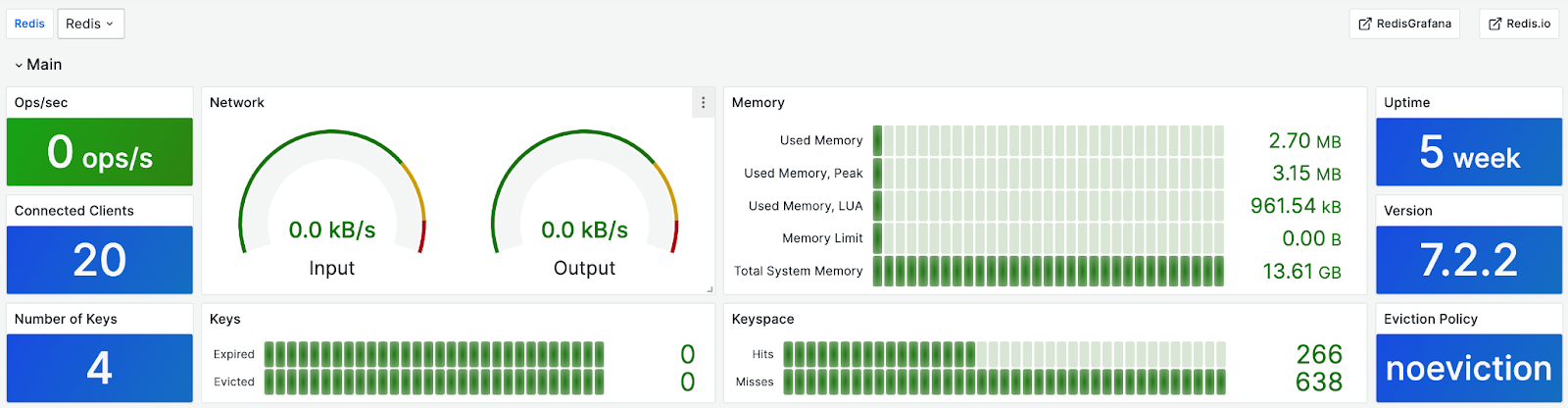
Redis is an extensive Open-source database, the tool is ideal for caching and data storage, as well as streaming and messaging. This Grafana dashboard provides monitoring capabilities for Redis, allowing users to clearly view metrics such as total system memory, used memory, and uptime.
If you wish to recreate this dashboard, you can view it here and learn more about the range of metrics provided for monitoring Redis.
27. Graphite
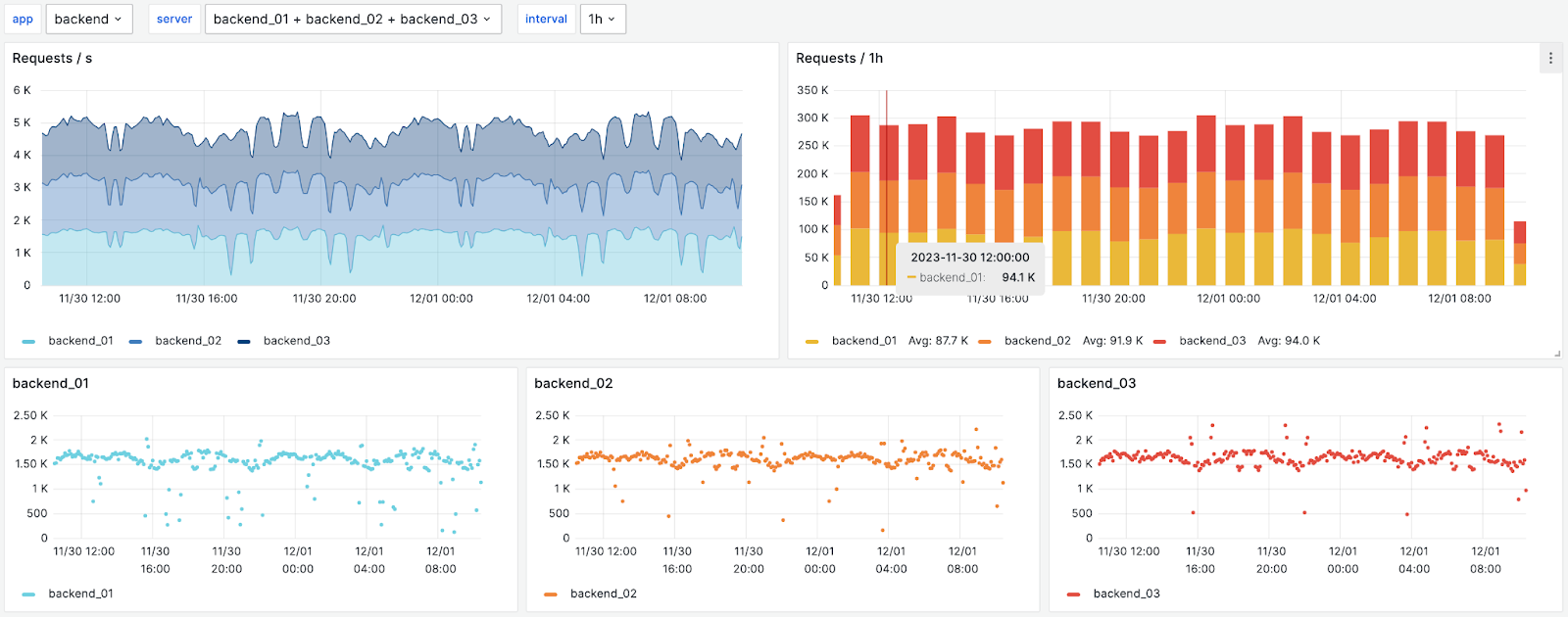
Graphite is a time-series database and visualization system utilized for monitoring and analytics, that can work equally well on when used on premise or cloud infrastructure. This Grafana dashboard supplies metrics for Graphite.
If you want to replicate this dashboard, access it here to explore the multiple metrics available for monitoring Graphite.
28. Grafana Billing Dashboard
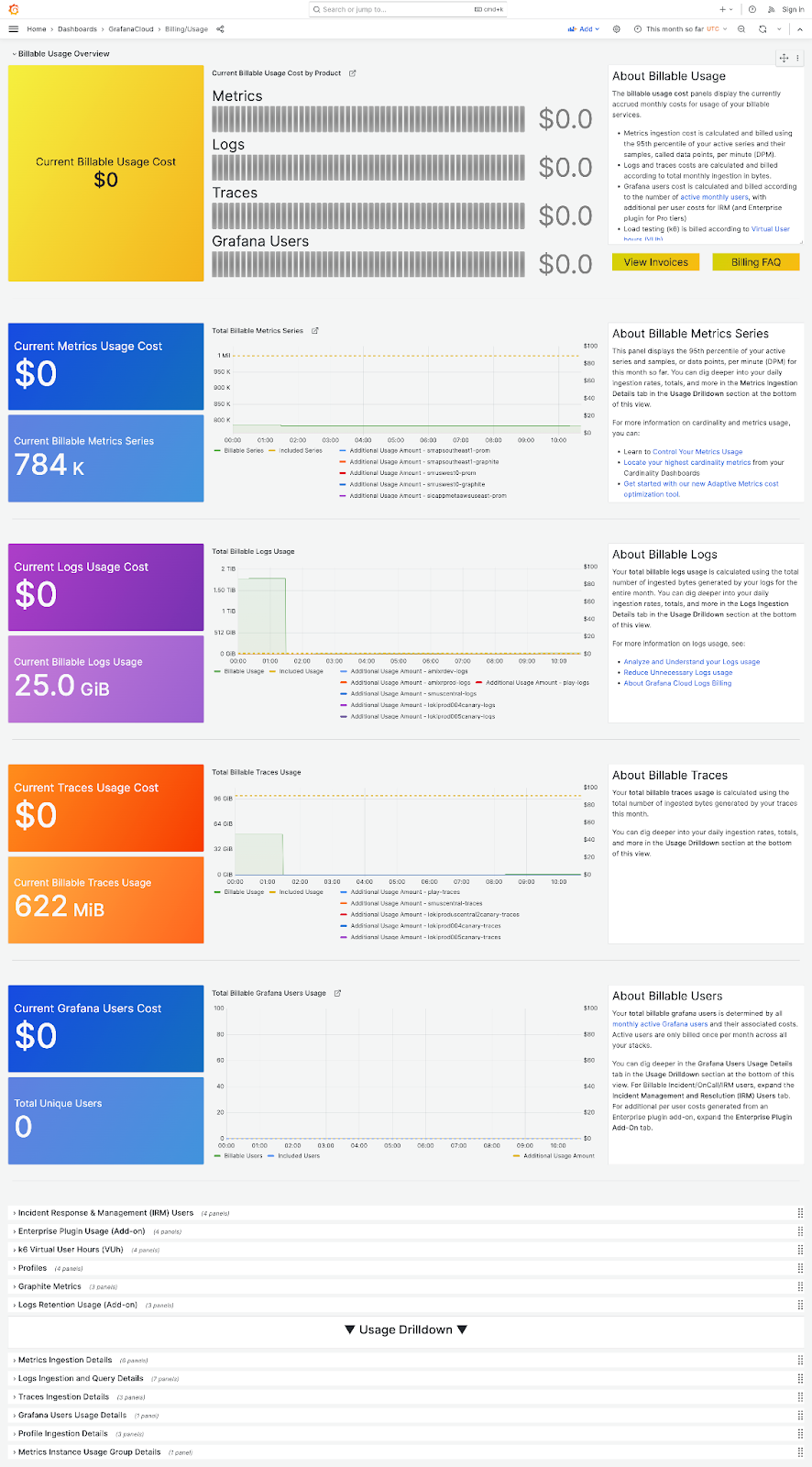
This Grafana billing usage dashboard is a powerful visualisation offering real-time insights into monthly costs associated with billable services. Providing a holistic view, it displays metrics, logs, traces, and user data, aiding in resource optimization. Users can conveniently access invoices and billing FAQs, promoting financial transparency and efficient cost management. To ensure seamless financial operations, it also clearly outlines the invoice payment terms, helping users understand the due dates, accepted payment methods, and any applicable penalties for late payments.
29. Kubernetes Integration Efficiency
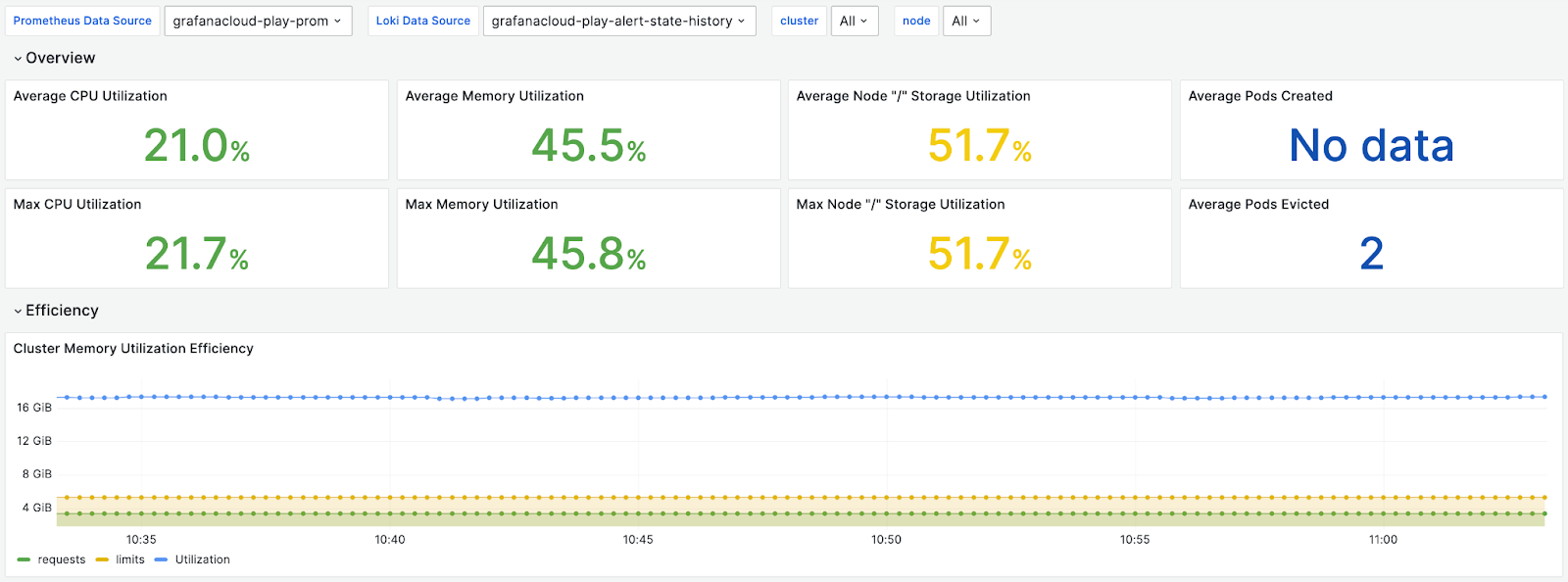
With the Kubernetes integration efficiency dashboard, you can easily view and monitor a range of metrics associated with the efficiency of your cluster. For example, you can monitor, average CPU utilization, average memory utilization, max CPU utilization, and cluster memory utilization efficiency.
Monitoring this enables you to acquire a complete picture of the performance and efficiency of your cluster. This allows you to maximise resources.
30. Loki NGINX Logs
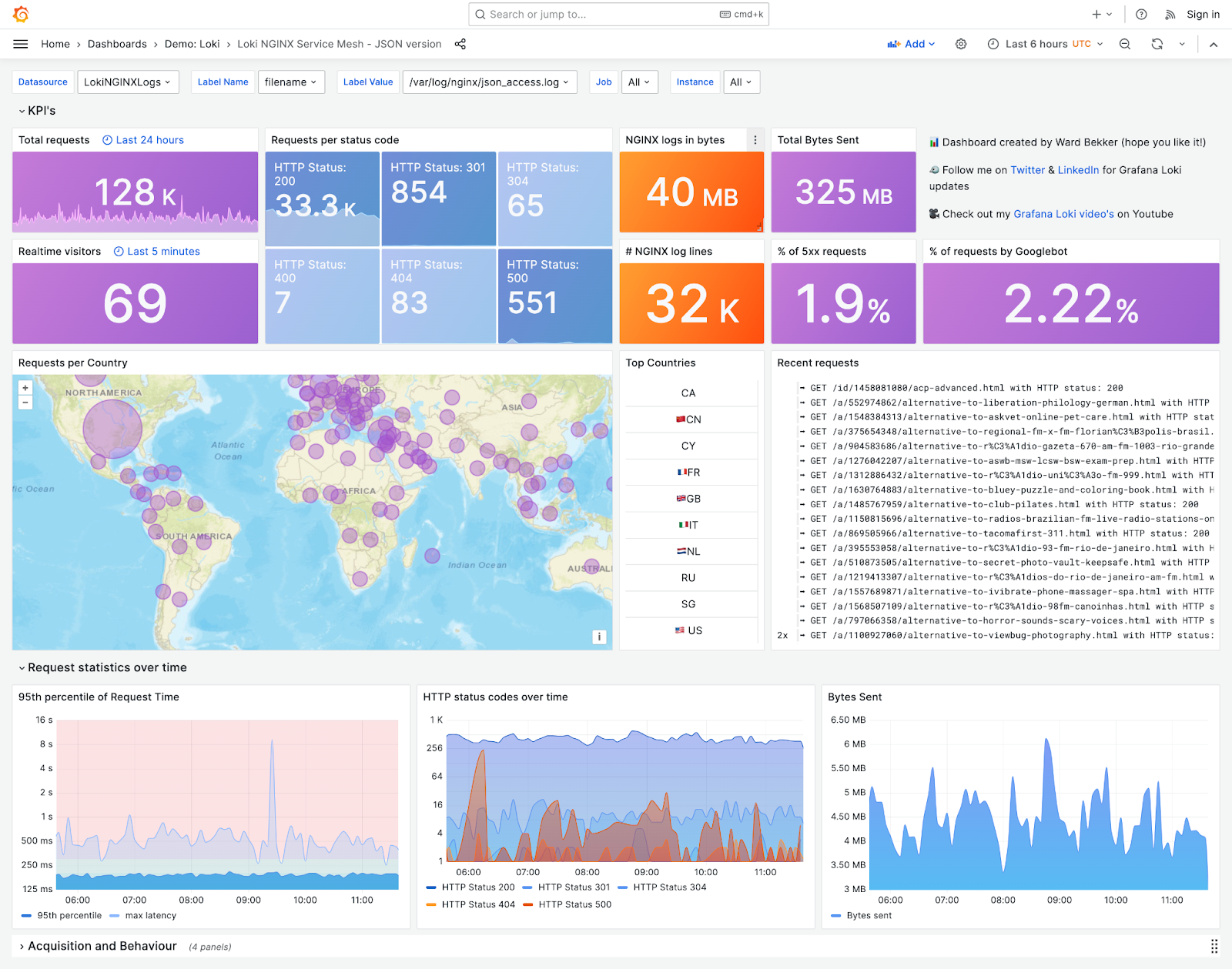
NGINX is a popular web server and reverse proxy server, it produces logs that record numerous events and transactions related to web requests and server activity. With this Grafana dashboard, you can view and monitor various KPIs related to your NGINX logs such as requests per status code, realtime visitors, and total requests.
These dashboards illustrate the vast uses of Grafana. If you’re looking for the simplest option to implement Grafana at your organization then Logit.io’s hosted Grafana is the perfect solution. You can utilize the best of Grafana almost instantly with a rapid onboarding process and if you encounter any issues or have specific requests our Grafana documentation and extensive integration guides can support your efforts. Also, we are here to help, feel free to contact us or reach out via live chat, found in the bottom right corner of our website and dashboard.
Unlock complete visibility with hosted ELK, Grafana, and Prometheus-backed Observability
Start Free Trial
If you enjoyed this post then why not check out our guide to the best Kibana dashboard examples or our previous post on SIEM tools?
