У меня на домашнем компьютере стоит две операционные системы, Windows 7 и Linux (Arch). Причем вторая появилась относительно недавно. Да и особых знаний о новой (для меня) ОС не было. Тем не менее систему я поставил и даже относительно настроил под себя. Энтузиазм и программерское любопытство меня пересиливало, поэтому, в качестве ознакомления, стал экспериментировать с различного рода пакетами. К сожалению, не всегда вчитываясь в детали.
Решил я переставить Grub, а точнее обновиться до Grub2. (Слышал я такое мнение, что в духе Linux принято держать последнюю версию пакета… Про изменения Grub2 хорошо написано тут.)
Ну и как результат «спешной» установки — перестала грузиться система. Единственное за что можно было зацепиться — это приглашение командной строки:
grub>
По нажатию на Tab вываливается список возможных команд. Их существенно меньше чем в командной строке Linux, но их достаточно для загрузки системы. Почитав про grub тут я решил загрузить Windows, все-таки тут я пока себя чувствую увереннее. Для этого нужно было указать где находиться загрузчик ОС и передать ему управление:
grub> root (hd0,2) [Устанавливаем корневой раздел и монтируем. Тут главное помнить, на каком разделе стоит операционная система]
Запись (hd0,2) означает устройство диска номер 0 (мастер), раздел номер 2.
что соответствует устройству /dev/sda2 (в моем случае). У вас это может быть или /dev/hd2, или еще что-нибудь, в зависимости от дистрибутива. Нумерация устройств идет по-порядку и начинается с (hd0,1) или /dev/sda1.
Далее вводим:
grub> chainloader +1 [пробел перед "+" важен. сhainloader - передает управление загрузкой по цепочке другому загрузчику. В моем случае это был NTLDR]
grub> boot
NTLDR — это загрузчик Windows.
Система стала грузиться, а раз это дало результат — можно копаться дальше (все-таки не Windows теперь предмет изучений).
Перезагружаемся и вводим снова.
grub> root (hd0,6)
grub> linux /boot/vmlinuz26 root=/dev/sda6 [Загружает указанное linux-ядро (/boot/vmlinuz26) с параметрами(root=/dev/sda6)]
Тут стоит различать команду root (hd0,6) и параметр root=/dev/sda6. Первое монтирует раздел к среде выполнения. А второе указывает где находиться root загружаемой ОС. В моем случае ядро и корень оказались на одном разделе, хотя это может быть не так.
grub> initrd /boot/kernel26.img [Загружает указанный initrd-образ]
grub> boot
Мне это помогло, надеюсь вам это не пригодиться, а если и пригодиться, то поможет.
Кстати, если неправильно указать root, процесс загрузки завершиться ошибкой и появиться приглашение вида:
[ramfs /]#
Можно набрать:
[ramfs /]# ls /dev
и посмотреть список устройств(если вы вдруг его забыли как я).
Моя проблема установки gurb2 была в том, что при установке затер файл меню grub (обычно он находиться /boot/grub/menu.lst), а новый файл не создал. Для создания файла конфигурации надо было выполнить grub-mkconfig.
Если у вас сбились настройки grub, то отличия в командах будут минимальными:
- для загрузки Windows вместо root (h d0,2) надо набирать rootnoverify (hd0,1). Нумерация устройств начинается с (hd0,0), а не (hd0,1). А командой rootnoverify вы устанавите корневое устройство, но не смонтируете его.
- для загрузки Linux поменяется другая команда: вместо linux вам понадобится команда kernel (полный аналог, даже параметры теже).
UPD: дописал про отличия загрузки с grub от grub2. Спасибо bliznezz
In this article, Let’s learn how to boot windows from grub rescue screen. Linux is the best platform available on the planet, it offers great customization. A highly customizable platform like Linux offers enormous benefits but has only one downside that it can potentially break your system and you can eventually land up in Linux grub rescue screen. If you are looking to boot Linux from grub rescue you can refer to this article.
Steps for how to boot windows from grub rescue.
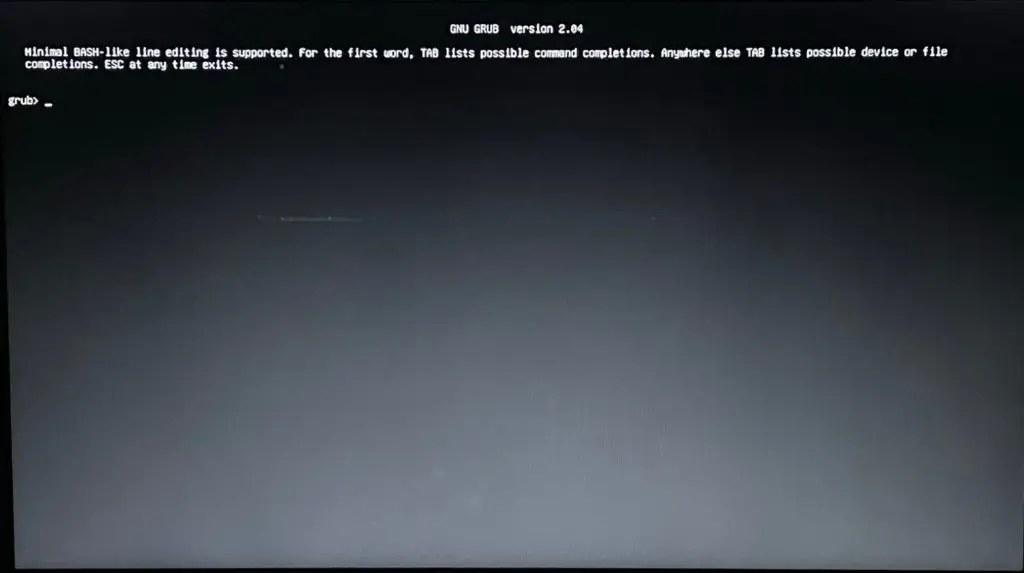
Step 1 — Listing Partitions from Grub Rescue:
First, we need to find out our EFI partition or the partition where your boot files are stored. In order to find that we need to see the available partition, so simply execute the ls command.
ls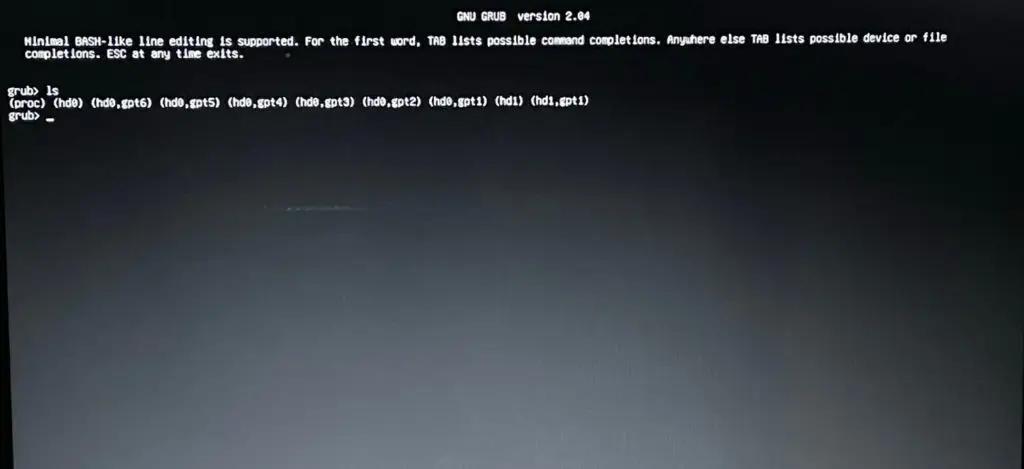
Step 2 — Listing EFI Partition from Grub Rescue
In the first step, we have got our directory listing. Now, we need to find the appropriate partitions where our boot files reside. Typically it resides in a partition that is very small in size (typically less than 1GB) and having an EFI/ partition in it. So, In order to find that you can simply execute the ls (hdx,gpty)/ one by one.
Note: You need to replace x with the hard disk number, and y with the partition number.
ls (hdx,gpty)/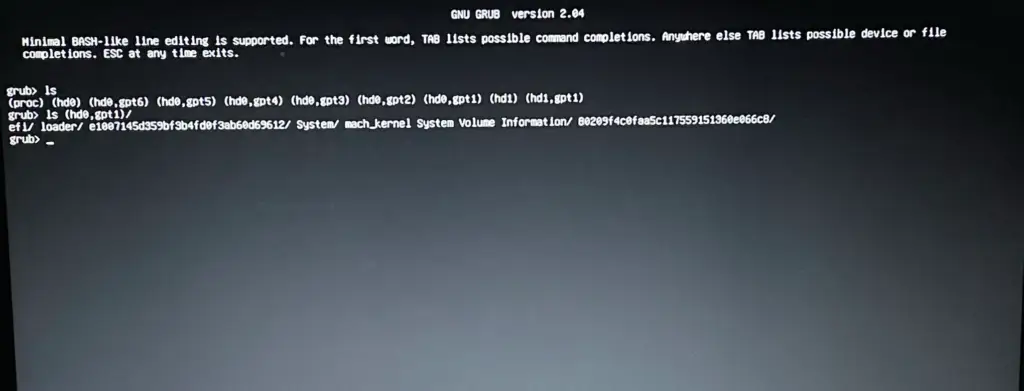
For me, the same is found in (hd0,gpt1)
Step 3 — Select the EFI Partition
Since we have found the partition, now we need to select the partition. So simply execute the below command.
set root=(hdx,gpty)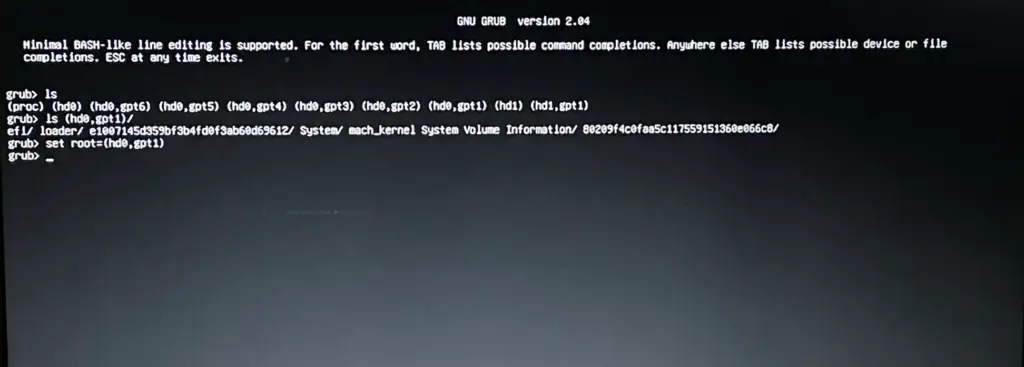
Step 4 — Chainloading the Windows EFI File.
Now, we have selected the partition in which our boot files are present, now we need to execute the command chainloader for loading a boot file, so we can boot from that.
chainloader /efi/Microsoft/Boot/bootmgfwi.efi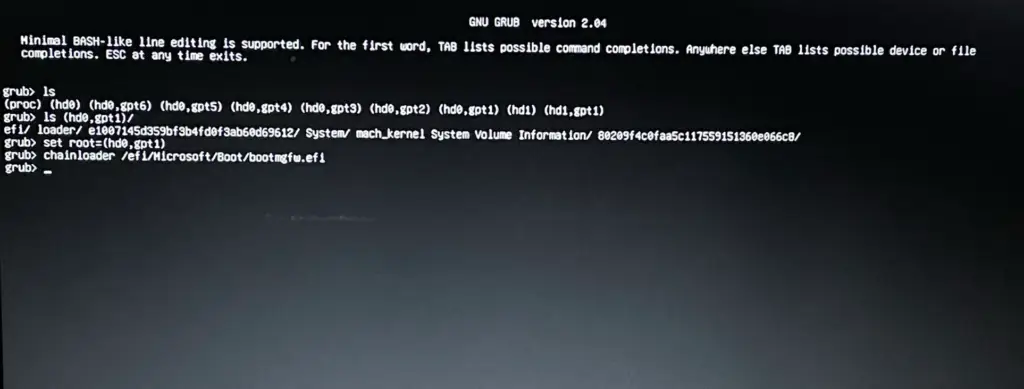
Step 5 — Boot Windows from Grub rescue:
Finally, you are all set to boot windows from grub rescue. Just we need to execute the below command.
bootConclusion — Boot windows:
ls
ls (hdx,gpty)/
set root=(hdx,gpty)
chainloader /efi/Microsoft/Boot/bootmgfw.efi
bootThat’s it for this article, If you have any queries or suggestion please write down in comment section below.
Check out our Latest Best Linux Picks
Linux roman 5.15.0-107-generic #117-Ubuntu SMP Fri Apr 26 12:26:49 UTC 2024 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Linuxmint
Description: Linux Mint 21.3
Release: 21.3
Codename: virginia
NAME="Linux Mint"
VERSION="21.3 (Virginia)"
ID=linuxmint
ID_LIKE="ubuntu debian"
PRETTY_NAME="Linux Mint 21.3"
VERSION_ID="21.3"
HOME_URL="https://www.linuxmint.com/"
SUPPORT_URL="https://forums.linuxmint.com/"
BUG_REPORT_URL="http://linuxmint-troubleshooting-guide.readthedocs.io/en/latest/"
PRIVACY_POLICY_URL="https://www.linuxmint.com/"
VERSION_CODENAME=virginia
UBUNTU_CODENAME=jammy
drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 0 мая 20 20:00 /sys/firmware/efi
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS
sda 8:0 0 465,8G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 50M 0 part
├─sda2 8:2 0 367,5G 0 part
├─sda3 8:3 0 520M 0 part
├─sda4 8:4 0 1K 0 part
├─sda5 8:5 0 513M 0 part /boot/efi
└─sda6 8:6 0 97,2G 0 part /
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
NAME FSTYPE FSVER LABEL UUID FSAVAIL FSUSE% MOUNTPOINTS
sda
├─sda1 ntfs Зарезервировано системой D07C1DB37C1D9576
├─sda2 ntfs 02A825CFA825C251
├─sda3 ntfs E06E1FE76E1FB56E
├─sda4
├─sda5 vfat FAT32 FADD-602A 505,9M 1% /boot/efi
└─sda6 ext4 1.0 8bc63f27-cd5c-4814-8ab8-d2bf8d833168 65,7G 26% /
sr0
Диск /dev/sda: 465,76 GiB, 500107862016 байт, 976773168 секторов
Disk model: CT500MX500SSD1
Единицы: секторов по 1 * 512 = 512 байт
Размер сектора (логический/физический): 512 байт / 4096 байт
Размер I/O (минимальный/оптимальный): 4096 байт / 4096 байт
Тип метки диска: dos
Идентификатор диска: 0x80b7a497
Устр-во Загрузочный начало Конец Секторы Размер Идентификатор Тип
/dev/sda1 2048 104447 102400 50M 7 HPFS/NTFS/exFAT
/dev/sda2 104448 770903343 770798896 367,5G 7 HPFS/NTFS/exFAT
/dev/sda3 975704064 976769023 1064960 520M 27 Скрытый NTFS WinRE
/dev/sda4 770904062 975704063 204800002 97,7G 5 Расширенный
/dev/sda5 * 770904064 771954687 1050624 513M ef EFI (FAT-12/16/32)
/dev/sda6 771956736 975704063 203747328 97,2G 83 Linux
Раздел 4 начинается не на границе физического сектора.
Элементы таблицы разделов упорядочены не так, как на диске.
BootCurrent: 000A
Timeout: 0 seconds
BootOrder: 0019,000C,0006,0007,0008,0009,000A,000B,000D,000E,000F,0010,0011,0012,0013
Boot0000 Setup FvFile(721c8b66-426c-4e86-8e99-3457c46ab0b9)
Boot0001 Boot Menu FvFile(126a762d-5758-4fca-8531-201a7f57f850)
Boot0002 Diagnostic Splash Screen FvFile(a7d8d9a6-6ab0-4aeb-ad9d-163e59a7a380)
Boot0003 Startup Interrupt Menu FvFile(f46ee6f4-4785-43a3-923d-7f786c3c8479)
Boot0004 ME Configuration Menu FvFile(82988420-7467-4490-9059-feb448dd1963)
Boot0005 Rescue and Recovery FvFile(665d3f60-ad3e-4cad-8e26-db46eee9f1b5)
Boot0006* USB CD VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,86701296aa5a7848b66cd49dd3ba6a55)
Boot0007* USB FDD VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,6ff015a28830b543a8b8641009461e49)
Boot0008* ATAPI CD0 VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,aea2090adfde214e8b3a5e471856a35401)
Boot0009* ATA HDD2 VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,91af625956449f41a7b91f4f892ab0f602)
Boot000A* ATA HDD0 VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,91af625956449f41a7b91f4f892ab0f600)
Boot000B* ATA HDD1 VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,91af625956449f41a7b91f4f892ab0f601)
Boot000C* USB HDD VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,33e821aaaf33bc4789bd419f88c50803)
Boot000D* PCI LAN VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,78a84aaf2b2afc4ea79cf5cc8f3d3803)
Boot000E* ATAPI CD1 VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,aea2090adfde214e8b3a5e471856a35403)
Boot000F* ATAPI CD2 VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,aea2090adfde214e8b3a5e471856a35404)
Boot0010 Other CD VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,aea2090adfde214e8b3a5e471856a35406)
Boot0011* ATA HDD3 VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,91af625956449f41a7b91f4f892ab0f603)
Boot0012* ATA HDD4 VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,91af625956449f41a7b91f4f892ab0f604)
Boot0013 Other HDD VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,91af625956449f41a7b91f4f892ab0f606)
Boot0014* IDER BOOT CDROM PciRoot(0x0)/Pci(0x16,0x2)/Ata(0,1,0)
Boot0015* IDER BOOT Floppy PciRoot(0x0)/Pci(0x16,0x2)/Ata(0,0,0)
Boot0016* ATA HDD VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,91af625956449f41a7b91f4f892ab0f6)
Boot0017* ATAPI CD: VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,aea2090adfde214e8b3a5e471856a354)
Boot0018* PCI LAN VenMsg(bc7838d2-0f82-4d60-8316-c068ee79d25b,78a84aaf2b2afc4ea79cf5cc8f3d3803)
Boot0019* ubuntu HD(4,MBR,0x80b7a497,0x2df30ffe,0xc350002)/HD(1,MBR,0x0,0x2df31000,0x100800)/File(\EFI\ubuntu\shimx64.efi)
# If you change this file, run 'update-grub' afterwards to update
# /boot/grub/grub.cfg.
# For full documentation of the options in this file, see:
# info -f grub -n 'Simple configuration'
GRUB_DEFAULT=0
GRUB_TIMEOUT_STYLE=menu
GRUB_TIMEOUT=10
GRUB_DISTRIBUTOR=`lsb_release -i -s 2> /dev/null || echo Debian`
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash"
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=""
# Uncomment to enable BadRAM filtering, modify to suit your needs
# This works with Linux (no patch required) and with any kernel that obtains
# the memory map information from GRUB (GNU Mach, kernel of FreeBSD ...)
#GRUB_BADRAM="0x01234567,0xfefefefe,0x89abcdef,0xefefefef"
# Uncomment to disable graphical terminal (grub-pc only)
#GRUB_TERMINAL=console
# The resolution used on graphical terminal
# note that you can use only modes which your graphic card supports via VBE
# you can see them in real GRUB with the command `vbeinfo'
#GRUB_GFXMODE=640x480
# Uncomment if you don't want GRUB to pass "root=UUID=xxx" parameter to Linux
#GRUB_DISABLE_LINUX_UUID=true
# Uncomment to disable generation of recovery mode menu entries
#GRUB_DISABLE_RECOVERY="true"
# Uncomment to get a beep at grub start
#GRUB_INIT_TUNE="480 440 1"
Boot Windows with GRUB
If you’re dual-booting Windows and Linux, you’ll need to use a bootloader to choose which operating system to load at startup. GRUB is a popular bootloader that can be used to boot both Windows and Linux. In this article, we’ll show you how to install and configure GRUB so that you can dual-boot Windows and Linux.
We’ll start by installing GRUB on a Linux system. Then, we’ll show you how to add Windows to GRUB’s boot menu. Finally, we’ll walk you through the process of booting Windows from GRUB.
By the end of this article, you’ll be able to dual-boot Windows and Linux with GRUB. So let’s get started!
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Title | Description | Link |
| How to Boot Windows with GRUB | This guide will show you how to boot Windows from GRUB, the bootloader that is used by most Linux distributions. | How to Boot Windows from GRUB |
| Troubleshooting GRUB Boot Problems | This guide will help you troubleshoot problems that you may encounter when trying to boot Windows from GRUB. | Troubleshooting GRUB Boot Problems |
GRUB is a boot loader that can be used to boot multiple operating systems from a single hard drive. It is a free and open-source software that is available for a wide range of operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS. GRUB is typically installed on the master boot record (MBR) of the hard drive, and it is responsible for loading the operating system kernel into memory.
This guide will show you how to install GRUB on a Windows PC so that you can boot into other operating systems, such as Linux or macOS.
What is GRUB?
GRUB is a Grand Unified Bootloader, and it is a popular bootloader for Linux distributions. It can also be used to boot other operating systems, such as Windows and macOS. GRUB is a modular bootloader, which means that it can be configured to boot different operating systems from different locations on the hard drive. This makes it a good choice for dual-booting or multi-booting systems.
GRUB is a free and open-source software project, and it is available for a wide range of operating systems. It is also supported by a large community of users and developers, which means that there is plenty of documentation and support available if you need it.
How to install GRUB?
To install GRUB, you will need to:
1. Create a bootable USB drive or CD-ROM.
2. Download the GRUB installation files.
3. Boot from the bootable media.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to install GRUB.
Creating a bootable USB drive or CD-ROM
The first step is to create a bootable USB drive or CD-ROM. You can use a variety of tools to do this, but the easiest way is to use the `dd` command.
To create a bootable USB drive, follow these steps:
1. Download the `dd` command-line utility.
2. Connect the USB drive to your computer.
3. Open a terminal window.
4. Type the following command:
dd if=/path/to/grub-install.iso of=/dev/sdX bs=4M
Where `/path/to/grub-install.iso` is the path to the GRUB installation ISO file, and `/dev/sdX` is the device node for your USB drive.
To create a bootable CD-ROM, follow these steps:
1. Download the `syslinux` package.
2. Create a new CD-ROM.
3. Open a terminal window.
4. Type the following command:
syslinux -i -c /dev/cdrom
Where `/dev/cdrom` is the device node for your CD-ROM drive.
Downloading the GRUB installation files
The next step is to download the GRUB installation files. You can download the latest version of GRUB from the GRUB website.
Once you have downloaded the GRUB installation files, extract them to a folder on your computer.
Booting from the bootable media
Now that you have created a bootable USB drive or CD-ROM, you can boot from it. To do this, you will need to change the boot order in your BIOS.
The exact steps for changing the boot order will vary depending on your motherboard, but the general process is as follows:
1. Power on your computer.
2. Press the BIOS key (usually F2, F10, or Delete).
3. Use the arrow keys to navigate to the Boot menu.
4. Use the arrow keys to select the bootable USB drive or CD-ROM.
5. Press Enter to save your changes.
Your computer will now boot from the bootable media.
Following the on-screen instructions
Once your computer has booted from the bootable media, you will be presented with a series of on-screen instructions. Follow these instructions to install GRUB.
The installation process will vary depending on your operating system, but the general process is as follows:
1. Select the operating system that you want to install GRUB for.
2. Select the location where you want to install GRUB.
3. Click Install.
GRUB will now be installed on your computer.
In this guide, you learned how to install GRUB on a Windows PC. GRUB is a powerful tool that can be used to boot multiple operating systems from a single hard drive. By following the steps in this guide, you can easily install GRUB and start enjoying the benefits of multi-booting.
Additional resources
*
GRUB is a boot loader that can be used to boot multiple operating systems from a single hard drive. This can be useful if you want to dual-boot Windows and Linux, or if you want to have multiple versions of Windows installed on the same computer.
To boot Windows with GRUB, you will need to:
1. Install GRUB on your computer.
2. Configure GRUB to boot Windows.
3. Set Windows as the default operating system.
Installing GRUB
To install GRUB, you will need to download the GRUB ISO file and burn it to a CD or USB drive. Once you have created the bootable media, you can boot your computer from it.
When you boot from the GRUB ISO file, you will be presented with the GRUB menu. From here, you can select the option to install GRUB.
The GRUB installation process is fairly straightforward. You will be asked to select the location where you want to install GRUB, and then you will be asked to confirm your selection.
Once GRUB has been installed, you will need to reboot your computer.
Configuring GRUB
Once GRUB has been installed, you will need to configure it to boot Windows. To do this, you will need to edit the GRUB configuration file.
The GRUB configuration file is located at `/boot/grub/grub.cfg`. You can open this file using any text editor.
In the GRUB configuration file, you will need to find the section that lists the operating systems that GRUB can boot. This section will look something like this:
menuentry “Windows 10” {
linuxefi /EFI/Microsoft/Boot/bootmgfw.efi
initrdefi /EFI/Microsoft/Boot/bootmgfw.efi
}
To add Windows to the GRUB menu, you will need to add a new entry to this section. The new entry should look something like this:
menuentry “Windows 10” {
linuxefi /EFI/Microsoft/Windows/grub/bootmgfw.efi
initrdefi /EFI/Microsoft/Windows/grub/bootmgfw.efi
}
Once you have added the new entry, you will need to save the GRUB configuration file and reboot your computer.
Setting Windows as the Default Operating System
By default, GRUB will boot the first operating system that it finds in the list. If you want to set Windows as the default operating system, you will need to edit the GRUB configuration file.
In the GRUB configuration file, you will need to find the line that starts with `default`. This line will look something like this:
default 0
The number on the right side of the equal sign represents the index of the operating system that GRUB should boot by default. To set Windows as the default operating system, you will need to change this number to 0.
Once you have changed the default operating system, you will need to save the GRUB configuration file and reboot your computer.
Booting Windows with GRUB
Once you have installed and configured GRUB, you can boot Windows by following these steps:
1. Power on your computer.
2. Press the key that you used to boot from the GRUB ISO file.
3. Select the Windows entry from the GRUB menu.
4. Press Enter.
Windows will start to boot.
How to Use GRUB?
Once GRUB has been installed and configured, you can use it to boot multiple operating systems from a single hard drive. To use GRUB, you will need to:
1. Boot your computer from the GRUB menu.
2. Select the operating system that you want to boot.
3. Press Enter to boot the operating system.
Booting your computer from the GRUB menu
To boot your computer from the GRUB menu, you will need to press the key that you used to boot from the GRUB ISO file. This key is usually the Escape key, the F10 key, or the Delete key.
Once you have pressed the key, you will be presented with the GRUB menu. From here, you can select the operating system that you want to boot.
Selecting the operating system that you want to boot
To select the operating system that you want to boot, you will need to use the arrow keys to highlight the operating system and then press Enter.
Once you have selected the operating system, you will
Q: What is GRUB?
GRUB is an acronym for GRand Unified Bootloader. It is a bootloader that can be used to boot multiple operating systems from a single hard drive. GRUB is free and open source software, and it is available for a wide variety of operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Q: How do I install GRUB?
To install GRUB, you will need to first create a bootable USB drive. You can do this using a tool like Rufus. Once you have created the bootable USB drive, you can follow these steps to install GRUB:
1. Boot your computer from the bootable USB drive.
2. Select the “Install GRUB” option.
3. Select the hard drive where you want to install GRUB.
4. Select the operating system that you want to boot from GRUB.
5. Click “Install”.
Q: How do I set GRUB as the default bootloader?
To set GRUB as the default bootloader, you will need to edit the /boot/grub/grub.cfg file. You can do this using a text editor like vi or nano. Once you have opened the file, find the line that starts with “default” and change the value to “0”. This will tell GRUB to boot the first operating system in the list.
Q: How do I change the GRUB boot menu?
To change the GRUB boot menu, you will need to edit the /boot/grub/grub.cfg file. You can do this using a text editor like vi or nano. Once you have opened the file, you can add or remove entries for the operating systems that you want to boot. You can also change the order of the entries.
Q: How do I troubleshoot GRUB problems?
If you are having problems with GRUB, there are a few things that you can check. First, make sure that you have installed GRUB correctly. You can do this by following the instructions in the “How do I install GRUB?” section above. If you are still having problems, you can try reinstalling GRUB. To do this, follow the instructions in the “How do I install GRUB?” section above, but make sure to delete the old GRUB installation first. If you are still having problems, you can try asking for help on a forum or mailing list.
Q: What are the advantages of using GRUB?
There are a few advantages to using GRUB. First, GRUB is free and open source software. This means that you can use it without having to pay any licensing fees. Second, GRUB is very versatile. It can be used to boot multiple operating systems from a single hard drive. Third, GRUB is very easy to use. You can easily create a bootable USB drive with GRUB, and you can also easily edit the GRUB boot menu.
Q: What are the disadvantages of using GRUB?
There are a few disadvantages to using GRUB. First, GRUB can be complex to configure. If you are not familiar with GRUB, you may have trouble setting it up correctly. Second, GRUB can be slow to boot. This is because GRUB has to scan the hard drive for operating systems every time it boots. Third, GRUB is not supported by all operating systems. For example, GRUB is not supported by macOS.
Q: Is GRUB the best bootloader?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question. The best bootloader for you will depend on your specific needs. If you need a bootloader that is free, open source, and easy to use, then GRUB is a good option. However, if you need a bootloader that is fast and supports all operating systems, then GRUB may not be the best option for you.
In this blog post, we discussed how to boot Windows with GRUB. We first introduced GRUB and its role in the boot process. Then, we showed you how to install GRUB on a hard drive and set it as the default boot loader. Finally, we walked you through the process of booting Windows from GRUB.
We hope that this blog post has been helpful. If you have any questions, please feel free to leave a comment below.
Here are some key takeaways from this blog post:
- GRUB is a bootloader that can be used to boot multiple operating systems from a single hard drive.
- To install GRUB, you must first create a bootable USB drive.
- Once you have created the bootable USB drive, you can install GRUB by following the steps in the tutorial.
- To boot Windows from GRUB, you must first select the Windows installation from the GRUB menu.
Author Profile
-
Hatch, established in 2011 by Marcus Greenwood, has evolved significantly over the years. Marcus, a seasoned developer, brought a rich background in developing both B2B and consumer software for a diverse range of organizations, including hedge funds and web agencies.
Originally, Hatch was designed to seamlessly merge content management with social networking. We observed that social functionalities were often an afterthought in CMS-driven websites and set out to change that. Hatch was built to be inherently social, ensuring a fully integrated experience for users.
Now, Hatch embarks on a new chapter. While our past was rooted in bridging technical gaps and fostering open-source collaboration, our present and future are focused on unraveling mysteries and answering a myriad of questions. We have expanded our horizons to cover an extensive array of topics and inquiries, delving into the unknown and the unexplored.
