В Windows 10 и Windows Server 2019 появился встроенный SSH клиент, который вы можете использовать для подключения к *Nix серверам, ESXi хостам и другим устройствам по защищенному протоколу, вместо Putty, MTPuTTY или других сторонних SSH клиентов. Встроенный SSH клиент Windows основан на порте OpenSSH и предустановлен в ОС, начиная с Windows 10 1809.
Содержание:
- Установка клиента OpenSSH в Windows 10
- Как использовать SSH клиенте в Windows 10?
- SCP: копирование файлов из/в Windows через SSH
Установка клиента OpenSSH в Windows 10
Клиент OpenSSH входит в состав Features on Demand Windows 10 (как и RSAT). Клиент SSH установлен по умолчанию в Windows Server 2019 и Windows 10 1809 и более новых билдах.
Проверьте, что SSH клиент установлен:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | ? Name -like 'OpenSSH.Client*'
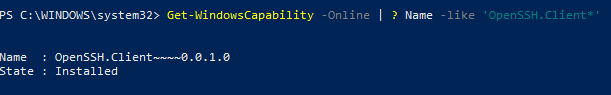
В нашем примере клиент OpenSSH установлен (статус: State: Installed).
Если SSH клиент отсутствует (State: Not Present), его можно установить:
- С помощью команды PowerShell:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Client* - С помощью DISM:
dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:OpenSSH.Client~~~~0.0.1.0 - Через Параметры -> Приложения -> Дополнительные возможности -> Добавить компонент. Найдите в списке Клиент OpenSSH и нажмите кнопку Установить.

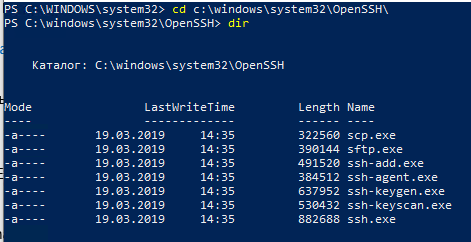
]Бинарные файлы OpenSSH находятся в каталоге c:\windows\system32\OpenSSH\.
- ssh.exe – это исполняемый файл клиента SSH;
- scp.exe – утилита для копирования файлов в SSH сессии;
- ssh-keygen.exe – утилита для генерации ключей аутентификации;
- ssh-agent.exe – используется для управления ключами;
- ssh-add.exe – добавление ключа в базу ssh-агента.
Вы можете установить OpenSSH и в предыдущих версиях Windows – просто скачайте и установите Win32-OpenSSH с GitHub (есть пример в статье “Настройка SSH FTP в Windows”).
Как использовать SSH клиенте в Windows 10?
Чтобы запустить SSH клиент, запустите командную строку
PowerShell
или
cmd.exe
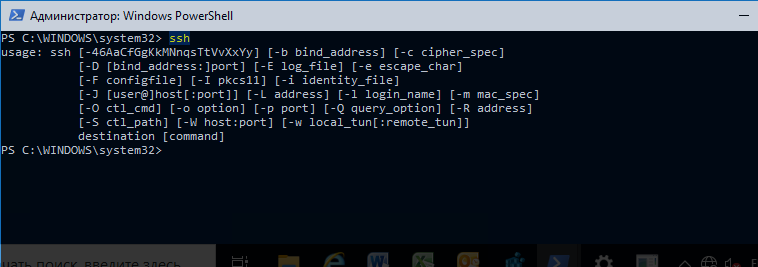
. Выведите доступные параметры и синтаксис утилиты ssh.exe, набрав команду:
ssh
usage: ssh [-46AaCfGgKkMNnqsTtVvXxYy] [-b bind_address] [-c cipher_spec]
[-D [bind_address:]port] [-E log_file] [-e escape_char]
[-F configfile] [-I pkcs11] [-i identity_file]
[-J [user@]host[:port]] [-L address] [-l login_name] [-m mac_spec]
[-O ctl_cmd] [-o option] [-p port] [-Q query_option] [-R address]
[-S ctl_path] [-W host:port] [-w local_tun[:remote_tun]]
destination [command]
Для подключения к удаленному серверу по SSH используется команда:
ssh username@host
Если SSH сервер запущен на нестандартном порту, отличном от TCP/22, можно указать номер порта:
ssh username@host -p port
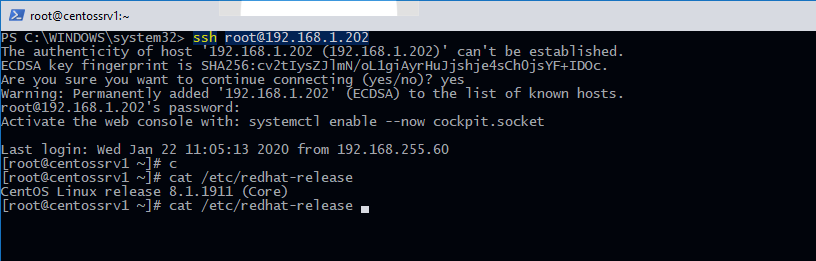
Например, чтобы подключиться к Linux хосту с IP адресом 192.168.1.202 под root, выполните:
ssh [email protected]
При первом подключении появится запрос на добавление ключа хоста в доверенные, наберите yes -> Enter (при этом отпечаток ключа хоста добавляется в файл C:\Users\username\.ssh\known_hosts).
Затем появится запрос пароля указанной учетной записи, укажите пароль root, после чего должна открытся консоль удаленного Linux сервера (в моем примере на удаленном сервере установлен CentOS 8).
С помощью SSH вы можете подключаться не только к *Nix подобным ОС, но и к Windows. В одной из предыдущих статей мы показали, как настроить OpenSSH сервер на Windows 10 и подключиться к нему с другого компьютера Windows с помощью SSH клиента.
Если вы используете SSH аутентификацию по RSA ключам (см. пример с настройкой SSH аутентификации по ключам в Windows), вы можете указать путь к файлу с закрытым ключом в клиенте SSH так:
ssh [email protected] -i "C:\Users\username\.ssh\id_rsa"
Также вы можете добавить ваш закрытый ключ в SSH-Agent. Сначала нужно включить службу ssh-agent и настроить ее автозапуск:
set-service ssh-agent StartupType ‘Automatic’
Start-Service ssh-agent
Добавим ваш закрытый ключ в базу ssh-agent:
ssh-add "C:\Users\username\.ssh\id_rsa"
Теперь вы можете подключиться к серверу по SSH без указания пути к RSA ключу, он будет использоваться автоматически. Пароль для подключения не запрашивается (если только вы не защитили ваш RSA ключ отдельным паролем):
ssh [email protected]
Еще несколько полезных аргументов SSH:
-
-C
– сжимать трафик между клиентом и сервером (полезно на медленных и нестабильных подключениях); -
-v
– вывод подробной информации обо всех действия клиента ssh; -
-R
/
-L
– можно использовать для проброса портов через SSH туннель.
SCP: копирование файлов из/в Windows через SSH
С помощью утилиты scp.exe, которая входит в состав пакета клиента SSH, вы можете скопировать файл с вашего компьютера на SSH сервер:
scp.exe "E:\ISO\CentOS-8.1.1911-x86_64.iso" [email protected]:/home

Можно рекурсивно скопировать все содержимое каталога:
scp -r E:\ISO\ [email protected]:/home
И наоборот, вы можете скопировать файл с удаленного сервера на ваш компьютер:
scp.exe [email protected]:/home/CentOS-8.1.1911-x86_64.iso e:\tmp
Если вы настроите аутентификацию по RSA ключам, то при копировании файлов не будет появляться запрос на ввод пароля для подключения к SSH серверу. Это удобно, когда вам нужно настроить автоматическое копирование файлов по расписанию.
Итак, теперь вы можете прямо из Windows 10 подключаться к SSH серверам, копировать файлы с помощью scp без установки сторонних приложений и утилит.
Уровень сложностиПростой
Время на прочтение5 мин
Количество просмотров304K

Программистов, сисадминов, devops’ов, тестировщиков часто объединяет использование некоторых общих технологий. Например, возможность иметь удалённый доступ к серверу пригодилось бы любому из указанной выше анекдотичной компании. Поэтому в этой статье мы рассмотрим основы работы с протоколом SSH на базовом уровня (без генерации ключей, подписей, мам, пап и кредитов). «Продвинутое» использование посмотрим уже отдельно, в следующий раз. Материал подготовил Макс, автор YouTube-канала PyLounge. Поехали!
Введение
SSH (Secure SHell — защищенная оболочка) — сетевой протокол прикладного уровня, предназначенный для безопасного удаленного доступа к различным системам (Linux, Windows, Mac).
Данный протокол шифрует всю передаваемую информацию по сети. По умолчанию, используется 22-й порт. В основном он нужен для удаленного управления данными пользователя на сервере, запуска служебных команд, работы в консольном режиме с базами данных.
Эта служба была создана в качестве замены не зашифрованному Telnet и использует криптографические техники, чтобы обеспечить, что всё сообщение между сервером и пользователем было зашифровано.
Чтобы установить SSH-соединение, необходимы два компонента: SSH-сервер и SSH-клиент. Сервер прослушивает определенный порт (по умолчанию это порт 22) и при успешной аутентификации дает доступ пользователю. Все команды, которые используются на SSH-клиенте, отправляются через защищенный канал связи на SSH-сервер, на котором они выполняются и откуда отправляют результат работы обратно клиенту.
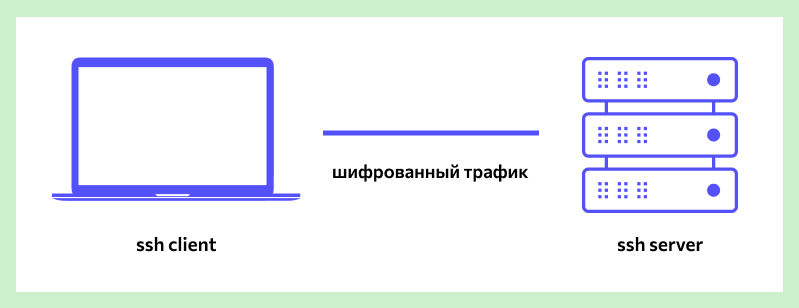
SSH-сервер
Устанавливается на управляемой операционной системе и принимает входящие подключения от клиентских машин, проверяя соединение одним из способов:
-
по IP-адресу клиента, что не слишком безопасно из-за риска подмены;
-
по публичному ключу клиента и имени пользователя. Нужно создать приватный (закрытый) и публичный (открытый) ключ. Зашифровав информацию одним ключом, можно расшифровать ее только другим;
-
по паролю клиента, который передается в зашифрованном виде. Это один из наиболее распространенных вариантов. Вводить его нужно при каждом подключении.
Платные и бесплатные SSH-серверы есть для всех распространенных ОС:
-
BSD — OpenSSH;
-
Linux — dropbear, lsh-server, openssh-server;
-
Windows — freeSSHd, copssh, WinSSHD, OpenSSH и т. д.
SSH-клиент
Используется для входа на удаленный сервер и выполнения команд. Через клиент выполняется управление удаленным компьютером.
SSH-клиенты разработаны для всех ОС. Имеют платные и бесплатные версии:
-
Linux/BSD — openssh-client, putty, ssh, Vinagre;
-
Windows — PuTTY, SecureCRT, ShellGuard;
-
Android — connectBot.
Встроенный SSH-клиент Windows, основанный на OpenSSH, предустановлен в ОС, начиная с Windows 10 1809.
Установка OpenSSH на Ubuntu
Установка с помощью менеджера пакетов apt-get:
sudo apt-get install openssh-serverПроверка SELinux
Security Enhanced Linux, или SELinux – это усовершенствованный механизм контроля доступа, встроенный в большинство современных дистрибутивов Linux. Первоначально он был разработан Агентством национальной безопасности США для защиты компьютерных систем от вторжения злоумышленников и взлома. SELinux также может помешать работе с ssh. Поэтому необходимо убедиться, что он отключен, либо отключить его.
Устанавливаем доп. инструменты для работы с сетью и настройками безопасности:
sudo apt-get install policycoreutils
sudo apt-get install net-toolsПроверяем статус SELinux. Состояние должно быть disable.
sestatusПодключение к виртуальной машине с типом подключения NAT
Если виртуальная машина использует тип сетевого подключения NAT, то первоначально необходимо настроить проброс портов. Пробросим порт хоста 2222 (или любой свободный) на гостевой порт виртуальной машины номер 22 (порт ssh по умолчанию).
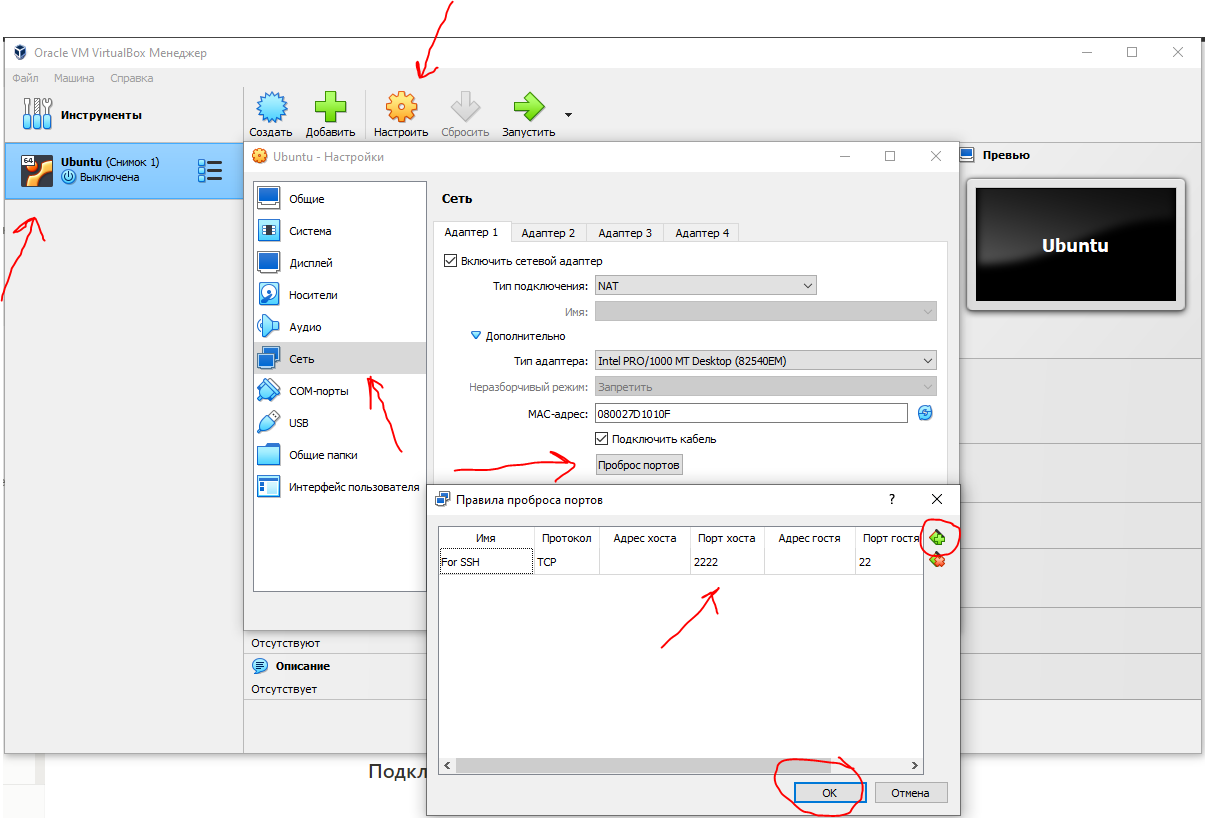
После этого мы можем подключиться из Windows к нашей виртуальной машине.
Подключение по ssh через PuTTY
Т.к. в качестве сетевого подключения у виртуальной машины используется NAT, при подключении мы будем указывать петлевой адрес localhost (127.0.0.1) c портом, на который был назначен проброс.
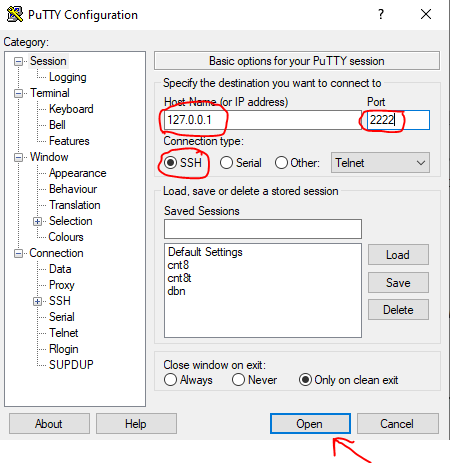
После этого вводим имя пользователя (пользователь должен существовать в linux!!!) и пароль от этого пользователя.
Подключение по ssh через Командную строку Windows (cmd)
Запускаем командную строку сочетанием клавиш Win + R . В открывшемся окне указываем cmd. Нажимаем OK.
В общем видео подключение по ssh имеет вид:
ssh имя_пользователя@ip_адрес_компьютера_к_которому_подключаемся -p портЕсли для подключения используется стандартный порт ssh — 22, то порт можно не указывать.
В открывшемся окне вводим команду:
ssh student@127.0.0.1 -p 2222Вводим пароль пользователя. Всё. Вы великолепны!
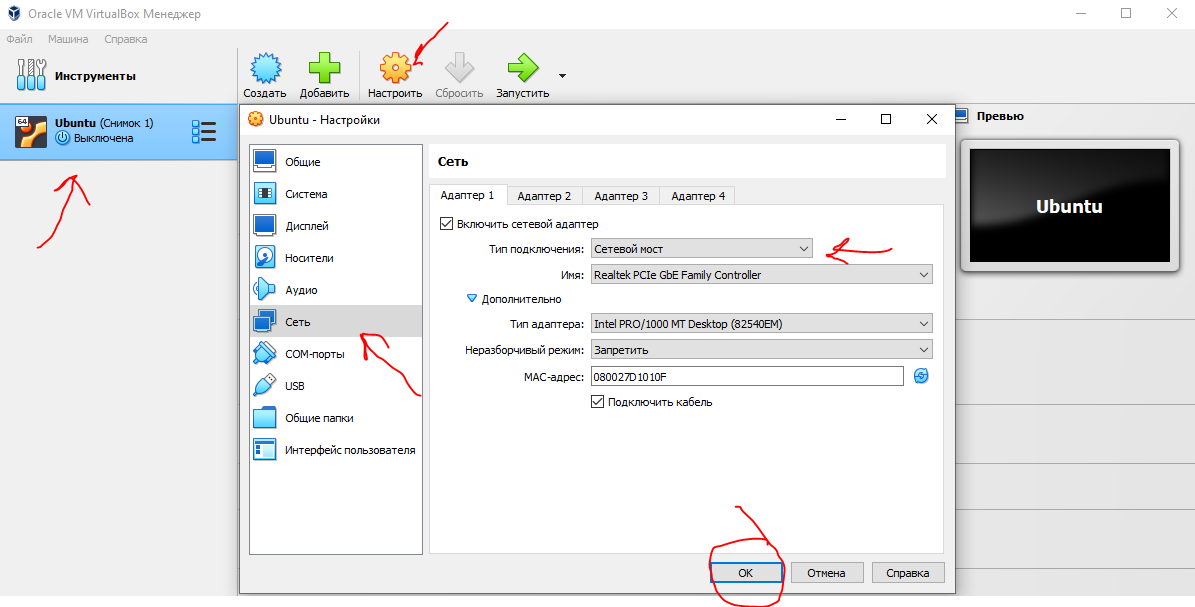
Подключение к виртуальной машине с типом подключение Сетевой мост
С типом подключения Сетевой мост необходимо выдать статический ip для Linux системы. Дальнейшее подключение будет уже по этому, выданному ip, а не через localhost.
Установка статического ip
Начиная с выпуска Ubuntu 17.10 NetPlan теперь это инструмент настройки сети по умолчанию для управления настройками сети, заменяющий файл конфигурации /etc/network/interfaces, который использовался в предыдущих версиях.
Файлы конфигурации для Netplan находятся в каталоге /etc/netplan и написаны на языке YAML. В этом каталоге вы найдете файлы конфигурации YAML.
Откроем конфигурационный файл:
sudo nano /etc/netplan/*.yamlОтредактируем конфигурационный файл:
network:
version: 2
renderer: NetworkManager
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: false
addresses: [10.40.0.224/24]
gateway4: 10.40.0.1
nameservers:
addresses: [10.2.0.8, 10.2.0.3]
Здесь:
-
ethernets — указывает на проводное Ethernet подключение;
-
enp0s3 — имя сетевого интерфейса (можно узнать командой ifconfig);
-
dhcp4 — автоматическая выдача ipv4-адреса с помощью службы dhcp (для ipv6 указывать dhcp6);
-
addresses — ip-адрес и маска сети, которые назначаются компьютеру;
-
gateway4 — шлюз по умолчанию;
-
nameservers — список dns-серверов.
Посмотреть настройки можно с хостовой машины на Windows с помощью команды ipconfig /all.
Чтобы применить изменения и перезагрузить сеть, вводим команду:
sudo netplan applyПодключение по ssh
Запускаем командную строку сочетанием клавиш Win + R . В открывшемся окне указываем cmd. Нажимаем OK.
В открывшемся окне вводим команду:
ssh student@10.40.0.224Вводим пароль пользователя. Всё. Вы великолепны (2)!
Заключение
Несмотря на высокую защиту протокола, использование стандартного порта значительно повышает риск взлома сервера. Например, это можно сделать при помощи brute-force (атака полным перебором). Порт 22 — открытый, поэтому злоумышленнику нужно только подобрать логин и пароль к серверу. Это сложно, но возможно. Чтобы максимально ограничить доступ к серверу для злоумышленников (настроить брандмауэр, iptables), можно сменить SSH-порты.
Ресурсы, которые использовал
-
Как включить SSH в Ubuntu 20.04 (Routerus):https://routerus.com/how-to-enable-ssh-on-ubuntu-20-04/
-
Коротко об SSH / Хабр: https://habr.com/ru/sandbox/166705/
-
Что такое SSH (блог REG.RU): https://help.reg.ru/support/hosting/dostupy-i-podklyucheniye-panel-upravleniya-ftp-ssh/chto-takoye-ssh
SSH software downloads
Download SSH client and server software. Find trials and demos of other
software solutions.
If you are an SSH customer, you can log in and download your software
from our customer download center.
SSH Client/Server
Free trial download of Tectia SSH Client/Server — no credit card required.
Now available with Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) algorithms.
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Test drive the lean PAM solution PrivX — no downloads or installation needed, browser-based interface.
SSH Key Management
Free test drive of the Universal SSH Key Manager — nothing to download, install, or configure.
SSH Key Discovery & Audit
Free SSH key and post-quantum resilience discovery and audit tool. Scan your entire SSH key estate or just a few selected servers.
Other software downloads
Windows SSH client alternatives
Mac SSH client alternatives
Free SSH servers
Most Linux systems come with the open source OpenSSH preinstalled.
What we do
PrivX®
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
PrivX is the next-generation PAM solution featuring unparalleled ease-of-use, cost-efficiency and automation.
PrivX is perfect for securing, managing and tracking superuser and power user access in the hybrid cloud — by also eliminating risky privileged passwords from critical infrastructures.
Universal SSH key manager®
Enterprise Key Management (EKM)
UKM Zero Trust is the leading full lifecycle SSH Encryption Key management solution trusted by many of the world’s largest enterprises.
UKM Zero Trust manages and automates the lifecycle of millions of encryption keys for risk mitigation and audit success — also by making access keyless.
NQX™
Quantum Safe Cryptography (QSC)
NQX is an ultra-secure quantum-safe encryption solution for transporting Ethernet and IP traffic across any network, private or public.
Software-based NQX features matchless performance and security using cost-effective off-the-shelf hardware for post quantum cryptography (PQC).
Tectia®
Fast and secure SSH file transfers
Tectia is the gold standard in secure remote access, encrypted file transfers and A2A tunneling, featuring enterprise-grade reliability, industry-leading efficiency and 24/7 support.
Available for all major operating systems, including Windows, Unix, Linux & z/OS.
SSH deltagon suite
Critical information sharing
Deltagon Suite protects your sensitive and confidential emails, signatures, webforms and shared files with a high level of security and encryption that also meets strict regulatory requirements like GDPR.
Share critical information between organizations in a secure fashion.
expertise for our customers
Professional services
We want to become your trusted advisors in all matters of encryption and secure access to ensure that your business runs without disruptions or security concerns.
We also provide 24/7 support for our products. Help is always just a phone call away.
Software demos and trials
We are happy to help with enterprise trials, POCs, demos, and comparisons for PrivX, UKM, Tectia, NQX, and Deltagon Suite.
- OpenSSH for Windows allows you to securely access remote computers with Windows-native tools using the command line interface.
- To install OpenSSH Client and Server on Windows, go to Settings > System > Optional features > View features, search for “OpenSSH“, and continue to install the components.
Windows users normally use the Remote Desktop Protocol to access other Windows devices remotely. As RDP offers a remote graphical user interface (GUI), it is a convenient method for remote access. However, it offers limited functionality, especially if you are a sysadmin. For that purpose, some people prefer to use the Secure Socket Shell (SSH) protocol.
SSH provides a command-line interface to remote computers and servers, and therefore, a more granular control over them. Previously, we used third-party apps like “PuTTY” and “MobaXterm” to develop an SSH connection with the remote devices. However, Microsoft has made a Windows-native SSH client available which can be used instead.
OpenSSH for Windows is a Feature on Demand (FoD) add-on for the Windows operating system. This means that although it is free, it is not installed by default, and needs to be installed manually. If you install it, you can use the SSH protocol through the native command line to access and control the remote computers, provided that your user account has the required privileges.
This guide will show you how to install and use OpenSSH for Windows. These will work on both Windows 11 and Windows 10 (version 1809 and above). Using this guide, you can install both OpenSSH Client and OpenSSH Server in a few easy steps.
Table of Contents
What is OpenSSH
The Secure Socket Shell, or Secure Shell is a networking protocol that allows a remote connection with another device securely. SSH uses a client-server model to communicate with remote computers and ensures data integrity through encryption. It uses multiple layers of the OSI reference model to make sure that the communicated data between the devices is secure.
Originally, OpenSSH was a tool used for remote connection with other devices which comes preinstalled in Linux-based operating systems. Since it is an open-source utility, it has been modified for other platforms, including Windows.
Microsoft has now made “OpenSSH for Windows” available that you can install with a small update package.
Before installing OpenSSH, your system needs to meet a few requirements.
Requirements for OpenSSH for Windows
Before proceeding to install either OpenSSH Client or Server, you must make sure that your PC satisfies the prerequisites, which are:
- OS should be Windows 10 version 1809 or later.
- The PowerShell version should be 5.1 or above
- The user account must be a member of the Administrators group.
To check the OS version, run the following command in the Run Command box:
WinVerTo check the PowerShell version, run the following command in PowerShell:
$PSVersionTable.PSVersionTo check if your user is a member of the Administrators group, run the following command in PowerShell. If it returns “True“, it means that you are a member of the Administrator group.
(New-Object Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal([Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent())).IsInRole([Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltInRole]::Administrator)Once you have made sure that your PC satisfies these requirements, you may continue to install OpenSSH Client, OpenSSH Server, or both.
Install OpenSSH on Windows
Implement the following steps to install OpenSSH on your Windows computer to access it remotely. Optionally, you can also install “OpenSSH Server” to access this device from another PC using the SSH protocol.
-
Press the Windows key + i to open the Settings app.
-
Click System.
-
Go to “Optional Features“.
Open the optional features settings page -
Click “View features“.
View optional features -
Search for “OpenSSH“.
-
Select “OpenSSH Client” and optionally, “OpenSSH Server“, and then click Next.
Select OpenSSH Client and Server -
Click Install.
Install OpenSSH Client and Server on Windows
After performing these steps, OpenSSH Client (and Server) will be installed on your computer.
Note: These features can take some time to install.
Alternative to the steps above, you can also run the following command in an elevated PowerShell instance to install OpenSSH for Windows:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object Name -like 'OpenSSH*'This command will install both OpenSSH Client and OpenSSH Server.
Using OpenSSH Client for Windows
Once OpenSSH Client for Windows has been installed, you can begin using it to connect with remote PCs on the network. Of course, OpenSSH has to be configured on the remote PC first, the method for which has been given below in this post.
First, confirm that it has been installed successfully by running the following command in Command Prompt:
ssh
Once confirmed, you can access a remote PC on the network which has SSH configured using this command:
ssh [Username]@[ServerName]
Note: You may be asked for user credentials if connecting for the first time.
Note that the command above will try to connect to the remote device using the default port, which is 22. If you want to use a different port, then you will need to use this command instead:
ssh [Username]@[ServerName] -p [PortNumber]
Configuring OpenSSH Server for Windows
If you have installed the OpenSSH Server on your Windows PC, you will need to configure it before you can connect to this PC using the SSH protocol.
Configuring the OpenSSH server can be a bit thicker. You need to make sure that it is allowed through the firewall and the proper ports. Therefore, it involves a few steps. Here is what you need to do:
-
First, run the following command in an elevated PowerShell to run the “sshd” service automatically.
Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic' -
Now start the service with this command:
Start-Service sshd -
Now use the following command to ensure that the SSH server is running and waiting for the connections on port 22:
netstat -na| find ":22" -
Now ensure that the Windows Defender Firewall allows inbound connections to Windows through the TCP port 22 with this command:
Get-NetFirewallRule -Name *OpenSSH-Server* |select Name, DisplayName, Description, EnabledConfirm rules for SSH server connection -
[Conditional] If you find that the rule is missing or disabled, run the following command to create a new inbound rule:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22 -
To change the default rules for the SSH connection, run the following command in PowerShell which will open the respective OpenSSH file in Notepad:
start-process notepad C:\Programdata\ssh\sshd_config -
Make the necessary changes in the file to manage the permissions, and then save the file using the CTRL + S shortcut keys.
Here are a few examples of the rules:
- Deny domain user:
DenyUsers itt\administrator@192.168.10.10 - Allow a domain group:
AllowGroups itt\sshadmins - Allow local groups:
AllowGroups Administrators
Manage SSH permissions - Deny domain user:
-
After making the changes, run the following command in PowerShell:
restart-service sshd
After performing the steps above, you should be able to connect to this PC using the SSH protocol. For that purpose, use the command ssh [Username]@[ServerName] as discussed above.
Conclusion
With SSH, you do not need to perform a long string of operations to perform a simple task. Instead, you can access it with Windows-native OpenSSH and continue to manage the remote PC using commands. This makes OpenSSH for Windows an excellent utility for network and system administrators.
In today’s digital landscape, SSH (Secure Shell) has become an integral tool for secure network management and secure data transfer. Windows 11, like its predecessor, incorporates several security features, making it a suitable environment for SSH usage. Whether you are a system administrator connecting to remote servers or a developer needing to transfer files securely, installing SSH on Windows 11 is a straightforward process. This guide will help you understand how to install and configure SSH on Windows 11, offering insights into its components, configurations, and best practices.
Understanding SSH
Before diving into the installation process, it’s essential to understand what SSH is and its significance. SSH is a cryptographic network protocol that enables secure communication between two devices over an unsecured network. Typically used for managing servers, SSH facilitates command execution on remote machines and allows secure file transfers.
Benefits of SSH
- Encryption: SSH encrypts the data transferred between the client and server, providing a secure channel, especially over insecure networks.
- Secure Authentication: SSH supports various authentication methods, including password and public-key authentication, adding multiple layers of security.
- Port Forwarding: SSH allows secure tunneling of traffic through arbitrary ports, making it useful for remote application access.
- Remote Command Execution: With SSH, users can execute commands on remote machines securely and conveniently.
- File Transfer Protocols: SSH supports SFTP and SCP, which are secure methods for transferring files to and from remote systems.
Prerequisites for Installing SSH on Windows 11
Before installing SSH, you should verify that your Windows 11 system is fully updated. Microsoft often includes important updates that could impact the installation process. Here are the steps to ensure your system is ready for the SSH installation:
-
Check for Windows Updates:
- Go to Settings by pressing
Win + I. - Click on Windows Update on the left menu.
- Click on Check for updates and install any necessary updates.
- Go to Settings by pressing
-
Verify System Requirements: Ensure your system meets the minimal hardware and software requirements for Windows 11 to have the best experience with SSH.
-
Administrative Privileges: You will need administrator rights on the computer to install SSH.
Installing OpenSSH on Windows 11
Windows 11 comes with OpenSSH built into the operating system, allowing for a smooth installation process. You can install OpenSSH via the Windows Settings app or using PowerShell.
Method 1: Installing OpenSSH via Windows Settings
-
Open Settings:
- Right-click on the Start menu.
- Select Settings.
-
Navigate to Optional Features:
- In the Settings window, click on Apps.
- Under Apps & features, select Optional features.
-
Add a Feature:
- Scroll down to the Add an optional feature section and click on it.
- In the search box, type
OpenSSHto quickly find the SSH features.
-
Install OpenSSH Client:
- Check for OpenSSH Client in the list, select it, and click on the Install button.
- For OpenSSH Server (if you intend to allow SSH connections to your machine), repeat this process by searching for the server and installing it.
-
Confirm Installation: Once installed, you can close the Settings window.
Method 2: Installing OpenSSH using PowerShell
For users comfortable with command lines, installing OpenSSH can be done using Windows PowerShell.
-
Open PowerShell as Administrator:
- Search for
PowerShellin the Start menu. - Right-click on Windows PowerShell and select Run as administrator.
- Search for
-
Install OpenSSH Client:
Use the following command to install the OpenSSH Client:Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Client~~~~0.0.1.0 -
Install OpenSSH Server (Optional):
If you want to install the SSH server too, you can do so by running:Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0 -
Verify the Installation:
After installation, you can check if the OpenSSH client is installed by running:ssh -V
If installed correctly, this command will return the version of OpenSSH.
Configuring OpenSSH
Once SSH is installed on Windows 11, you may want to configure it to suit your needs. Configurations can involve setting up public key authentication, modifying the SSH daemon configuration (if the server is installed), and more.
Configuring OpenSSH Client
Generating SSH Key Pair
If you want to use key-based authentication, you need to generate an SSH key pair.
- Open PowerShell or Command Prompt.
- Run the following command:
ssh-keygen - Follow the prompts:
- Press Enter to accept the default file location to save the key pair (usually
C:UsersYourUsername.sshid_rsa). - You can set a passphrase for additional security or leave it empty.
- Press Enter to accept the default file location to save the key pair (usually
- After completion, your public key will be located at
C:UsersYourUsername.sshid_rsa.pub.
Adding your Public Key to a Remote Server
- Copy your public key to the remote server. If you have SSH access, you can use the
ssh-copy-idcommand (from a Unix-like system) or copy it manually. - For manual copying, log into your server and append your public key:
cat $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> $HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys - Ensure the permissions are correct on the server for the
.sshdirectory and its contents:chmod 700 $HOME/.ssh chmod 600 $HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys
Configuring OpenSSH Server
If you installed the OpenSSH Server and want to configure its settings, follow these steps:
-
Locate the Configuration File:
The configuration file for the OpenSSH server is located at:C:ProgramDatasshsshd_config -
Edit Configuration File:
Open the file using any text editor with administrative rights. Some key settings to consider modifying include:Port: Change the default port from22to another number for added security.PermitRootLogin: Set it tonoto prevent root login.PasswordAuthentication: Disable password authentication if using key-based authentication.
-
Restart the SSH Server: After making changes to the configuration, restart the SSH server for changes to take effect. Use PowerShell to do this:
Restart-Service sshd
Testing Your SSH Installation
After installation and configuration, you want to test one’s SSH client and server.
Testing SSH Client
- Open PowerShell or Command Prompt.
- To test connecting to a remote server, use:
ssh username@hostnameReplace
usernamewith your remote username andhostnamewith the IP address or domain of the remote server.
Testing SSH Server
To test your SSH Server installation:
- Try connecting from another device using an SSH Client (such as PuTTY or any Linux terminal).
- If you can successfully log in, the server is functioning correctly.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with a correct installation and configuration, you might run into issues. Here are some common problems and solutions:
-
Connection Refused:
- Ensure the SSH server is running. You can check its status using:
Get-Service -Name sshd - Verify your firewall settings. Ensure that TCP port
22(or the port you have configured) is open.
- Ensure the SSH server is running. You can check its status using:
-
Permission Denied:
- If you are using public key authentication and see this error, make sure that your public key is properly set up in the
authorized_keysfile on the remote server. - Double-check file permissions.
- If you are using public key authentication and see this error, make sure that your public key is properly set up in the
-
Timeout Issues:
- Get network issues or firewall settings. If using a VPN or proxy, ensure they are configured correctly.
Conclusion
Installing and configuring SSH on Windows 11 is a straightforward process that enhances your machine’s security and usability when accessing remote servers and securely transferring files. With the built-in OpenSSH client and server, Windows 11 users can take advantage of SSH’s capabilities without the need for third-party software.
As you become familiar with the SSH command line and its functions, it’s important to remember to maintain security best practices. Regularly update your keys, use secure passwords, and keep your systems up to date to protect against security vulnerabilities.
By following this guide, you’re now equipped to install, configure, and utilize SSH on your Windows 11 machine, empowering you with the tools needed for secure remote interactions and efficient file management. Whether for personal use, remote work, or enterprise applications, SSH opens up a realm of secure possibilities. Happy connecting!






