Watch VIDEO
This How to is based on Windows 10×64 Pro image installation. The other windows versions are supported
For this you will need an actual Windows installation ISO.
We are using: Windows-10×64-Pro.iso. Be sure that distro name does not have spaces in the filename!
The procedure is the same for any other Windows version 7, 8.1, 10, 11 hosts.
1. Create a new directory for this image according to the naming convention:
root@eve:~# mkdir /opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10x64-PRO/
2. Use WinSCP or FileZilla SFTP or SCP (port 22) to copy distro ISO image into the newly created directory path: /opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10×64-PRO/
3. Go to that directory via CLI
root@eve:~# cd /opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10x64-PRO/
4. Rename this ISO file to cdrom.iso
root@eve:~#/opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10x64-PRO# mv Windows-10x64-Pro.iso cdrom.iso
5. Create a new virtual HDD named virtioa.qcow2 inside of your new image folder. Size you can choose per your needs. This example is used 60Gb HDD.
root@eve:~# cd /opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10x64-PRO/
root@eve:~#/opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10x64-PRO# /opt/qemu/bin/qemu-img create -f qcow2 virtioa.qcow2 60G
6. Create a new lab and add the newly created win-10×64-PRO node
7. Connect the node to your home LAN cloud/internet in order for it to be able to get updates from the internet
8. Start the node inside the lab and customize the installation of your Windows as you like, as you have connected it to your home LAN and internet this installation will be like any normal Windows installation
9. IMPORTANT: When windows installation asks you to choose an HDD where Windows will be installed, choose Load driver, Browse, choose FDD B/storage/2003R2/AMD64 or x86, (AMD or x86 depends which version of windows you are installing 64 or 32 bit), click next and you will see HDD RedHat VIRTIO SCSI HDD now.
10. Select this HDD and continue to install Windows as usual.
11. Optional: if you would like to use this image with the EVE RDP console, then you have to allow RDP on this Windows machine and create a user and password. In this example, we use user/Test123. Be sure that in the Windows Firewall the Remote Access inbound rules are permitted for Public access.
12. Finish installation and shutdown properly the VM from inside VM OS. Start/shutdown
IMPORTANT: Commit the installation to set it as the default image for further use in EVE-NG:
13. On the left side-bar within the lab in the EVE Web-UI choose “Lab Details” to get your lab’s UUID details: In this example: UUID: 3491e0a7-25f8-46e1-b697-ccb4fc4088a2
14. Find out the POD ID of your used and the Node ID of your newly installed node.
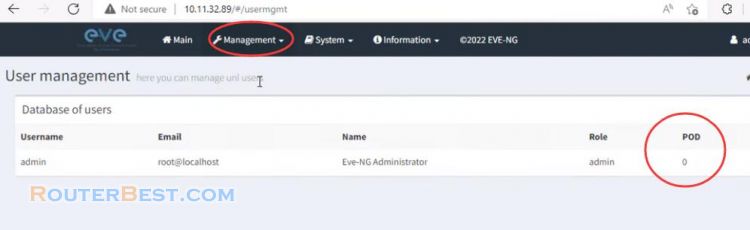
The POD number is assigned to your username, and can be found in the EVE GUI, Management/User Management. The Admin user uses POD number 0 by default.
The Node ID can be obtained by right clicking the node on the topology. In this Example it is 8
15. From the EVE CLI, locate the installed image and commit your changes to be used as default for further use in EVE-NG:
root@eve:~# cd /opt/unetlab/tmp/0/3491e0a7-25f8-46e1-b697-ccb4fc4088a2/8/
root@eve:~#/opt/unetlab/tmp/0/3491e0a7-25f8-46e1-b697-ccb4fc4088a2/8/ /opt/qemu/bin/qemu-img commit virtioa.qcow2
16. Remove cdrom.iso from /opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10×64-PRO/
root@eve:~# cd /opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10x64-PRO/
root@eve:~#/opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10x64-PRO/ rm -f cdrom.iso
DONE
Advanced instructions on how to make your image smaller in size (sparsify&compress).
- After you have done all the steps above and your default image is created, you can compress its HDD and make it smaller.
IMPORTANT: for compressing an image you must have sufficient free space on your EVE host, the free space must exceed the total space (60GByte in this example) of the HDD you plan to shrink. The space needed can vary but will be the total space of the disk to be shrunk plus the size of the final sparsified and compressed image. To be safe you should have double the size of the HDD you want to shrink as free space on your EVE host. In our example we needed 65Gb of free HDD space. Once this process is done, the temporary file(s) will be deleted and free space reclaimed.
- From the CLI: go to your windows image directory:
root@eve:~# cd /opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10x64-PRO
and perform the sparsify command:
root@eve:~#/opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10x64-PRO/ virt-sparsify --compress virtioa.qcow2 compressedvirtioa.qcow2
- This will take some time and another compressed image will be created in the same image directory (win-10×64-PRO)
- now you can rename your original virtioa.qcow2 file to orig.qcow2
root@eve:~#/opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10x64-PRO/ mv virtioa.qcow2 orig.qcow2
- Rename the compressed image name to virtioa.qcow2:
root@eve:~#/opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10x64-PRO/ mv compressedvirtioa.qcow2 virtioa.qcow2
- now you can test your new compressed image on a lab, just wipe the node and start it.
- If the compressed node works fine, you can delete your original source image orig.qcow2:
It’s a mistake if your EVE-NG doesn’t have a Windows virtual machine. In this article, I will show you how to install Windows 10 in an EVE virtual environment.
Windows 10 iso file
First you need to prepare a Windows 10 iso file.
Next you copy and paste the iso file into eve using WinSCP.
File directory: opt/unetlab/addons/qemu
You create a new folder according to eve’s naming convention, here I name it «win-10«. Note that you must not name the wrong convention. Next, drag and drop the iso file into the newly created folder. You rename the iso file to «cdrom.iso«.
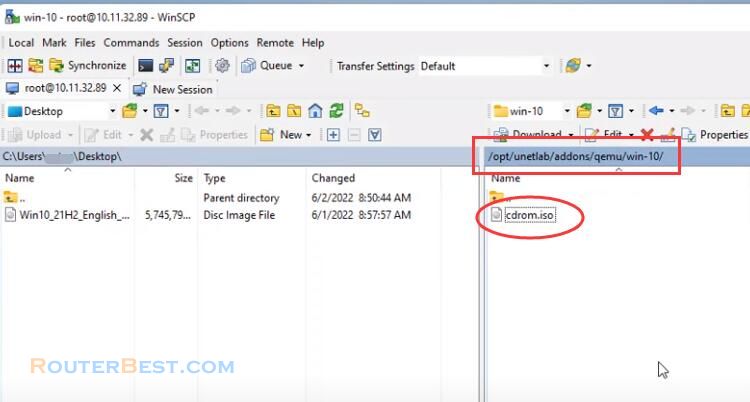
Next you open a command window access EVE with SSH.
cd /opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10/ /opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10# ls
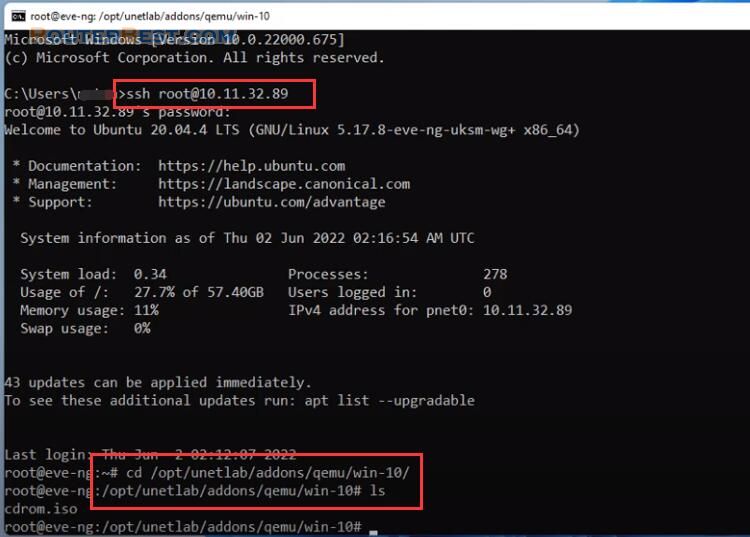
You create a new hard drive for the Windows 10 virtual machine.
You can completely perform the previous steps using the command line according to the instructions.
Here you are instructed to create a hard drive of size 30G, because I installed Windows 10 so I increased the size to 40G.
/opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/win-10# qemu-img create -f qcow2 virtioa.qcow2 40G
Next, you create a new lab and name it as you like. I created a new lab named «win10». In the device list, I go to the Windows category and add a new computer.
Next, you connect the virtual computer to the internet to update, install software or check the network connection.
Installing the Windows 10 operating system
You start the computer and start installing the Windows 10 operating system. You won’t find the hard drive like when you install Windows 10 on a real machine.
To find the hard drive, click «Load Driver» > «Browse» > «Floppy disk drive» > «storage» > «2003R2» > «AMD64».
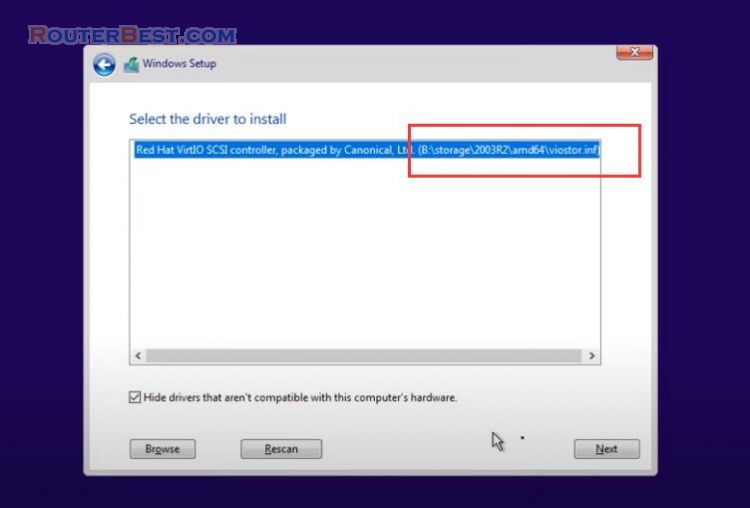
Wait a while you will see the hard drive appear and you install Windows 10 on it. The next installation steps will be the same as on a physical computer so I will fast forward the steps so you don’t have to wait too long.
At this point, you have installed Windows 10 for the virtual machine, but you still have an important step to take.
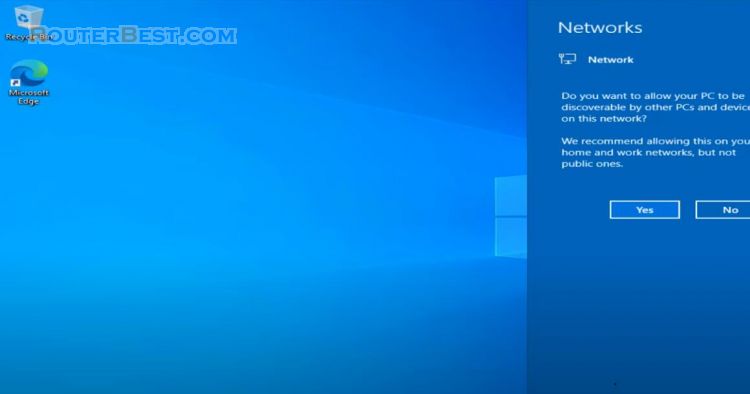
Please follow the next steps.
So the virtual machine works fine, has an internet connection, next you turn off the virtual machine and move on to the next step.
You go to Lab details and write down the UUID information.
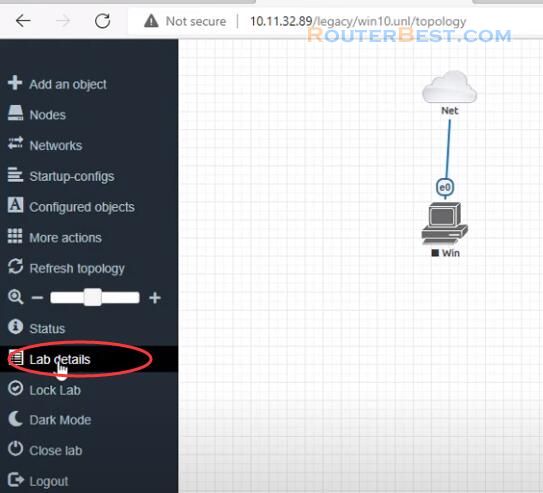
Next, Find out the POD ID of your used and the Node ID of your newly installed node.
As in this article, POD ID is 0.
Here is a sample command with the information you need to find.
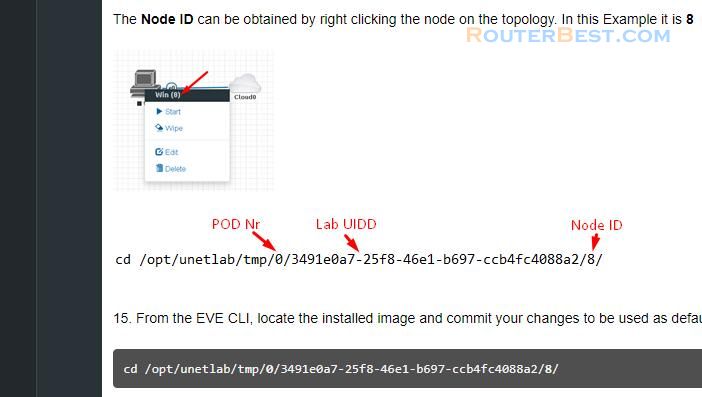
You right click on the newly created virtual machine to find the node id, and as you can see the node id is 1.
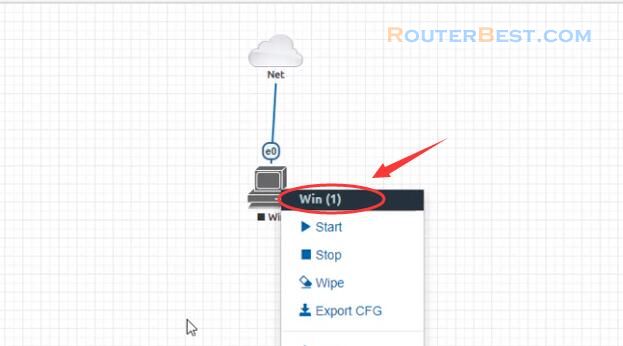
Next you create the image from the Windows virtual machine created in the previous step.
You notice the change in the size of the file virtioa.qcow2, which will increase in size after completion.
And here is the image file you obtained.
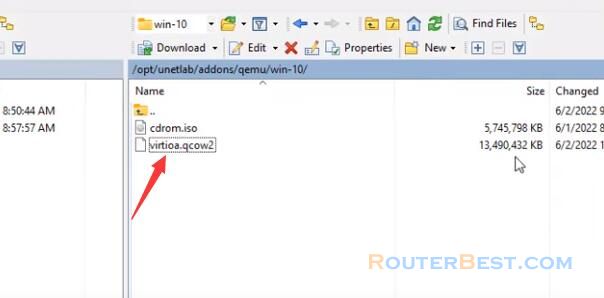
It will take you about 5 minutes to complete this step, so please wait patiently.
Now you can remove Windows 10 ISO file from Eve.
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/routerbest
Twitter: https://twitter.com/routerbestcom
Tags: EVE-NG Windows 10
- Prepare the Windows ISO: Obtain a Windows installation ISO file. You can download these from the Microsoft website or use an existing ISO file you have.
- Upload the ISO to EVE-NG: Log in to the EVE-NG web interface. In the top menu, go to “Images” and then click on “Browse” to select the Windows ISO file from your local machine. Click on “Upload” to upload the ISO file to EVE-NG.
- Create a QEMU VM: In the EVE-NG web interface, go to the “Node” section and click on “Add Node.” Select the type as “QEMU” and configure the settings for the VM. You can specify the number of CPUs, amount of RAM, and the size of the hard disk.
- Map the Windows ISO: In the QEMU VM settings, go to the “Console” tab. Under the “CD/DVD” section, select the Windows ISO file you uploaded earlier as the CD/DVD image.
- Start the VM: After configuring the VM settings, click on “Add Node” to create the QEMU VM. Start the VM by clicking on the play button in the EVE-NG interface.
- Install Windows: Access the VM console by right-clicking on the VM in the EVE-NG interface and selecting “Console.” The VM will boot from the Windows ISO. Follow the on-screen instructions to install Windows. You may need to format the virtual hard disk and select the installation partition during the process.
- Complete the Installation: After Windows is installed, the VM will restart. You can then log in to Windows and configure it as needed.
- Optional: Install VirtIO Drivers: For better performance, you can install VirtIO drivers in Windows. These drivers are included in the EVE-NG installation and can be found in the
/opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/virtio-windirectory. To install the drivers, mount the VirtIO ISO in Windows and run the installer. - Access Windows from EVE-NG: Once Windows is installed and running, you can access it from EVE-NG by right-clicking on the VM in the EVE-NG interface and selecting “Console.”
- Activate Windows: After installation, you’ll need to activate Windows using a valid product key. You can do this by going to “Settings” > “Update & Security” > “Activation” in Windows.
Remember to comply with Microsoft’s licensing terms and ensure that you have a valid license for Windows when using it on EVE-NG or any other virtualization platform.
EVE-NG (Emulated Virtual Environment Next Generation) is an advanced network emulator that enables the simulation of complex networking situations. It’s a vital tool for network engineers, developers, and cybersecurity professionals who need a platform for creating, testing, and learning about different network configurations. This article will guide you through the step-by-step installation of EVE-NG on Windows 11, including the necessary prerequisites, installation process, and additional configurations.
Prerequisites
Before starting the installation, ensure that your Windows 11 system meets the following requirements:
-
Hardware Specifications:
- A minimum of 8 GB of RAM (16 GB recommended).
- At least 20 GB of free disk space for a smooth experience.
- A multi-core processor (Intel or AMD).
-
Software Requirements:
- Windows 11 Professional, Enterprise, or Education edition (Home edition is not supported for Hyper-V).
- Virtualization support (Intel VT-x or AMD-V) must be enabled in BIOS.
- Hyper-V feature must be activated on Windows to run EVE-NG.
-
Download Links:
- Download EVE-NG Community Edition from the official EVE-NG website.
- Download and install Oracle VM VirtualBox or VMware Workstation Player if you plan to use these platforms instead of Hyper-V.
Step 1: Enable Virtualization and Hyper-V
To run EVE-NG on Windows 11, you must ensure that virtualization is enabled in your system’s BIOS settings:
- Restart your computer and enter the BIOS setup. This usually involves pressing a key like F2, Delete, or Esc during the boot process (the specific key depends on your motherboard).
- Locate the Virtualization Settings in the BIOS menu. This setting might be under the «Advanced», «CPU Configuration», or «Security» tab, depending on your motherboard.
- Enable Intel VT-x or AMD-V option (based on your CPU).
- Save the changes and exit the BIOS.
Next, enable Hyper-V in Windows:
- Right-click the Start button and select Apps and Features.
- Click on Optional features and then on the More Windows features link.
- In the Windows Features window, check the box next to Hyper-V, then click OK.
- Wait for the installation to complete and restart your computer if prompted.
Step 2: Download EVE-NG
- Navigate to the official EVE-NG website (https://www.eve-ng.net/).
- Go to the Download section and select the Community Edition.
- Fill in the necessary information to register, and then download the EVE-NG OVA file (which is essentially a virtual machine file).
- This OVA file will be used to import EVE-NG into the virtualization application you choose to use (Hyper-V, VirtualBox, or VMware).
Step 3: Install Virtualization Software
If you’ve decided to use Oracle VirtualBox or VMware Workstation Player instead of Hyper-V, you’ll need to install one of these applications first.
Installing Oracle VirtualBox:
- Go to the official VirtualBox website (https://www.virtualbox.org/).
- Download the latest version available for Windows hosts.
- Open the downloaded installer and follow the on-screen instructions. Ensure you have checked the options to create shortcuts and to register the VirtualBox network interfaces.
- After installation, initiate VirtualBox to verify it’s working correctly.
Installing VMware Workstation Player:
- Go to the VMware official site (https://www.vmware.com/products/workstation-player.html).
- Download the latest version of VMware Workstation Player for Windows.
- Run the installer and follow the installation process.
- When installation is complete, run VMware Workstation Player to confirm it is working properly.
Step 4: Import EVE-NG OVA File
Here’s how to import the EVE-NG OVA file using either VirtualBox or VMware:
Importing with Oracle VirtualBox:
- Open VirtualBox.
- Click on File, then select Import Appliance.
- Browse to the location of the downloaded EVE-NG OVA file and select it.
- Click on Next and review the appliance settings. Make sure to allocate adequate resources (e.g., RAM and CPU) based on your system specifications. The suggested settings are generally acceptable.
- Click on Import and wait for the process to finish.
Importing with VMware Workstation Player:
- Open VMware Workstation Player.
- Click on File, then choose Open.
- Navigate to the EVE-NG OVA file and select it.
- Ensure that the Virtual Machine is edited to allocate sufficient resources for your needs.
- Click on Import and wait for the import to complete.
Step 5: Configure Networking Settings
For EVE-NG to work effectively, appropriate networking configurations must be set up. This step involves adjusting network settings according to your virtualization software.
For Oracle VirtualBox:
- In VirtualBox, select your imported EVE-NG VM and click on Settings.
- Navigate to Network. You should see adapters labeled Adapter 1 through Adapter 4.
- Set Adapter 1 to Bridged Adapter. This will allow your EVE-NG instance to communicate with your local network.
- Ensure the other adapters follow the recommended configuration: Adapter 2, Adapter 3, and Adapter 4 should usually be set to Host-only Adapter.
- Click OK to save.
For VMware:
- In VMware Workstation Player, select your imported EVE-NG VMs and click on Edit virtual machine settings.
- In the Network Adapter properties, set the first adapter to Bridged. Similar to VirtualBox, this allows for communication with the local network.
- Ensure other adapters are set to Host-only as necessary, based on usage.
- Apply the changes and exit the settings.
Step 6: Start EVE-NG for the First Time
Now that everything is set up, it’s time to start EVE-NG for the first time:
- Select the EVE-NG VM in your virtualization software (VirtualBox or VMware).
- Click on Start to power up EVE-NG.
- On the first boot, EVE-NG will take some time to initialize. Monitor the console for the IP address it will use.
- Once booted, note the IP address provided in the terminal.
Step 7: Access EVE-NG via Web Browser
- Open a web browser on your Windows 11 machine.
- Type the IP address you noted from the VM console into the address bar. It should be something like
http://192.168.x.x. - You will be prompted for a username and password:
- Use
adminas the username. - Use
eveas the password.
- Use
- This should bring you to the EVE-NG dashboard.
Step 8: Configure EVE-NG
After logging in, it is advisable to configure some settings and upload images for use in EVE-NG.
Uploading Images:
- Prepare your networking images (e.g., Cisco IOU images, GNS3 compatible images, etc.).
- Use WinSCP or FileZilla to connect to your EVE-NG instance.
- Connect using the IP address and your admin credentials.
- Upload your images to the respective directories under
/opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/. - Make sure to set the appropriate permissions on each of the uploaded images by logging into the console with SSH and running the following command within that directory:
chmod +x - Finally, run the command to consolidate the images in EVE-NG:
/opt/unetlab/wrappers/unl_wrapper -a fixpermissions
Configure Preferences:
- Go to settings on the EVE-NG dashboard to adjust preferences as needed.
- This may include changing the default language, configuring network settings, or adjusting the node types.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully installed EVE-NG on your Windows 11 machine. This robust platform will now allow you to create various network topologies, perform simulations, and enhance your networking skills. EVE-NG opens up a world of possibilities for network design and testing, significantly aiding those in network engineering, development, and cybersecurity. For future endeavours, always keep your EVE-NG images and the software itself up to date to ensure optimal performance and access to the latest features.
Remember, practice is key to mastering EVE-NG, so utilize your new setup to experiment, learn, and grow in the field of networking. If you encounter issues during your use, the EVE-NG community forums and official documentation are valuable resources. Happy simulating!
Introduction to EVE-NG
EVE-NG (Emulated Virtual Environment Next Generation) is a popular network emulation tool that allows users to design, implement, and test complex network topologies in a virtual environment. It is widely used by network professionals, engineers, and students for practicing configuration, troubleshooting, and developing networking skills. EVE-NG supports various network operating systems, including Cisco IOS, Juniper, and virtual machines, and it enables users to create a lab environment that closely mirrors real-world scenarios.
If you’re running Windows 11 and want to install EVE-NG, this guide will walk you through the entire process step by step. Ensuring that you can set up your virtual lab environment smoothly.
System Requirements
Before diving into the installation process, it’s essential to ensure that your system meets the necessary prerequisites to run EVE-NG effectively. Here are the minimum system requirements:
- Processor: Intel or AMD 64-bit processor
- RAM: At least 8 GB (16 GB or more recommended)
- Storage: At least 50 GB of free disk space
- OS: Windows 11 (64-bit version)
- Virtualization: Hardware Virtualization support in your BIOS (Intel VT-x or AMD-V)
- Network Adapter: Ethernet adapter for external connections
- Hypervisor: VMware Workstation or Oracle VirtualBox
Step 1: Enable Hardware Virtualization
To run EVE-NG smoothly, hardware virtualization should be enabled on your machine. Here’s how to check and enable it:
-
Access BIOS/UEFI: Restart your Windows 11 computer and enter the BIOS setup. This usually involves pressing a key like F2, Delete, or Esc immediately after powering on, depending on your motherboard manufacturer.
-
Locate Virtualization Settings: Once in the BIOS, look for settings related to CPU configuration. This might be under «Advanced,» «CPU Configuration,» or «Security.» Look for options such as «Intel VT-x» or «AMD-V.»
-
Enable Virtualization: Change the setting to “Enabled.”
-
Save and Exit: Save your changes and exit the BIOS setup.
Step 2: Download EVE-NG
With virtualization enabled, the next step is to download the EVE-NG ISO from the official website:
-
Visit the EVE-NG Website: Go to the official EVE-NG website (http://www.eve-ng.net/).
-
Select the Right Version: Choose the community edition if you are looking for a free option. You may also find additional features in the professional edition but for most users, the community edition suffices.
-
Download the ISO: Locate the ISO image for the version you want to install and download it to your computer. Ensure the file is fully downloaded before proceeding.
Step 3: Install VMware Workstation or Oracle VirtualBox
EVE-NG can be run either on VMware Workstation or Oracle VirtualBox. For this guide, we will focus on using VMware Workstation since it’s widely used and provides robust features. However, if you prefer VirtualBox, the steps are similar.
Installing VMware Workstation
-
Download VMware Workstation: Go to the VMware website (https://www.vmware.com/) and download the latest version of VMware Workstation Player (or Pro, if you have a license).
-
Run the Installer: Once downloaded, run the installer and follow the prompts to complete the installation. Accept the license agreement and choose the necessary installation options.
-
Finish Installation: Once the installation is complete, open VMware Workstation to begin setting up your EVE-NG virtual lab.
Step 4: Create the EVE-NG Virtual Machine
Now that VMware is installed, it’s time to create a new virtual machine for EVE-NG.
-
Open VMware Workstation: Launch VMware Workstation and select «Create a New Virtual Machine.»
-
Select the Configuration Type: Choose «Typical» installation and click «Next.»
-
Use the EVE-NG ISO: When prompted to select the operating system installer, select “I will install the operating system later.” Click “Next.”
-
Choose Guest Operating System: Select “Linux” as the operating system and “Other Linux 5.x or later kernel 64-bit” as the version. Click “Next.”
-
Name Your Virtual Machine: Enter a name for your EVE-NG virtual machine (e.g., “EVE-NG”) and choose a location to store it.
-
Specify Disk Capacity: Allocate at least 50 GB for the virtual machine disk capacity. Choose to store the virtual disk as a single file for better performance.
-
Customize Hardware: Before finishing, click on “Customize Hardware.” Here are the recommended settings:
- Memory: At least 4 GB (8-16 GB recommended for larger labs).
- Processors: 2 or more, and ensure the option “Virtualize Intel VT-x/EPT or AMD-V/RVI” is enabled.
- Network Adapter: Set it to Bridged mode for easier access to the virtual machine over your home network.
- CD/DVD Drive: Use the EVE-NG ISO file you downloaded earlier.
-
Finish the Setup: Click “Close” to exit the hardware settings and then “Finish” to create the virtual machine.
Step 5: Install EVE-NG on the Virtual Machine
-
Power On the Virtual Machine: Right-click on your EVE-NG VM in VMware Workstation and select «Power On.»
-
Start the Installation: Once the virtual machine boots, it will load the EVE-NG installation process.
-
Follow the Prompts: Navigate through the installation prompts. Generally, the default settings will suffice. Select Yes when prompted to proceed with the installation, and allow the installation process to complete which will take several minutes.
-
Reboot the Virtual Machine: After installation completes, you’ll be prompted to restart the VM. Do so.
Step 6: Accessing EVE-NG
-
Find the IP Address: After the reboot, you’ll see a terminal interface showing the IP address assigned to your EVE-NG instance. Note this IP address for the next steps.
-
Open a Web Browser: On your Windows 11 host machine, open a web browser.
-
Enter EVE-NG IP Address: Type the IP address of your EVE-NG instance in the address bar preceded by
http://(e.g.,http://192.168.1.100). -
Login: Use the default credentials:
- Username:
admin - Password:
eve
- Username:
-
Change Password: Once logged in, it is recommended to change your password for security purposes.
Step 7: Setting Up EVE-NG
Now that you’ve successfully logged into EVE-NG, it’s time to set up the environment to start creating network topologies.
-
Upload Network Images: To use different network operating systems, you need to upload the appropriate images to EVE-NG. This usually entails downloading the images (like Cisco IOS, etc.) from a reputable source and transferring them to the appropriate directories in EVE-NG.
-
Use WinSCP or FileZilla: You can use a file transfer tool like WinSCP or FileZilla to transfer the images into EVE-NG. Connect using the IP address, username, and password, then navigate to the
/opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/directory. -
Follow Image Installation Instructions: Each type of network image might come with specific installation instructions. Follow them carefully to ensure your images are correctly configured.
Step 8: Creating Your First Lab
-
Create a New Lab: In the EVE-NG web interface, click ‘Lab’ and ‘Add a new lab’. Provide a name and description for your lab.
-
Add Devices: Once your lab is created, click on it and then start adding devices by dragging them from the left panel. Choose the network images you’ve just uploaded.
-
Connect Devices: Use the connection tool to link devices as required in your topology.
-
Start Devices: After the devices are configured, click the ‘Start’ button to power them on.
-
Access Console: Click on the console icon next to each device to access its terminal.
Conclusion
Installing EVE-NG on Windows 11 is straightforward if you follow the detailed steps outlined in this guide. Once set up, you can leverage EVE-NG’s powerful features to simulate complex network environments and hone your networking skills. As you become more comfortable with EVE-NG, you may explore its extensive capabilities, including integrating additional virtual machines, utilizing various network protocols, and more.
Whether you’re studying for certifications, preparing for a job in networking, or just playing with new technologies, EVE-NG provides a comprehensive platform for learning and experimentation. Enjoy building your virtual networks and dive deep into the world of network emulation!
