Lesson Contents
Introduction
To make wireless networks secure, you should use a RADIUS server to authenticate your users instead of using a pre-shared key. The RADIUS server will handle the authentication requests and uses EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) to communicate with users. There are many EAP types, and the most popular ones are:
- PEAP (Protected EAP)
- EAP-TLS
PEAP is usually used to authenticate users by using a username and password. The RADIUS server will show a certificate to the users so that they can verify that they are talking to the correct RADIUS server. EAP-TLS is the most secure form of wireless authentication because it replaces the client username/password with a client certificate.
This lesson walks you through the installation and configuration of Windows Server 2008 using NPS (Network Policy Server) as the RADIUS server for a Cisco wireless LAN controller. We will configure the server so that it supports PEAP using MS-CHAPv2 for password authentication but we’ll also look at EAP-TLS which can be used to authenticate clients using certificates that we will generate on the server. In this lesson, we will configure the following components on the server:
- Active Directory
- DNS
- Certificate Services
- IIS
- NPS
Active Directory (AD) is where we store all the user accounts, it’s the central database that we use for authentication. Whenever you install an AD you also require a DNS server. Certificate services will be used to install the server as a root CA so that we can generate a computer certificate that will be presented to wireless clients and to generate the client certificates for EAP-TLS.
IIS is the web server and we will use it so that EAP-TLS clients can easily request a certificate with their web browser for their wireless connection. Last but not least, NPS is the RADIUS server and that’s where we will configure some wireless policies.
I realized that many network engineers are comfortable configuring switches and wireless equipment but might be new to Windows Server 2008. This “how to” was written so anyone without “Windows Server” experience should be able to get the job done.
This is the topology that I will use for this example:
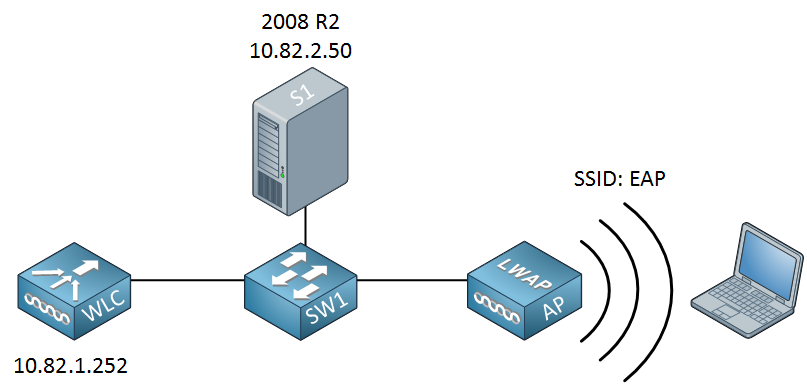
A simple topology with a single switch that connects the server, WLC, and access point together. I’m using a Cisco wireless LAN controller to demonstrate this, but the configuration will be the same for any other wireless LAN controller or access point. The configuration for Windows Server 2008 will be the same. There’s plenty of work so let’s get started!
Basic Network Configuration
Before we start with the installation of Active Directory we’ll fix some basics like setting the correct computer name and IP address.
Computer Name
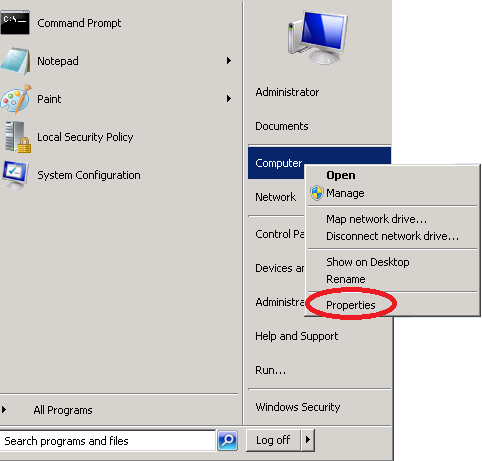
Click Start > Computer (right mouse click) > Properties.
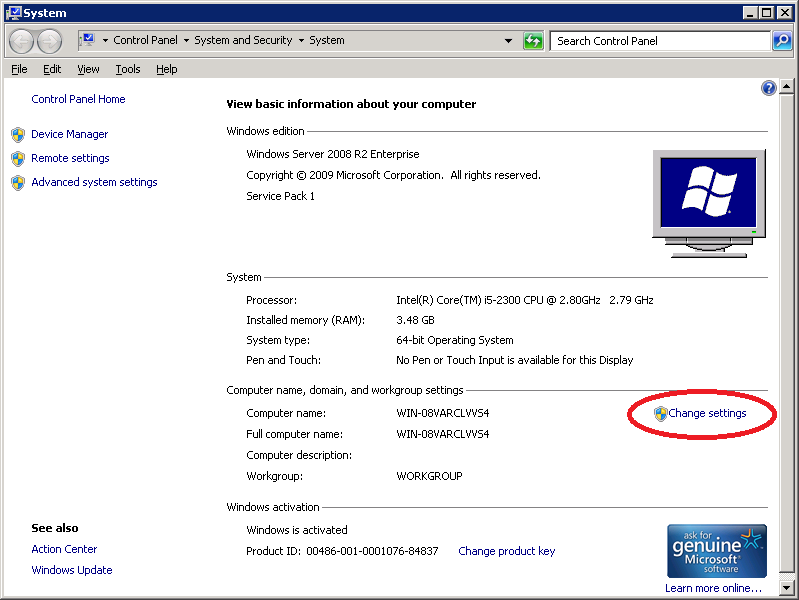
Click on Change Settings.
Click the Change button.
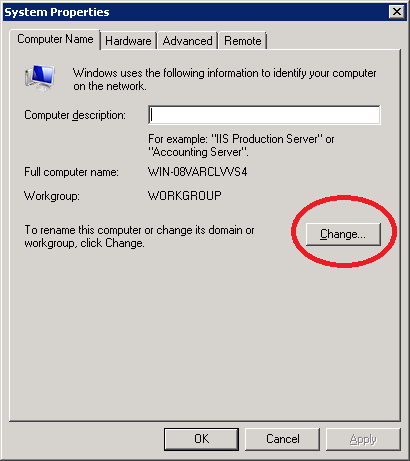
Here’s where you will enter the computer name. I’ll use “AD” (Active Directory). You don’t have to change the workgroup name as we’ll turn this computer into a domain controller in a minute. Make your changes and click on OK.
Once you change the computer name you will have to reboot before the changes will occur. Once your server is rebooted, you’ll have to change the IP address.
IP address
Make sure you don’t configure any DNS servers as this server will become a DNS server. You don’t have to configure a default gateway, but if you have a router that leads to the outside world, you can enter it here:
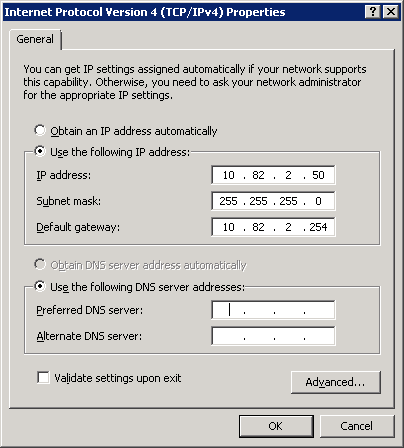
Once you have configured your computer name and IP address we can continue with the installation of Active Directory.
Installing Active Directory
Active Directory is where we store all the usernames in a central database. To install it we need to add a new role to the server.
Click on Start > Administrative Tools > Server Manager.
Click on Roles > Add Roles.
You will be presented with the following wizard. Click on Next.
Select Active Directory Domain Services and click on Next.
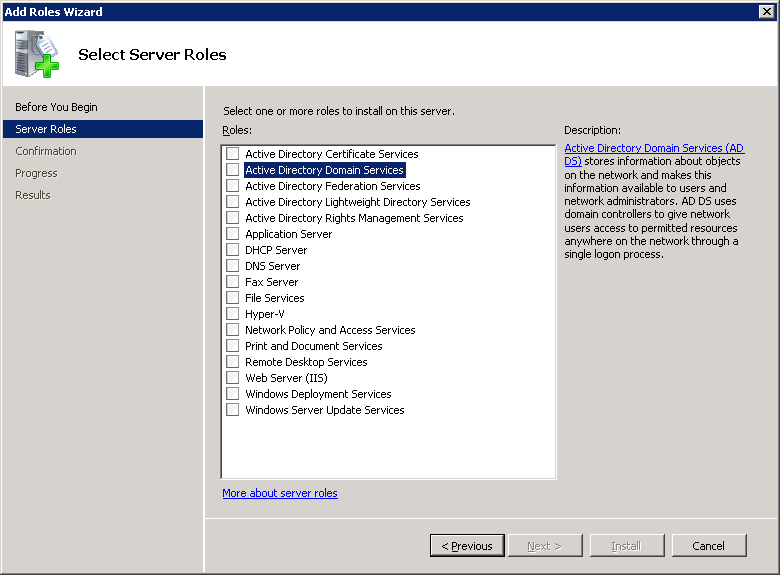
You will get a notification about adding the .NET Framework feature. Click on Add Requires Features.
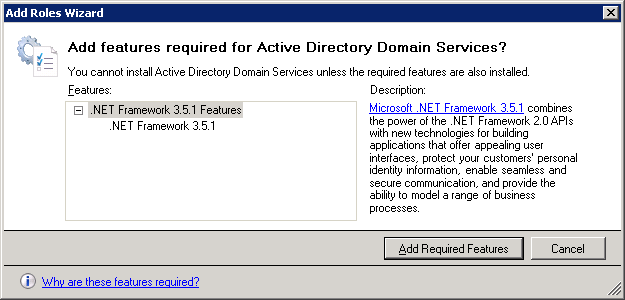
Click Next to continue.
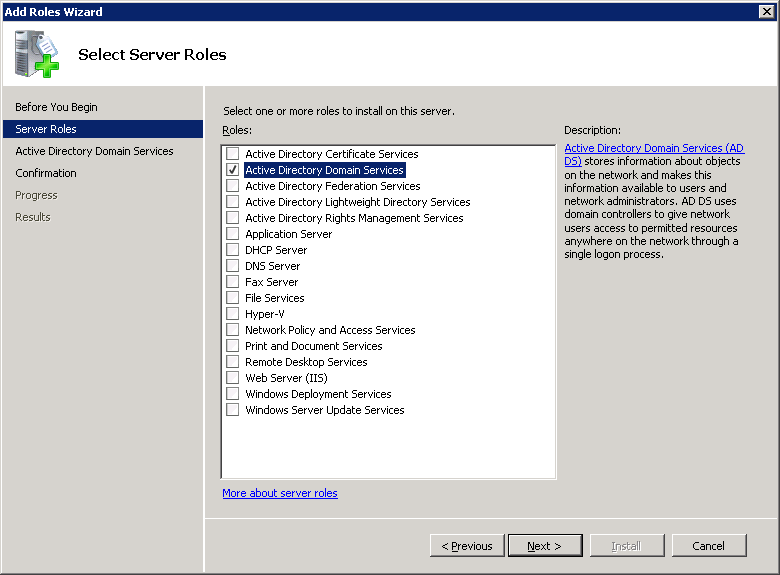
You will see an introduction to Active Directory Domain Services. Click Next to continue.
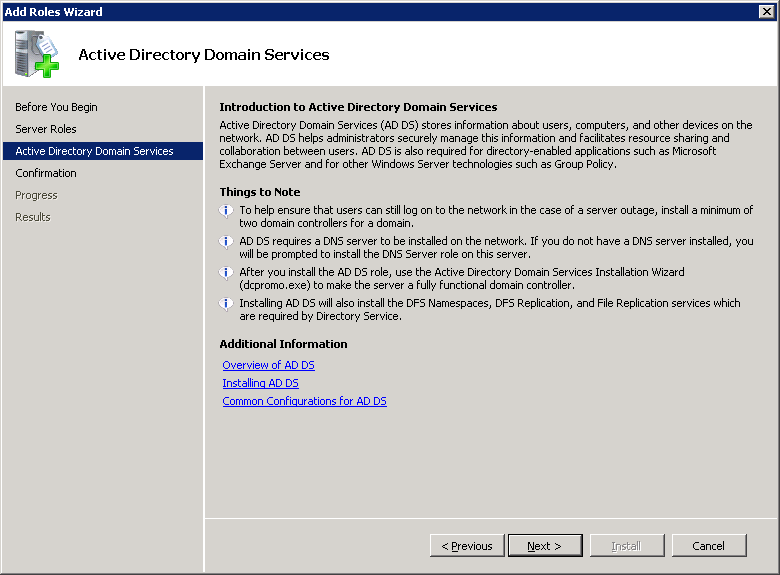
Click Next to confirm the installation options.
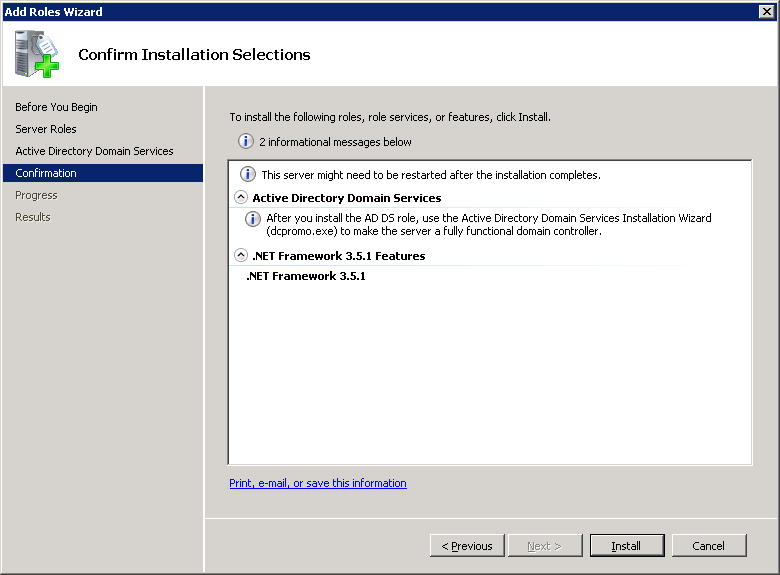
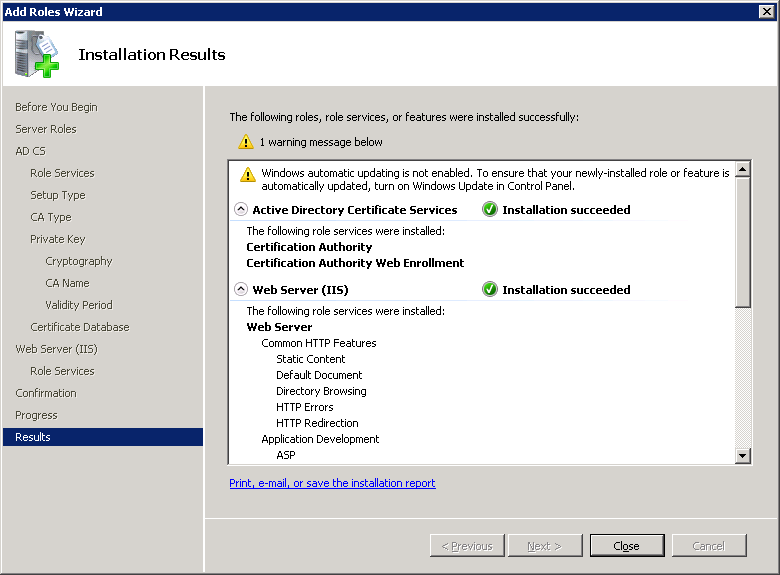
You will see the following screen that indicates the installation progress:
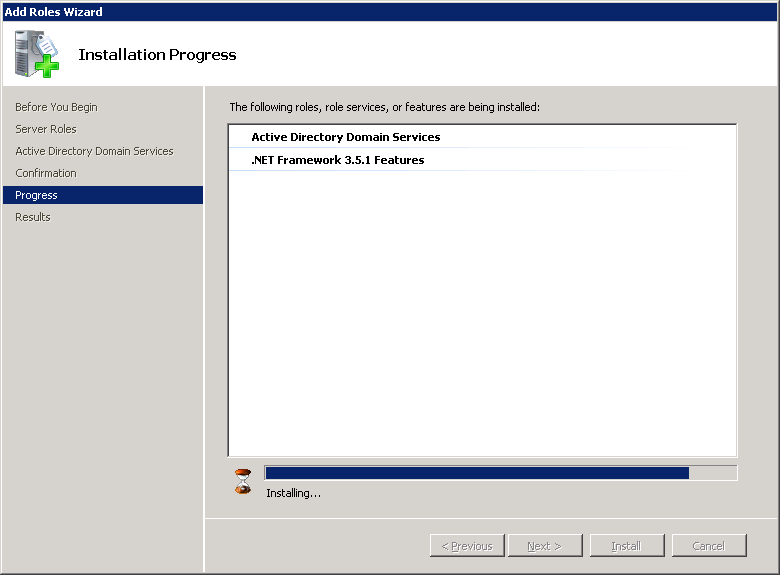
Once the installation is done you might receive a warning about Windows automatic updating. If this is a production server, make a mental note to enable windows updates in the future. Click on Close to continue.
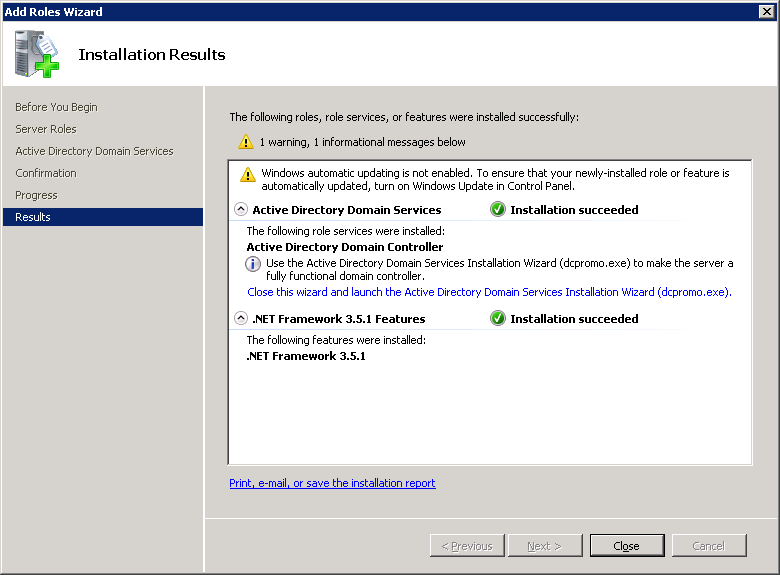
Once Active Directory Domain Services is installed we can create a new domain. Click on the start button and type “dcpromo” (without the quotes):
You will see a welcome screen, leave “use advanced mode installation” unchecked, and click on Next.
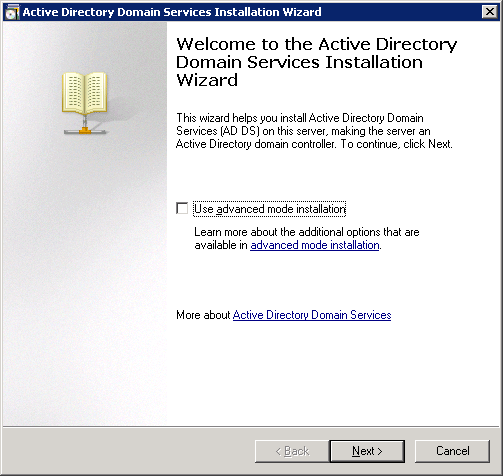
You will be presented with some information about operating system compatibility. Click Next to continue.
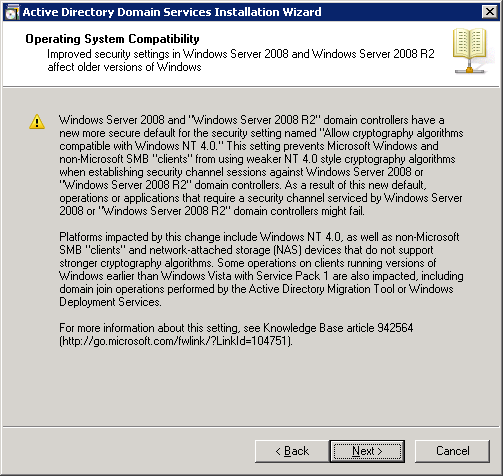
We will create a new forest with a new domain. Select the second option and click on Next.
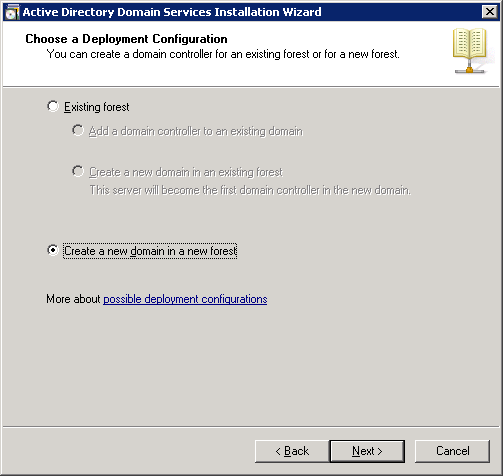
The FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) of my forest root domain will be “NETWORKLESSONS.LOCAL”. Click Next to continue.
We will have to select the Forest Functional Level. If you only use Server 2008 R2 or later versions then you can select the “Windows Server 2008 R2” functional level. If you plan to use older versions of Windows Server, you should use a “lower” functional level. I don’t plan to add any other servers to this network so I’ll select “Windows Server 2008 R2” and click on Next.
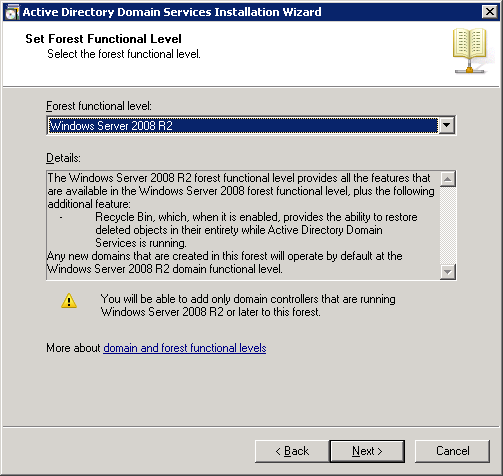
Select “DNS server” and click on Next.
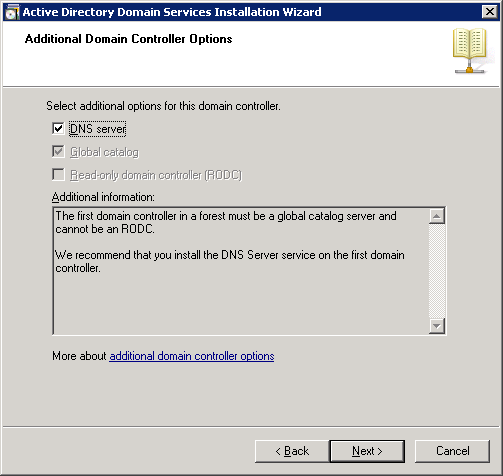
You will receive a notification that the server is unable to create a DNS entry. This is OK because the DNS server isn’t installed yet. Click on Yes to continue.
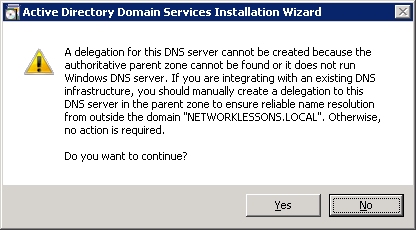
The default folder structure is fine. Click on Next to continue.
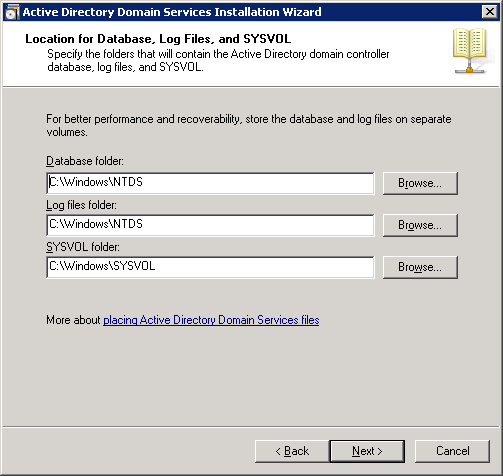
A separate password is used in case you need to restore your Active Directory. I recommend using a different password than the administrator password for this. Click on Next to continue.
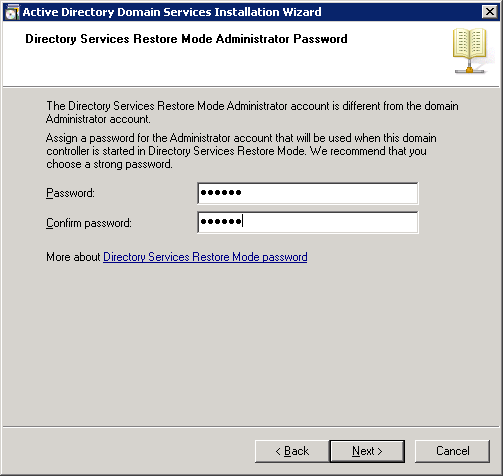
You will receive a summary. Click on Next to continue.
It will take a couple of minutes to install everything. You will see this progress screen:
Click on Finish to continue.
The server will ask you to restart. Click on Restart Now.
Once your server is restarted, you will have a working Active Directory and DNS server. The next step will be to install the certificate server.
Installing Certificate Server
When PEAP wireless clients try to connect to the network, the RADIUS server will present a computer certificate to the user to authenticate itself. It’s up to the client to accept only valid certificates, and this will help to prevent spoofing attacks where an attacker might run a fake RADIUS server. EAP-TLS will also use require the computer certificate from the RADIUS server, but we’ll also require a client certificate for each user that wants to connect to the wireless network.
In order to do this, we will configure our server to become a root CA (Certificate Authority). This allows us to generate a computer certificate and also to generate client certificates.
Click on Start > Administrative Tools > Server Manager.

Click on Roles > Add Roles.

Click on Next to continue.

Select Active Directory Certificate Services and click on Next.
You will see an introduction to Active Directory Certificate Services. Click on Next to continue.
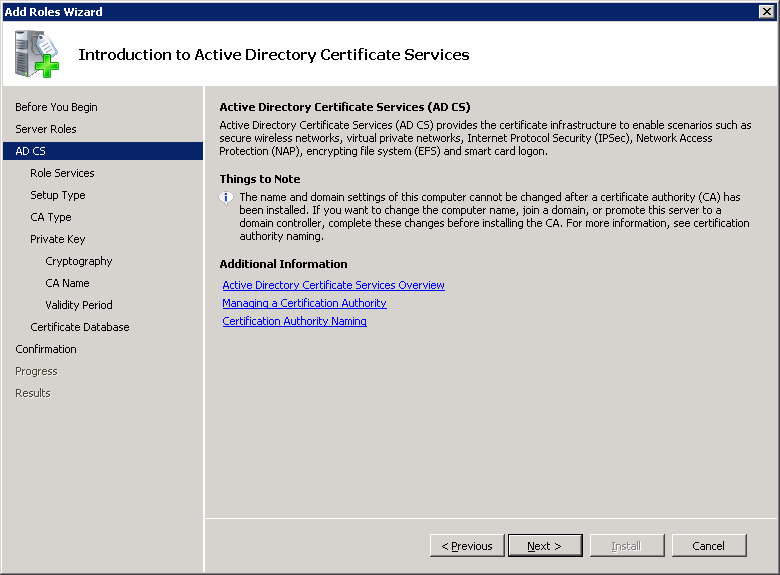
Select Certification Authority. If you want to use EAP-TLS then you should also select Certification Authority Web Enrollment. This will allow us to request client certificates through the web browser which is very convenient.
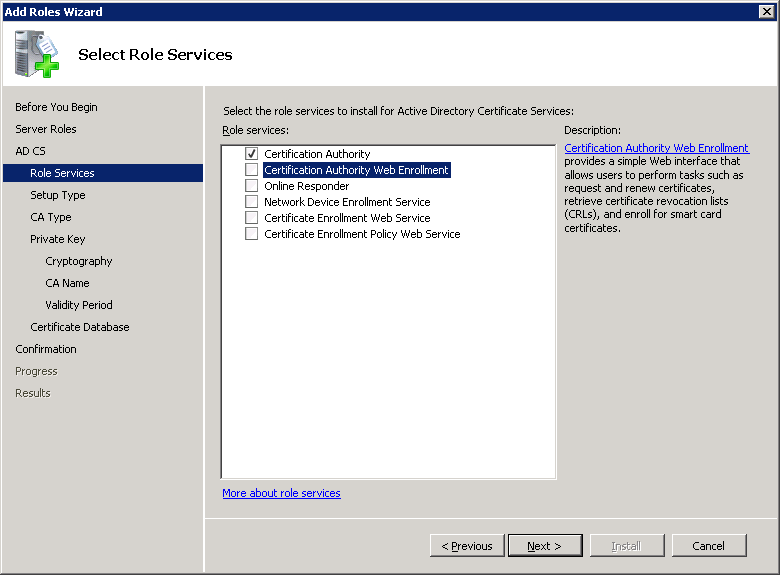
Once you select Certification Authority Web Enrollment you will receive a notification that we need to install IIS (Web Server). Click on Add Required Role Services to continue.
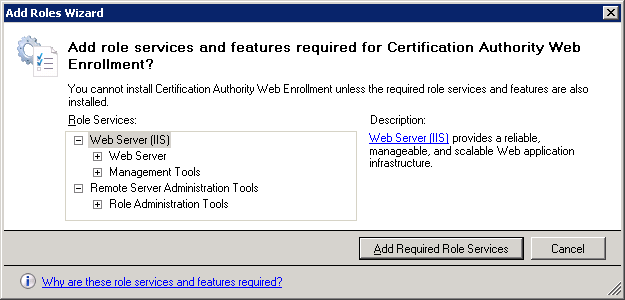
Make sure both services are selected and click on Next to continue.
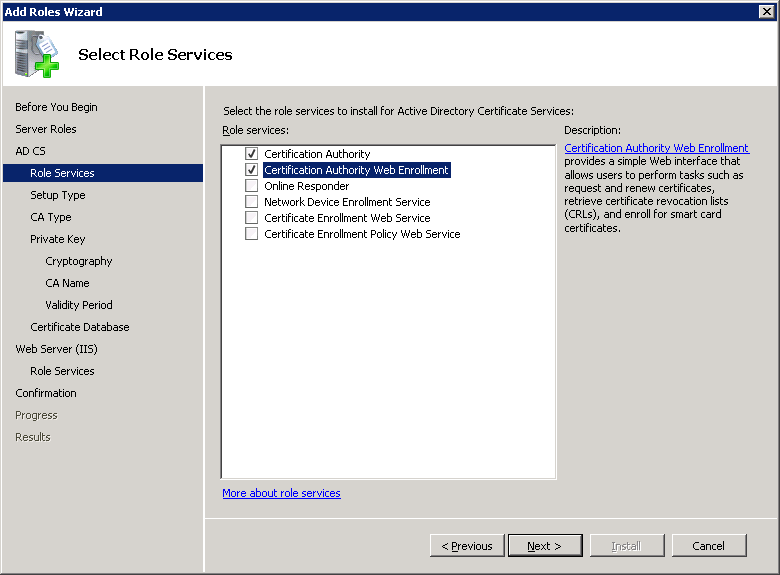
The certificate server can be part of the domain and use active directory or run as stand-alone. We want it to use the active directory so select Enterprise and click on Next.
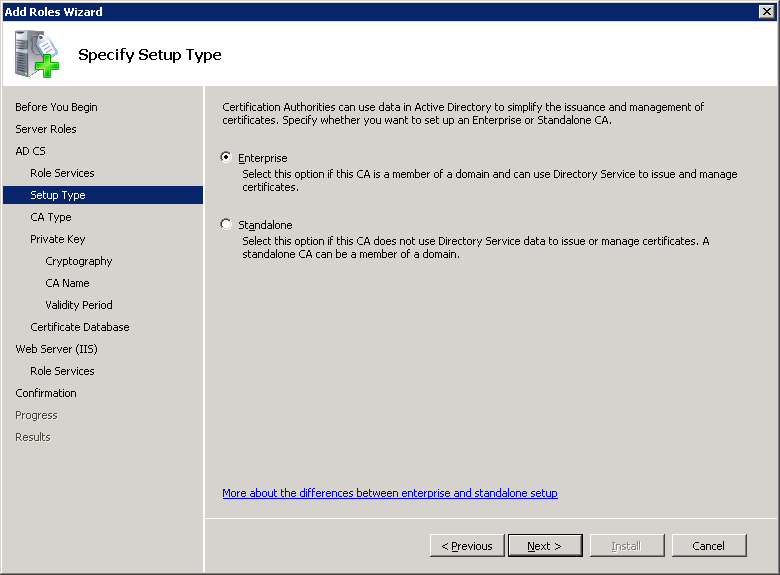
You can specify if you want this server to be a new Root CA or if you want it to be a Subordinate CA. Select Root CA and click on Next to continue.
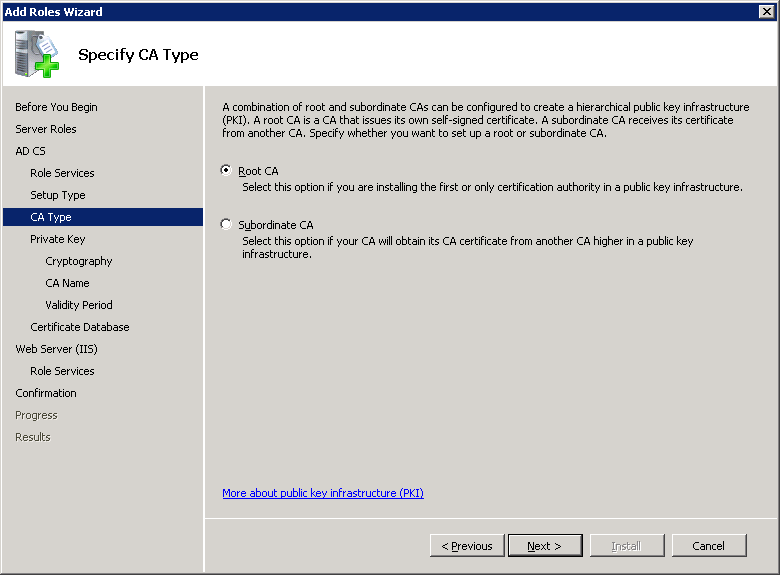
Select Create a new private key and click on Next.
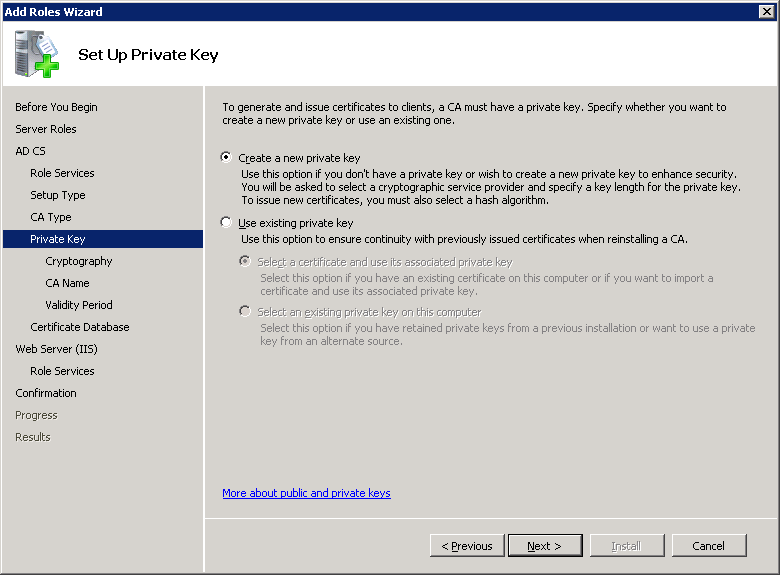
The default cryptography parameters are fine. Click Next to continue.
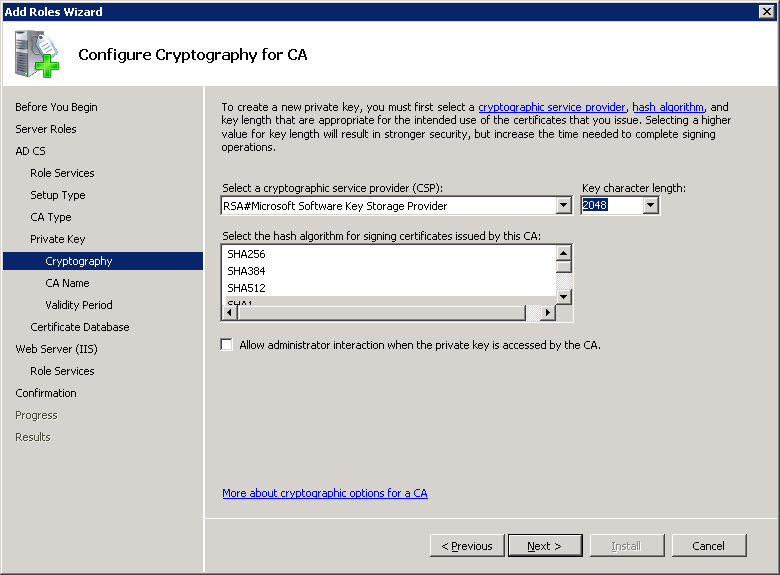
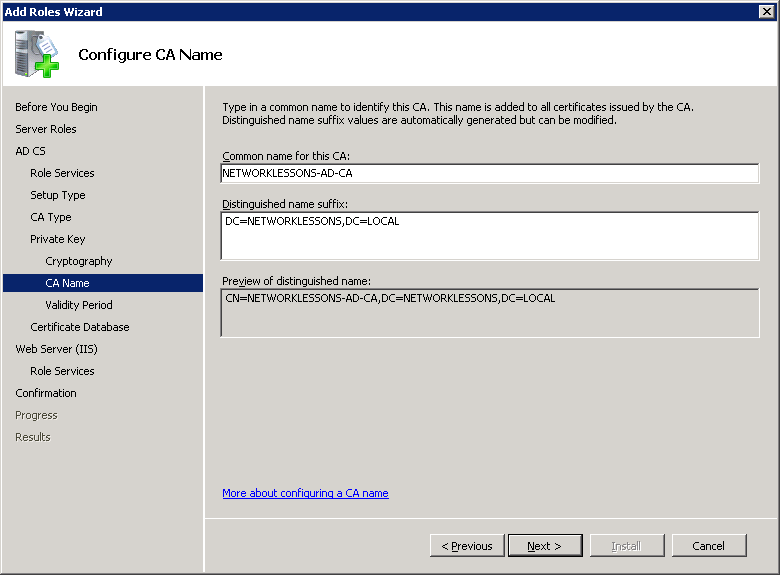
The default CA name is also fine. It will use the computer name and domain name for this. Click on Next to continue.
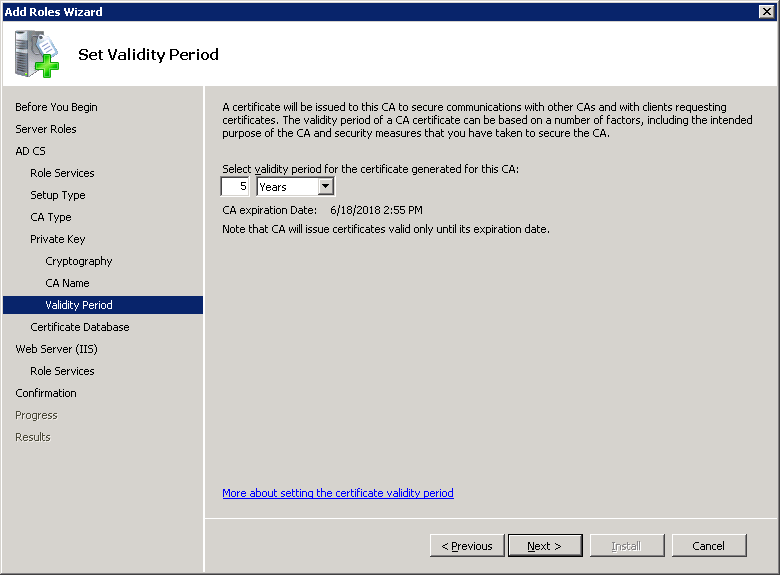
The default validity period for the root CA certificate is five years. Click Next to continue.
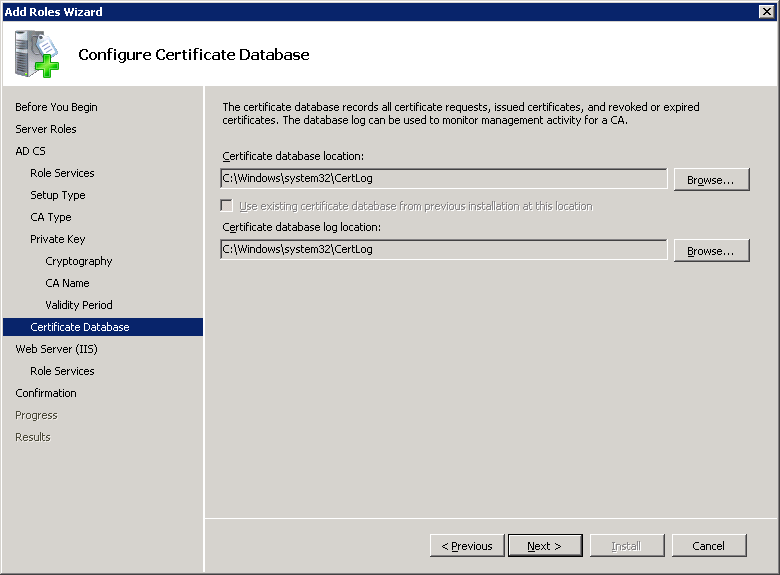
Click Next to continue.
If you selected the web enrollment option, you will see the installation wizard for IIS. You can read the introduction if you like or click on Next to continue.
The default role services are fine. Click Next to continue.
In the confirmation screen, you will be warned that you can’t make any changes to the computer name or domain name once you installed the certificate services. Click Install to continue.
You will see the following Installation Progress. Grab a quick drink…
Once the installation is done, you will see another notification that you should enable Windows updates. Click on Close.
Right now you have a working Certificate Authority and IIS is running to serve web requests. If you plan to use EAP-TLS we need to enable HTTPS support for IIS, by default it is disabled. If you only want to use PEAP, then you can skip this step. Click on Start > Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
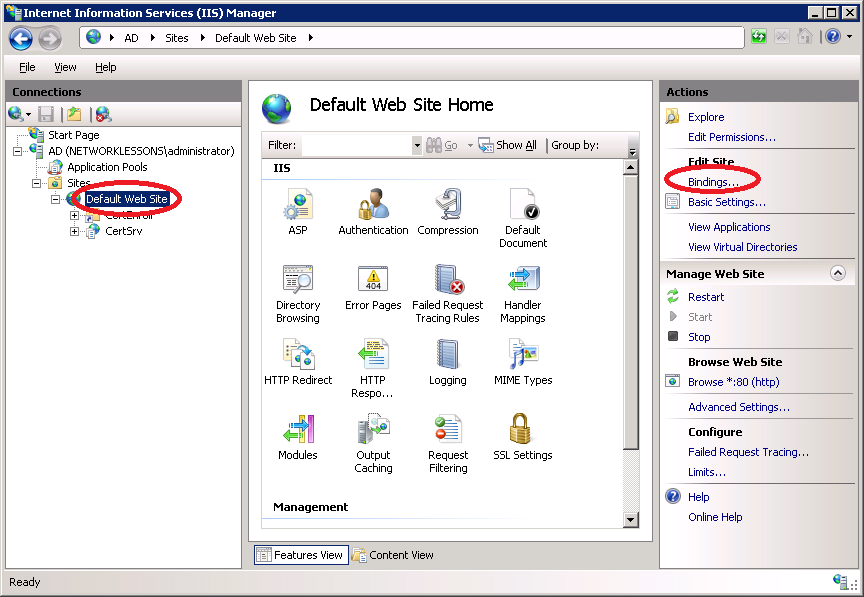
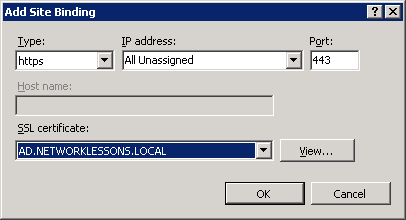
Click on AD (server name) > Sites > Default Web Site and select Bindings on the right side of the screen.
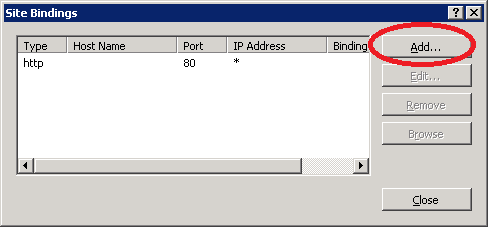
Click on Add.
Select https in the Type dropdown box and make sure the SSL certificate has been selected. Click on OK to continue.
This concludes the installation of the certificate server and IIS. We can now move onto the configuration of the RADIUS server.
Installing Network Policy Server
Network Policy Server (NPS) is the RADIUS server you can find on Windows Server 2008. It has a lot of features and is pretty easy to configure. First, we will have to install it.
Click on Start > Administrative Tools > Server Manager.

Click on Roles > Add Roles.

Click Next to continue.

Select Network Policy and Access Services and click Next to continue.
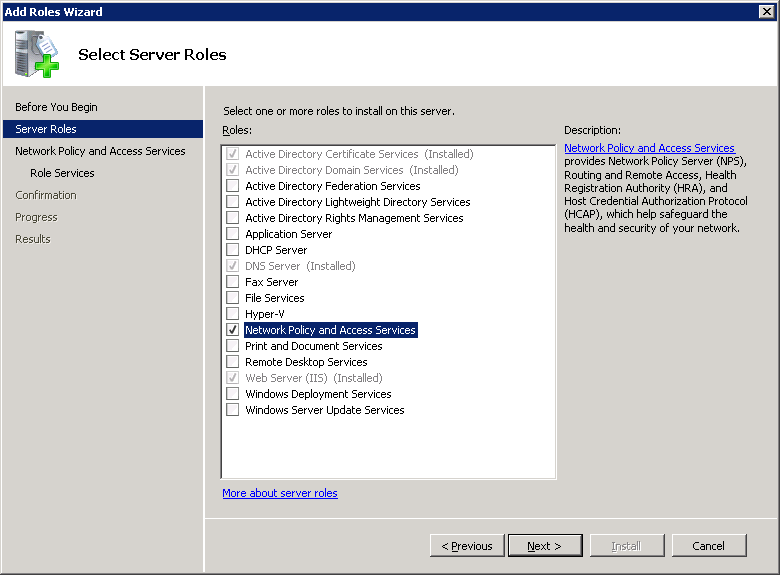
Make sure Network Policy Server is selected and click on Next to continue.
You will see the confirmation screen. Click Next to continue.
You’ll see the installation progress…
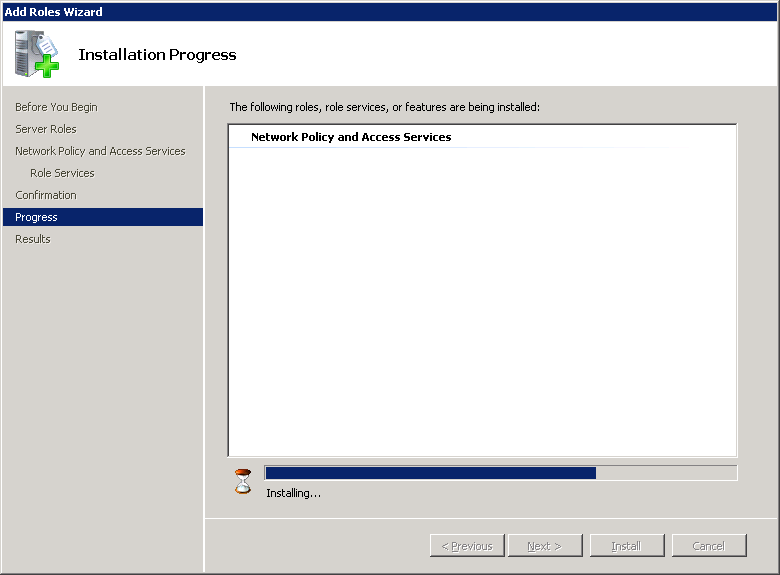
And you’ll see the installation results…
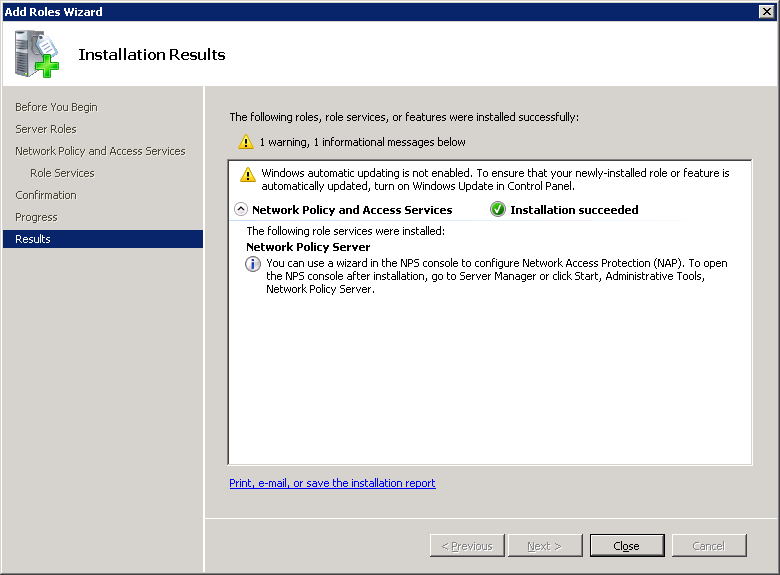
Click on Close.
The Network Policy server is now installed. In the next part, we’ll install a computer certificate that we can use to authenticate the RADIUS server to the wireless clients.
Create RADIUS Computer Certificate
With NPS up and running, we are ready to create user and computer certificates. The RADIUS server will have to present a certificate to the wireless users so that they can verify if they are talking to the correct RADIUS server. Let me show you how to check if you have a computer certificate and otherwise how to generate one.
Click on Start and type “mmc” (without the quotes), and press enter.
Click on File > Add/Remove Snap-in.
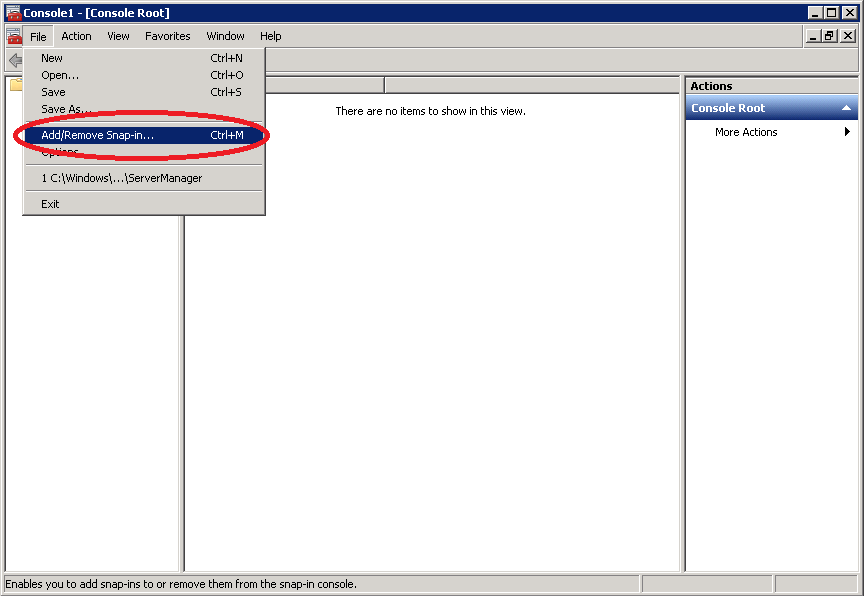
Select Certificates from Available snap-ins and click on Add.
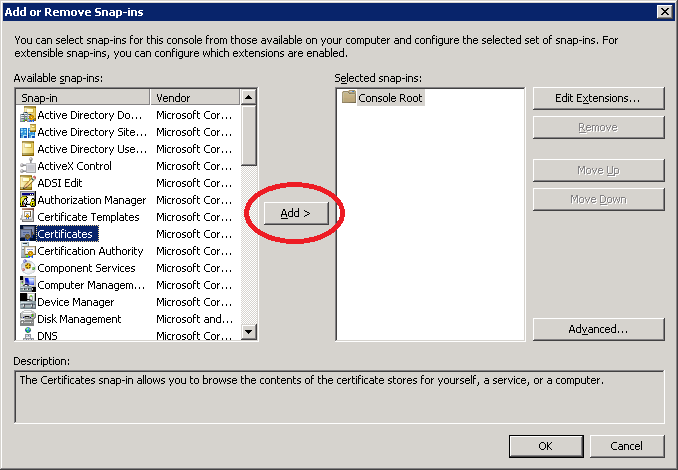
Select Computer account and click on Next.
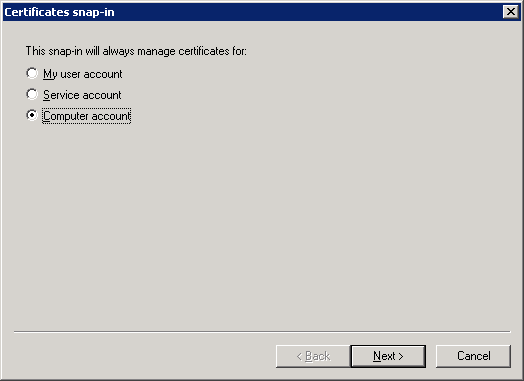
Select Local computer and click on Finish.
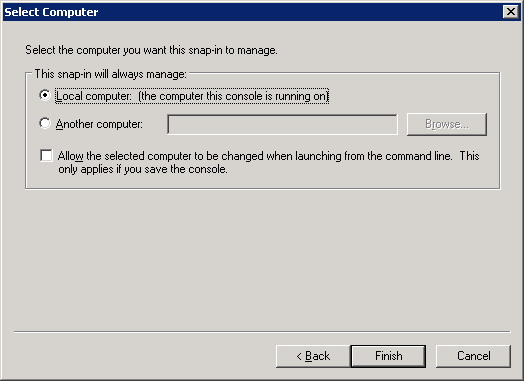
On the right side, you can see that the computer certificates are now selected. Click on OK.
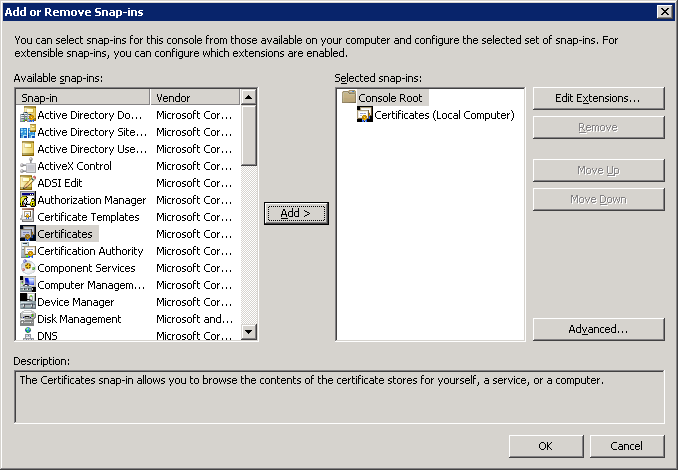
Click on Personal > Certificates to see all computer certificates. If everything went OK, you should see a certificate that says “Intended Purposes” with Client and Server Authentication.
If you installed NPS on a separate Windows Server 2008 installation, you won’t see a computer certificate here, and you’ll have to generate one as well.
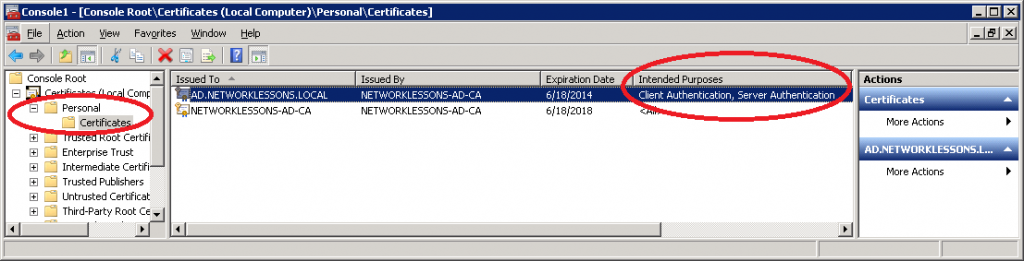
If there’s no certificate, we’ll create a new one. Right-mouse click on the white space and select Request New Certificate.
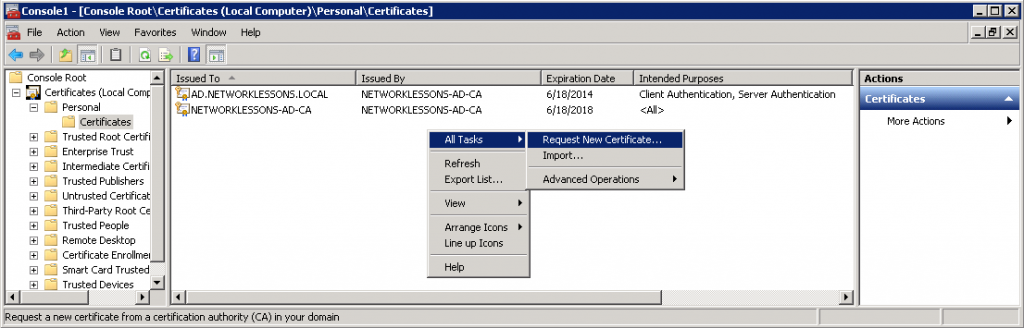
You will see the following screen. Click Next to continue.
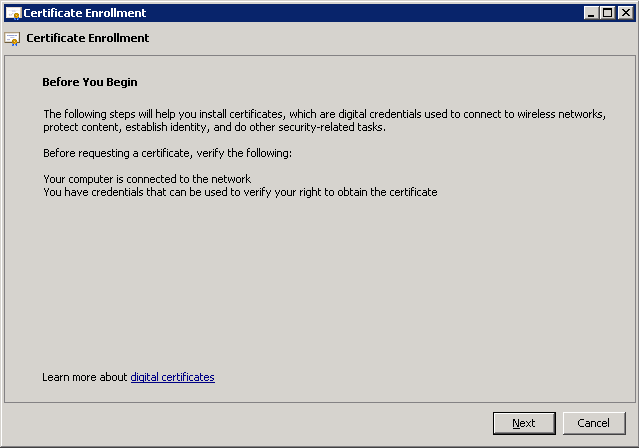
Select Active Directory Enrollment Policy and click Next to continue.
Click on Finish.
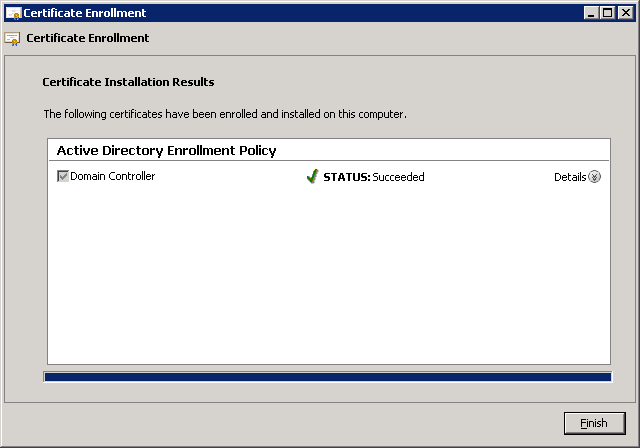
You’ll be back at the MMC, and you’ll see the installed certificate. Make sure you see that it can be used for client and server authentication before you continue.

Your server now has a certificate that can be presented to wireless clients when they request the identity of the RADIUS server. Now we can configure a wireless policy…
Configure Network Policy for EAP Authentication
Network Policy Server is running, but we’ll still have to create a policy for our wireless users.
Click on Start > Administrative Tools > Network Policy Server.
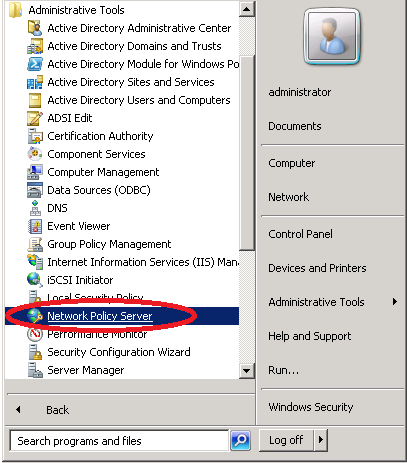
Do a right mouse click on NPS > Register server in Active Directory.
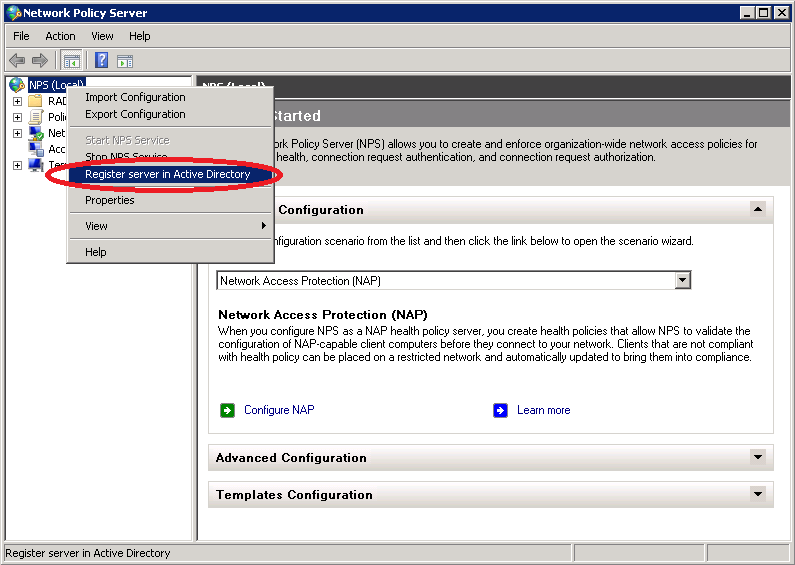
You’ll be presented with the following screen. Click OK to continue.
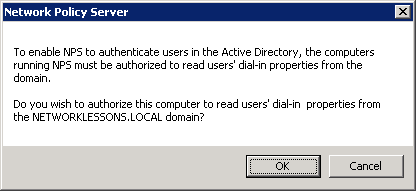
And a notification that it has been registered, click OK to continue.
Add Cisco WLC as RADIUS Client
Now we can add a RADIUS client. Don’t confuse the RADIUS client with the wireless clients. We are talking about the wireless LAN controller here. Select NPS > RADIUS Clients and Servers > RADIUS Clients (right mouse click) and click on New.
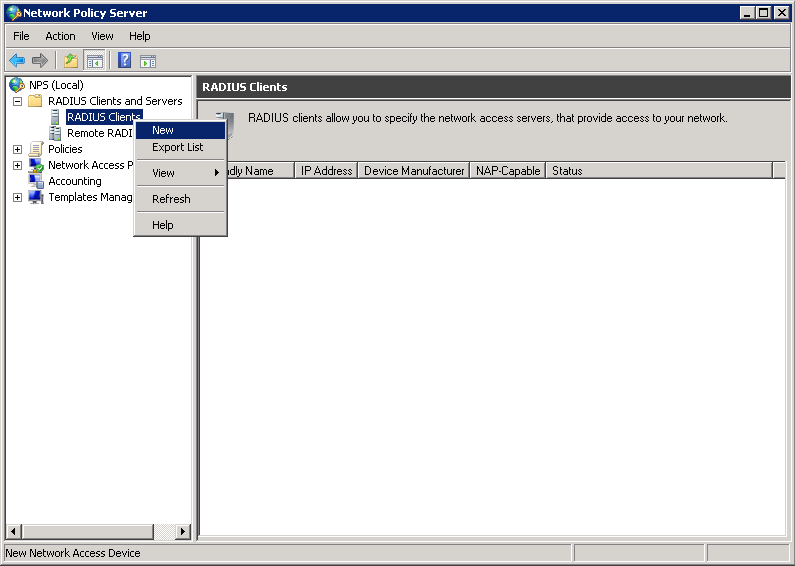
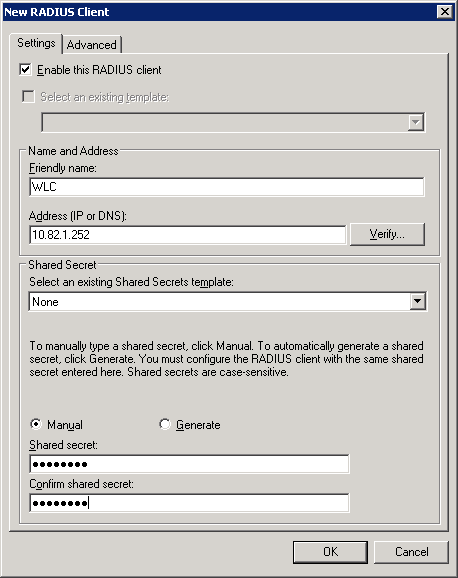
Enter a friendly name (it can be everything, but I suggest using the hostname of the WLC) and the IP address of the WLC. Enter a password in the Shared secret field. We’ll need this once we configure the wireless LAN controller.
Click on OK to continue.
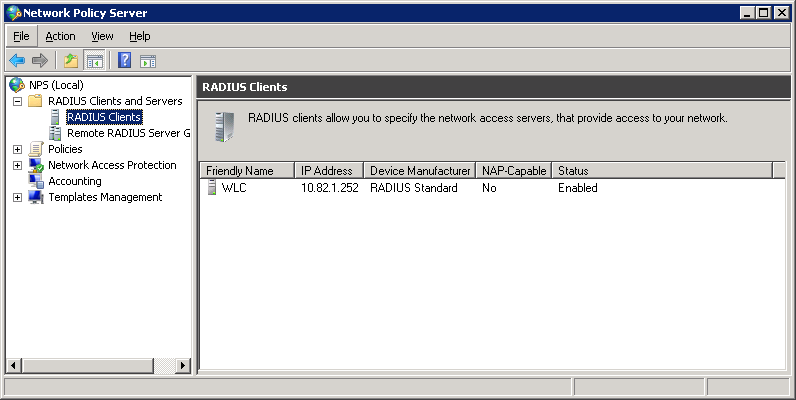
You’ll be back at the main screen, and you will see that the RADIUS client has been added.
Create Wireless Policy
Now we can create a network policy. Click on Policies > Network Policies (right mouse click) and click on New.
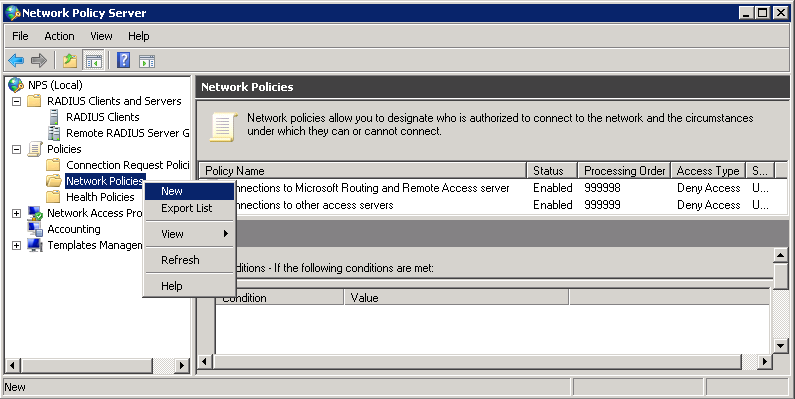
Give the policy a name. I’ll call it “Wireless”. Leave the type of network access server Unspecified.
Click Next to continue.
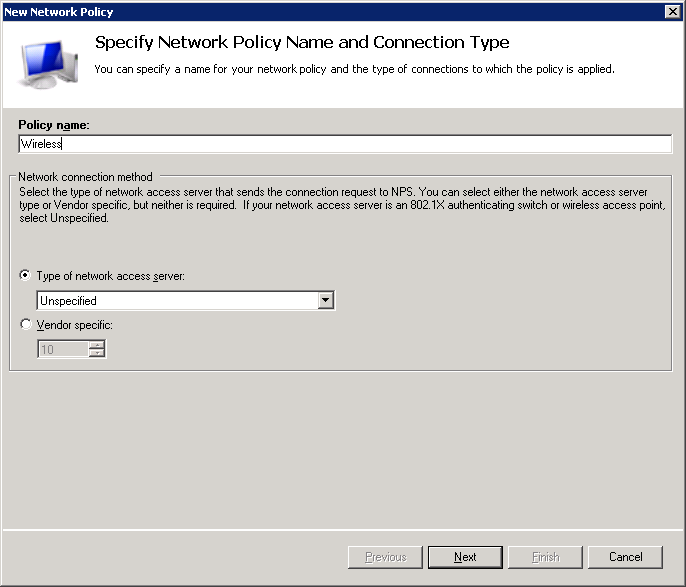
Now we can specify some conditions. I’ve set the following conditions:
- Windows Groups: NETWORKLESSONS\Domain Users. By default, all users in our Active Directory are members of the domain users group. If you only want certain users to be able to connect to the wireless network, then it’s better to create a new domain group for this.
- NAS Port Type: Wireless – IEEE 802.11. This ensures that the network policy only applies to wireless users.
- Authentication Type: EAP
Click on Next to continue.
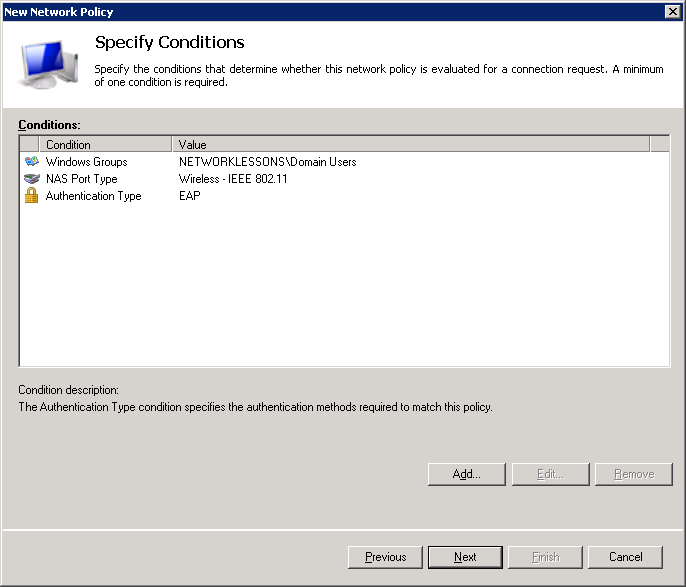
Select Access granted and click on Next.
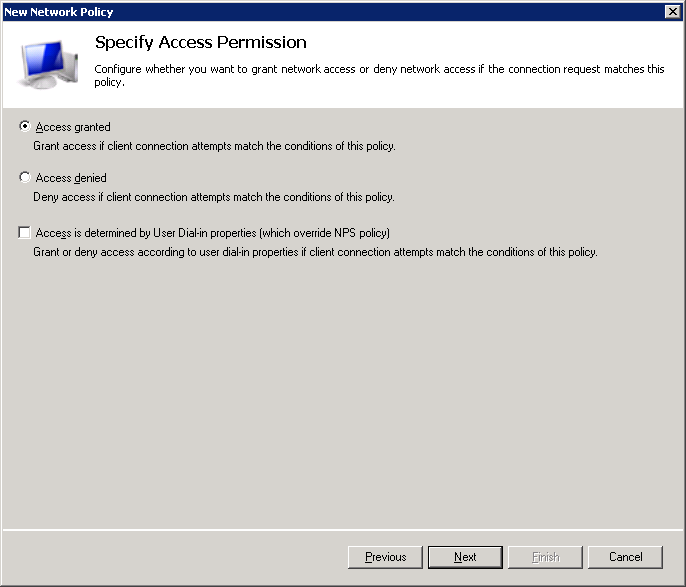
De-select all options in the following screen. We only want to allow PEAP and/or EAP-TLS.
Wireless Policy – PEAP Authentication
First, we will add PEAP authentication to our wireless policy. Click on Add.
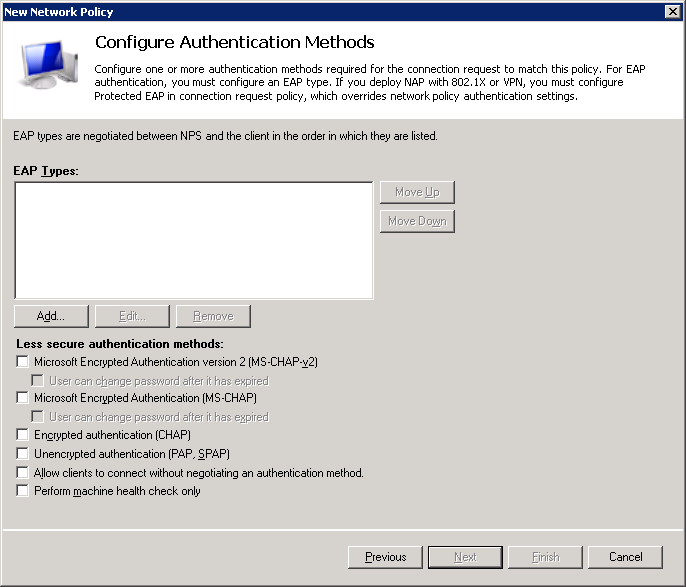
Here you can select the authentication types that you want. I’ll start with PEAP. Click on Microsoft: Protected EAP (PEAP) and click on OK.
You will see it in the overview. Select Microsoft: Protected EAP (PEAP) and click on Edit.
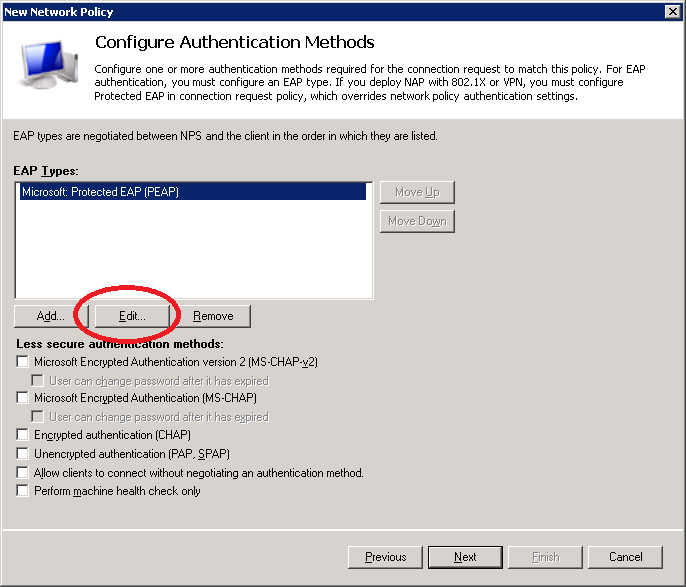
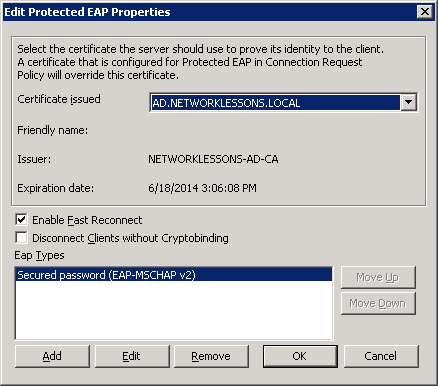
Make sure you have selected the correct certificate. This is the computer certificate that will be presented to wireless users when they connect using PEAP. It allows our wireless clients to confirm the identity of the RADIUS server.
Click OK to continue.
Wireless Policy – EAP-TLS Authentication
I’m also going to add support for EAP-TLS. Click Add and select Microsoft: Smart Card or other certificate.
Click OK to continue.
Select Microsoft: Smart Card or other certificate and click on Edit.
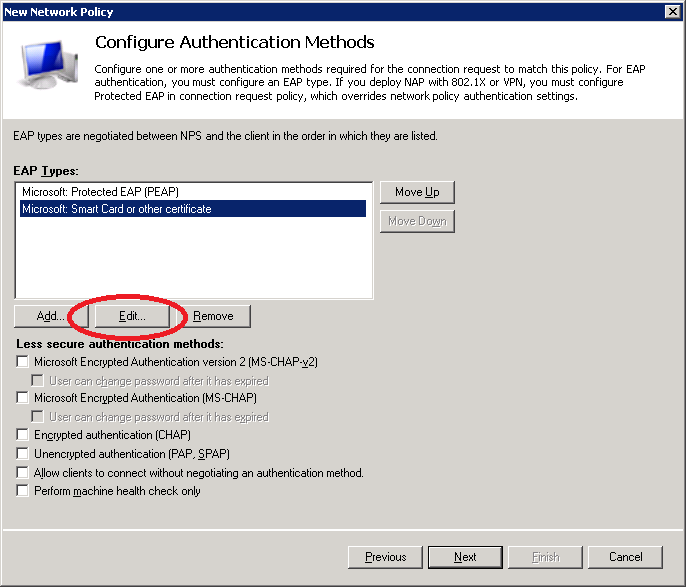
Make sure the correct computer certificate has been selected and click on OK.
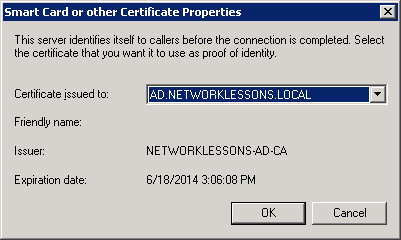
You will now see both EAP types in the list.
Click Next to continue.
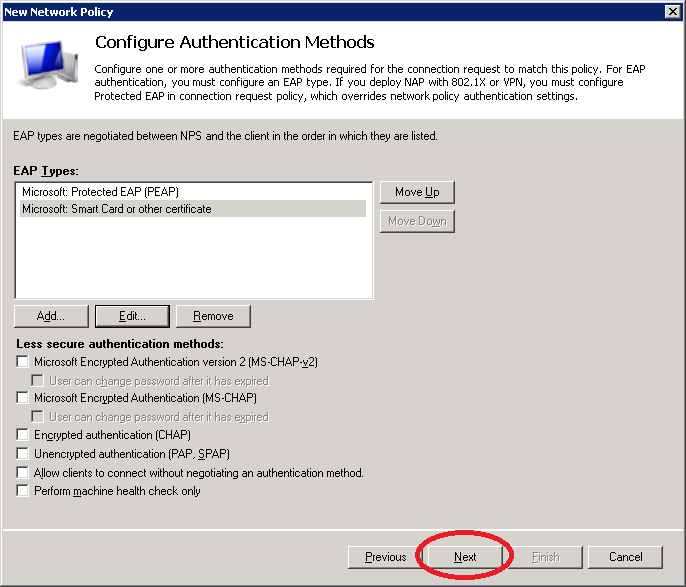
You will see an option to configure constraints. You can use these if you want to restrict access to the wireless network…for example, you can set a day and time restriction. If you want to do this, it’s best to leave it alone for now and first make sure that everything is working.
Click Next to continue.
Click Next to continue.
And click on Finish to complete the configuration of our wireless policy.
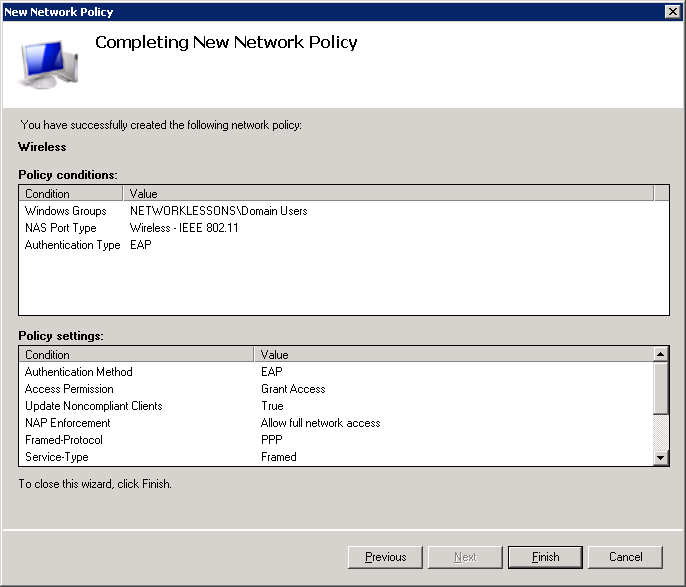
NPS is running, and we have successfully created a policy for wireless users.
Add Wireless User to Active Directory
The wireless policy we created in NPS allows all users in the “domain users” group to access the wireless network, but we still have to create a user account.
Click on Start > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers.
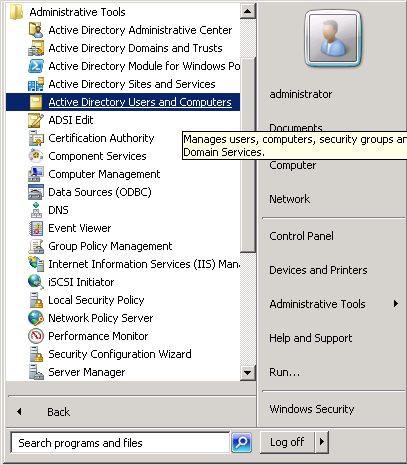
Select Active Directory Users and Computers > NETWORKLESSONS.LOCAL > Users and do a right mouse click on the white space on the right side. Select New > User.
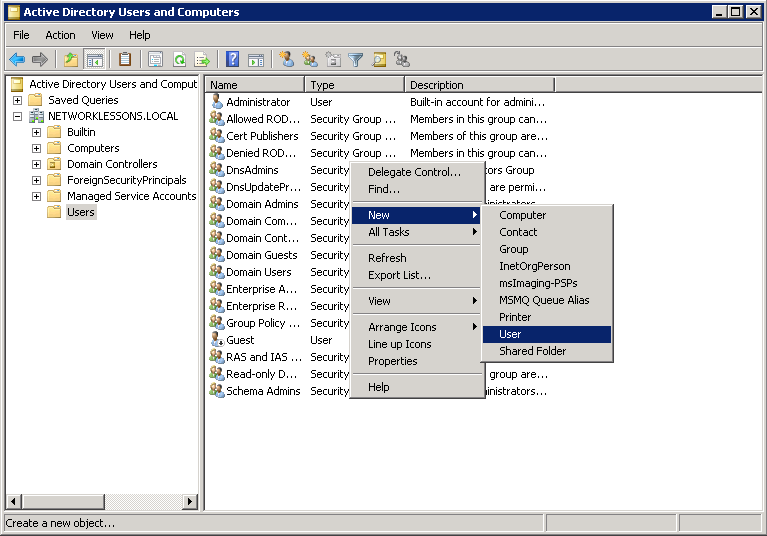
You will have to enter some details for the new user account. I’ll call my user “Wifi1”. Click on Next to continue.
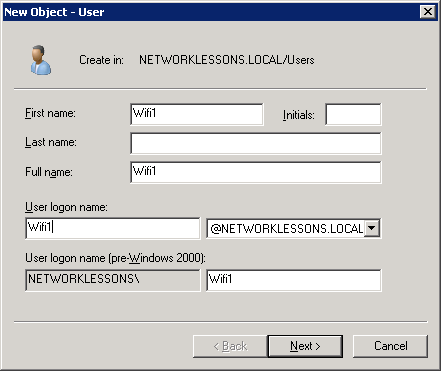
Enter a password and ensure the “User must change password at next logon” field is unchecked. Click Next to continue.
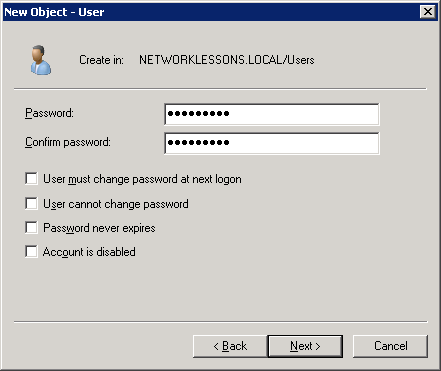
Click on Finish to create the new user account.
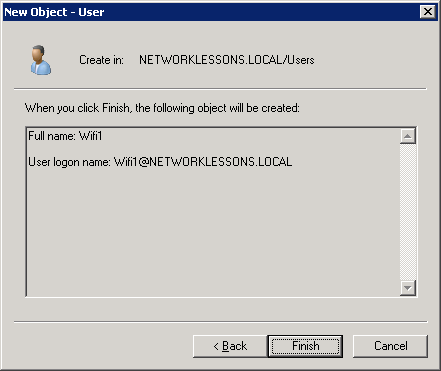
So far, so good…Active Directory is up and running with a user account, our server is a root CA and has a computer certificate, and we configured NPS for wireless users. Now we’ll have to configure the Cisco Wireless LAN controller to use the RADIUS server for authentication.
Configure Cisco Wireless LAN Controller to use Radius Authentication
Configuring a RADIUS server on the Cisco WLC isn’t difficult. First, we’ll have to configure the RADIUS server, and the next step is to configure a WLAN profile to use WPA(2)-enterprise mode.
Start your web browser and log into the WLC:
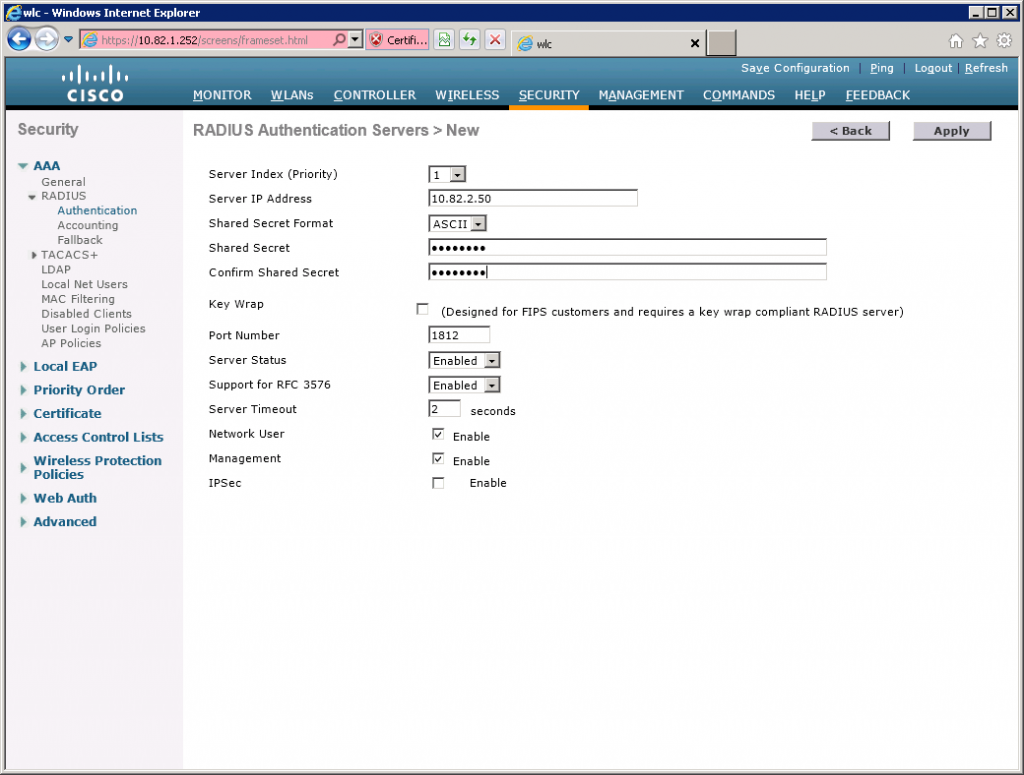
Add RADIUS server
Select Security > RADIUS > Authentication.
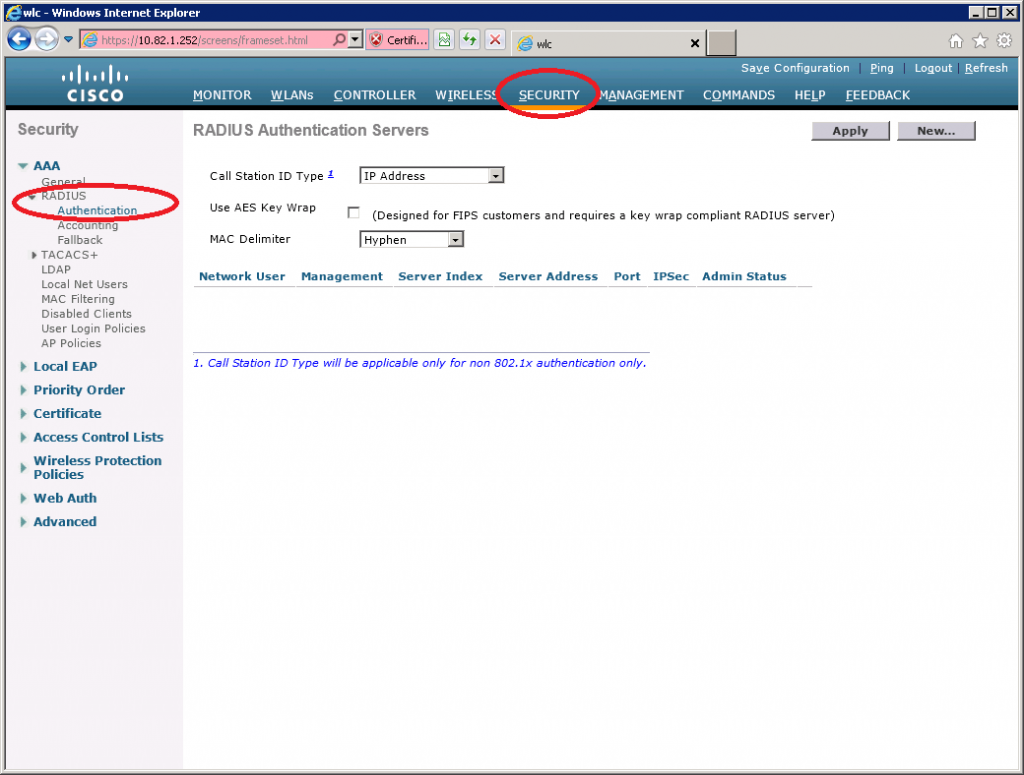
Click on New.
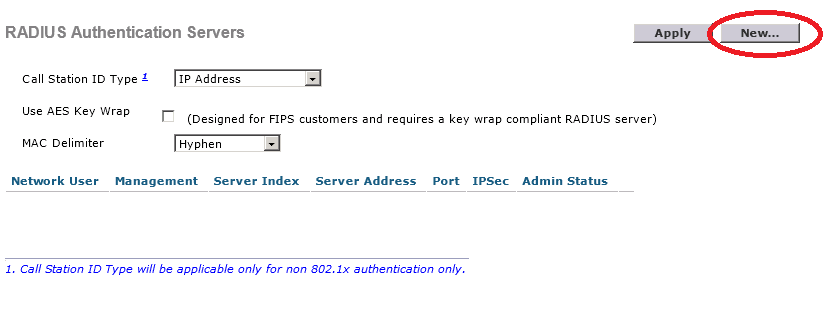
Here you need to enter the IP address and the shared secret (password) you created when configuring the RADIUS client in NPS.
Click Apply to continue.
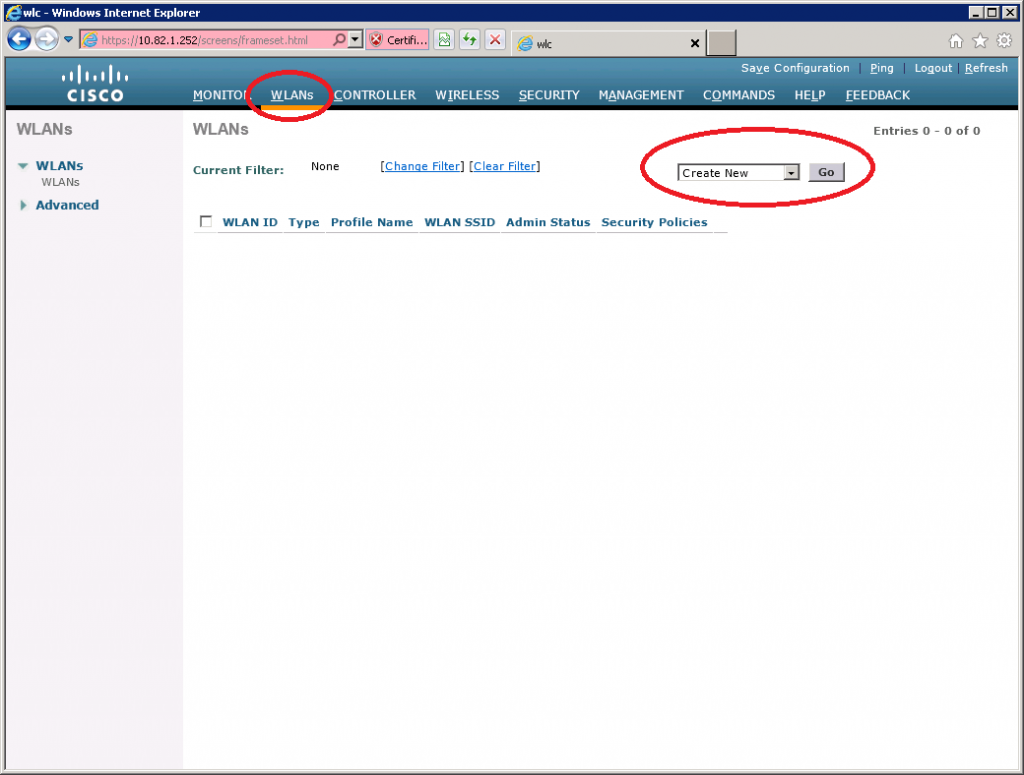
Create WLAN for RADIUS Authentication
Now we can create a new WLAN and configure it to use WPA-enterprise mode so it will use RADIUS for authentication.
Select WLANs from the main menu, click on Create New and click on Go.
I will call the new WLAN “EAP”. Click Apply to continue.
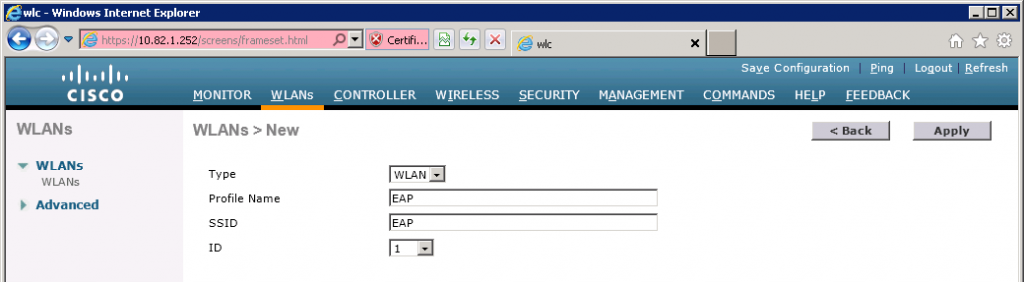
Select the General Tab and ensure Status is Enabled. The default security policy is 802.1X authentication and WPA2.
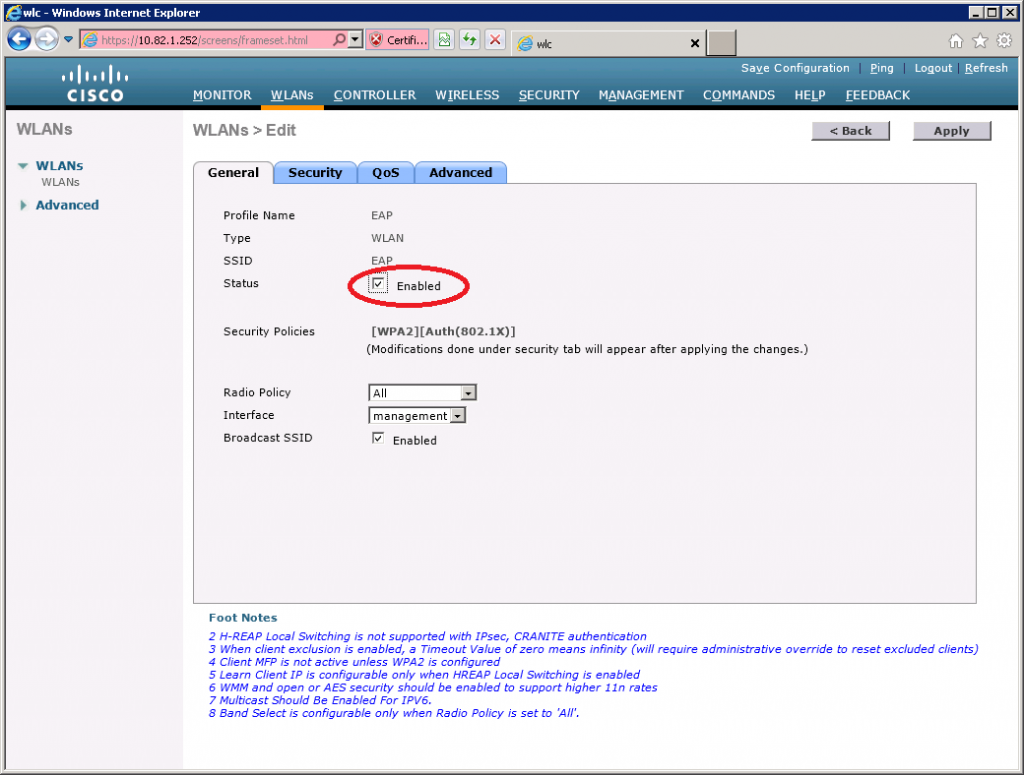
Now select the Security > AAA Servers tab and select the RADIUS server that you just configured.
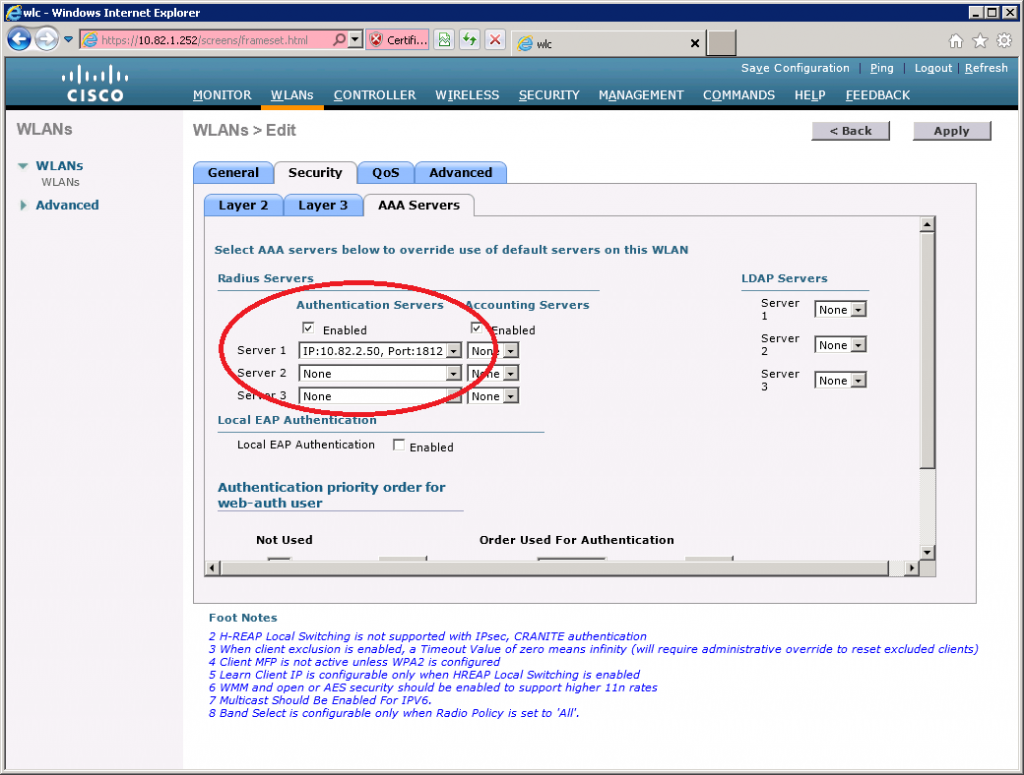
That’s all you have to configure on the Wireless LAN Controller. It’s a good idea to verify that you can reach the RADIUS server from the WLC before you continue. RADIUS uses UDP port 1812, so make sure you don’t have any access-lists or firewalls blocking your traffic between the server and WLC.
Configure Wireless Client (Windows 7)
This is where the real fun starts…it’s time to configure a wireless client to connect to our wireless network. I will use Windows 7 to demonstrate how to connect using PEAP and EAP-TLS.
If your Windows 7 computer is in workgroup mode (the default), then you will have to import the root CA from the windows 2008 server yourself otherwise, you will get an error that the client doesn’t recognize the root CA. This is normal because we created a new root CA and generated a new certificate. When your computer has joined the domain, you can skip this step because it will automatically receive the root CA from the domain controller.
Let me show you how to import the root CA on your Windows 7 computer. If you joined the domain, then you can skip this step…
Export root CA from Server
First, we will have to export the root CA from the server. Normally you can find it in a shared folder on the server. Connect your client using a network cable and open the shared folder on the server:
10.82.2.50CertEnrollIf you don’t have a network cable or you can’t access the shared folder, then it’s also possible to export the root CA from the server ourselves. Go to the server and open MMC:
Click on Start > type “MMC” (without the quotes) and hit enter.

Select File > Add/Remove Snap-In.

Select Certificates from the available snap-ins and click on Add.

Select Computer account and click on Next.

When you see Certificates (Local Computer) on the right side, you can click on OK.

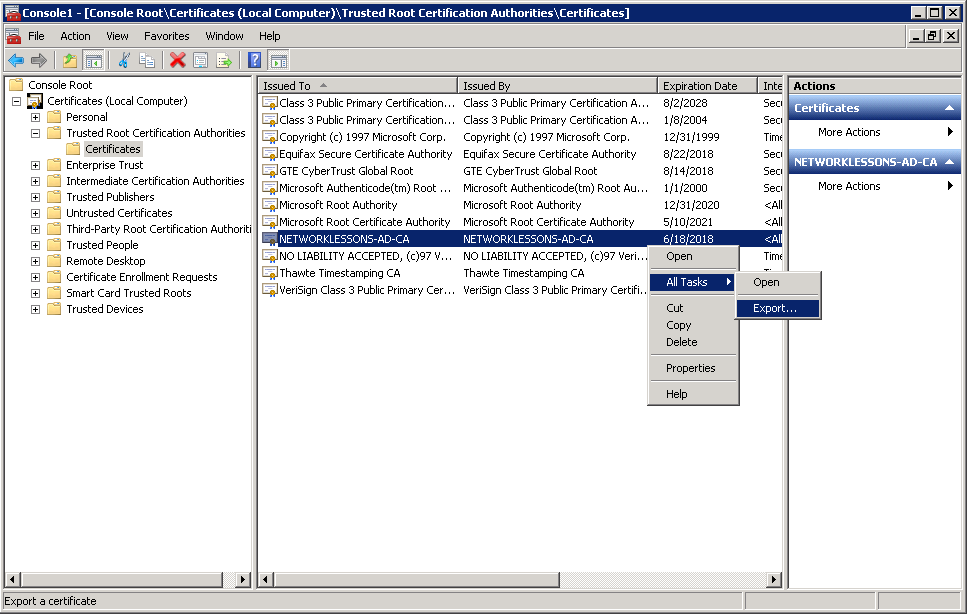
Select Certificates (Local Computer) > Trusted Root Certification Authorities > Certificates. On the right side, you will see your root CA. Select it, do a right-mouse click, and select All Tasks > Export.
You will see the Certificate Export Wizard. Click Next to continue.
Don’t export the private key. Click Next to continue.
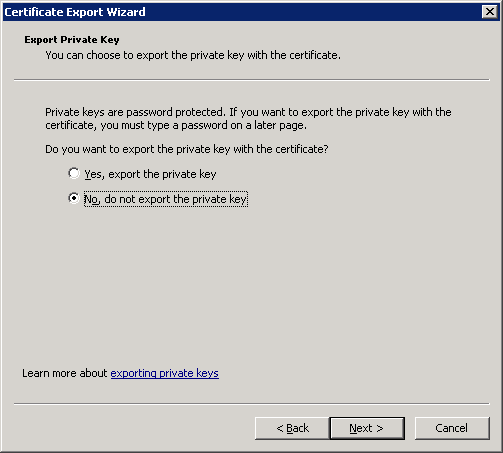
Select the DER encoded binary X.509 (CER) file format and click Next.
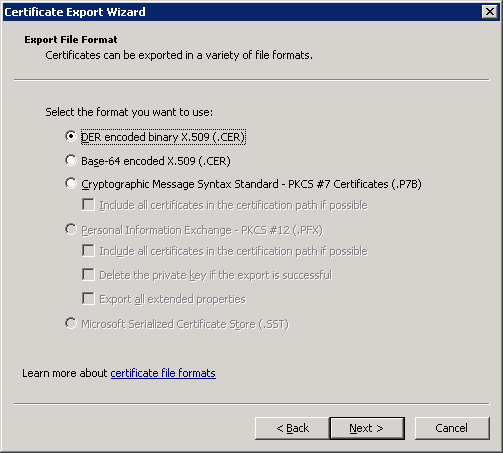
Choose a folder and filename, and select Next.
And click on Finish to complete the export.
Copy the certificate you just exported to a USB stick or something and move it to your Windows 7 computer.
Import Root CA to Windows 7
Double-click on the certificate file that you just exported on your Windows 7 computer, and you will see the following screen. Click on Install Certificate.
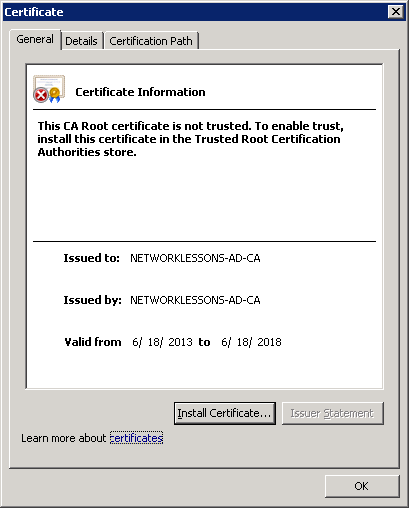
Click Next to continue.
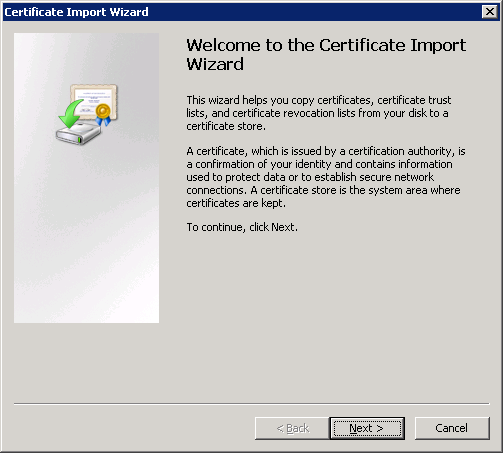
Make sure the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store has been selected. If not, click on the Browse button and select it. Click Next to continue.
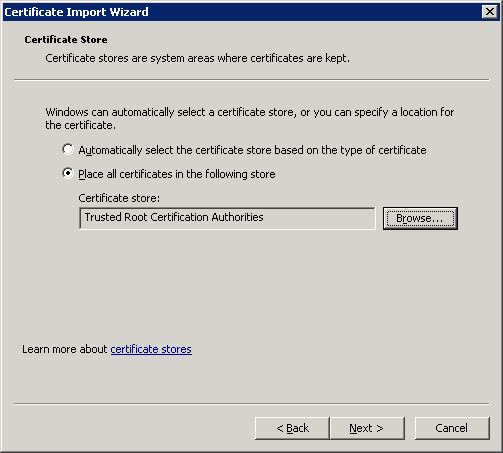
Click Finish to complete the certificate import wizard.
You might get a security warning that you are about to trust a new root certificate. Click Yes to continue.
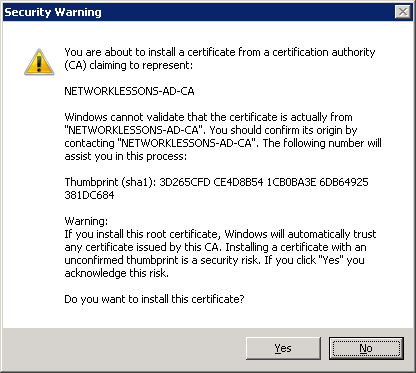
We are almost done. We must add this certificate to the Windows registry, or your computer will still not trust the root CA. If you want to know the exact reason, you can look at KB 2518158 on the Microsoft Website.
Click on Start > type “cmd” (without the quotes) and hit CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER. This will open a command prompt with administrative rights.
C:UsersvmwareDesktop>certutil -f -enterprise -addstore NTAuth AD.crt
NTAuth
Signature matches Public Key
Certificate "CN=NETWORKLESSONS-AD-CA, DC=NETWORKLESSONS, DC=LOCAL" added to store.
CertUtil: -addstore command completed successfully.
Your computer now trusts the root CA. We can now connect to the wireless network.
Configure Wireless Profile for PEAP
We’ll create a new profile to connect using PEAP.
Open Control Panel and select Manage wireless networks.
Click on Add.
Select “Manually create a network profile“.
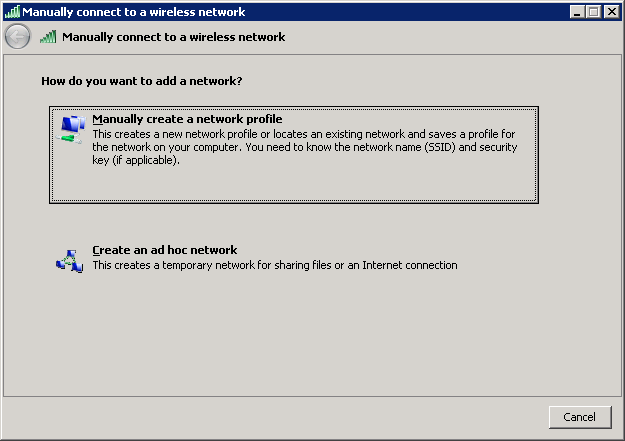
Enter the network name, select WPA-Enterprise or WPA2-Enterprise, and click on Next.
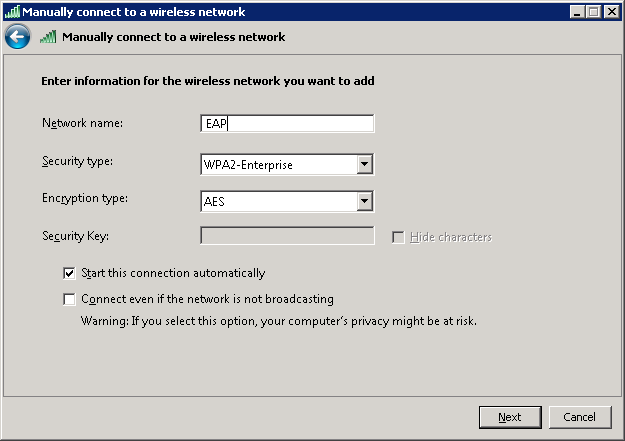
Select Change connection settings.
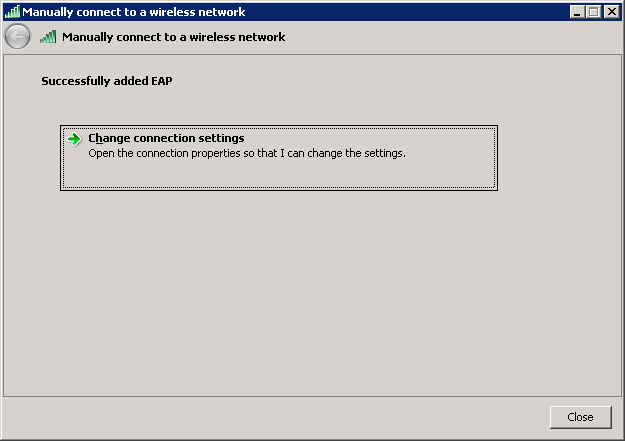
Select the Security tab, choose Microsoft: Protected EAP (PEAP), and click on Settings.
Select Validate server certificate. You should see the root CA that we imported here, but you don’t have to select it. Your computer will trust all root CAs in this list by default when you connect to a wireless network.
Make sure the authentication method is Secured password (EAP-MSCHAP v2) and press the configure button.
Uncheck the button that wants to automatically use the windows username/password for authentication. Click OK to continue.
Click OK until you return to the EAP Wireless Network Properties and select Advanced Settings.
Select specify authentication mode and choose user authentication. Click OK to continue.
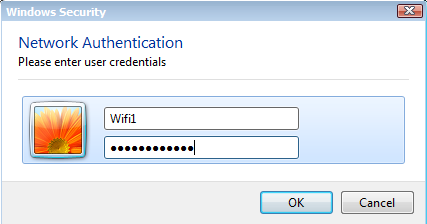
Keep clicking on OK until you are out of the wireless profile configuration. You are now ready to connect to the wireless network using PEAP. Look for the wireless icon in the taskbar, select the wireless network and click on Connect.
You will see a pop-up that asks for your credentials. Enter the username and password that you configured in Active Directory and click on OK.
And you will see that you are now connected:
Congratulations! You just authenticated a user through PEAP. In the next part, I’ll show you how to authenticate the user using EAP-TLS and a client certificate.
Configure Wireless Profile for EAP-TLS
To authenticate a wireless user through EAP-TLS instead of PEAP, we will have to generate a client certificate. Connect your Windows 7 computer to the network so that you can access the server, open a web browser and enter the following address:
https:///certsrv
You will see a pop-up that asks for credentials. Enter the username and password of the wireless user that requires a client certificate and click on OK.
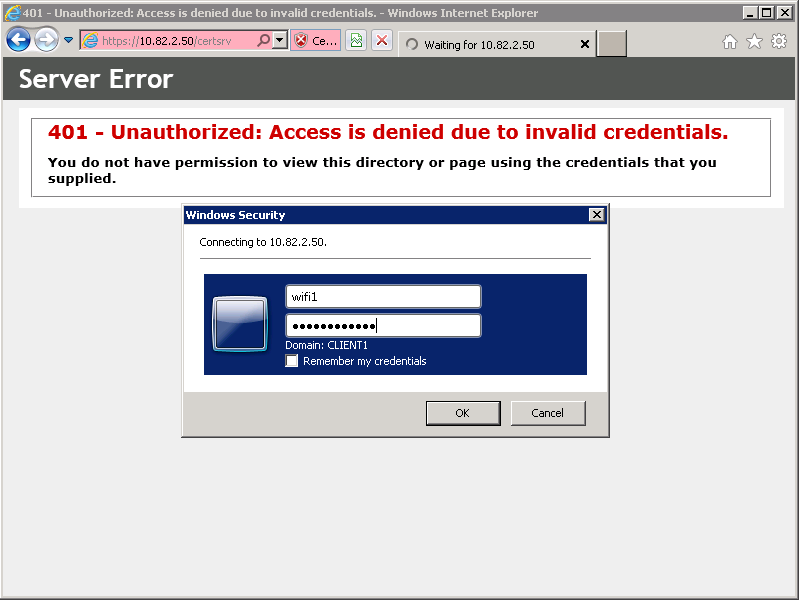
Select Request a Certificate.
If you are using Internet Explorer 10, you might receive a warning that says, “This Web browser does not support the generation of certificate requests.”. You need to enable IE10 compatibility mode to solve this problem.
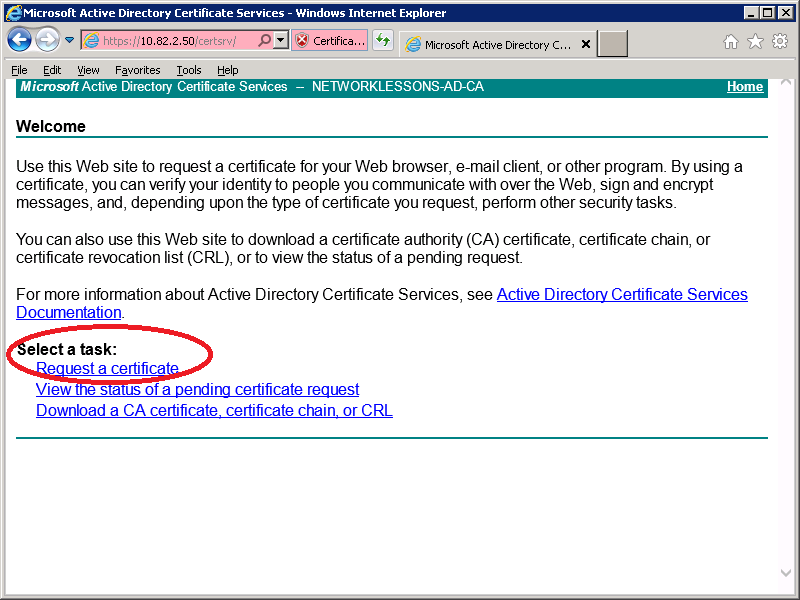
Select User Certificate.
Select Yes.
And click on Install this certificate.
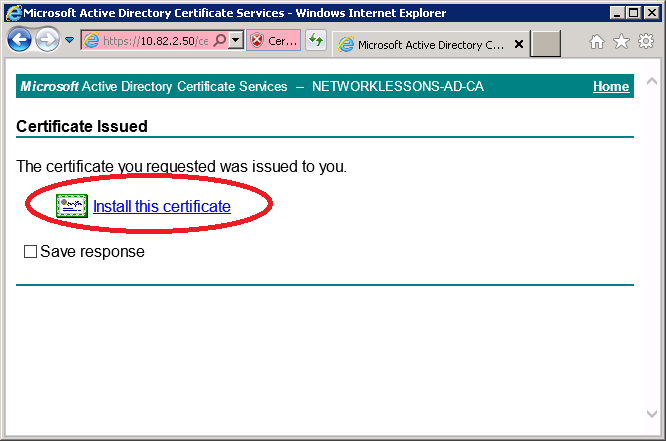
You will see a notification that the certificate has been installed.
Now we can change the wireless profile we created earlier for PEAP to use EAP-TLS instead. Do a right mouse click on the EAP wireless profile and select Properties.
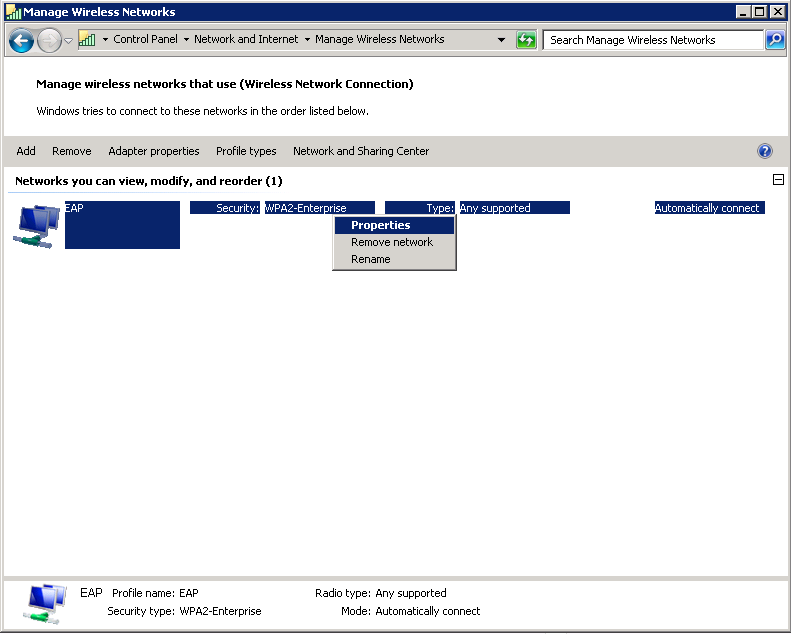
Select Microsoft: Smart Card or other certificate and click on OK.
Now try to connect again to the wireless network, select the correct profile, and click Connect.
And you will be connected to the wireless network!
Congratulations…you just connected using EAP-TLS!
Troubleshooting
If everything went OK, you now have a working wireless network offering PEAP and EAP-TLS authentication. This lesson has many components, so troubleshooting might be complex sometimes. Your best friend is the Windows event viewer on the server, as it will give you all errors. It’s best to look for the security event log and check the network policy server notifications. These will give you a lot of information when you cannot authenticate your wireless users.
Conclusion
I hope this lesson has been helpful to you in installing a Windows Server 2008 machine to act as the RADIUS server for your (Cisco) wireless network that offers EAP-TLS and/or PEAP authentication. If you have any additions or questions, feel free to leave a comment, and I’ll do my best to answer them. If you enjoyed this lesson, please share it!
Here is how to implement 802.1X authentication in a Windows Server 2008 R2 domain environment using Protected-EAP authentication. I have designed the tutorial to be worked on in the specific order to prevent downtime if deployed during the day. By creating the Network Policy server first, once we switch the authentication type from whatever to 802.1X via RADIUS, our Network Policy Server will immediately start processing requests and allowing machines on the domain. By configuring the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller or Group Policy first, clients will try connecting to a RADIUS server that doesn’t exist or present invalid credentials. If you have any suggestions on how to better the implementation I demonstrate here, please drop a comment below to improve security/stability of these types of deployments. 🙂
First, we need to create a security group in Active Directory to allow a list of specific users and computers to login to the domain. In this example, we will allow any authenticated user or machine on the domain to authenticate successfully to the RADIUS sever. In the screenshot below, we can see I have added both Domain Users and Domain Computers to a security group called WirelessAccess. Here is a screenshot with the above settings.
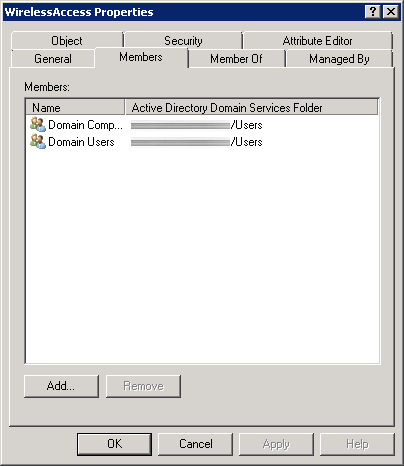
Network Policy Server
- Create a new Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows Server 2012 machine
- Add the machine to the domain
- Give the machine a static IP: (I’ll use 10.10.10.15 throughout this document as a reference to this server)
- Open up Server Manager, click Add Roles, click Next on the Before You Begin screen, check Network Policy and Access Services and click Next, click Next on the Introduction screen, check Network Policy Server (leave the rest unchecked) and click Next, click Install.
- Once Network Policy Server is installed, launch the Network Policy Server snap-in (via MMC or Administrative Tools)
- Inside of Network Policy Server, on NPC (Local), select RADIUS server for 802.1X Wireless or Wired Connections from the dropdown and click Configure 802.1X
- On the Select 802.1X Connections Type page, select Secure Wireless Connections, and enter My Company’s Wireless. Click Next.
- Click on the Add… button. Enter the following settings:
- Friendly name: Cisco WLAN Controller
- Address: 10.10.10.10 (Enter your WLAN Controller’s IP address)
- Select Generate, click the Genereate button, and then copy down the Shared Secret the wizard generated (we will use this later to get the WLAN Controller to talk to the RADIUS server). Click OK.
- Click Next.
- On the Configure an Authentication Method, select Microsoft: Protected EAP (PEAP). Click Next.
- Click Next on the Specify User Groups (we will come back to this).
- Click Next on the Configure Traffic Controls page.
- Click Finish
- Click on NPS (Local) -> Policies -> Network Policies. Right click Secure Wireless Connections and click Properties.
- Click on the Conditions tab, select NAS Port Type, and click Remove.
- Still on the Conditions tab, click Add…, select Windows Groups and click Add…, click Add Groups…, search for WirelessAccess and click OK. Click OK on the Windows Groups dialog box, click Apply on the Secure Wireless Connections Properties box. You should now have something like the image below:
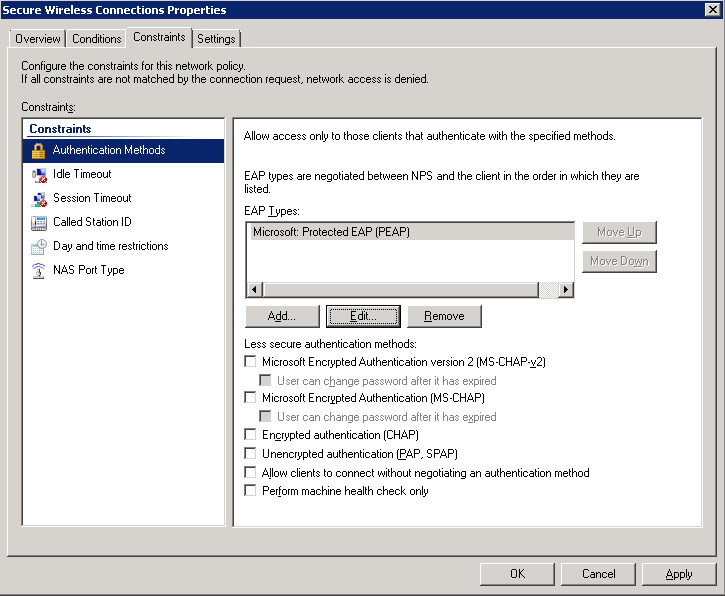
- Click on the Constraints tab.
- Uncheck all options under Less secure authentication methods like the image below:
- Click Apply
- Uncheck all options under Less secure authentication methods like the image below:
Cisco WLAN
- Login to your Cisco Wireless Lan Controller
- Add a RADIUS server to your controller
- Click on the Security tab
- Select AAA -> Radius -> Authentication on the left side
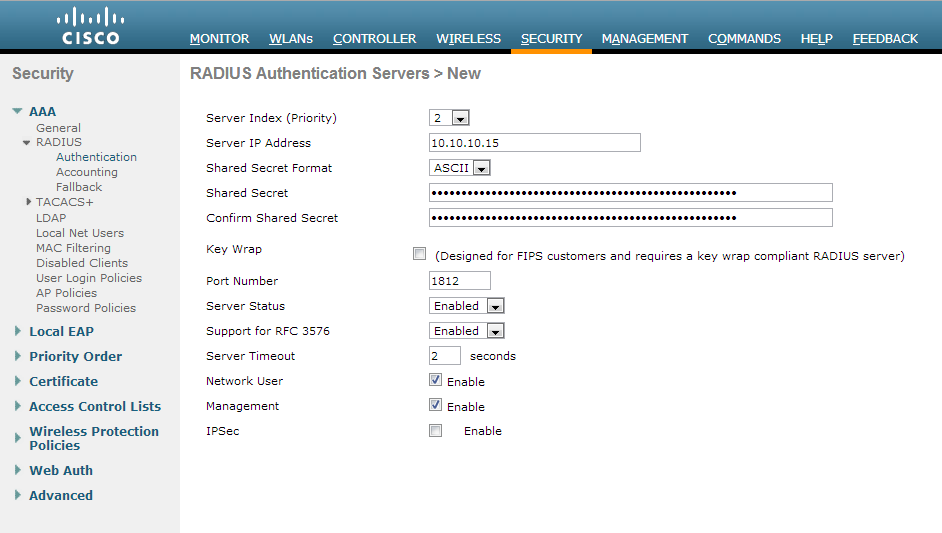
- Click the New… button in the top right
- Server IP Address: 10.10.10.15 (The IP address of your NPS server we setup earlier)
- Shared Secret Format: ASCII
- Shared Secret: The long generated password you wrote down when setting up the Network Policy Server
- Confirm Shared Secret: Same password in previous step
- Key Wrap: unchecked
- Port Number: 1812
- Server Status: Enabled
- Support for RFC 3576: Enabled
- Server Timeout: 2
- Network User: Checked
- Management: Checked
- IP Sec: Unchecked
- Here is a screenshot with the above settings
- Create or modify a wireless network to use 802.1X
- Click on the WLANs tab
- Create a new wireless network or select an existing WLAN ID to edit
- On the «WLANs > Add/Edit ‘My SSID'» page, use the following settings
- Security Tab
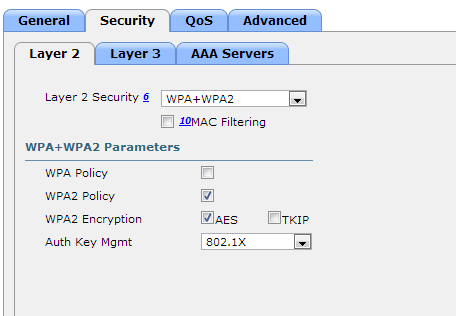
- Layer 2 Tab
- Layer 2 Security: WPA+WPA2
- MAC Filtering: Unchecked
- WPA+WPA2 Parameters
- WPA Policy: Unchecked
- WPA2 Policy: Checked
- WPA2 Encryption: AES checked, TKIP unchecked
- Auth Key Mgmt: 802.1X
- Here is a screenshot of the above settings
- Layer 3 Tab
- Layer 3 Security: none
- Web Policy: unchecked
- AAA Servers Tab
- Authentication Servers: checked Enabled
- Server 1: Select your RADIUS server from the dropdown
- Local EAP Authentication: Unchecked
- Authentication priority order for web-auth user: Move RADIUS over to the right
- Here is a screenshot of the above settings
- Click Apply
- Layer 2 Tab
- Security Tab
Group Policy
- Go to your domain controller and open up the Group Policy Management console.
- Right click the Organizational Unit you want to apply to policy to and select Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here…
- Note, the policy must be linked to the OU containing a group of machines you want to have WiFi access to or a parent of the OU.
- Enter in 802.1X WiFi Policy for the Name and click OK
- Right click your new GPO and click Edit
- Navigate to Computer Configuration->Policies->Windows Settings->Security Settings->Wireless Network (IEEE 802.11) Policies
- Right click and select Create A New Wireless Network Policy for Windows Vista and Later Releases
- Ensure the following settings are set for your Windows Vista and Later Releases policy
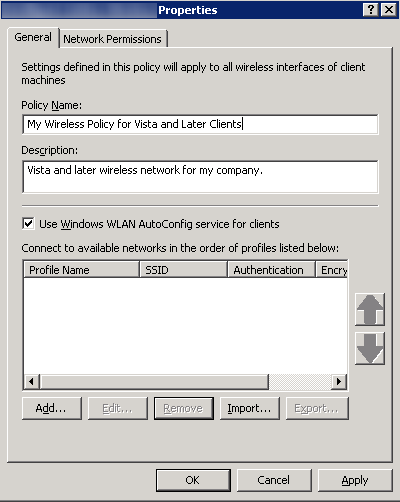
- General Tab
- Policy Name: My Wireless Policy for Vista and Later Clients
- Description: Vista and later wireless network for my company.
- Check Use Windows WLAN AutoConfig service for clients
- Here is a screenshot with the above settings
- Click the Add… button and select Infrastructure
- Connection Tab
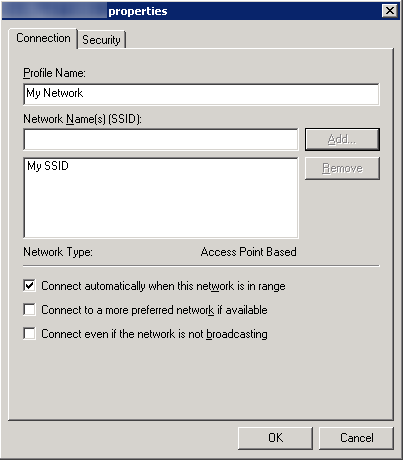
- Profile Name: My Network
- Enter in your SSID (Wireless network name that gets broadcasted) and click the Add… button
- Check Connect Automatically when this network is in range
- Here is a screenshot of the above settings
- Security Tab
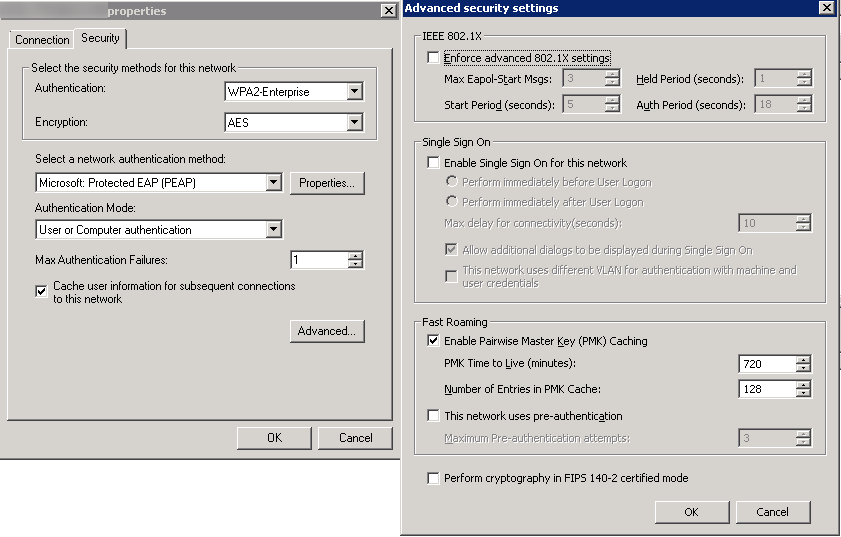
- Authentication: WPA2-Enterprise
- Encryption: AES
- Select a network authentication method: Microsoft Protected EAP (PEAP)
- Authentication Mode: User or Computer authentication
- Max Authentication Failures: 1
- Check Cache user information for subsequent connections to this network
- Here is a screenshot of the above settings with the Advanced tab open as well
- Click OK
- Connection Tab
- Network Permissions Tab
- Enter your network into Define permissions for viewing and connection to wireless networks if it hasn’t been added already.
- Uncheck Prevent connections to ad-hoc networks
- Uncheck Prevent connections to infrastructure networks
- Check Allow user to view denied networks
- Check Allow everyone to create all user profiles
- Uncheck Only use Group Policy profiles for allowed networks
- Leave all Windows 7 policy settings unchecked
- Here is a screenshot with the above settings (note, you may change the settings above to be in accordance to your policy. Just ensure you don’t check Prevent connections to infrastructure networks).
- Click OK
- General Tab
- Right click and select Create A New Windows XP Policy
- Ensure the following settings are set for your Windows XP Policy
- General Tab
- XP Policy Name: My Wireless Policy for XP Machines
- Description: My wireless policy for XP machines.
- Networks to access: Any available network (access point preferred)
- Check Use Windows WLAN AutoConfig service for clients
- Uncheck Automatically connect to non-preferred networks
- Here is a screenshot of the above settings.
- Preferred Networks Tab
- Click the Add… button and select Infrastructure
- Network Properties Tab
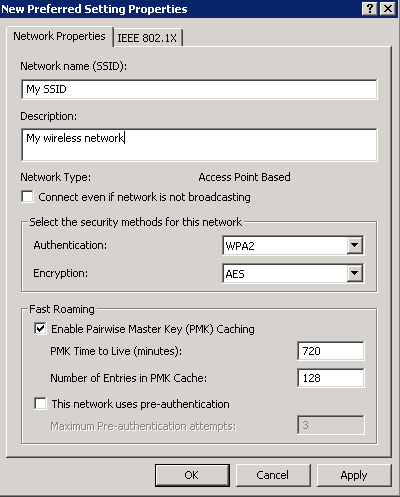
- Network name (SSID): My SSID
- Description: My wireless network
- Uncheck Connect even if network is not broadcasting
- Authentication: WPA2
- Encryption: AES
- Check Enable Pairwise Master Key (PMK) Caching
- Uncheck This network uses pre-authentication
- Here is a picture of the above settings
- IEEE 802.1X Tab
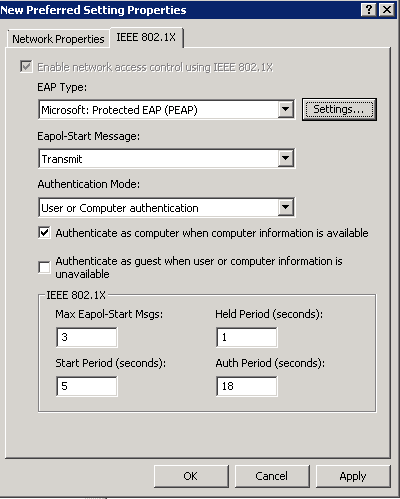
- EAP Type: Microsoft: Protected EAP (PEAP)
- Eapol-Start Message: Transmit
- Authentication Mode: User or Computer Authentication
- Check Authenticate as computer when computer information is available
- Uncheck Authente as guest when user or computer information is unavailable
- Screenshot of above settings
- Click OK
- Network Properties Tab
- Click the Add… button and select Infrastructure
- Click OK
- General Tab
Written on . Posted in Windows Server 2008
Удаленный доступ (Remote Access) на сегодняшний день очень важен. С ростом числа людей, нуждающихся в доступе к информации, хранящейся на домашних и рабочих компьютерах, возможность получать такой доступ из любой точки стала решающей. Прошли те дни, когда люди говорили: «я отправлю вам эту информацию, как только доберусь до своего компьютера». Вам нужна эта информация немедленно, если вы хотите достойно конкурировать в сегодняшнем деловом мире.
В каменном веке компьютеризации способом получения удаленного доступа к своему компьютеру было использование dial-up соединения. RAS dial-up соединения работали через обычные POTS (Простая старая телефонная служба — Plain Old Telephone Service) линии при скорости передачи данных примерно до 56kbps. Скорость была основной проблемой таких соединений, но еще более серьезной проблемой была цена соединения, когда получение доступа требовало больших расстояний.
С ростом популярности сети Интернет, соединения RAS стали использоваться все реже. Причиной этого стало появление соединений по VPN (виртуальная частная сеть). Соединения VPN обеспечивали такую же подключаемость точек между собой, как и соединения dial-up RAS, но делали это быстрее и дешевле, поскольку скорость VPN соединения может быть одинаковой со скоростью подключения к Интернет, а стоимость соединения не зависит от расположения места назначения. Единственное, за что приходится платить, это подключение к Интернет.
Виртуальные частные сети (Virtual Private Networking)
Соединение VPN позволяет компьютеру создавать виртуальное и частное подключение к сети через Интернет. Соединение виртуальное, потому что когда компьютер создает VPN подключение через Интернет, то создающий это подключение компьютер выполняет функцию узла, напрямую подключенного к сети, как если бы он был соединен с сетью посредством кабеля локальных сетей Ethernet. Пользователь имеет такой же доступ к ресурсам, какой он имел бы при прямом подключении к сети с помощью кабеля. Однако в случае VPN подключения клиента к VPN серверу соединение виртуально, поскольку нет действительного подключения Ethernet с местом назначения. VPN соединение частное, поскольку содержание потока данных внутри этого соединения зашифровано, поэтому никто в Интернет не может перехватить и прочесть данные, передаваемые посредством VPN соединения.
Серверы Windows Servers и клиенты поддерживали VPN соединения со времен Windows NT и Windows 95. Хотя клиенты и серверы Windows поддерживают VPN соединения на протяжении десятилетия, тип поддержки VPN эволюционировал со временем. Windows Vista Service Pack 1 и Windows Server 2008 на сегодняшний день поддерживают три типа VPN соединений. Это следующие типы:
- PPTP
- L2TP/IPSec
- SSTP
PPTP – это туннельный протокол от точки к точке. PPTP – это самый простой способ создания VPN соединения, но, к сожалению, он и наименее безопасен. Причина, по которой этот тип наименее безопасный, заключается в том, что мандаты пользователя передаются по небезопасному каналу. Говоря другими словами, шифрование VPN соединения начинается после того, как мандаты были переданы. Хотя действительная информация мандатов не передается между клиентами и серверами VPN, переданные значения хэш-функции могут использоваться опытными хакерами для получения доступа к VPN серверам и подключения к корпоративной сети.
Более надежным является VPN протокол L2TP/IPSec. L2TP/IPSec был совместно разработан компаниями Microsoft и Cisco. L2TP/IPSec более безопасен чем PPTP, поскольку безопасная сессия IPSec создается до того, как мандаты пересылаются по проводам. Хакеры не могут получить доступ к мандатам, а, следовательно, не смогут украсть их, чтобы впоследствии использовать. Более того, IPSec обеспечивает взаимную аутентификацию машин, поэтому неизвестные машины не смогут соединиться с каналом L2TP/IPSec VPN. IPSec обеспечивает взаимную аутентификацию, целостность данных, конфиденциальность и невозможность отказа от авторства. L2TP поддерживает PPP и EAP механизмы аутентификации пользователей, которые обеспечивают высокую безопасность входа, поскольку требуется аутентификация как машины, так и пользователя.
Windows Vista SP1 и Windows Server 2008 на сегодняшний день поддерживают новый тип VPN протокола ‘ Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol или SSTP. SSTP использует зашифрованные в SSL HTTP соединения, чтобы создавать VPN подключения к VPN шлюзам. SSTP безопасен, так как мандаты пользователя не передаются до тех пор, пока безопасный туннель SSL для соединения с VPN шлюзом не будет открыт. SSTP также известен как PPP через SSL, это означает, что вы можете использовать PPP и EAP механизмы аутентификации, чтобы сделать ваше SSTP соединение более безопасным.
Приватный не значит безопасный
Следует отметить, что VPN соединения скорее частные, чем безопасные. Хотя я и признаю, что приватность является основным компонентом безопасности коммуникаций, однако сама по себе не обеспечивает этой безопасности. Технологии VPN обеспечивают частный компонент при соединении через Интернет, который не позволяет посторонним лицам читать содержимое вашей коммуникации. Технологии VPN также позволяют вам быть уверенными в том, что только авторизированные пользователи могут подключаться к данной сети через шлюз VPN. Однако частный компонент, аутентификация и авторизация не обеспечивают всеобъемлющей безопасности.
Допустим, у вас есть сотрудник, которому вы открыли доступ VPN. Поскольку ваш Windows Server 2008 VPN протокол поддерживает EAP аутентификацию пользователя, вы решили создать смарт-карты для ваших пользователей и использовать L2TP/IPSec VPN протокол. Комбинация смарт-карт и протокола L2TP/IPSec позволяет требовать аутентификации пользователя и использования здоровой машины. Ваше решение по использованию смарт-карт и протокола L2TP/IPSec работает отлично, и все довольны.
Все довольны до тех пор, пока однажды один из ваших пользователей не заходит на ваш SQL сервер, чтобы получить бухгалтерскую информацию, и начинает делиться ею с другими сотрудниками. Что произошло? Разве соединение VPN было небезопасным? Нет, VPN соединение было безопасным ровно настолько, чтобы обеспечить частный (приватный) компонент, аутентификацию и авторизацию, но оно не обеспечивало контроля над доступом, а контроль над доступом является одним из основополагающих компонентов компьютерной безопасности. На самом деле можно даже говорить о том, что без контроля над доступом все остальные меры безопасности представляют сравнительно малую ценность.
Для VPN, чтобы быть на самом деле безопасными, вам нужно убедиться в том, что ваш VPN шлюз способен обеспечить контроль над доступом пользователей/групп с тем, чтобы вы смогли открывать необходимый уровень доступа пользователям VPN. Более совершенные VPN шлюзы и брандмауэры, такие как ISA Firewall, могут обеспечивать такой контроль на VPN соединениях. Плюс ко всему, такие брандмауэры, как ISA Firewall, могут обеспечивать проверку адресных пакетов и уровня приложений на клиентских VPN соединениях.
Хотя сервер Windows Server 2008 VPN не обеспечивает контроль над доступом пользователей и групп, есть другие способы, посредством которых вы можете настраивать контроль доступа на самом сервере, если вы не хотите платить за приобретение более совершенных брандмауэров и VPN шлюзов. В данной статье мы заостряем наше внимание только на компонентах VPN серверов. Если вы хотите узнать больше о брандмауэрах ISA и их возможностях для VPN серверов, перейдите по ссылке www.isaserver.org
Зачем использовать новый VPN протокол?
Microsoft уже создали два жизнеспособных протокола VPN, позволяющих пользователям соединяться с корпоративной сетью, так зачем же создавать третий? SSTP – это отличное дополнение для пользователей Windows VPN, поскольку SSTP не имеет проблем с брандмауэрами и устройствами NAT в отличие от протоколов PPTP и L2TP/IPSec. Для того чтобы PPTP работал через устройство NAT, это устройство должно поддерживать PPTP с помощью редактора NAT для PPTP. Если такой NAT редактор для PPTP отсутствует на данном устройстве, то PPTP соединения не будут работать.
L2TP/IPSec имеет проблемы с устройствами NAT и брандмауэрами, поскольку брандмауэру необходимо иметь L2TP порт UDP 1701, открытый для исходящих соединений, IPSec IKE порт, UDP 500 открытый для исходящих соединений, и IPSec NAT порт просмотра-обхода, UDP 4500 открыт для исходящих соединений (порт L2TP не требуется при использовании NAT-T). Большинство брандмауэров в общественных местах, таких как гостиницы, центры конференций, рестораны и т.д. имеют малое количество портов, открытых для исходящих соединений, например, HTTP, TCP порт 80 и HTTPS (SSL), TCP порт 443. Если вам нужна поддержка не только протоколов HTTP и SSL, когда вы покидаете офис, ваши шансы на успешное соединение значительно снижаются. Вы можете и не получить порты, требуемые для протоколов PPTP или L2TP/IPSec.
В отличие от предыдущих протоколов, SSTP VPN соединения проходят по каналу SSL, используя TCP порт 443. Поскольку все брандмауэры и устройства NAT имеют открытый порт TCP 443, вы сможете использовать протокол SSTP где угодно. Это значительно облегчает жизнь путешественникам, которые используют VPN соединения для подключения к офису, а также значительно облегчает жизнь корпоративных администраторов, которым нужно поддерживать путешественников, а также помогать служащим в общественных местах обеспечивать доступ к Интернет в гостиницах, конференц-центрах и т.д.
Процесс соединения SSTP
Далее будет показано, как работает процесс SSTP соединения:
- SSTP VPN клиент создает TCP соединение с SSTP VPN шлюзом между случайным TCP портом источника клиента SSTP VPN и TCP портом 443 шлюза SSTP VPN.
- SSTP VPN клиент отправляет SSL Client-Hello сообщение, указывая на то, что он хочет создать SSL сеанс с SSTP VPN шлюзом.
- SSTP VPN шлюз отправляет сертификат компьютера клиенту SSTP VPN.
- Клиент SSTP VPN подтверждает сертификат компьютера, проверяя базу сертификатов Trusted Root Certification Authorities, чтобы убедиться в том, что CA сертификат, подписанный сервером, находится в этой базе. Затем SSTP VPN клиент определяет способ шифрования для SSL сеанса, генерирует ключ SSL сеанса и шифрует его с помощью SSTP VPN ключа публичного шлюза, после чего отправляет зашифрованную форму ключа SSL сеанса на SSTP VPN шлюз.
- Шлюз SSTP VPN расшифровывает зашифрованный ключ SSL сеанса с помощью личного ключа сертификатов компьютера. Все последующие соединения между SSTP VPN клиентом и SSTP VPN шлюзом будут зашифрованы оговоренным методом шифрования и ключа SSL сеанса.
- SSTP VPN клиент отправляет HTTP через SSL (HTTPS) сообщение запроса на SSTP VPN шлюз.
- SSTP VPN клиент обсуждает SSTP канал с SSTP VPN шлюзом.
- SSTP VPN клиент обсуждает PPP соединение с SSTP сервером. Эти переговоры включают аутентификацию мандатов пользователя посредством стандартного PPP метода аутентификации (или даже EAP аутентификации) и конфигурирование настроек для трафика Интернет протокола четвертой версии (IPv4) или Интернет протокола шестой версии (IPv6).
- Клиент SSTP начинает отправку IPv4 или IPv6 трафика через PPP соединение.
Те, кому интересны характеристики архитектуры VPN протоколов, могут посмотреть их на рисунке ниже. Обратите внимание, что SSTP имеет дополнительный заголовок в отличие от двух других VPN протоколов. Это благодаря дополнительному HTTPS шифрованию, помимо заголовка SSTP. L2TP и PPTP не имеют заголовков уровня приложений для шифровки соединения.

Рисунок 1
Мы возьмем для примера простую сеть из трех машин, чтобы посмотреть, как работает SSTP. Названия и характеристики этих трех машин следующие:
Vista:
Vista Business Edition
Vista Service Pack 1
Non-domain member
W2008RC0-VPNGW:
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Edition
Two NICs ‘ Internal and External
Domain member
WIN2008RC-DC:
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Edition
Domain Controller of MSFIREWALL.ORG domain
DHCP Server
DNS Server
Certificate Server (Enterprise CA)
Обратите внимание, что Vista Service Pack 1 используется в качестве VPN клиента. Хотя в прошлом были обсуждения по поводу Windows XP Service Pack 3, поддерживающей SSTP, дело может закончиться совсем не так. Я недавно установил пробную версию Windows XP Service Pack 3 на тестовый компьютер и не нашел никаких доказательств поддержки SSTP. И это действительно плохо, поскольку на сегодняшний день слишком много ноутбуков используют ОС Windows XP, а факты говорят о том, что Vista слишком медлительна для работы ноутбуков. Возможно, проблемы производительности Vista будут решены с помощью пакета обновления Vista Service Pack 1.
Высокоуровневая конфигурация примерной сети показана на рисунке ниже.

Рисунок 2
Конфигурирование Windows Server 2008 в качестве сервера Remote Access SSL VPN Server
Я не собираюсь рассматривать все шаги, начиная с самых основ. Смею предположить, что вы установили контроллер домена и активировали DHCP, DNS и Certificate Services роли на этом сервере. Тип сертификации сервера должен быть Enterprise, и вы имеете CA в вашей сети. Сервер VPN должен быть подключен к домену, прежде чем продолжать выполнять следующие шаги. Прежде чем начинать, нужно установить пакет обновления SP1 для клиента Vista.
Нам нужно выполнить следующие процедуры для того, чтобы наше решение работало:
- Установить IIS на VPN сервер
- Запросить сертификат машины для сервера VPN, используя мастера запроса сертификатов IIS Certificate Request Wizard
- Установить роль RRAS на сервере VPN
- Активировать RRAS Server и настроить его на работу в качестве VPN и NAT сервера
- Настроить NAT сервер на публикацию CRL
- Настроить учетную запись (User Account) на использование dial-up соединений
- Настроить IIS на Certificate Server, чтобы разрешить HTTP соединения для директории CRL
- Настроить HOSTS файл для VPN клиента
- Использовать PPTP для связи с VPN сервером
- Получить CA Certificate из Enterprise CA
- Настроить клиента на использование SSTP и соединение с сервером VPN с помощью SSTP
Установка IIS на VPN сервер
Возможно, вам покажется странным, что мы начинаем именно с этой процедуры, так как я рекомендую никогда не устанавливать вебсервер на устройство безопасности сети. Хорошая новость заключается в том, что нам не придется хранить вебсервер на VPN сервере, он понадобится нам лишь на некоторое время. Причина кроется в том, что регистрационный сайт, включенный в Windows Server 2008 Certificate Server, более не является полезным для запроса сертификатов компьютера. На самом деле он вообще бесполезен. Интересно то, что если вы все же решите использовать регистрационный сайт для получения сертификата компьютера, все будет выглядеть так, словно сертификат получен и установлен, однако на самом деле это не так, сертификат не установлен.
Для решения этой проблемы мы воспользуемся преимуществом того, что используем enterprise CA. При использовании Enterprise CA, можно посылать запрос на интерактивный сервер сертификации. Интерактивный запрос на получение сертификата компьютера возможен, когда вы используете мастера IIS Certificate Request Wizard и запрашиваете то, что теперь называется сертификатом домена ‘Domain Certificate’. Это возможно только в том случае, если запрашивающая машина принадлежит тому же домену, что и Enterprise CA.
Для установки роли IIS Web server на сервере VPN выполните следующие шаги:
- Откройте Windows 2008 Server Manager.
- В левой панели консоли кликните на вкладке Роли.

Рисунок 1
- Жмем в меню Добавить роли с правой стороны правой панели.
- Жмем Далее на странице Прежде чем начать.
- Ставим галочку напротив строкиWeb Server (IIS) на странице Выбрать роли сервера. Жмем Далее.

Рисунок 2
- Можете прочесть информацию на странице Web Server (IIS), если пожелаете. Это довольно полезная общая информация об использовании IIS 7 в качестве вебсервера, но поскольку мы не собираемся использовать IIS вебсервер на VPN сервере, эта информация не совсем применима в нашей ситуации. Жмем Далее.
- На странице Выбрать службы ролей несколько опций уже выбраны. Однако если вы используете опции по умолчанию, вы не сможете воспользоваться мастером Certificate Request Wizard. По крайней мере, так было, когда я тестировал систему. Нет службы роли для мастера Certificate Request Wizard, поэтому я пытался ставить галочки напротив каждой опции Безопасность, и, кажется, сработало. Сделайте то же самое у себя и нажмите Далее.

Рисунок 3
- Просмотрите информацию на странице Подтвердить выбор установок и нажмите Установить.
- Нажмите Закрыть на странице Результаты установки.

Рисунок 4
Запрос сертификата машины (Machine Certificate) для VPN сервера с помощью мастера IIS Certificate Request Wizard
Следующий шаг – это запрос сертификата машины для VPN сервера. VPN серверу требуется сертификат машины для создания SSL VPN соединения с компьютером клиента SSL VPN. Общее название сертификата должно соответствовать имени, которое VPN клиент будет использовать для соединения с компьютером шлюза SSL VPN. Это означает, что вам нужно будет создать публичную DNS запись для имени на сертификате, который будет разрешать внешний IP адрес VPN сервера, или IP адрес NAT устройства перед VPN сервером, которое будет переадресовывать соединение на SSL VPN сервер.
Для запроса сертификата машины на сервер SSL VPN выполните следующие шаги:
- В Server Manager, разверните вкладку Роли в левой панели, а затем разверните вкладку Web Server (IIS). Нажмите на Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
Рисунок 5
- В консоли Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager, которая появится справа в левой панели, нажмите на имени сервера. В этом примере имя сервера будет W2008RC0-VPNGW. Нажмите на иконку Сертификаты сервера в правой панели консоли IIS.

Рисунок 6
- В правой панели консоли жмем на ссылку Создать сертификат домена.

Рисунок 7
- Введите информацию на странице Определенные свойства имени. Самым важным объектом здесь будет Общее имя. Это то имя, которое VPN клиенты будут использовать для соединения с VPN сервером. Вам также понадобится публичная DNS запись для этого имени с тем, чтобы распознавать внешний интерфейс VPN сервера, или публичный адрес NAT устройства перед VPN сервером. В этом примере мы используем общее имя sstp.msfirewall.org. Позже мы создадим записи HOSTS файла на компьютере VPN клиента, чтобы он мог распознавать это имя. Жмем Далее.

Рисунок 8
- На странице Интерактивный источник сертификатов жмем кнопку Выбрать. В диалоговом окне Выбрать источник сертификатов, жмем на имени Enterprise CA и нажимаем OK. Вводим дружественное имя в строке Friendly name. В этом примере мы использовали имя SSTP Cert, чтобы знать, что оно используется для шлюза SSTP VPN.

Рисунок 9
- Жмем Закончить на странице Интерактивный источник сертификатов.

Рисунок 10
- Мастер будет запущен, а затем исчезнет. После этого вы увидите, как появится сертификат в консоли IIS. Кликнем дважды на сертификате и увидим общее имя в секции Назначен для, и теперь у нас есть частный ключ, соответствующий сертификату. Жмем OK, чтобы закрыть диалоговое окно Сертификат.

Рисунок 11
Теперь, когда у нас есть сертификат, мы можем установить роль RRAS Server Role. Обратите внимание на то, что очень важно установить сертификат до того, как устанавливать роль RRAS Server Role. Если вы этого не сделаете, вы наживете себе большие головные боли, поскольку вам придется использовать довольно сложную рутину командных строк, чтобы связать сертификат с клиентом SSL VPN.
Установка роли RRAS Server Role на VPN сервере
Для установки роли RRAS Server Role нужно выполнить следующие шаги:
- В Server Manager, нажмите на вкладку Роли в левой панели консоли.
- В секции Общие сведения ролей нажмите на ссылку Добавить роли.
- Нажмите Далее на странице Прежде чем начать.
- На странице Выбрать роли сервера поставьте галочку напротив строки Политика сети и службы доступа. Нажмите Далее.

Рисунок 12
- Прочтите информацию на странице Политика сети и службы доступа. Большая ее часть касается Network Policy Server (который ранее назывался Internet Authentication Server [IAS] и по сути был RADIUS сервером) и NAP, ни один из элементов не применим в нашем случае. Нажимаем Далее.
- На странице Выбрать службы роли ставим галочку напротив строки Маршрутизация и службы удаленного доступа. В результате этого будут выбраны пункты Службы удаленного доступа и Маршрутизация. Жмем Далее.

Рисунок 13
- Жмем Установить в окне Подтвердить выбранные установки.
- Жмем Закрыть на странице Результаты установки.
Активация RRAS Server и его настройка в качестве VPN и NAT сервера
Теперь, когда роль RRAS установлена, нам нужно активировать сервисы RRAS, также как мы делали это в предыдущих версиях Windows. Нам нужно активировать функцию VPN сервера и сервисы NAT. С активацией компонента VPN сервера все понятно, но вы можете поинтересоваться, зачем нужно активировать NAT сервер. Причина активации сервера NAT кроется в том, что внешние клиенты могут получать доступ к серверу сертификации (Certificate Server), чтобы соединяться с CRL. Если клиент SSTP VPN не сможет загрузить CRL, SSTP VPN соединение работать не будет.
Для того, чтобы открыть доступ к CRL, мы настроим VPN сервер в качестве NAT сервера и опубликуем CRL, используя обратимый NAT. В сетевом окружении компаний у вас, скорее всего, будут брандмауэры, например ISA Firewall, перед сервером сертификации, поэтому вы сможете публиковать CRL с помощью брандмауэров. Однако в этом примере единственный брандмауэр, которым будем пользоваться, это брандмауэр Windows Firewall на сервере VPN, поэтому в этом примере нам нужно настроить VPN сервер в качестве NAT сервера.
Для активации сервисов RRAS выполните следующие шаги:
- В Server Manager разверните вкладку Роли в левой панели консоли. Разверните вкладку Политика сети и Службы доступа и кликните по вкладке Маршрутизация и Удаленный доступ. Правой клавишей кликните по вкладке Маршрутизация и Удаленный доступ и нажмите Настроить и активировать маршрутизацию и удаленный доступ.

Рисунок 14
- Нажмите Далее в окне Welcome to the Routing and Remote Access Server Setup Wizard.
- На странице Конфигурация выберите опцию Доступ к виртуальным частным сетям и NAT и нажмите Далее.

Рисунок 15
- На странице VPN соединение выберите NIC в секции Интерфейсы сети, которая представляет внешний интерфейс VPN сервера. Затем нажмите Далее.

Рисунок 16
- На странице Назначение IP адресов выберите опцию Автоматически. Мы можем выбрать эту опцию, потому что у нас установлен DHCP сервер на контроллере домена за VPN сервером. Если у вас нет DHCP сервера, тогда вам нужно будет выбрать опцию Из определенного списка адресов, а затем внести список адресов, которые VPN клиенты смогут использовать при подключении к сети через шлюз VPN. Жмем Далее.

Рисунок 17
- На странице Управление удаленным доступом нескольких серверов выбираем Нет, использовать маршрутизацию и удаленный доступ для аутентификации запросов соединения. Эту опцию мы используем, когда недоступны NPS или RADIUS серверы. Поскольку VPN сервер является членом домена, можно аутентифицировать пользователей, используя учетные записи домена. Если VPN сервер не входит в домен, тогда только локальные учетные записи VPN сервера можно использовать, если только вы не решите использовать NPS сервер. Я напишу статью об использовании NPS сервера в будущем. Жмем Далее.

Рисунок 18
- Прочтите общую информацию на странице Завершение работы мастера настройки маршрутизации и удаленного доступа и нажмите Закончить.
- Нажмите OK в диалоговом окне Маршрутизация и удаленный доступ, которое говорит вам о том, что распределение DHCP сообщений требует агента распределения DHCP.
- В левой панели консоли разверните вкладку Маршрутизация и удаленный доступ и затем нажмите на вкладке Порты. В средней панели вы увидите, что WAN Miniport соединения для SSTP теперь доступны.

Рисунок 19
Настройка NAT сервера для публикации CRL
Как я говорил ранее, клиент SSL VPN должен иметь возможность загружать CRL для подтверждения того, что сертификат сервера на сервере VPN не был поврежден или отозван. Для этого нужно настроить устройство перед сервером сертификации для направления HTTP запросов о расположении CRL на Сервер сертификации.
Как узнать, к какому URL нужно подключиться SSL VPN клиенту, чтобы загрузить CRL? Эта информация содержится в самом сертификате. Если вы снова перейдете на VPN сервер и дважды кликните на сертификате в IIS консоли, как делали прежде, вы сможете найти эту информацию.
Жмем на кнопку Детали на сертификате и листаем вниз до записи Точки распределения CRL, затем жмем на эту запись. В нижней панели показаны различные точки распределения, основанные на протоколе, используемом для получения доступа к этим точкам. В сертификате, показанном на рисунке ниже, видно, что нам нужно открыть доступ клиенту SSL VPN к CRL через URL:
http://win2008rc0-dc.msfirewall.org/CertEnroll/WIN2008RC0-DC.msfirewall.org.crl

Рисунок 20
Именно поэтому нужно создавать публичные записи DNS для этого имени, чтобы внешние VPN клиенты смогли относить это имя к IP адресу или устройству, которое будет выполнять обратимый NAT или обратимый proxy для получения доступа к вебсайту сервера сертификации. В этом примере нам нужно связать win2008rc0-dc.msfirewall.org с IP адресом на внешнем интерфейсе VPN сервера. Когда соединение достигает внешнего интерфейса VPN сервера, VPN сервер перенаправит NAT соединение на сервер сертификации.
Если вы используете расширенный брандмауэр, например ISA Firewall, вы можете сделать публикацию CRL сайтов более безопасной, открывая доступ только к CRL, а не ко всему сайту. Однако в этой статье мы ограничим себя возможностью простого NAT устройства, такого, которое обеспечивает RRAS NAT.
Следует отметить, что использование имени CRL сайта по умолчанию может быть менее безопасной опцией, поскольку оно раскрывает частное имя компьютера в Интернете. Вы можете создавать пользовательскую CDP (CRL Distribution Point), чтобы этого избежать, если считаете, что раскрытие частного имени вашей CA в публичной DNS записи создает угрозу безопасности.
Для настройки RRAS NAT для направления HTTP запросов на сервер сертификации выполните следующие шаги:
- В левой панели Server Manager разверните вкладку Маршрутизация и удаленный доступ, а затем разверните вкладку IPv4. Кликните по вкладке NAT.
- Во вкладке NAT кликните правой клавишей на внешнем интерфейсе в средней панели консоли. В данном примере имя внешнего интерфейса было Local Area Connection. Нажмите на Свойства.

Рисунок 21
- В диалоговом окне Свойства Local Area Connection поставьте галочку напротив Web Server (HTTP). Это вызовет диалоговое окно Служба редактирования. В текстовой строке Частный адрес введите IP адрес сервера сертификации во внутренней сети. Нажмите OK.

Рисунок 22
- Нажмите OK в диалоговом окне Свойства Local Area Connection.

Рисунок 23
Теперь, когда NAT сервер установлен и настроен, мы можем перенести наше внимание на настройку сервера CA и клиента SSTP VPN.
Настройка учетной записи пользователя на использование Dial-up соединений
Учетные записи пользователей требуют разрешений для доступа dial-up, прежде чем смогут подключиться к серверу Windows VPN, который входит в домен Active Directory. Самый лучший способ сделать это – это использовать сервер Network Policy Server (NPS), а также разрешение учетной записи пользователя по умолчанию, которое разрешает удаленный доступ на основе политики NPS. Однако в нашем случае мы не устанавливали сервер NPS, поэтому нам придется настраивать разрешение пользователю для доступа dial-in вручную.
Следующую статью я посвящу использованию NPS сервера и аутентификации EAP User Certificate для создания соединений с SSL VPN сервером.
Для того чтобы разрешить определенной учетной записи пользователя доступ dial-in для подключения к SSL VPN серверу, нужно выполнить следующие шаги. В этом примере мы будем активировать разрешение dial-in доступа для учетной записи администратора домена по умолчанию:
- На контроллере домена откройте консоль Active Directory пользователи и компьютеры из меню Инструменты администрирования.
- В левой панели консоли разверните имя домена и кликните по вкладке пользователи. Дважды кликните на учетной записи Администратор.
- Перейдите по вкладке Dial-in. Параметром по умолчанию будет Контроль доступа через NPS политику сети. Поскольку у нас нет NPS сервера в этом сценарии, мы изменим параметр на Разрешить доступ, как показано ниже на рисунке 1. Жмем OK.

Рисунок 1
Настройка IIS на сервере сертификации (Certificate Server) для разрешения HTTP соединений для CRL Directory
По каким-то причинам, когда мастер установки устанавливает Certificate Services (службы сертификации) веб сайт, он настраивает CRL директорию на запрос SSL соединения. Хотя с точки зрения безопасности это кажется вполне хорошей идеей, проблема заключается в том, что унифицированный идентификатор ресурса (URI) на сертификате не настроен под использование SSL. Полагаю, что вы сможете самостоятельно создать CDP запись для сертификата, чтобы он смог использовать SSL, но могу поспорить, что компания Microsoft нигде не упоминала об этой проблеме. Поскольку в этой статье мы используем стандартные параметры для CDP, нам необходимо отключить требование SSL на веб сайте CA для пути CRL директории.
Чтобы дезактивировать требование SSL для директории CRL выполните следующие шаги:
- В меню Инструменты администрирования откройте менеджера Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
- В левой панели консоли IIS разверните имя сервера, а затем разверните вкладку Сайты. Разверните вкладку Веб сайт по умолчанию и кликните на вкладке CertEnroll, как показано на рисунке 2.
Рисунок 2
- Если вы посмотрите на среднюю панель консоли, вы увидите, что CRL находится в этой виртуальной директории, как показано на рисунке ниже. Чтобы посмотреть содержимое этой виртуальной директории, вам нужно нажать кнопку Посмотреть содержимое в нижней части средней панели.

Рисунок 3
- Нажмите на кнопку Просмотр параметров внизу средней панели. Внизу средней панели дважды кликните на иконке Параметры SSL.
Рисунок 4
- В средней панели появится страница Параметры SSL. Уберите галочку в строке Требовать SSL. Нажмите Применить в правой панели консоли.

Рисунок 5
- Закройте консоль IIS после того, как увидите уведомление Изменения были успешно сохранены.
Рисунок 6
Настройка HOSTS файла для VPN клиента
Теперь мы можем уделить все внимание VPN клиенту. Первое что нам необходимо сделать с клиентом, это настроить HOSTS файл, чтобы мы смогли имитировать публичную DNS инфраструктуру. Есть два имени, которые нам необходимо внести в HOSTS файл (то же самое нужно сделать и для публичного DNS сервера, который вы будете использовать в производственных сетях). Первое имя – это имя VPN сервера, как определено общим/субъектным именем сертификата, который мы привязали к SSL VPN серверу. Второе имя, которое нам нужно ввести в HOSTS файл (и публичный DNS сервер), — это имя CDP URL, которое находится на сертификате. Мы рассматривали расположение информации CDP во второй части этой серии.
Два имени, которые необходимо ввести в HOSTS файл в этом примере будут:
192.168.1.73 sstp.msfirewall.org
192.168.1.73 win2008rc0-dc.msfirewall.org
Для настройки HOSTS файла для Vista SP1 VPN клиента выполните следующие процедуры:
- В меню Пуск введите c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts в строку поиска и нажмите ENTER.
- В диалоговом окне Открыть с помощью выберите Блокнот.
- Введите записи в HOSTS файл в формате, как показано на рисунке ниже. Обязательно нажмите enter после последней строки, чтобы курсор находился под ней.

Рисунок 7
- Закройте файл и выберите опцию сохранить изменения.
Использование PPTP для подключения к VPN серверу
Мы постепенно приближаемся к созданию SSL VPN соединения! Следующим шагом будет создание VPN коннектора на Vista SP1 клиенте, который позволит нам создать начальное VPN соединение с VPN сервером. В нашем случае это нужно сделать, потому что компьютер клиента не является членом домена. Так как машина не является членом домена, сертификат CA не будет автоматически установлен в ее хранилище Trusted Root Certificate Authorities. Если бы машина входила в домен, автоматическая регистрация позаботилась бы за нас об этой проблеме, так как мы установили Enterprise CA.
Самый простой способ выполнить этот шаг заключается в создании PPTP подключения Vista SP1 VPN клиента к Windows Server 2008 VPN серверу. По умолчанию VPN сервер будет поддерживать PPTP соединения, и клиент сначала попробует PPTP, перед тем как пробовать L2TP/IPSec и SSTP. Для этого нам нужно создать VPN Коннектор или объект соединения.
Для создания коннектора на VPN клиенте выполните следующие шаги:
- На VPN клиенте кликните правой клавишей на иконке сети и нажмите Сеть и коммутационный центр (Sharing Center).
- В окне Сеть коммутационного центра нажмите на ссылке Создать соединение или сеть в левой части окна.
- На странице Выбрать опции подключения нажмите на записи Подключиться к рабочему месту, затем нажмите Далее.

Рисунок 8
- На странице Как вы хотите подключиться выберите опцию Использовать мое Интернет соединение (VPN).

Рисунок 9
- На странице Введите Интернет адрес для подключения введите имя SSL VPN сервера. Убедитесь в том, что это имя и общее имя на сертификате, используемом сервером SSL VPN, одинаковое. В этом примере имя было sstp.msfirewall.org. Введите Имя адресата. В этом примере мы будем использовать имя адресата SSL VPN. Нажмите Далее.

Рисунок 10
- На странице Введите имя пользователя и пароль введите Имя пользователя, Пароль и Домен. Нажмите Соединить.

Рисунок 11
- Нажмите Закрыть на странице Вы подключены.

Рисунок 12
- На странице Выберите расположение для «ЅSSL VPN» сети выберите опцию Работа.

Рисунок 13
- Нажмите Продолжить в подсказке UAC.
- Нажмите Закрыть на странице Успешно настроенные параметры сети.

Рисунок 14
- В окне Сеть и коммутационный центр, нажмите на ссылку Показать статус в разделе SSL VPN, как показано на рисунке ниже. В диалоговом окне Статус SSL VPN вы увидите, что тип соединения VPN — это PPTP. Нажмите Закрыть в диалоговом окне Статус SSL VPN.

Рисунок 15
- Откройте окно командной строки и отправьте команду ping на контроллер домена. В этом примере IP адрес контроллера домена будет 10.0.0.2. Если ваше VPN соединение успешное, вы получите ping ответ с контроллера домена.

Рисунок 16
Получение CA Certificate с Enterprise CA
Клиент SSL VPN должен доверять CA, который выпустил сертификат, используемый VPN сервером. Чтобы создать это доверие, нам нужно установить CA сертификат на CA, выпустивший сертификат для VPN сервера. Мы можем это сделать, подключившись к веб сайту регистрации на CA во внутренней сети и установив сертификат VPN клиента в его хранилище Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
Для получения сертификата с сайта регистрации выполните следующие шаги:
- На клиенте VPN, подключенном к VPN серверу через PPTP соединение, введите http://10.0.0.2/certsrv в строке адреса в обозревателе Internet Explorer и нажмите ENTER.
- Введите имя пользователя и пароль, используемый в мандатном диалоговом окне. В этом примере мы будем использовать имя пользователя и пароль учетной записи администратора домена по умолчанию.
- На странице Приветствие сайта регистрации перейдите по ссылке Загрузить сертификат CA, цепь сертификатов или CRL.

Рисунок 17
- В диалоговом окне, предупреждающем вас о том, что Веб сайт хочет открыть веб содержимое, используя эту программу на вашем компьютере, нажмите Разрешить. Затем нажмите Закрыть в диалоговом окне Вы заметили информационное окно, если оно появится.

Рисунок 18
- Обратите внимание на то, что информационное окно информирует вас о том, что веб сайт мог быть отображен некорректно, поскольку контроль элементов ActiveX заблокирован. Это не должно вызывать никаких проблем, так как мы будем загружать CA сертификат, и использовать консоль Certificates MMC для его установки. Нажмите на ссылку Загрузить CA сертификат.

Рисунок 19
- В диалоговом окне Предупреждение безопасности загрузки файла жмем кнопку Сохранить. Сохраняем сертификат на рабочий стол.

Рисунок 20
- Нажимаем Закрыть в диалоговом окне Загрузка завершена.
- Закрываем Internet Explorer.
Теперь нам нужно установить сертификат CA в хранилище Trusted Root Certification Authorities Certificate Store машины клиента VPN. Для этого нужно сделать следующее:
- Жмем Пуск, затем вводим mmc в строку поиска и нажимаем ENTER.
- Жмем Продолжить в диалоговом окне UAC.
- В окне Консоль1 жмем меню Файл, а затем жмем Добавить/Удалить оснастку.
- В диалоговом окне Добавить или Удалить оснастки выбираем Сертификаты в списке Доступные оснастки, затем нажимаем Добавить.
- На странице Оснастки сертификатов выбираем опцию Учетная запись компьютера и жмем Закончить.
- На странице Выбрать компьютер выбираем опцию Локальный компьютер и жмем Закончить.
- Жмем OK в диалоговом окне Добавить или удалить оснастки.
- В левой панели консоли разворачиваем вкладку Сертификаты (Локальный компьютер) и затем разворачиваем вкладку Trusted Root Certification Authorities. Жмем по вкладке Сертификаты. Правой клавишей нажимаем на вкладке Сертификаты, выбираем Все задания и жмем Импорт.

Рисунок 21
- Жмем Далее в окне Welcome to the Certificate Import Wizard.
- На странице Импортируемый файл жмем кнопку Обзор, чтобы найти сертификат, и затем жмем Далее.

Рисунок 22
- На странице Хранилище сертификатов смотрим, что опция Разместить все сертификаты в данном хранилище выбрана, и, что хранилище Trusted Root Certification Authorities есть в списке. Жмем Далее.

Рисунок 23
- Жмем Закончить на странице Завершение импорта сертификатов.
- Жмем OK в диалоговом окне, информирующем о том, что импорт прошел успешно.
- Теперь в консоли появится сертификат, как показано на рисунке ниже.

Рисунок 24
- Закрываем консоль MMC.
Настройка клиента на использование SSTP и подключение к VPN серверу через SSTP
И вот почти все готово! Теперь нам нужно отключить VPN соединение и настроить VPN клиента на использование SSTP для VPN протокола. В производственном окружении вам не придется использовать этот шаг для пользователей, так как вы будете использовать пакет Connection Manager Administration Kit для создания VPN объекта соединения для пользователя, который будет включать клиента, использующего SSTP, или вы будете настраивать только SSTP порты на VPN сервере.
Все зависит от конфигурации окружения, поскольку вам нужно распределить время так, чтобы пользователи смогли в течение некоторого времени использовать PPTP, пока вы устанавливаете сертификаты. Конечно, вы можете установить сертификаты CA не через сеть, то есть посредством загрузки с веб сайта или по электронной почте, и в этом случае вам не придется разрешать пользователям PPTP. Но тогда, если какие-то клиенты не поддерживают SSTP, вам потребуется разрешить PPTP или L2TP/IPSec, и вы не сможете отключить все не-SSTP порты. В таком случае вам придется полагаться на ручную настройку или на обновленный пакет CMAK.
Еще одним вариантом здесь может стать привязка SSTP клиента к определенному IP адресу на RRAS сервере. В этом случае вы сможете создать пользовательский пакет CMAK, который ссылается только на IP адрес на SSL VPN сервере, прослушивающем сеть на предмет входящих SSTP соединений. Другие адреса на сервере SSTP VPN будут прослушивать сеть на предмет PPTP и/или L2TP/IPSec соединений.
Выполните следующие шаги для того, чтобы отключить PPTP сеанс и настроить объект подключения VPN клиента на использование SSTP:
- На компьютере VPN клиента откройте окно Сеть и коммутационный центр, как делали ранее.
- В окне Сеть и коммутационный центр нажмите на ссылку Разъединить, которая находиться прямо под ссылкой Показать статус. Раздел SSL VPN исчезнет из окна Сеть и коммутационный центр.
- В окне Сеть и коммутационный центр нажмите на ссылку Управление сетевыми подключениями.
- Правой клавишей кликните по ссылке SSL VPN и выберите вкладку Свойства.

Рисунок 25
- В диалоговом окне Свойства SSL VPN перейдите по вкладке Сеть. В окне Тип VPN нажмите стрелку вниз и выберите опцию Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP), затем нажмите OK.
Рисунок 26
- Дважды кликните по объекту подключения SSL VPN в окне Сетевые подключения.
- В диалоговом окне Подключить SSL VPN нажмите кнопку Соединить.
- Когда подключение выполнено, кликните правой клавишей на объекте подключения SSL VPN в окне Сетевые подключения и выберите опцию Статус.

Рисунок 27
- В диалоговом окне Статус SSL VPN вы увидите, что было создано соединение SSTP WAN Miniport.
Рисунок 28
- Если вы зайдете на VPN сервер и откроете Консоль маршрутизации и удаленного доступа, вы убедитесь в том, что SSTP соединение было создано.

Рисунок 29
Томас Шиндер (Thomas Shinder)
Authentication
in any networking environment is critical for validating whether the
individual wanting access should be allowed access to network resources.
Authentication is an important component in the Windows Server 2008 R2
security initiative. Windows Server 2008 R2 can authenticate a remote
access user connection through a variety of PPP authentication
protocols, including the following:
-
Password Authentication Protocol (PAP)
-
Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP)
-
Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (MS-CHAP)
-
MS-CHAP version 2 (MS-CHAP v2)
-
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)
-
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP)
Authentication Protocols for PPTP Connections
For PPTP
connections, only four authentication protocols (MS-CHAP, MS-CHAP v2,
EAP, and PEAP) provide a mechanism to generate the same encryption key
on both the VPN client and VPN server. Microsoft Point-to-Point
Encryption (MPPE) uses this encryption key to encrypt all PPTP data sent
on the VPN connection. MS-CHAP and MS-CHAP v2 are password-based
authentication protocols.
Without a Certificate
Authority (CA) server or smart cards, MS-CHAP v2 is highly recommended
because it provides a stronger authentication protocol than MS-CHAP.
MS-CHAP v2 also provides mutual authentication, which allows the VPN
client to be authenticated by the VPN server and the VPN server to be
authenticated by the VPN client.
If a password-based
authentication protocol must be used, it is good practice to enforce the
use of strong passwords (passwords greater than eight characters) that
contain a random mixture of upper- and lowercase letters, numbers, and
punctuation. Group policies can be used in Active Directory to enforce
strong user passwords.
EAP and PEAP Authentication Protocols
Extensible
Authentication Protocol (EAP) and Protected Extensible Authentication
Protocol (PEAP) are designed to be used along with a certificate
infrastructure that uses user certificates or smart cards.
With EAP, the VPN client
sends its user certificate for authentication, and the VPN server sends a
computer certificate for authentication. This is the strongest
authentication method because it does not rely on passwords. Third-party
CAs can be used as long as the certificate in the computer store of the
Network Policy Server (NPS) server contains the Server Authentication
certificate purpose (also known as a certificate usage or certificate
issuance policy). A certificate purpose is identified using an object
identifier (OID). If the OID for Server Authentication is
1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1, the user certificate installed on the Windows remote
access client must contain the Client Authentication certificate purpose
(OID 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2).
PEAP does not specify
an authentication method, but rather secures EAP by creating an
encrypted channel between the client and the server. As such, it
provides additional security on top of EAP. PEAP can even be used with
MS-CHAP v2 to provide additional security to the password authentication
protocol.
Authentication Protocols for L2TP/IPSec Connections
For L2TP/IPSec connections,
any authentication protocol can be used because the authentication
occurs after the VPN client and VPN server have established a secure
connection known as an IPSec security association (SA). The use of a
strong authentication protocol such as MS-CHAP v2, EAP, or PEAP is
recommended to provide strong user authentication.
Choosing the Best Authentication Protocol
Organizations
spend very little time choosing the most appropriate authentication
protocol to use with their VPN connections. In many cases, the lack of
knowledge about the differences between the various authentication
protocols is the reason a selection is not made. In other cases, the
desire for simplicity is the reason heightened security is not chosen as
part of the organization’s authentication protocol decisions. Whatever
the case, we make the following suggestions to assist you in selecting
the best authentication protocol for VPN connections:
-
Using the EAP or PEAP
authentication protocol for PPTP, L2TP, and SSTP connections is highly
recommended if the following conditions exist in an organization. If a
smart card will be used, or if a certificate infrastructure that issues
user certificates exists, then EAP is the best and most secure option.
Note that EAP is supported only by VPN clients running Windows XP,
Windows 2000 client, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 2000 Server,
Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, and Windows Server 2008 R2. -
Use
PEAP with EAP-MS-CHAP v2 as a method of easing the deployment burden.
In this configuration, certificates are required only for the VPN server
infrastructure and not for the clients. However, the key generation is
done using Transport Level Security (TLS) with mutual authentication for
greatly enhanced security. -
Use
MS-CHAP v2 and enforce strong passwords using Group Policy if you must
use a password-based authentication protocol. Although not as strong of a
security protocol as PEAP or EAP, MS-CHAP v2 is supported by computers
running Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server
2003, Windows 2000 Server, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows XP, Windows
2000 client, Windows NT 4.0 with Service Pack 4 and higher, Windows Me,
Windows 98, and Windows 95 with the Windows Dial-Up Networking 1.3 or
higher Performance and Security Update.
Q
What is «Extensible Authentication Protocol» in my Windows Server 2008 service list?
And how is «Extensible Authentication Protocol» service related to eapsvc.dll?
A
«Extensible Authentication Protocol» is a Windows Server 2008 service that
«The Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) service provides network authentication in such scenarios as 802.1x wired and wireless, VPN, and Network Access Protection (NAP). EAP also provides application programming interfaces (APIs) that are used by network access clients, including wireless and VPN clients, during the authentication process. If you disable this service, this computer is prevented from accessing networks that require EAP authentication.»
«Extensible Authentication Protocol» service is provided by eapsvc.dll DLL file.
Detailed information on «Extensible Authentication Protocol» service:
Service name: EapHost Display name: Extensible Authentication Protocol Execution command: C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe -k netsvcs Start type: Manual Service status: Started Dependencies: Remote Procedure Call (RPC) CNG Key Isolation
«Extensible Authentication Protocol» service is provided
by the svchost.exe program,
see «svchost.exe Executable Program on Windows Server 2008» for details.
Disabling «Extensible Authentication Protocol» service may cause issues
when running Windows Server 2008 system.
⇒List of Services on Windows Server 2008
⇒⇒Windows Server 2008 Tutorials