Одно из частых действий, необходимых при решении проблем с работой Интернета (таких как ошибка ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED и других) или при смене адресов DNS серверов в Windows 10, 8 или Windows 7 — очистка кэша DNS (кэш DNS содержит соответствия между адресами сайтов в «человеческом формате» и их фактическим IP-адресом в интернете).
В этой инструкции подробно о том, как очистить (сбросить) кэш DNS в Windows, а также некоторые дополнительные сведения по очистке данных DNS, которые могут оказаться полезными.
Очистка (сброс) кэша DNS в командной строке
Стандартный и очень простой способ сброса кэша DNS в Windows — использовать соответствующие команды в командной строке.
Шаги, чтобы очистить кэш DNS при этом будут следующими.
- Запустите командную строку от имени администратора (в Windows 10 для этого можно начать набирать «Командная строка» в поиске на панели задач, затем нажать правой кнопкой мыши по найденному результату и выбрать «Запуск от имени администратора» в контекстном меню (см. Как запустить командную строку от имени администратора в Windows).
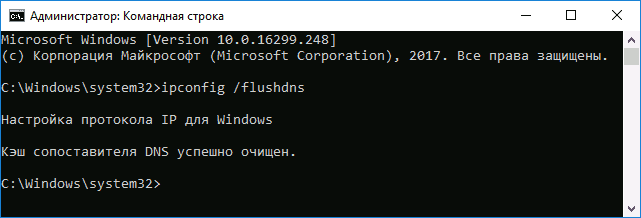
- Введите простую команду ipconfig /flushdns и нажмите Enter.
- Если всё прошло успешно, в результате вы увидите сообщение о том, что «Кэш сопоставителя DNS успешно очищен».
- В Windows 7 дополнительно можно выполнить перезапуск службы DNS-клиент, для этого там же в командной строке по порядку выполните следующие команды
- net stop dnscache
- net start dnscache
После выполнения описанных действий сброс кэша DNS Windows будет завершена, однако в некоторых случаях могут возникнуть проблемы, вызванные тем, что и у браузеров есть собственная база данных соответствий адресов, которую также можно очистить.
Очистка внутреннего кэша DNS Google Chrome, Яндекс Браузера, Opera
В браузерах на базе Chromium — Google Chrome, Opera, Яндекс Браузер присутствует собственный кэш DNS, который также можно очистить.
Для этого в браузере введите в адресную строку:
- chrome://net-internals/#dns — для Google Chrome
- browser://net-internals/#dns — для Яндекс Браузера
- opera://net-internals/#dns — для Оперы
На открывшейся странице вы можете посмотреть содержимое кэша DNS браузера и очистить его, нажав кнопку «Clear host cache».
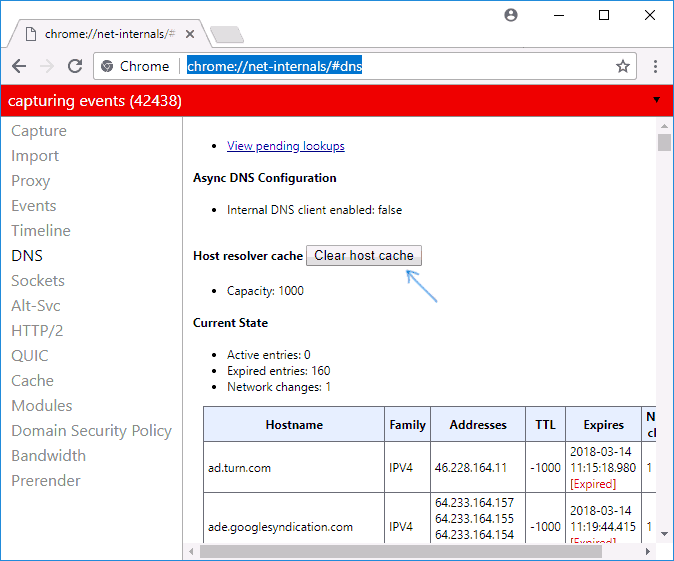
Дополнительно (при проблемах с соединениями в конкретном браузере) может помочь очистка сокетов в разделе Sockets (кнопка Flush socket pools).
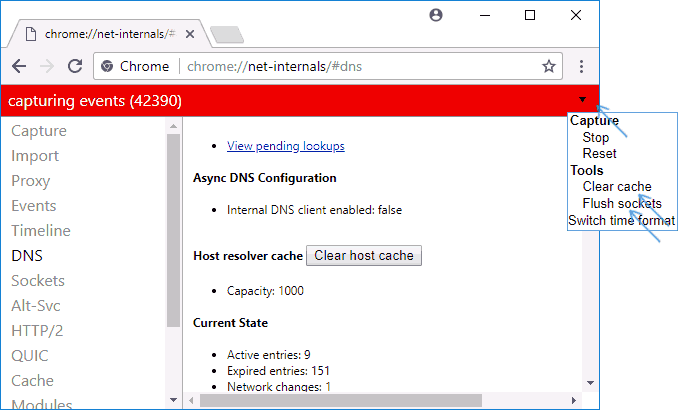
Также, оба этих действия — сброс кэша DNS и очистку сокетов можно быстро выполнить, открыв меню действий в правом верхнем углу страницы, как на скриншоте ниже.
Дополнительная информация
Существуют и дополнительные способы сброса кэша DNS в Windows, например,
- В Windows 10 присутствует опция автоматического сброса всех параметров подключений, см. Как сбросить настройки сети и Интернета в Windows 10.
- Многие программы для исправления ошибок Windows имеют встроенные функции для очистки кэша DNS, одна из таких программ, направленная именно на решение проблем с сетевыми подключениями — NetAdapter Repair All In One (в программе присутствует отдельная кнопка Flush DNS Cache для сброса кэша DNS).
Если простая очистка не срабатывает в вашем случае, при этом вы уверены, что сайт, к которому вы пробуете получить доступ работает, попробуйте описать ситуацию в комментариях, возможно, у меня получится вам помочь.
If you are experiencing DNS problems on your Windows 10, then this can help you. Normally, when you visit any website, the IP address of that web server gets stored on your DNS. All the web pages have an IP address that is saved on your DNS, even on this page your system is saving the DNS of our site.
There will be times when the browser takes the data and puts it in the wrong entry or the local cache got mixed up. Such situations can cause DNS problems, and here we can clear(flush) DNS cache on Windows 10 (both server and workstation) using CMD, Windows Server DNS console, and PowerShell.
Related Topic: How to Flush DNS Cache on Windows 11?
Table of Contents

Here is how to clear the DNS cache on Windows 10 using CMD (command prompt).
Step 1- Run CMD
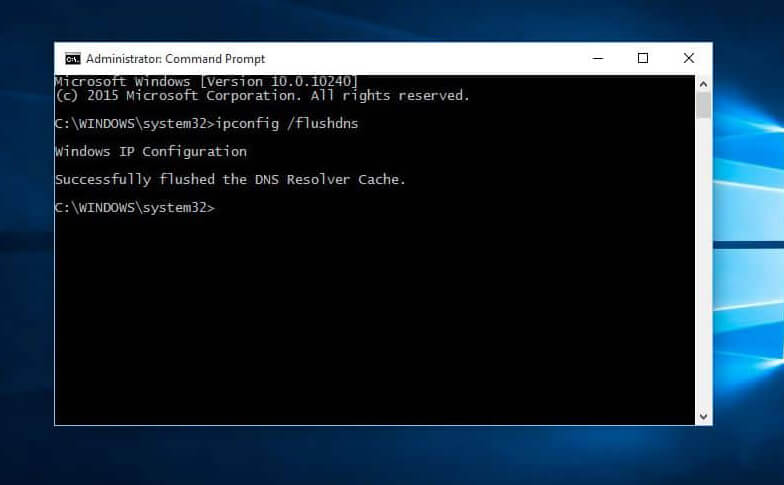
First, you will need to open CMD (command prompt) on your system. You can open CMD by clicking on Start, type CMD, and right-click on it. Run the CMD as Administrator.
Note: you will need to run CMD as admin due to security issues. Running CMD without admin authority won’t affect your system.
Step 2- Flush local cache
Now in the CMD, use the following command:
Ipconfig/flushdnsThis command will help you to flush the local cache of your system.
Step 3- check local cache (optional)
This step is quite optional. For users who want to check their local cache, they can use the command below in CMD.
Ipconfig/displaydnsAfter using the command in CMD, you will find something like this on your screen:
[fl_builder_insert_layout slug=”ad_sw_ip_address_tracker_incontent”]Flush DNS Windows Server
Most of the time, it is not the local client issues that users are experiencing (mostly on Windows Server). There are also moments, where the issue is caused due to bad cache entries too. For such moments, here is how to deal with them.
You will need to open DNS Console. Right-click on DNS Server, there you will find the Clear Cache option. Click on Clear Cache, and you have flushed your DNS on Windows Server.
Flushing DNS with PowerShell on Windows 10
Here are some commands that can be used to deal with DNS on your system in PowerShell.
To clear Client use: Clear-DnsClientCache
To clear DNS Server: Clear-DNsServerCache
If you want to specify your DNS: Clear-DnsServerCache –ComputerName “DC1” –Force
Remember one thing, that here you will need to replace “ComputerName” in the command and use your computer’s name.
Cleaning DNS on other Windows OS
If you want to perform the same procedure on other Windows OS that includes Windows 2003, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, and Windows Server 2016.
Go to Start and run CMD as administrator.
Now, inside the CMD type this command:
Ipconfig/flushdnsThe command above will clear DNS from your system and your DNS will start working again.
DNS cache is crucial in speeding up internet access and improving browsing experiences by storing recent domain name lookups and their corresponding IP addresses.
Clearing this cache periodically can enhance your browsing speed and resolve connectivity issues.
Modern operating systems generally cache DNS lookup results and IP addresses to process requests more quickly. Whenever you write a URL in your browser, it sends a request to the DNS servers to “locate” the site. But instead of sending that request every single time, the browser often caches the information. This way, the next time you type in that address, the browser looks it up through the DNS cache, allowing it to return the results much faster.
However, cached DNS records can become outdated or corrupted over time, potentially leading to browsing issues, including connection errors or the display of outdated website versions. Flushing your DNS cache occasionally is a good practice to ensure you’re accessing up-to-date versions of websites and protecting yourself from security risks like DNS spoofing.
In this article we will explain how to flush the DNS cache on different operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, as well as detailing the several reasons why it is so important to flush the DNS regularly.
How to Flush DNS on Different Operating Systems
How to Flush DNS on Windows 10 & 11
If you’re using Windows 10 or 11, here are the steps you can follow to flush the DNS cache:
- Click on Start, then search for Command Prompt. Right-click it and select “Run as Administrator.”
- Once the Command Prompt is open, type
ipconfig /flushdnsand press Enter. - A message will appear confirming that the DNS Resolver Cache was flushed.

In addition to flushing the DNS, performing an IP release and renewal can help resolve network connection problems. Here’s how to do it:
How to Perform an IP Release, Renew, and DNS Flush on Windows
- Open Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
- Type
ipconfig /releaseand press Enter to release the current IP address. - Next, type
ipconfig /renewto obtain a new IP address. - Finally, type
ipconfig /flushdnsto clear the DNS cache.
How to Flush DNS on macOS
Flushing the DNS cache on macOS involves using the Terminal app. Follow these steps:
- Press cmd + space to open Spotlight Search.
- Type Terminal and open the application (you can also find it in the Other section in the Launchpad).
- Type the following command:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder. - Enter your administrator password when prompted. Once you do, you will receive confirmation that the DNS cache has been flushed.
Note: The command can vary depending on your macOS version. Here’s how to check your macOS version:
- Click on the Apple menu in the upper-left corner of your screen.
- Select About This Mac.
Depending on your macOS version, use the appropriate command:
- Monterey, Big Sur, Catalina:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder - Mojave, High Sierra, Sierra, El Capitan, Mavericks, Mountain Lion, Lion:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
How to Flush DNS on Linux
If you’re using a Linux distro such as Ubuntu, here’s how to flush the DNS cache:
- Open the terminal by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T or searching for “Terminal” in the Activities menu.
- Run the following command:
- If you are running Ubuntu 20.04 LTS or older, use:
sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches. - If you are running Ubuntu 22.04 LTS or newer, use:
sudo resolvectl flush-caches.
- If you are running Ubuntu 20.04 LTS or older, use:
- Enter your administrator password when prompted, and the DNS cache will be flushed.

How to Flush DNS Cache in Google Chrome
If you experience issues accessing websites on Google Chrome, your browser’s DNS cache may also need to be flushed. Here’s how to do it:
- Type
chrome://net-internals/#dnsin the address bar and press Enter. - Click the Clear Host Cache button to flush the browser’s DNS cache.

This action will ensure that Chrome fetches fresh DNS data from the websites you visit.
Why Should You Flush Your DNS Cache?
There are several reasons why flushing the DNS cache periodically is important:
Resolve DNS Errors
If you’re encountering issues such as DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN or CONNECTION_TIMED_OUT, flushing the DNS cache may help resolve the problem. These errors often arise due to outdated or incorrect DNS information.
Speed Up DNS Propagation
After making changes to your DNS records, such as transferring a domain to a new hosting provider, DNS propagation can take time to fully update across the internet. Flushing your DNS cache ensures that your device picks up these changes more quickly, allowing you to see the updates sooner.
Prevent DNS Spoofing
DNS spoofing (or poisoning) occurs when an attacker manipulates DNS cache entries to redirect users to fraudulent or malicious websites. Flushing your DNS cache helps mitigate this risk by clearing any potentially corrupted entries.
Avoiding 404 Errors
A 404 error might indicate that your system is pulling up an outdated version of a website. Flushing the DNS cache ensures that your browser accesses the most current version of the site, which can help you avoid such errors.
Remove Old DNS Data
When you change DNS providers, such as switching to Google DNS or OpenDNS, it’s important to flush your DNS cache. This ensures that your system doesn’t use outdated data from the previous provider, helping to prevent connectivity issues.
After Action Report – Flush Your DNS Cache Periodically
Flushing your DNS cache is a simple yet effective way to resolve connectivity issues, speed up website access, and prevent security risks like DNS spoofing. Whether you’re using Windows, macOS, Linux, or even just browsing on Google Chrome, clearing your DNS cache periodically is a good habit to ensure optimal performance.
Do you regularly flush your DNS cache? Let us know if you have any tips or questions! Join the conversation below by leaving a comment! 💬
Wrapping Up
RunCloud is a powerful and easy-to-use platform that helps you manage your websites on any cloud server. With RunCloud, you don’t need to be a Linux expert to set up, secure, and optimize your web applications. You can do everything from a simple and intuitive dashboard, saving you time and hassle.
RunCloud supports various web servers, PHP versions, databases, and frameworks. You can also monitor your server performance, back up your data, and automate your tasks with RunCloud. Whether you are a developer, a freelancer, or a business owner, RunCloud can help you run your websites faster and smoother.
What are you waiting for? Join RunCloud today and enjoy the best web hosting solution for your websites. It’s free for 7 days, no strings attached!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is clearing the DNS cache safe?
Clearing the DNS cache is safe and does not affect your saved passwords, browser history, or other personal data. It removes outdated DNS information, ensuring your computer can fetch up-to-date DNS records.
How often should I flush my DNS cache?
There’s no hard rule on how often you should flush the DNS cache, but it’s a good idea to do it when you experience connection issues or DNS errors or after making changes to your network configuration (such as switching DNS providers).
Does flushing the DNS cache affect my internet speed?
Flushing the DNS cache may temporarily slow down website access on the first visit, as the DNS lookup will need to be performed again. However, once the cache is refreshed, your browser will store the new DNS records, which can speed up access to frequently visited websites.
How do I know if my DNS cache was successfully flushed?
After running the appropriate command to flush the DNS cache (such as ipconfig /flushdns on Windows), your system usually displays a message confirming that the DNS Resolver Cache was successfully flushed.
Will clearing the DNS cache fix DNS errors?
In many cases, yes. If you encounter errors like DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN or CONNECTION_TIMED_OUT, flushing the DNS cache can help resolve these problems by removing outdated or corrupted DNS entries.
DNS-кэш сохраняет IP-адреса посещенных сайтов на локальном компьютере, чтобы в следующий раз загружать их быстрее.
Если у вас регулярно возникает ошибка 404, то вам может помочь очистка DNS-кэша. Например, вы перенесли сайт на другой сервер и у сайта изменился IP-адрес. Чтобы браузер открывал сайт с нового IP-адреса, необходимо удалить закэшированный IP из DNS-кэша.
Как очистить DNS-кэш в операционной системе
Очистить DNS-кэш в операционных системах не трудно — нужно всего лишь ввести одну команду через консоль.
Windows 10, 11
- Откройте меню Пуск и в строке поиска введите cmd. Найдется пункт Командная строка (cmd.exe). Кликните на него правой кнопкой мыши и выберите пункт Запуск от имени администратора.
- В открывшемся окне введите команду ipconfig/flushdns и нажмите Enter. Готово!

Ubuntu
- Найжмите сочетание клавиш ctrl+alt+T. Откроется Терминал. Его также можно найти в списке приложений..
- Введите команду sudo systemd-resolve —flush-caches, а затем укажите пароль администратора. Готово!

macOS 10.14 Mojave
- Нажмите на иконку поиска в правом верхнем углу и найдите в поиске Терминал.
- В Терминале введите команду sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder; sleep 2; а затем укажите пароль администратора. Готово!

Как очистить DNS-кэш в браузере
У современных браузеров есть свой DNS-клиент, который тоже кэширует IP-адреса. После очистки кэша в системе рекомендуем дополнительно очистить DNS-кэш в браузере.
Google Chrome, Opera, Яндекс.Браузер, Vivaldi
Этот способ подходит для очистки DNS-кэша в браузерах, основанных на Chromium.
- В строке браузера введите адрес chrome://net-internals/#dns. В открывшемся окне нажмите кнопку Clear host cache.
- В том же окне нажмите на пункт Sockets и нажмите Flush socket pools. Готово!

Mozilla Firefox
- Откройте меню и выберите пункт Настройки.
- Откройте раздел Приватность и защита и найдите пункт Куки и данные сайтов.
- Нажмите кнопку Удалить данные. Откроется новое окно, в нем нужно снять галочку напротив пункта Куки и данные сайтов и нажать кнопку Удалить.
- Готово! Можно закрывать окно с настройками.

Если этот метод не сработал, то очистите DNS-кэш через окно тонких настроек браузера.
- Откройте страницу about:config и нажмите кнопку Я принимаю на себя риск.
- В поле поиска введите network.dnsCacheExpiration. Измените найденное значение на 0, нажмите ОК, а затем снова верните его на 60.
- Затем в поле поиска найдите значение network.dnsCacheEntries и после, как и с прошлым пунктом, измените его значение на 0, нажмите ОК и снова верните значение на 60.
- Готово!

Если вам понравилась статья, то подписывайтесь на наш телеграм-канал, чтобы не пропустить другие полезные материалы.
Управляйте DNS и веб-сервером с ispmanager!
Ispmanager — панель управления сайтами, веб-сервером и сервисами на нём. Подходит для хостинга на Linux и делает администрирование проще.
- Управление сервером без консоли, в простом интерфейсе.
- DNS-сервер.
- Автоустановщик CMS и веб-приложений.
- Мощный файловые менеджер.
- Установка различных видов СУБД SQL на один сервер.
- Поддержка мультиверсионности PHP.
Скачайте бесплатную пробную версию и попробуйте сами!
Попробовать ispmanager

You’ve probably noticed that, after visiting a website for the first time, the website loads much quicker the next time you visit.
This is because your operating system, or browser in the case of Google Chrome, cache IP addresses and DNS (Domain Name System) information of any website you visit. The DNS cache contains:
- the website address or hostname, technically called the resource data (rdata)
- the domain name of the website
- record type (IPv4 or IPv6)
- the validity of the cache or TTL (time to live)
When the TTL expires, the cache will be cleared, and the DNS is flushed for you automatically. But there are times when you don’t want to wait hours or days for the TTL to expire, and want to flush your DNS manually.
In this article, I’ll go over why you should flush your DNS, and how to do that in Windows 10 and Chrome.
So, Why Should You Flush (or Clear) Your DNS?
Flushing your DNS has several advantages, such as:
- hiding your search behavior from data collectors who might show you ads based on your search history
- requesting that an updated version of a website or web app is loaded. This can help resolve 404 issues if a website or web app was migrated to a new domain
- preventing DNS cache poisoning – a security situation in which black hat hackers gain maliciously gain access to your DNS cache and alter them so you get redirected to a website where sensitive information might be collected from you
To flush your DNS records on Windows 10, follow the steps below:
Step 1: Click on Start or hit the Windows [logo] key on your keyboard
Step 2: Type «cmd», then select «Run as Administrator» on the right
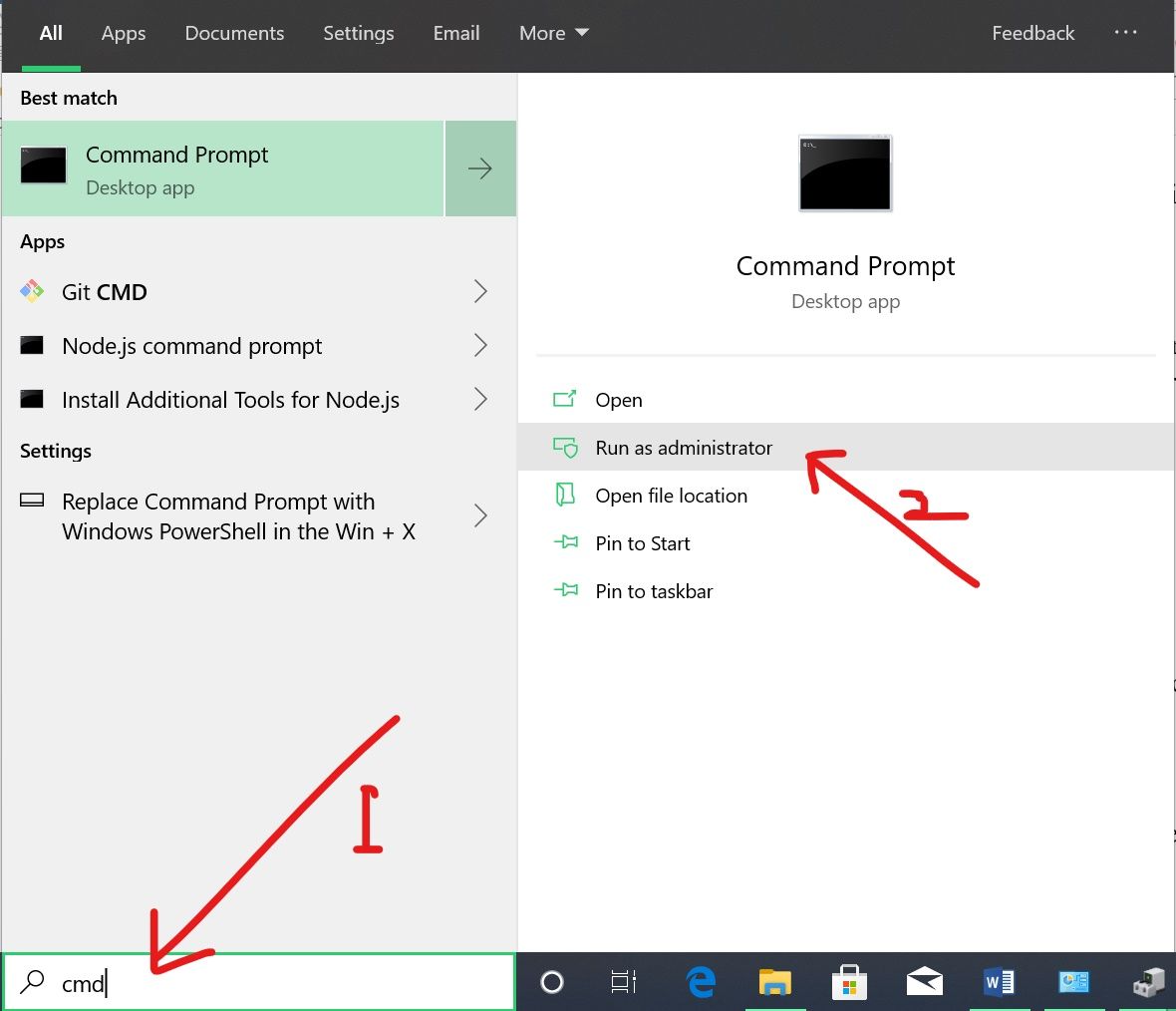
Step 3: Type in «ipconfig /flushdns» and hit ENTER
You should get a response that the DNS cache has been flushed like the one below:
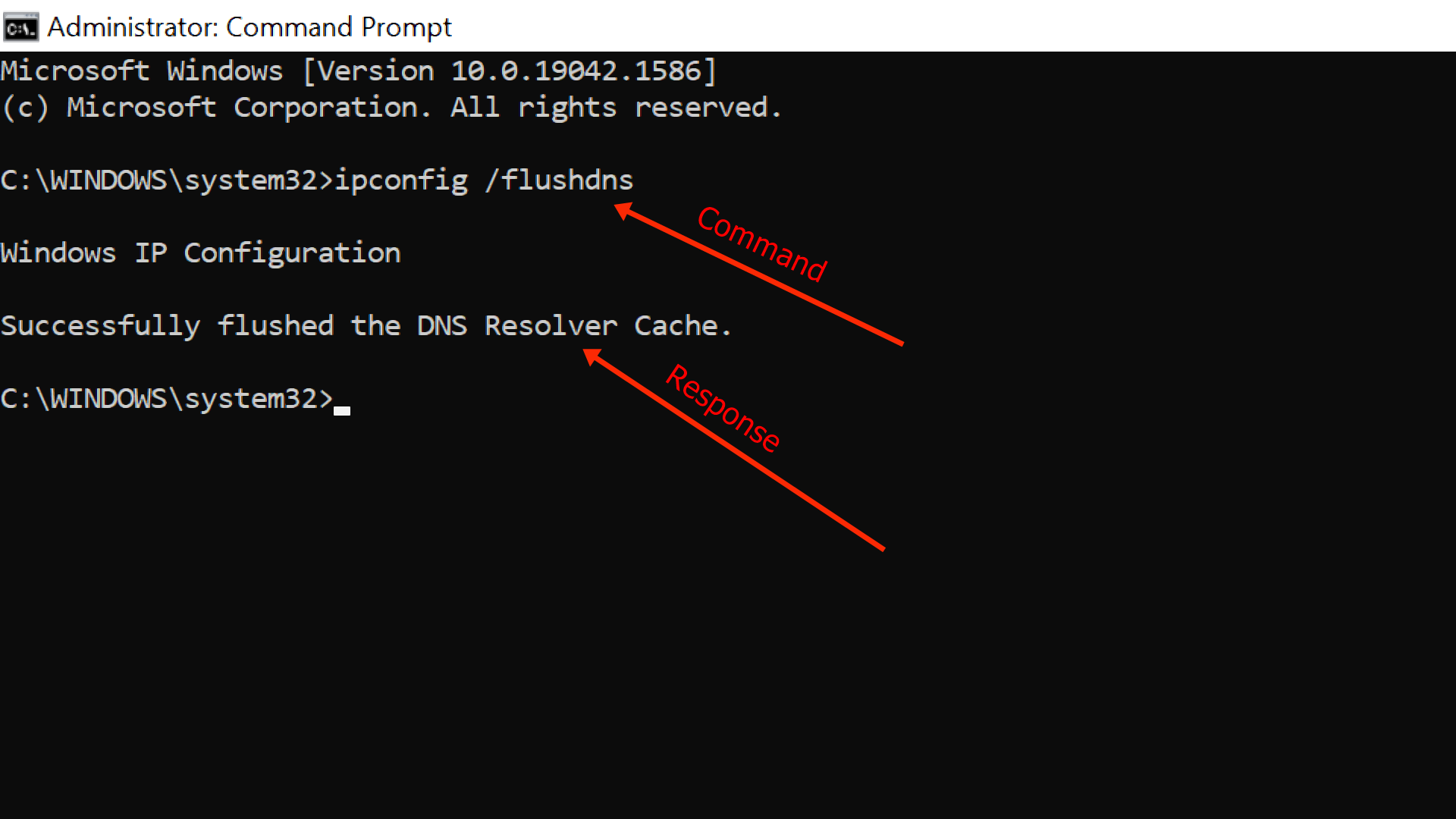
This means that your cache has been completely cleared, and fresh versions of any website you visit will be loaded.
How to Clear the DNS Cache on Google Chrome
Despite not being an operating system, Chrome keeps a DNS cache of its own to help personalize your browsing experience.
To flush Chrome’s DNS, all you need to do is type chrome://net-internals/#dns in the address bar and hit ENTER.
Then click “Clear host cache”:
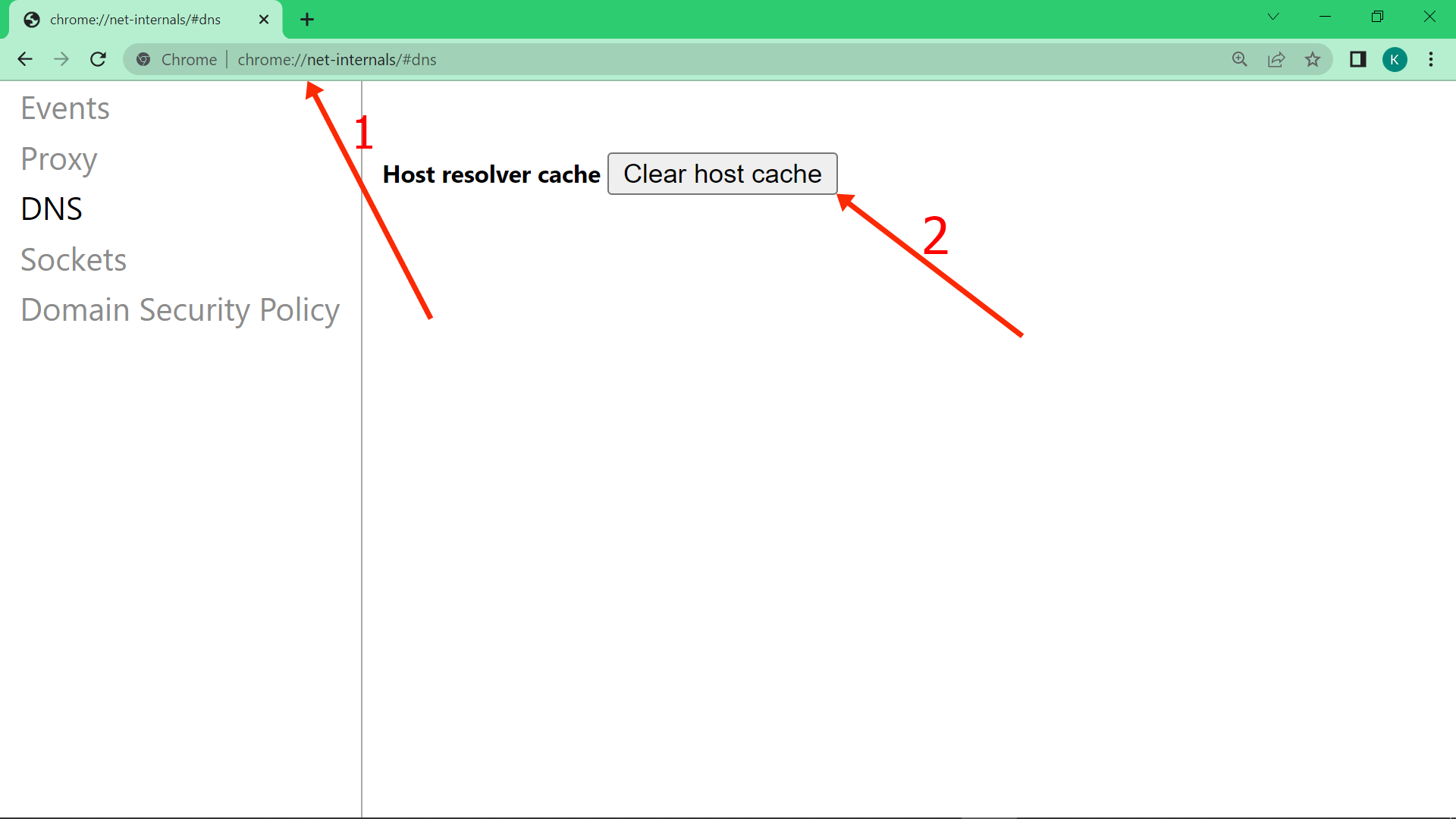
Conclusion
As you’ve learned in this article, flushing your DNS gives you a lot of advantages that can make your internet experience safer.
Even though the cache gets cleared after the TTL expires, you should flush your DNS as often as possible so you can get these advantages.
Thank you for reading!
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started