Большинство администраторов терминальных серверов Windows заметили, что начиная с Windows Server 2012, на RDS серверах пропали оснастки управления tsadmin.msc (Remote Desktop Services Manager — Диспетчер служб удаленных рабочих столов) и tsconfig.msc (Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration — Конфигурация узла сеансов удаленных рабочих столов). Разработчики Microsoft решили, что большинством параметров сервера RDS можно управлять через Server Manager, консоль редактора групповых политик (gpedit.msc) или в настройках RDS коллекций. Однако все эти инструменты не настолько просты и удобны как старые остатки.
Разберёмся, как можно вернуть оснастки tsadmin.msc и tsconfig.msc на RDS серверах под управлением Windows Server 2016 (инструкция также к Windows Server 2019 и 2012 R2 окружению).
Для этого нам понадобится скопировать 6 файлов и 2 ветки реестра с любого сервера под управлением Windows Server 2008 R2 в аналогичный каталог C:\Windows\System32 на Windows Server 2016. Скопируйте следующие 7 файлов:
- c:\windows\system32\tsadmin.dll
- c:\windows\system32\tsconfig.dll
- c:\windows\system32\wts.dll
- c:\windows\system32\tsconfig.msc
- c:\windows\system32\tsadmin.msc
- c:\windows\system32\en\tsconfig.resources.dll
- c:\windows\system32\en\tsadmin.resources.dll
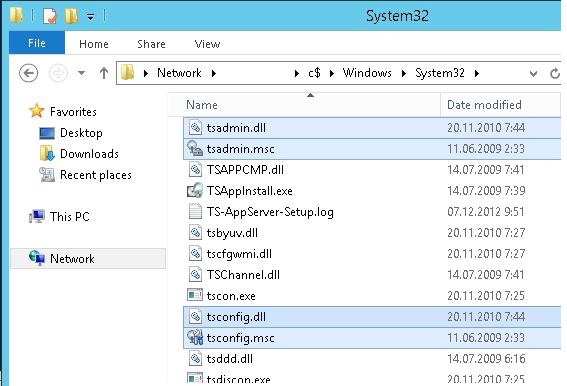
Затем на Windows Server 2008 R2 с помощью редактора regedit нужно экспортировать в файлы reg две ветки реестра:
- [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MMC\SnapIns\FX:{80aaa290-abd9-9239-7a2d-cf4f67e42128}]
- [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MMC\SnapIns\FX:{3FCE72B6-A31B-43ac-ADDA-120E1E56EB0F}]
И по очереди импортировать эти ветки в реестр Windows Server 2016. Достаточно дважды щелкнуть по reg файлу и согласится с внесением изменений в реестр.
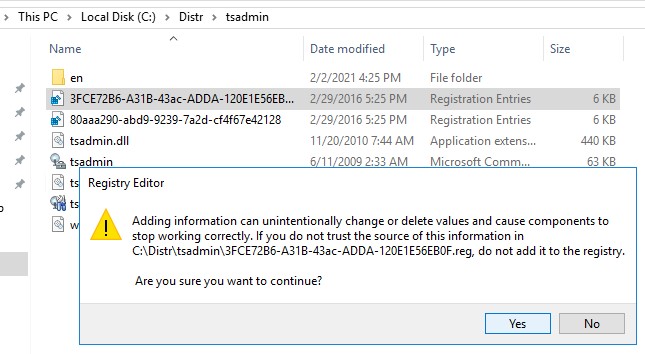
Осталось скопировать dll и msc файлы в каталог C:\Windows\System32 на хосте с Windows Server 2016. Регистрировать файлы dll библиотек не обязательно.
Примечание. Если у вас нет под рукой развернутого сервера с Windows Server 2008 R2 (их сейчас сложно найти в связи с окончанием поддержки), вы можете скачать архив с необходимыми файлами с нашего сайта.
- Комплект файлов с английской версии ОС — tsadmin-winsrv.zip
- с русской версии — tsadmin-winsrv_ru.zip
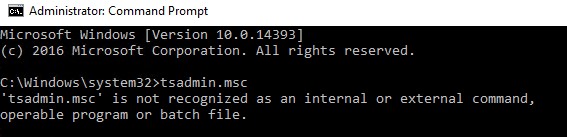
После этого попробуйте запустить нужную оснастку командами
tsadmin.msc
:
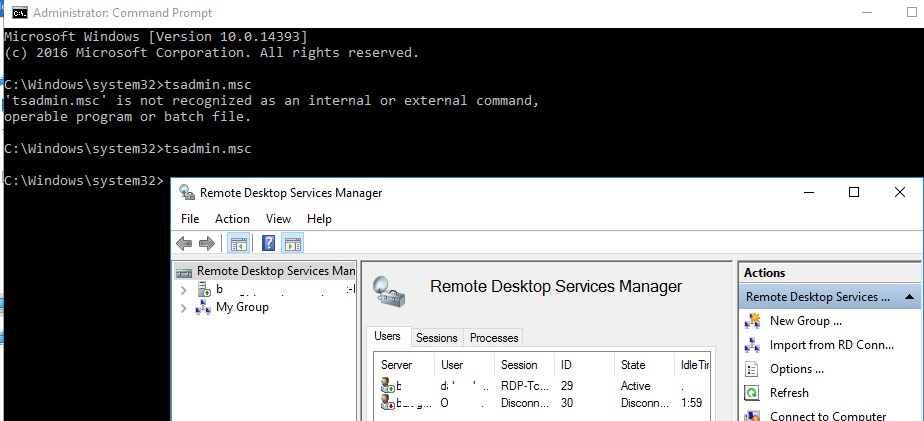
В этой консоли вы можете удобно управлять сессиями пользователей – можно отключить нужную сессию, отправить сообщение, инициировать корректный logoff и т.д. Оснастка tsadmin позволяет выбрать сразу нескольких пользователей и выполнить нужное действие сразу со всеми.
Можно запустить консоль
tsconfig.msc
:
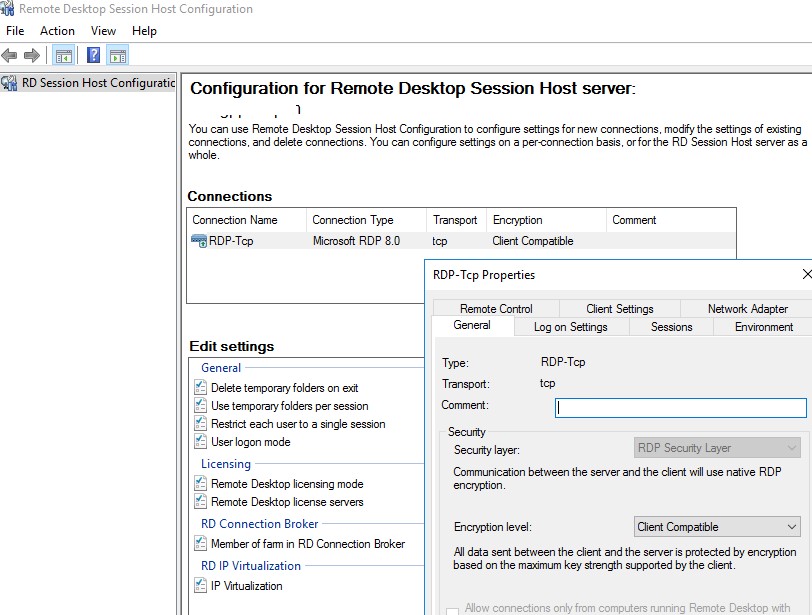
В консоли tsconfig.msc можно гораздо проще и удобнее настроить базовые параметры RDS хоста: задать сервер лицензирования и тип RDS лицензий, добавить хост в ферму RD Connection Broker (настроить вес хоста в ферме), настроить уровни шифрования RDP, настроить автозапуск программы при входе пользователя в сеанс, настроить таймауты отключения неактивных сессий пользователей на отдельно стоящем RDS хосте и т.д.
Обратите внимание, что не обязательно ставить эти консоли на все RDS хосты. С помощью опции Connect to Remote Desktop Session Host Server вы можете подключится к любому другому RDS хосту в вашей сети.
Примечание. Естественно, что использование старых консолей в новых версиях Windows Server это не поддерживаемое MS решение и вы можете использовать его на свой риск. ИМХО, проблем быть не должно.
Отметим, что с помощью консоли tsadmin.msc не получится подключиться к терминальной сессии пользователя (Ошибка: Access is denied). Подключение к RDS сессиям пользователей возможно по сценарию, описанному в статье RDS Shadow в Windows Server. Также в консоли tsconfig.msc в свойствах подключения RDP-Tcp отсутствует вкладка Security, через которую было удобно раздавать права группам сопровождения (без права администраторов) на подключение и управление RDP сессиями пользователей. Я использую следующую команду для предоставления определенной группе полные права на управления сессиями на сервере:
wmic /namespace:\\root\CIMV2\TerminalServices PATH Win32_TSPermissionsSetting WHERE (TerminalName ="RDP-Tcp") CALL AddAccount "domain\support_rds",2
Для просмотра текущий разрешений можно использовать PowerShell:
get-WmiObject -Namespace "root/cimv2/terminalservices" -Class win32_tspermissionssetting
Для установки и настройки роли RemoteApp, имеем подготовленный сервер с операционной системой Windows Server 2019, на котором будем производить нижеописанные действия.
Установка служб Удаленных рабочих столов
На первом этапе установим службы Удаленных рабочих столов, для этого в окне Диспетчер серверов выбираем Добавить роли и компоненты.
Обращаем внимание перед установкой роли на предупреждение → далее.
Устанавливаем чекбокс Установка служб удаленных рабочих столов → далее.
Устанавливаем чекбокс Cтандартное развертывание → далее.
Устанавливаем чекбокс Развертывание рабочих столов на основе сеансов → далее.
Выбираем сервер, на который будут установлены службы роли посредника → далее.
Устанавливаем чекбокс Установить службы роли веб-доступа к удаленным рабочим столам на сервере посредника подключений к удаленному рабочему столу → далее.
Выбираем сервер, на который будут установлены службы роли узлов сеансов удаленных рабочих столов → далее.
Устанавливаем чекбокс Автоматически перезапускать конечный сервер, если это потребуется → развернуть.
Закрываем установку после завершения и перезагружаем сервер.

Рисунок 1 — Завершение установки
Бесплатный сервер 1С для подписчиков нашего telegram-канала !
Создание коллекции сеансов
Заходим в диспетчер серверов → Службы удаленных рабочих столов → Создание коллекции сеансов.
Нажимаем далее → Указываем имя коллекции → Выбираем наш сервер → Выбираем группу пользователей для доступа к коллекции → Снимаем чекбокс с включить диски профилей пользователей → Нажимаем создать → закрыть.
Выбираем нашу коллекцию и нажимаем публикация удаленных приложений RemoteApp.
Выбираем из списка приложения, которые необходимо опубликовать, нажимаем далее → опубликовать → закрыть.
Проверка публикации RemoteApp
Переходим в браузере по адресу https://localhost/rdweb и выбираем приложение.
После сохранения файла RDP, можем заходить в него под пользователем.

Рисунок 2 — Выбор опубликованного приложения

Рисунок 3 — Проверка работоспособности RemoteApp
Нужна помощь? Наша компания может оказать помощь в реализации ИТ-задач, для этого напишите в чат. Также мы предоставляем готовый сервер с RemoteApp-приложениями, например, с различными конфигурациями 1С.
A step by step guide to build a Windows Server 2019 Remote Desktop Services deployment.
I posted this before based on Windows Server 2012 R2 RDS and thought it was high time to update this post to a more modern OS version.
I will provide all the steps necessary for deploying a single server solution using the GUI tools.
Although it is called a single server installation, we will need 2 servers as shown below.
Software used in this guide:
Windows Server 2019 ISO (evaluation can be downloaded here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/evalcenter/evaluate-windows-server-2019).
SQL Server 2017 Express x64 (free version can be downloaded here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=55994).
SQL Server 2016 Native Client (free version can be downloaded here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=52676. After clicking the download button select ENU\x64\sqlncli.msi). Although I’m installing SQL Express 2017, there are no newer client tools available.
SQL Server Management Studio (free, and can be downloaded here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/ssms/download-sql-server-management-studio-ssms).
And a certificate. I got mine for free from https://www.sslforfree.com/. This certificate needs to contain the FQDN you will use as the RD Web Access URL (mine is rds.it-worxx.nl in this guide). It needs to be in .pfx format and you need to have the private key in it.
This guide will not focus on building a domain using a single domain controller and adding the second server as a member server to this domain.
Also some basic knowledge is assumed in this guide. I will not detail how to create a Security Group and adding a computer account to it. I will also not detail how to install SQL Express, or adding logins to a SQL Server Instance security context. If you need extra help with this, Bing it or drop me a mail with details, and I will provide steps to continue.
I will be using Hyper-V on my Windows 10 1809 laptop and I have prepared 2 servers:
ITWDC (1 vCPU, 1024MB memory, dynamic, 60GB Harddisk)
Installed Windows
IPv4 192.168.0.4/24
Added .NET Framework 3.5 as a feature
Added Active Directory Domain Services as a role
Configured this server as a Domain Controller in a new forest: it-worxx.lab
ITWRDS (1 vCPU, 1024MB memory, dynamic, 60GB Harddisk)
Installed Windows
Added .NET Framework 3.5 as a feature
IPv4 192.168.0.10/24, DNS server 192.168.0.4
Configured it as a member server in the it-worxx.lab domain
Installing the Remote Desktop Services Roles
Log on to the Domain Controller, and in Server Manager right-click the All Servers node and add the second server using the Add Servers command (or select the All Servers node, click Manage and click Add Servers).

Now that all servers needed in this deployment scenario are present, click Manage, and click Add Roles & Features.
Before you begin

Click Next.
Select Installation Type

Select Remote Desktop Services installation.
Click Next.
Select Deployment Type

Although Quick Start might be a valid option for a single server deployment, leave the default selected. This will explain the steps necessary to install Remote Desktop Services in greater detail.
Click Next.
Select Deployment Scenario

Select Session-based desktop deployment.
Click Next.
Review Role Services

Review the services that will be installed.
Click Next.
Specify RD Connection Broker server

Click the member server and click the Add button.
Click Next.
Specify RD Web Access server

Check Install the RD Web Access role on the RD Connection Broker server.
Click Next.
Specify RD Session Host server

Click the member server and click the Add button.
Click Next.
Confirm selections

Check Restart the destination server automatically if required.
Click Deploy.
View progress

Wait until all role services are deployed and the member server has restarted.
Click Close.
In Server Manager click Remote Desktop Services and scroll down to the overview.

As you can see the deployment is missing a RD Gateway server and a RD Licensing server.

Click the Add RD Licensing server button.
Select a server

Click the domain controller and click the Add button.
Click Next.
Confirm selections

Click Add.
View progress

Wait until the role service is deployed. No restart is needed.
Click Close.

Click the Add RD Gateway server button.
Select a server

Click the member server and click the Add button.
Click Next.
Name the self-signed SSL certificate

The wizard creates a self-signed certificate. We will deal with certificates in this deployment in a little bit. We will replace the self-signed certificate.
Enter the external Fully Qualified Domain Name which you will also use for the Web Access URL. In my case, for lack of a better name, I used “rds.it-worxx.nl”. I didn’t want to use “remote.it-worxx.nl” or “desktop.it-worxx.nl” or anything else.
Click Next.
Confirm selections

Click Add.
View progress

Wait until the role service is deployed. Again, no restart is needed.
Notice that “rds.it-worxx.nl” was configured for the deployment.
Also notice that even more certificate configuring is needed, but we’ll get to that later. Pay no attention to it for now. The same goes for the RD Gateway properties for the deployment. We’ll get to that later.
Click Close.
Review role installation and setting License Mode
Let’s have a quick look at the configuration we have so far.

In Server Manager, Remote Desktop Services, Overview, click Tasks and click Edit Deployment Properties.
Configure the deployment

Review the RD Gateway settings and notice what settings are available.
Click RD Licensing.
Configure the deployment

Notice that an RD License server is available, but no license type is selected yet.
I selected Per User, but since this is just a guide setup, it really doesn’t matter.
Click RD Web Access.
Configure the deployment

By default the RD Web Access IIS application is installed in /RdWeb.
If you want to know how to change this, check another post: https://msfreaks.wordpress.com/2013/12/07/redirect-to-the-remote-web-access-pages-rdweb/
This is for Windows Server 2012 R2 RDS, but it also works for Windows Server 2019 RDS.
Click Certificates.
Configure the deployment

Notice that the certificate level currently has a status of Not Configured.
As you can see, certificates are used for different goals within the deployment.
The RD Gateway certificate is used for Client to gateway communication and needs to be trusted by the clients. Either install the self-signed certificate on all clients, or use a certificate for which the complete certificate chain is already trusted by all clients. As it said in the wizard, the external FQDN should be on the certificate.
The RD Web Access certificate is used by IIS to provide a server identity to the browser clients.
The RD Connection Broker actually has two goals for which it needs certificates. To enable single sign on (server to server authentication), and for publishing (signing RDP files). If you look in the deployment you’ll see that the Connection Broker is now configured to use “itwrds.it-worxx.lab”, so we have to change it to use an external FQDN as well.
If we use the same FQDN for all goals described above, we need only 1 certificate, and only 1 external IP address.
We’ll come back to this wizard later to assign the certificate. First order of business is to change the internal FQDN for the Connection Broker to an external FQDN.
Click OK (no reason why we shouldn’t commit the change we made on the licensing tab, remember?)
Changing the Connection Broker FQDN to an externally resolvable FQDN
Open DNS Manager on the domain controller and browse to Forward Lookup Zones.

Right click Forward Lookup Zones and click New Zone… Go through this wizard accepting the defaults until you have to enter a Zone Name.

Enter the external FQDN which will also be used by the Connection Broker.
Finish the rest of the wizard accepting the defaults.
Browse to the newly created zone.

Right click the newly created zone and click New Host (A or AAAA)…
New Host
Leave the Name field blank, but enter the member server’s (holding the RD Connection Broker role) IPv4 address.
Click Add Host.
Now the configuration will be able to resolve “rds.it-worxx.nl” to the server holding the Connection Broker role, and this will work because “rds.it-worxx.nl” is also on the certificate that we will configure later.
Create a new Global Security Group called “RD Connection Brokers” and add the computer account for the member server to it as a group member.
We need this group to be able to convert the RD Connection Broker to a highly available RD Connection Broker. You’ll see why we need to do this in a few steps.
Reboot the member server to let it know it’s a member of the RDS Connection Brokers security group.
The next steps in re-configuring the RD Connection Broker depend on an SQL database shared by all Connection Brokers in the deployment. Without this configuration the RD Connection Broker will rely on the Windows Internal Database that was created during the initial deployment of the roles.
Install SQL Express on the Domain Controller (or use an existing SQL Server if you already have one).
It’s not best practice to install SQL onto a Domain Controller, but it’ll do for this guide.
Here’s a list of needed features:


Use the Default Instance (so click Default, and do not leave the wizard’s selection on Named instance: SQLEXPRESS).

Set the SQL Service to start using SYSTEM because the default account of SQLSERVER cannot be used on a Domain Controller.
When the installation is done open SQL Configuration manager and browse to Client Protocols under SQL Native Client 11.0 Configuration.

Check if TCP/IP is enabled under Client Protocols. SQL Express install enables this by default, but check it just to be sure, especially if you use an existing SQL Server.
Browse to Protocols for MSSQLSERVER under SQL Server Network Configuration.

Enable TCP/IP. If this is a new SQL installation, this will be disabled by default.
Restart the SQL Server service if you changed this setting.
On the SQL Server, make sure port 1433 is not being blocked by Windows Firewall.

I added the SQL Server executable to the exception list to allow all inbound traffic, but TCP 1433 inbound should suffice.
If you installed SQL Server using the default folder locations, the sqlservr.exe executable is found in “C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Binn”.
Open SQL Server Management Studio, connect to the default instance on the Domain Controller and browse to Logins under Security.

Remember the Management Studio is no longer available with the SQL Server download, but is a different download.
Right click Logins and click New Login…
Login – New

Click Search…
Select User, Service Account, or Group

Click Object Types… and select Group.
Type the RDS Connection Brokers security group name and click Check Names.
Click OK.
Login – New

Click Server Roles and select dbcreator.
Click OK.
We have just effectively granted the RDS Connection Broker server the right to create databases.
We need this because the RDS Connection Broker service will try to migrate from WID (Windows Internal Database to a (high available) SQL Server instance when we convert the Broker to a high available broker.
Install the SQL Native Client on the member server (Client Components only). If you used the member server in this setup to install the SQL Management Studio, you can skip this step because the Native Client was installed with installing the Management Studio.
Everything we need is in place to convert the RD Connection Broker, so let’s do just that.
In Server Manager click Remote Desktop Services and scroll down to the overview.

Right click RD Connection Broker and click Configure High Availability.
Before you begin

So we’re building a single node cluster here 
Look at the pre-requisites.
If you have more than one RD Connection Broker they need to be configured using DNS Round Robin.
Click Next.
Configure RD Connection Broker for High Availability

Since we just installed an SQL Server for this, leave the default selected. You’d use the other option for instance if you’d like to use Azure SQL for this deployment.
Click Next.
Configure RD Connection Broker for High Availability

DNS name for the RD Connection Broker cluster:
The DNS Zone name we configured in DNS earlier: rds.it-worxx.nl
Connection string:
DRIVER=SQL Server Native Client 11.0;SERVER=ITWDC;Trusted_Connection=Yes;APP=Remote Desktop Services Connection Broker;DATABASE=ITWRDCB
Folder to store database files:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA
I used the instance default folder.
Click Next.
Confirmation

If you get an error before this page:
- Check if TCP/IP is enabled in client protocols and for your instance
- Check if you can reach port 1433 on the SQL Server from the member server
Click Configure.
Progress

If you get an error on this page:
- Check SQL permissions for the security group
- Check if the database path you entered is correct
Click Close.

The RD Connection Broker is now in High Availability Mode, and configured as “rds.it-worxx.nl” and we are finally ready to complete the configuration.
Configuring Certificates

In Server Manager, Remote Desktop Services, Overview, click Tasks and click Edit Deployment Properties, then click Certificates.
Configure the deployment

Click RD Connection Broker – Enable Single Sign On and click Select Existing certificate.

Browse to the .pfx file, enter its password, and check Allow the certificate..
Click OK.

So click Apply. This takes a little while, be patient.
Configure the deployment

Click RD Connection Broker – Publishing and click Select Existing certificate.

Browse to the .pfx file, enter its password, and check Allow the certificate..
Click OK.

Click Apply. This again takes a little while, be a little more patient.
Configure the deployment

Click RD Web Access and click Select Existing certificate.

Note: Did you notice the warning when you select RD Web Access?

Browse to the .pfx file, enter its password, and check Allow the certificate..
Click OK.

Click Apply again. This takes another little while longer, be slightly more patient.
Configure the deployment

Last one. Click RD Gateway and click Select Existing certificate.

Browse to the .pfx file, enter its password, and check Allow the certificate..
Click OK.
Click OK to apply the final certificate step.
Configured all servers, configured certificates..
One thing left to do: Tell our RDS environment exactly what to publish.
Publishing resources to your users
In fact you can use this setup to either provide full desktop sessions on the Session Host, or you can choose to publish only applications on the Session Host.
Let’s publish full desktop sessions.

In Server Manager, Remote Desktop Services, Session Collections, click Tasks and click Create Session Collection.
Before you begin

Review the requirements. This won’t be an issue in this setup, but you could restrict access to this collection by selecting a select group of people.
Click Next.
Name the collection

Enter a descriptive name. This name will be displayed under its icon in the Web Access interface.
Click Next.
Specify RD Session Host servers

Click the member server and click the Add button.
Click Next.
Specify user groups

You can limit access to the resource here if you want. Add one or more groups to restrict access to these groups only. In this setup the default selection of Domain Users will do fine. Groups you specify here will be added to the list of groups of users that are allowed to connect using RDP to the Session Host server(s).
Click Next.
Specify user profile disks

User profile disks are not in focus in this guide. Since I have no file shares configured in this setup, uncheck Enable user profile disks for now.
Click Next.
Confirm selections

Review the information and click Create.
View Progress

Wait until the collection is created and the server is added to the collection.
Click Close.
Time to test the setup!
Testing the setup
On a machine that has access to your test setup (you may have to add the external FQDN to your hosts file if you didn’t publish it to the internet) open https://rds.it-worxx.nl/rdweb

Hey! At least the RD Web Access application works 
Enter a valid username and password (IT-WORXX\username or username@it-worxx.lab).
Create a user for this, or simply use the domain admin account.
Click Sign in.

After logging in you are presented with the full desktop session collection we created.

After clicking the Full Desktop icon you get the warning that devices are going to be redirected.

And when you click Connect, you connect 
Enjoy.
Arjan
In today’s digital world, remote access to computers and servers has become crucial for businesses and individuals alike. Whether you need to access your work computer from home or manage servers in a data center, enabling Remote Desktop Services (RDS) on your Windows Server 2019 is the key to achieving this. RDS allows users to connect to remote desktop sessions, providing a virtual desktop environment that can be accessed from any device.
Enabling RDS on Windows Server 2019 might seem like a complex task, but it doesn’t have to be. In this blog post, we will explore the challenge of enabling RDS and provide you with detailed instructions on how to do it using different methods. We will also discuss some alternative solutions and share bonus tips to optimize your experience. Let’s dive in!
The Challenge of Enabling Remote Desktop Services
Enabling Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019 can present some challenges, especially for those who are not familiar with the process. Here are a few points to consider:
- Complex Configuration: The configuration process for enabling RDS involves several steps and settings that need to be properly configured to ensure secure remote access.
- Network Considerations: Remote access requires proper network configuration to establish a secure connection. Firewall settings, port forwarding, and network infrastructure need to be configured correctly.
- Security Concerns: Enabling RDS opens a potential entry point for unauthorized access if not properly secured. Security measures such as strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and limiting access to authorized users are crucial.
Now that we understand the challenges, let’s explore different methods to enable Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019.
Video Tutorial:
Method 1: How to Enable Remote Desktop Services using Server Manager
Enabling Remote Desktop Services using Server Manager is a straightforward method that allows you to quickly configure and enable RDS on your Windows Server 2019. Follow these steps:
Pros:
1. Easy and intuitive process.
2. Allows for granular control over session settings.
3. Provides a user-friendly interface for managing RDS.
Cons:
1. Requires administrative access to the Windows Server.
2. Limited customization options compared to other methods.
Step 1: Access Server Manager
1. Log in to the Windows Server 2019 using an administrative account.
2. Launch Server Manager by clicking on the «Windows» icon in the taskbar and searching for «Server Manager.«
Step 2: Add Roles and Features
1. In Server Manager, click on «Manage» in the top-right corner and select «Add Roles and Features.«
2. Follow the wizard and select «Role-based or feature-based installation» when prompted.
3. Select the local server from the server pool and click «Next.«
Step 3: Select Remote Desktop Services
1. In the «Server Roles» section of the wizard, scroll down and expand «Remote Desktop Services.«
2. Check the box next to «Remote Desktop Session Host» and click «Next.«
3. Review the information provided on the «Features» page and click «Next.«
Step 4: Configure Session Collections
1. On the «Role Services» page, leave the default selection of «Automatically restart the destination server if required.«
2. Click «Next» and review the confirmation page.
3. Click «Install» to start the installation process.
4. Once the installation is complete, click «Close» to exit the wizard.
Step 5: Configure Licensing
1. After the installation, Server Manager will display a warning sign next to «Remote Desktop Services» in the left-hand menu.
2. Click on «Configure Remote Desktop Licensing» in the «Overview» section.
3. Follow the wizard to select the appropriate licensing mode and add the licensing server if necessary.
4. Complete the configuration process by selecting the licensing mode and adding the licensing server.
Congratulations! You have successfully enabled Remote Desktop Services using Server Manager.
Method 2: How to Enable Remote Desktop Services using PowerShell
Using PowerShell to enable Remote Desktop Services provides a scriptable and automated approach. This method allows you to perform the configuration steps using PowerShell commands, ideal for administrators who prefer command-line interfaces.
Pros:
1. Scriptable and automated process.
2. Provides advanced customization options.
3. Saves time for repetitive tasks.
Cons:
1. Requires knowledge of PowerShell commands.
2. May not be suitable for users unfamiliar with command-line interfaces.
Step 1: Open PowerShell
1. Log in to the Windows Server 2019 using an administrative account.
2. Launch PowerShell by clicking on the «Windows» icon in the taskbar and searching for «PowerShell.«
Step 2: Install Remote Desktop Session Host
1. Run the following command to install the Remote Desktop Session Host role:
«`
Install-WindowsFeature -Name RDS-RD-Server -IncludeAllSubFeature -Restart
«`
2. Wait for the installation to complete and for the server to restart.
Step 3: Configure Remote Desktop Licensing
1. Run the following command to configure Remote Desktop Licensing:
«`
Set-RDLicenseConfiguration -LicenseServer -Mode -ConnectionBroker
«`
Replace « with the name or IP address of the license server and « with the preferred licensing mode.
Replace « with the name or IP address of the connection broker server.
Congratulations! You have successfully enabled Remote Desktop Services using PowerShell.
Method 3: How to Enable Remote Desktop Services using Group Policy
Using Group Policy to enable Remote Desktop Services allows you to centrally manage and enforce RDS settings across multiple servers. This method is ideal for large-scale deployments where consistent configuration is essential.
Pros:
1. Centralized management of RDS settings.
2. Enforces consistent configuration across multiple servers.
3. Provides granular control over RDS via Group Policy settings.
Cons:
1. Requires Active Directory Domain Services.
2. Requires knowledge of Group Policy and Active Directory administration.
Step 1: Open Group Policy Management
1. Log in to a domain controller or a machine with the Group Policy Management Console installed.
2. Launch Group Policy Management from the Start Menu or by typing «gpmc.msc» in the Run dialog.
Step 2: Create or Edit Group Policy Object
1. Expand the forest and domain in the left-hand pane of Group Policy Management.
2. Right-click on the desired organizational unit (OU) or domain and select «Create a GPO in this domain and Link it here» or «Edit» if the GPO already exists.
Step 3: Configure Remote Desktop Services Policies
1. In the Group Policy Management Editor, navigate to «Computer Configuration» > «Policies» > «Administrative Templates.«
2. Expand «Windows Components» and select «Remote Desktop Services.«
3. Configure the desired policies, such as «Allow users to connect remotely using Remote Desktop Services,» «Set rules for remote control of Remote Desktop Services sessions,» and more.
4. Apply the changes and close the Group Policy Management Editor.
Congratulations! You have successfully enabled Remote Desktop Services using Group Policy.
Method 4: How to Enable Remote Desktop Services using RD-Licensing PowerShell Module
Using the RD-Licensing PowerShell module offers an alternative method for managing and configuring Remote Desktop Services licensing on your Windows Server 2019. This method provides more control over licensing settings and helps streamline the management process.
Pros:
1. Flexible and powerful licensing management.
2. Allows for easy tracking and reporting of licenses.
3. Provides advanced customization options.
Cons:
1. Requires knowledge of PowerShell commands.
2. May not be suitable for users unfamiliar with command-line interfaces.
Step 1: Open PowerShell
1. Log in to the Windows Server 2019 using an administrative account.
2. Launch PowerShell by clicking on the «Windows» icon in the taskbar and searching for «PowerShell.«
Step 2: Install RD-Licensing PowerShell Module
1. Run the following command to install the RD-Licensing PowerShell module:
«`
Install-WindowsFeature -Name Remote-Desktop-Services-RD-Licensing -IncludeAllSubFeature -Restart
«`
2. Wait for the installation to complete and for the server to restart.
Step 3: Configure RD-Licensing
1. Run the following command to configure the RD-Licensing mode:
«`
Set-RDLicenseConfiguration -LicenseServer -Mode
«`
Replace « with the name or IP address of the license server and « with the preferred licensing mode.
Congratulations! You have successfully enabled Remote Desktop Services using the RD-Licensing PowerShell module.
Alternatives: What to Do If You Can’t Enable Remote Desktop Services
While enabling Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019 is the preferred method for remote access, there are alternatives available if you encounter difficulties or limitations. Here are a few alternative solutions:
Q1: Use Third-Party Remote Access Tools
A: If enabling Remote Desktop Services is not feasible, you can explore third-party remote access tools such as TeamViewer, AnyDesk, or LogMeIn. These tools provide similar functionality and allow remote access to computers and servers.
Q2: Utilize Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
A: Setting up a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can provide secure remote access to your network resources without enabling Remote Desktop Services. With a VPN connection, you can access your on-premises servers and resources as if you were physically present in the network.
Q3: Consider Cloud-Based Solutions
A: If managing your own servers and configuring Remote Desktop Services is not ideal, you can explore cloud-based solutions such as Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop or Amazon WorkSpaces. These services provide virtual desktop infrastructure in the cloud, eliminating the need for on-premises server management.
Bonus Tips
Here are a few bonus tips to enhance your Remote Desktop Services experience:
1. Use Network Level Authentication (NLA): Enable NLA for better security by verifying the user’s credentials before establishing a remote session.
2. Optimize Network Bandwidth: Adjust the display and connection settings in the remote desktop client to optimize network bandwidth usage. Lowering the color depth and disabling unnecessary features can improve performance.
3. Implement Remote Desktop Gateway: Set up a Remote Desktop Gateway for secure connections over the internet. RD Gateway acts as a middleman between the client and the remote desktop session host, providing an extra layer of security.
5 FAQs about Enabling Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019
Q1: Can I enable Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019 without internet access?
A: Yes, you can enable Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019 without internet access. However, internet access might be required for certain features, such as licensing activation.
Q2: Can I modify the default Remote Desktop port on Windows Server 2019?
A: Yes, you can modify the default Remote Desktop port on Windows Server 2019. It can be changed using the Registry Editor in the following registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp.
Q3: Can I use Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019 for multiple concurrent users?
A: Yes, Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019 supports multiple concurrent users. Depending on the licensing mode and CALs installed, you can have multiple users accessing the server simultaneously.
Q4: Are there any limitations on the number of Remote Desktop Services connections in Windows Server 2019?
A: The number of Remote Desktop Services connections in Windows Server 2019 depends on the licensing mode and the number of Client Access Licenses (CALs) installed. Make sure to review the licensing terms and consult Microsoft’s documentation for more information.
Q5: Can I enable Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019 Core?
A: Yes, you can enable Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019 Core. You can use PowerShell or Server Manager remotely to configure and manage RDS settings on a Windows Server 2019 Core installation.
In Conclusion
Enabling Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019 is an essential task for achieving remote access to computers and servers. While the process may seem daunting, the methods described in this blog post provide clear instructions to enable RDS using Server Manager, PowerShell, Group Policy, and the RD-Licensing PowerShell module.
Whether you choose to enable RDS using a graphical interface or prefer a command-line approach, always ensure that you follow best practices for security and network configuration. Additionally, consider alternative solutions such as third-party remote access tools, VPNs, or cloud-based services if enabling Remote Desktop Services is not an option.
With the proper configuration and security measures in place, Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2019 can greatly enhance productivity and enable seamless remote access for both individuals and organizations.
Если нужно создать удаленное подключение для нескольких пользователей, то сперва необходимо настроить терминальный сервер на Windows Server. Он позволит предоставлять ровно такое количество мощностей, которое требуется для решения конкретной задачи – например, для работы с 1С или CRM.
Настройка в версиях Windows Server 2012, 2016, 2019 выполняется по одному алгоритму.
Базовая настройка терминального сервера
Сначала проверим имя рабочей группы и описание компьютера.
- Открываем «Панель управления», переходим в раздел «Система».
- Нажимаем «Изменить параметры».
- На вкладке «Имя компьютера» смотрим, как он идентифицируется в сети. Если имя компьютера или рабочей группы слишком сложное, нажимаем «Изменить» и задаем другие идентификаторы. Для применения нужно перезагрузить систему.
После проверки имени смотрим и при необходимости меняем сетевые настройки. В «Панели управления» открываем раздел «Сетевые подключения».
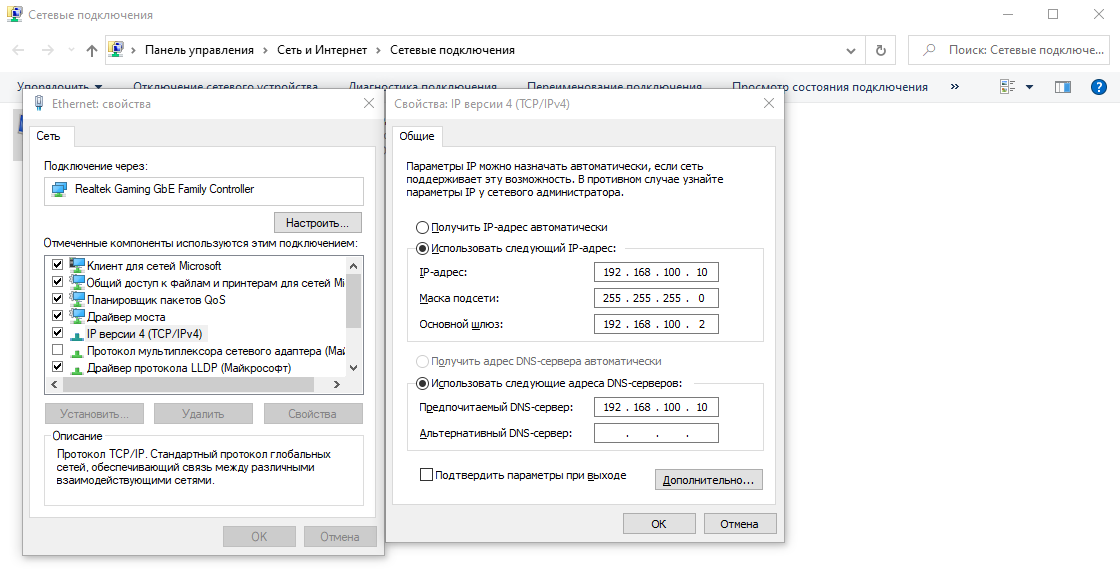
Переходим в свойства используемого подключения, открываем свойства «IP версии 4». Указываем настройки своей сети. IP, маска и шлюз должны быть статичными.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Добавление ролей и компонентов
Открываем меню «Пуск» и запускаем «Диспетчер серверов». Далее:
- Нажимаем «Добавить роли и компоненты».
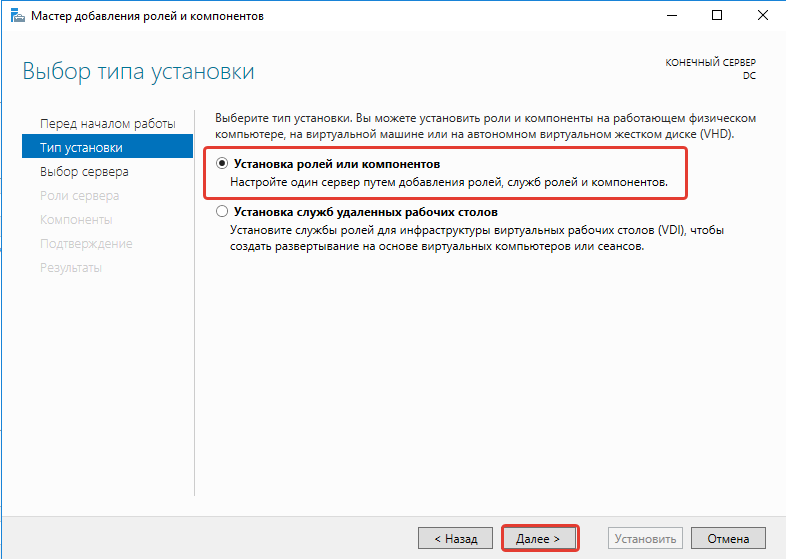
- Выбираем пункт «Установка ролей или компонентов».
- Выбираем сервер из пула серверов.
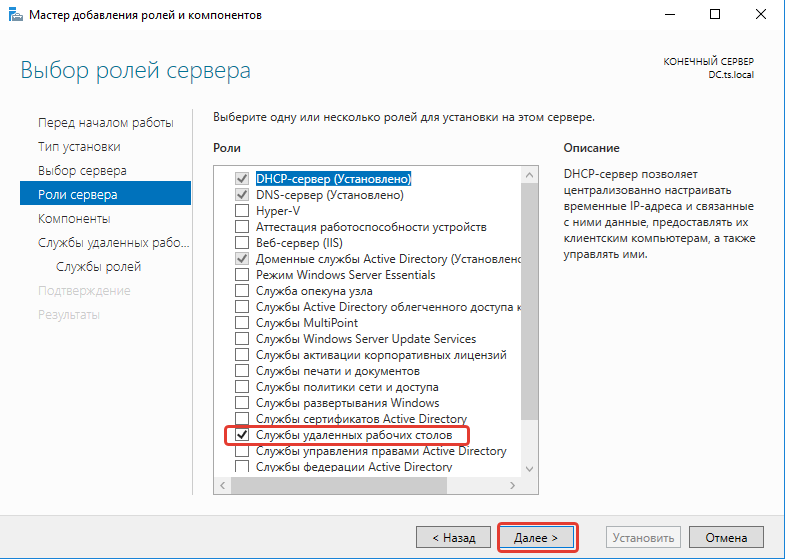
- В разделе «Роли сервера» отмечаем DHCP-сервер, DNS-сервер, доменные службы Active Directory, службы удаленных рабочих столов.
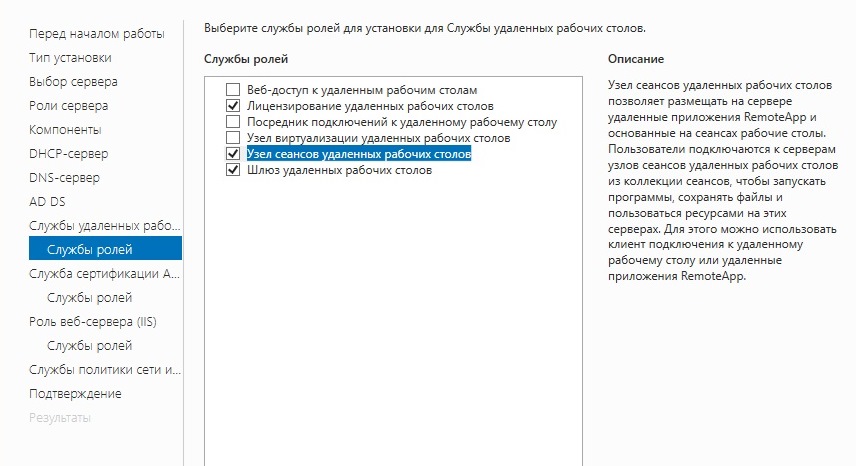
- В разделе «Службы ролей» отмечаем лицензирование удаленных рабочих столов, узел сеансов удаленных рабочих столов и шлюз удаленных рабочих столов.
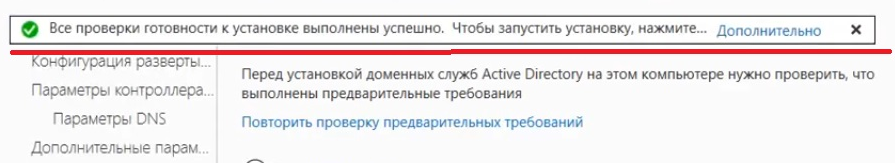
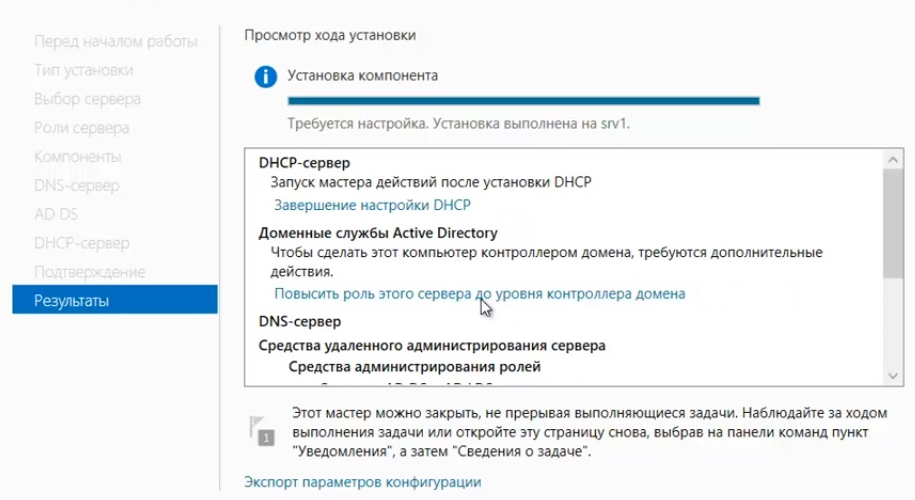
- Нажимаем «Далее» до раздела «Подтверждение». Здесь нажимаем «Установить».
После завершения установки выбираем повышение роли этого сервера до уровня контроллера доменов.
Настройка конфигурации развертывания
Теперь нужно настроить корневой домен:
- В мастере настройки доменных служб Active Directory выбираем операцию добавления нового леса и указываем имя корневого домена. Оно может быть любым.
- В разделе «Параметры контроллера» придумываем и подтверждаем пароль.
- Проходим до раздела «Дополнительные параметры». Указываем имя NetBIOS, если его там нет.
- Проходим до раздела «Проверка предварительных требований». Если проверка готовности пройдена, нажимаем «Установить». Если нет, устраняем недостатки.
После завершения установки необходимо перезагрузиться.
Настройка зоны обратного просмотра
В «Диспетчере серверов» раскрываем список средств и выбираем DNS. Далее:
- Нажимаем «Зона обратного просмотра» – «Создать новую зону».
- Выделяем пункт «Основная зона».
- Выбираем режим «Для всех DNS-серверов, работающих на контроллере домена в этом домене».
- Выбираем зону обратного просмотра IPv4.
- Указываем идентификатор сети – часть IP адресов, которые принадлежат этой зоне.
- Нажимаем «Готово» для применения конфигурации.
Проверить, что все установилось, можно в «Диспетчере DNS».
Настройка DHCP
Возвращаемся в «Диспетчер серверов». Здесь нужно завершить настройку DHCP.
- Указываем данные для авторизации.
- Проверяем сводку и нажимаем «Закрыть».
- После завершения установки снова открываем «Диспетчер серверов» – «Средства» – DHCP.
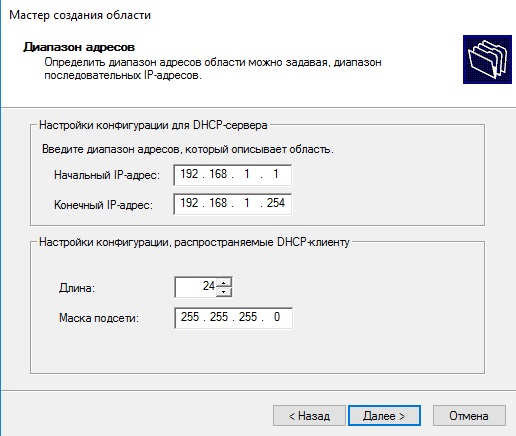
- В окне DHCP проходим по пути «Имя сервера» – «IPv4» – «Создать область».
- Задаем любое имя DHCP.
- Указываем начальный и конечный IP-адреса для интервала, который будет раздавать сервер.
- Выбираем настройку этих параметров сейчас.
- В окне DHCP переходим по пути «Имя сервера» – «Область» – «Пул адресов». Проверяем, что в списке указан тот диапазон IP-адресов, который мы задали в настройках.
Установка служб удаленных рабочих столов
После настройки DHCP снова открываем «Диспетчер серверов».
- Нажимаем «Управление» – «Добавить роли и компоненты».
- Выбираем установку служб удаленных рабочих столов.
- В разделе «Тип развертывания» выбираем «Быстрый запуск».
- В разделе «Сценарий развертывания» выбираем развертывание рабочих столов на основе сеансов.
- Отмечаем пункт «Автоматически перезапускать конечный сервер, если это потребуется» и нажимаем «Развернуть».
Настройка лицензирования удаленных рабочих столов Windows
Чтобы сервер работал корректно, нужно настроить службу лицензирования.
- Открываем «Диспетчер серверов».
- Переходим по пути «Средства» – «Remote Desktop Services» – «Диспетчер лицензирования удаленных рабочих столов».
- Выбираем в списке сервер, кликаем по нему правой кнопкой и нажимаем «Активировать сервер».
- Нажимаем «Далее» несколько раз, снимаем отметку «Запустить мастер установки лицензий» и затем – «Готово».
- Снова открываем «Диспетчер серверов».
- Переходим в «Службы удаленных рабочих столов».
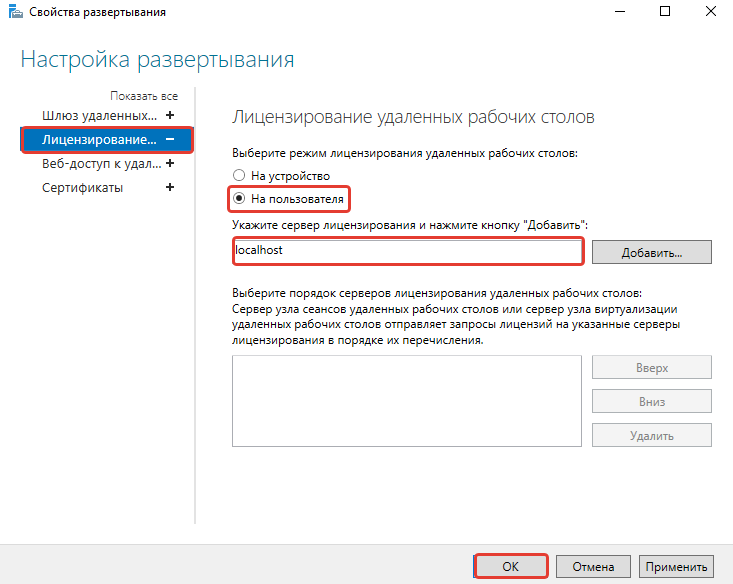
- В обзоре развертывания нажимаем на меню «Задачи» и выбираем «Изменить свойства развертывания».
- Переходим в раздел «Лицензирование».
- Выбираем тип лицензии.
- Прописываем имя сервера лицензирования – в данном случае это локальный сервер localhost. Нажимаем «Добавить».
- Нажимаем «ОК», чтобы применить настройки.
Добавление лицензий
Осталось добавить лицензии.
- Открываем «Диспетчер серверов».
- Переходим по пути «Средства» – «Remote Desktop Services» – «Диспетчер лицензирования удаленных рабочих столов».
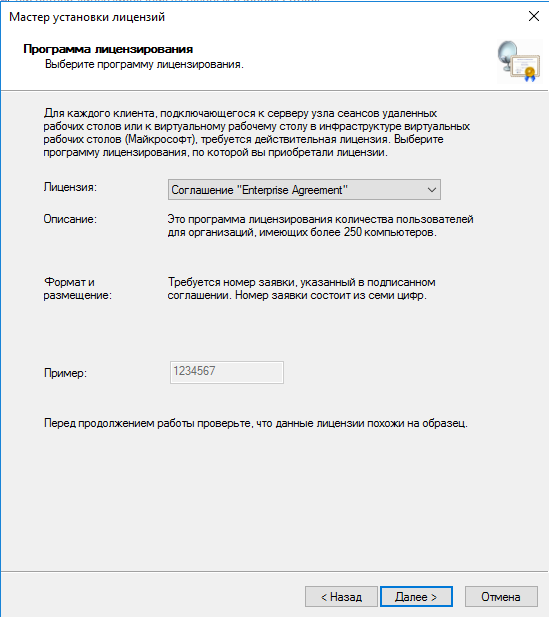
- Кликаем по серверу правой кнопкой и выбираем пункт «Установить лицензии».
- В мастере установки лицензий выбираем программу, по которой были куплены лицензии.
- Указываем номер соглашения и данные лицензии.
- Применяем изменения.
Чтобы проверить статус лицензирования, открываем «Средства» – «Remote Desktop Services» – «Средство диагностики лицензирования удаленных рабочих столов».
На этом настройка терминального сервера на Windows Server завершена. Теперь к серверу могут подключаться удаленные пользователи для выполнения разных задач.