Introduction to Dependency Walker
Dependency Walker (also known as depends.exe) is a powerful tool for anyone involved in Windows development, system administration, or troubleshooting applications. This free utility allows users to view the entire hierarchy of dependencies required by an executable file or dynamic link library (DLL). By providing insight into the components that are loaded at runtime, Dependency Walker assists in debugging issues related to missing or improperly configured dependencies.
When applications fail to launch due to unresolved dependencies, or when they operate suboptimally owing to mismatched versions of libraries, Dependency Walker can be your first line of defense. This guide explains how to effectively use Dependency Walker on Windows systems, covering installation, interface navigation, interpreting results, and troubleshooting techniques.
Installation of Dependency Walker
Downloading the Application
- Visit the Official Website: Go to the official Dependency Walker website. Note that the application might not be actively developed anymore, but it is still widely used.
- Choose the Correct Version: Depending on your system architecture (32-bit or 64-bit), download the corresponding version of Dependency Walker. For modern systems, it’s advisable to download the 64-bit version.
Installation Steps
- Extract the Files: Dependency Walker typically comes in a zip file. Right-click the downloaded file and select «Extract All.» Choose a destination directory.
- Locate the Executable: Navigate to the extracted folder and find the executable file named
depends.exe. - Create a Shortcut: For easier access, consider creating a shortcut to
depends.exeon your desktop or in the Start Menu.
Launching Dependency Walker
To start Dependency Walker, simply double-click the depends.exe file. You may need administrative privileges to analyze certain system files or applications.
Using Dependency Walker
Basic Navigation
Upon launching Dependency Walker, you’ll be greeted with a minimalist interface. The main components of the interface include:
- Menu Bar: Similar to other Windows applications, the menu bar contains options for opening files, saving results, and modifying settings.
- Module List View: This section lists all the modules (executables and DLLs) required by the selected application.
- Tree View: Hierarchically displays the dependencies of the selected module, allowing you to drill down into further levels of dependent modules.
- Detail View: Provides detailed information about the selected dependency, including its path, version, and other relevant information.
Opening a File
- Open an Executable or DLL: Click on
Filein the menu bar, then selectOpen. Locate the .exe or .dll file you want to analyze. - Load the Executable: Once loaded, Dependency Walker will begin scanning the selected file for any dependencies.
Understanding the Displayed Information
-
Primary Modules: The top section of the Module List displays the main executable. The modules are generally color-coded:
- Green: Indicates a module that has been found successfully.
- Yellow: Indicates a module that may be a potential problem. This could be due to version mismatches or other issues that need attention.
- Red: Indicates missing modules which could be the cause of application failure.
- White: Modules that are present but unverified.
-
Dependency Levels: Clicking on a module will refresh the tree view to display all its dependencies. You can expand each module to view its own dependencies.
-
Details Panel: Select any module in the list, and the details panel will show information such as:
- File Name: The name of the file.
- File Path: Full path to the file on disk.
- Version Information: Version number of the module.
- Required/Optional Dependencies: Indicating whether a dependency is critical or optional.
Profiling an Application
Dependency Walker can also be used to profile applications and record their behavior. This is particularly useful for identifying dynamically loaded libraries.
-
Select Profile Mode: Navigate to the
Profilemenu in the menu bar and selectStart Profiling. -
Choose Options: You’ll receive various profiling options, such as monitoring for API calls and tracking all dynamically loaded modules.
-
Run the Application: When prompted, select your application to run, and click
OK. The profiler will begin collecting data regarding dependencies and API calls. -
Analyze the Profile Results: Once the application has finished running, Dependency Walker will present the profile result, allowing you to analyze which modules were loaded at runtime.
Advanced Features of Dependency Walker
Viewing Function Imports and Exports
A critical component of understanding dependencies is analyzing the actual functions that are being imported and exported between modules.
- Select the Module of Interest: Click on any module of interest in the Module List.
- Switch to Import or Export Panel: Navigate to the lower part of the window, which can be toggled to show either Import or Export functions.
Examining Known Issues
Dependency Walker comes with a built-in feature to identify known issues with modules:
- View Known Issues: Right-click on a module and select
Check for Known Issues. This will compile a list of common problems associated with that module. - Interpreting Results: The output may suggest potential fixes, external dependencies that might be missing, or version mismatches.
Generating Reports
For professional use, Dependency Walker allows the generation of reports for documentation or troubleshooting.
-
Export Module Dependencies: Click on
File, then selectSave Asto export the list of dependencies in various formats, including text-based reports. This can be particularly useful for developers and system administrators to document application structures. -
Save Profile Data: After profiling an application, you can save the profile data for future reference or analysis.
Command Line Usage
For advanced users, Dependency Walker can also be run via the command line, offering a way to batch process files or automate responses.
- Open Command Prompt: Press
Windows + R, typecmd, and hit Enter. - Navigate to Dependency Walker Directory: Use the
cdcommand to navigate to the folder wheredepends.exeresides. - Run with Parameters: Use command line parameters to analyze files or generate reports automatically.
Common Issues and Solutions
Dependency Walker is invaluable, but it does come with its quirks. Here are some of the common challenges users face and their solutions:
Missing Dependencies
If Dependency Walker indicates that a dependency is missing:
- Verify Installation: Ensure the required application or DLL is installed.
- Check PATH Variables: Ensure the directory containing the module is included in the system PATH variable.
- Use Public Repositories: Some modules, especially third-party libraries, may not be installed by default. Check package repositories for missing dependencies.
Version Conflicts
Dependency Walker can highlight modules with version conflicts:
- Check Version Compatibility: Ensure that the versions of the dependencies align with the application requirements.
- Install Required Versions: If an incompatible version is causing issues, consider reverting to the required version.
Loading Order Issues
Sometimes, applications may misbehave due to incorrect loading sequences:
- Reassess the Load Order: Look at how the modules are loading and assess any interdependencies that may be causing conflicts.
- Modify Initialization Logic: If applicable, change initialization logic within the application code to manage dependency load order.
64-bit vs 32-bit Issues
Dependency Walker operates differently based on the architecture of the executable:
- Use the Correct Version: Always use the 64-bit version of Dependency Walker for 64-bit applications, and vice versa for 32-bit applications.
- Cross-Profile Applications: You can profile 32-bit applications on a 64-bit system using the 32-bit version of Dependency Walker.
Best Practices
- Regularly Analyze Executables: Make it a habit to analyze executables for dependencies during application development or updates.
- Keep Dependencies Updated: Regularly update both your application and its dependencies to prevent compatibility issues.
- Document Dependency Structures: For larger applications, conducting periodic audits of dependency structures ensures clarity and helps in diagnosing future issues.
Conclusion
Dependency Walker is an invaluable tool for understanding and debugging the complex relationships between various components in Windows systems. Whether you’re developing applications, troubleshooting issues, or managing deployments, mastering Dependency Walker allows you to confidently handle dependency-related challenges. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can effectively diagnose problems, optimize application performance, and ensure smooth operation across Windows environments.
With continuous use and exploration of the advanced features, Dependency Walker can elevate your proficiency in managing Windows applications, making it a crucial addition to your toolkit. If you stand to gain from deeper insights into the workings of executable files and libraries, Dependency Walker is an essential companion for your development and administration tasks.
An open-source modern Dependency Walker

Overview
Dependencies is a rewrite of the legacy software Dependency Walker which was shipped along Windows SDKs, but whose developement stopped around 2006.
Dependencies can help Windows developers troubleshooting their dll load dependencies issues.
Releases
- v1.8 :
- Add x86/x64 variants for Dependencies
- v1.7 :
- Add CLI tool “dependencies.exe”
- v1.6 :
- Add appx packaging
- v1.5 :
- Support of Sxs parsing
- Support of api set schema parsing
- API and Modules list can be filtered
- v1.0 – Initial release
Installation and Usage
Dependencies is currently shipped as a binary (no installer present). Just uncompress the archive and click on it.
Since the binary is not signed, SmartScreen might scream at runtime. Dependencies also bundle ClrPhTester.exe, a dumpbin-like executable used to test for non-regressions.
Dependencies currently does not recursively resolve child imports when parsing a new PE since it can be really memory-hungry to do so ( it can go over a GB even for “simple” PEs ). This behaviour can be overriden (app-wide) via a property located in “Options->Properties->Tree build behaviour”.
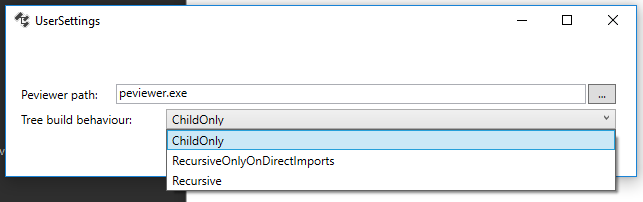
Tree build behaviours available :
ChildOnly(default) : only process PE child imports and nothing beyond.RecursiveOnlyOnDirectImports: do not process delayload dlls.Recursive: Full recursive analysis. You better have time and RAM on your hands if you activate this setting.
Limitations
At the moment, Dependencies recreates features and “features” of depends.exe, which means :
- Only direct, forwarded and delay load dependencies are supported. Dynamic loading via
LoadLibraryare not supported (and probably won’t ever be). Min-windlls are not propertly supported. (UPDATED : support of api set schema redirection in 1.5)- There are no checks between Api Imports and Exports for the moment, only dll presence is supported.
- No support of esoteric dll load paths (via
AppPathsorSxSmanifests entries). (UPDATED : minimal support of sxs private manifests search).
Credits and licensing
Special thanks to :
- ProcessHacker2 for :
phlib, which does the heavy lifting for processing PE informations.peview, a powerful and lightweight PE informations viewer.
- Dragablz a C#/XAML library which implement dockable and dragable UI elements, and can recreate the MDI programming model in
WPF. - @aionescu, @zodiacon and Quarkslab for their public infos on ApiSets schema.
- Thomas levesque’s blog which pretty much solved all my
WPFprogramming issues. HisAutoGridSortis used in this project
Copyright (c) lucasg and licensed under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for full details.
More
Read depends.exe’s FAQs and rationale.
.
Special Offer
Instructions
The following steps should fix the depends.exe issue:
- Step 1.Download Outbyte PC Repair application See more information about Outbyte uninstall instructions EULA Privacy Policy
- Step 2.Install and launch the application
- Step 3.Click the Scan Now button to detect issues and abnormalities
- Step 4.Click the Repair All button to fix the issues
| Compatibility | Win 11, 10, 8, 7 |
| Download Size | 21.2 MB |
| Requirements | 300 MHz Processor, 256 MB RAM, 50 MB HDD |
Limitations: trial version offers an unlimited number of scans, backups and restores of your Windows system elements for free. Registration for the full version starts from USD 29.95.
EXE issues may happen due to a number of different factors. The causes mentioned below are only the most common ones. In certain cases, depends.exe issue may occur when your computer system becomes overloaded or important program files go missing, get accidentally deleted or become corrupted. These types of malfunctions may occur on computers that do not undergo regular maintenance, which may lead to critical glitches and system malfunctions. It may be possible to resolve EXE issues with special software that repairs system elements and tunes system settings to restore stability.
The article provides details on what the issue means, potential causes, and ways to resolve the issue.
- 1Meaning of «depends.exe» issue
- 2Causes of «depends.exe» issues
- 3Ways to repair «depends.exe» issues
Meaning of depends.exe issue
.EXE is a file name extension referencing an executable file (i.e., a software program) in the Windows operating system. These files run your programs and also contain other embedded resources such as bit maps, Windows icons, etc. which the software might call and use for its user interface.
When the depends.exe issue occurs on your computer, you are generally notified via a pop-up style warning that you’re experiencing a malfunction and what kind of EXE issue you’re having. Normally, such issues are attributed to specific software programs, the names of which should be mentioned in the warning.
No matter what EXE issue you are experiencing, the result can be a slow PC that may freeze or crash, and an overall decline in user experience.
Common causes of depends.exe issues
EXE issues may occur for a variety of reasons. One of the common causes is the EXE file being overridden or shared with an older version of a program across other applications.
Another possibility would be the installation or uninstallation of a program that ran incorrectly, or the downloaded installer files being corrupted.
Ignoring the depends.exe issue may eventually lead to PC slowdown or a full system crash, so fixing the issue is important to maintaining optimal computer performance.
Ways to fix depends.exe issues
For an immediate fix of such issues, advanced PC users may be able to repair it by manually editing system elements, and others may want to hire a technician to do it for them. However, since any manipulations with Windows system elements carry a risk of rendering the operating system unbootable, whenever a user is in any doubt of their technical skills or knowledge, they may use a special type of software that is meant to repair Windows system elements without requiring any special skills from the user.
The following steps may help fix the issue:
- Download Outbyte PC Repair application Special offer. See more information about Outbyte uninstall instructions EULA Privacy Policy
- Install and launch the application
- Click the Scan Now button to detect potential issue causes
- Click the Repair All button to fix found abnormalities
The same application can be used to run preventative measures to reduce the chance of this or other system issues appearing in the future.
Программное обеспечение, с помощью которого пользователь можно просматривать структуру определенных файлов, а также библиотек. Вся информация предоставляется юзеру, как иерархический список.
Depends является приложением, которое распространяется на бесплатной основе. По большей части – это утилита, которая сделанная для анализа структуры, а также осуществления отслеживания двух типов зависимостей между файлами, которые исполняются и библиотеками. Программное обеспечение корректно работает с файлами всевозможных форматов, установить ее можно на компьютер с операционной системой от Microsoft, вне зависимости от ее разрядности.
Как работать с утилитой?
Для того, чтобы начать работать с утилитой, вам необходимо выбрать файлы, которые вы будете отслеживать и анализировать. На обработку данных, программе необходимо около минуты, по истечению юзер получает полноценный список в виде дерева, в котором четко прослеживаются зависимости между модулями в системе. Слева вы сможете посмотреть на само дерево, а в правой части будет находится вся необходимая информация, о выбранном вами файле или элементе. По желанию, вы имеете возможность автоматически создать отчет, который будет выполнен в одном из актуальных форматов.
Дополнительная функция программного обеспечения – это отслеживания проблем, а также исправления их. Depends мгновенно находит ошибки в работе файла или библиотеки, после чего исправляет их. Стоит отметить, что приложение также способно находить недостающие модули, а также составлять полноценный отчет о всевозможных найденных ошибках. С помощью данной опции можно получить полную информацию о Debug-данных.
Интерфейс
Пользовательский интерфейс приложения представляет собой несколько окон. Все находится там, где и должно, после нескольких часов работы привыкаешь и запоминаешь расположение всех инструментов и панелей. Пользователь по желанию, также имеет возможность изменять размеры рабочих окон, а также панелей инструментов. Опытные юзеры, которые не любят работать с графической оболочкой, могут изменить режим работы, после чего откроется привычная для них командная строка. В общем, работать с данным приложением удобна как опытным пользователям, так и новичкам. На данный момент нормальных альтернатив данной утилиты не было создано, поэтому все пользователи делают выбор в пользу Depends.
Dependencies — An open-source modern Dependency Walker
Download here
(If you’re running an AV, use this download instead)
NB : due to limitations on /clr compilation, Dependencies needs Visual C++ Redistributable installed to run properly.

Overview
Dependencies is a rewrite of the legacy software Dependency Walker which was shipped along Windows SDKs, but whose development stopped around 2006.
Dependencies can help Windows developers troubleshooting their dll load dependencies issues.
Releases
- v1.11 :
- lots of bugfixes and incremental improvements
- covid pandemic
- v1.10 :
- lots of bugfixes and incremental improvements
- support of Windows 8.1 apisets parsing
- v1.9 :
- Display imports and exports the way Depends.exe does.
- Added user customization for search folders and working directory
- Added LLVM demangler to availables symbol demangling
- Fixed Wow64 FsRedirection bugs
- F5 can now refresh the analysis
- Added CLR assembly dependencies enumeration
- Added a packaging option without Peview.exe (which triggers some AV).
- v1.8 :
- Add x86/x64 variants for Dependencies
- v1.7 :
- Add CLI tool «dependencies.exe»
- v1.6 :
- Add appx packaging
- v1.5 :
- Support of Sxs parsing
- Support of api set schema parsing
- API and Modules list can be filtered
- v1.0 — Initial release
Installation and Usage
Dependencies is currently shipped as two binaries (no installer present) : Dependencies.exe as a CLI tool and DependenciesGui.exe for its GUI counterpart (see screenshot). Just click on one of the release numbers above (preferably the latest), download and uncompress the archive and run DependenciesGui.exe.
Since the binary is not signed, SmartScreen might scream at runtime. Dependencies also bundle ClrPhTester.exe, a dumpbin-like executable used to test for non-regressions.
Dependencies currently does not recursively resolve child imports when parsing a new PE since it can be really memory-hungry to do so ( it can over a GB even for «simple» PEs ). This behavior can be overridden (app-wide) via a property located in «Options->Properties->Tree build behaviour».

Tree build behaviours available :
ChildOnly(default) : only process PE child imports and nothing beyond.RecursiveOnlyOnDirectImports: do not process delayload dlls.Recursive: Full recursive analysis. You better have time and RAM on your hands if you activate this setting :
Limitations
At the moment, Dependencies recreates features and «features» of depends.exe, which means :
- Only direct, forwarded and delay load dependencies are supported. Dynamic loading via
LoadLibraryare not supported (and probably won’t ever be). - Support of api set schema redirection since 1.5
- Checks between Api Imports and Exports.
- Minimal support of sxs private manifests search only.
Building
Building is pretty straightforward.
The only caveat is you need to select the «Debug» or «Release» configuration and «x64» or «x86» platform which may not be the default.
Credits and licensing
Special thanks to :
- ProcessHacker2 for :
phlib, which does the heavy lifting for processing PE informations.peview, a powerful and lightweight PE informations viewer.
- Dragablz a C#/XAML library which implement dockable and dragable UI elements, and can recreate the MDI programming model in
WPF. - @aionescu, @zodiacon and Quarkslab for their public infos on ApiSets schema.
- Thomas levesque’s blog which pretty much solved all my
WPFprogramming issues. HisAutoGridSortis used in this project - Venkatesh Mookkan for it’s
FilterControlfor ListView used in this project - demumble for demangling GCC symbols on Windows
