On Windows 10, when there is a crash, the system creates a «dump» file containing the memory information at the time of the error, which can help determine the reason for the problem.
The «.dmp» file includes the stop error message, a list of the drivers loaded at the time of the problem, kernel, processor, and process details, as well as other information depending on the type of dump file you have.
Although Windows 10 automatically creates dump files, the only problem is that you won’t find any built-in tools to open this type of file, and this is when the Microsoft Windows Debugging (WinDbg) tool can help. WinDbg is an advanced tool designed for debugging kernel-mode and user-mode code, reviewing processor registries, and analyzing crash dumps.
This guide will walk you through the steps to open a dump file to determine what caused the crash to resolve the problem on your computer.
How to open dump file with WinDbg on Windows 10
On Windows 10, you may find multiple ways to open and review a dump error file, but the easiest way is to use the WinDbg tool available through the Microsoft Store.
Install WinDbg
To install the WinDbg tool on Windows 10, use these steps:
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
- Open the WinDbg download page.
- Click the Install button.
- Click the Open button.
- Click the Install button.
Once you complete the steps, the application will install, and it will be available through the Start menu.
Analyze dump file
To open and analyze a dump file created by a crash on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for WinDbg, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Click the File menu.
- Click on Start debugging.
- Select the Open sump file option.
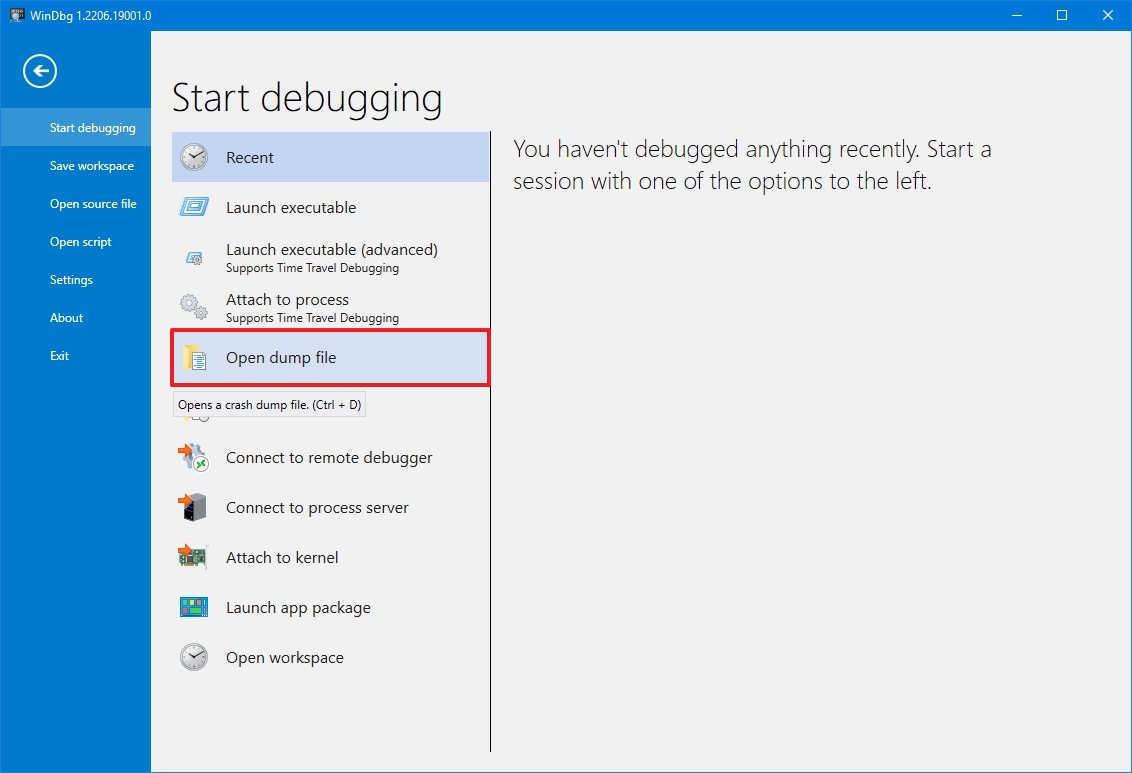
- Select the dump file from the folder location — for example, %SystemRoot%\Minidump.
- Click the Open button.
- Click the Open button again.
- Check the progress bar until it loads the dump file (this may take a while).
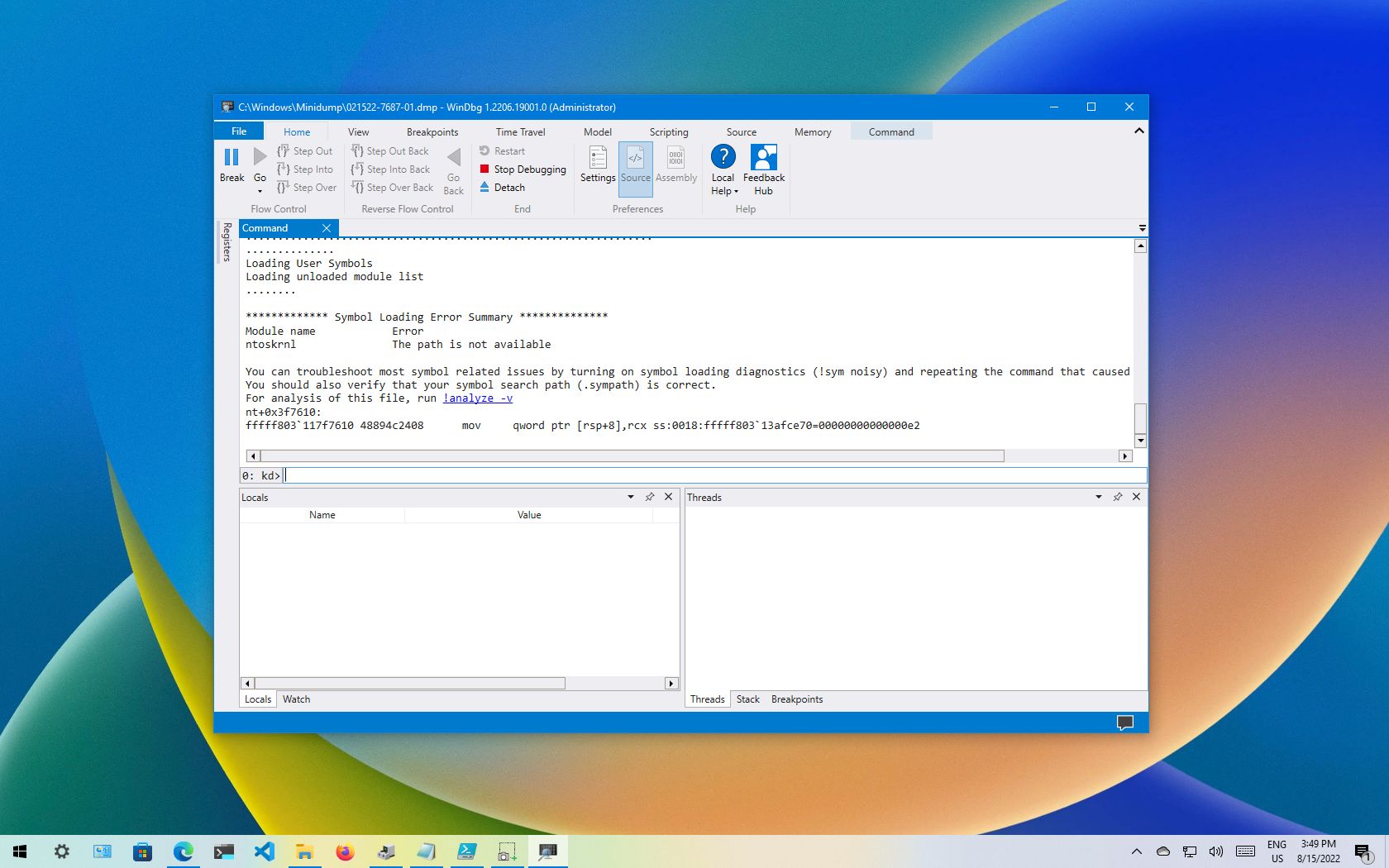
- Type the following command in the run command and press Enter: !analyze -v
- Quick tip: You can also click the !analyze -v link if available from the main area if available after loading the dump file.
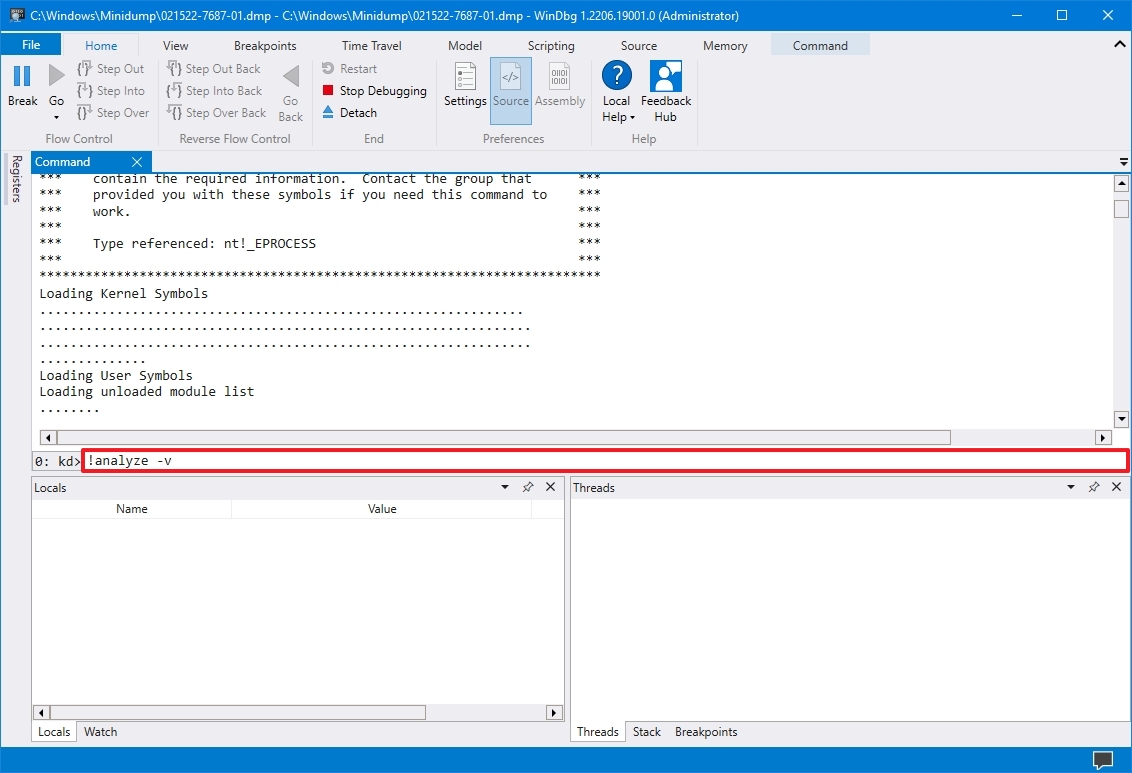
- Check the progress bar until the analysis is complete (this may take a long time depending on the data size).
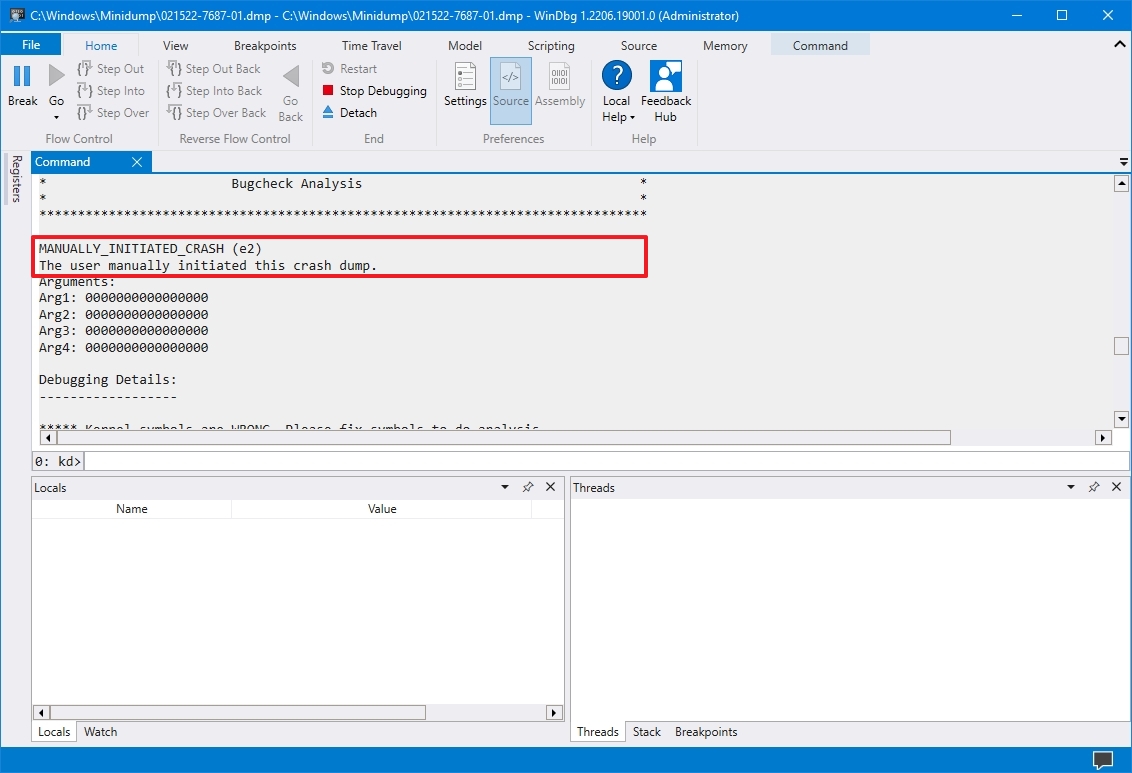
After you complete the steps, the application will return the dump file analyses, which you can then review to determine the reason for the problem to help you resolve the issue.
The information will be different depending on the problem. For example, this result points out that this was a manually initiated crash with an «e2» error code, which is correct since, for this guide, we use these instructions to force a dump file. The WinDbg even makes an excellent job describing the crash in a language anyone can understand («The user manually initiated this crash dump»).
As you continue reviewing the dump file, you will also find more information, such as «FAILURE_BUCKET_ID» and «MODULE_NAME,» which could indicate what is causing the problem.
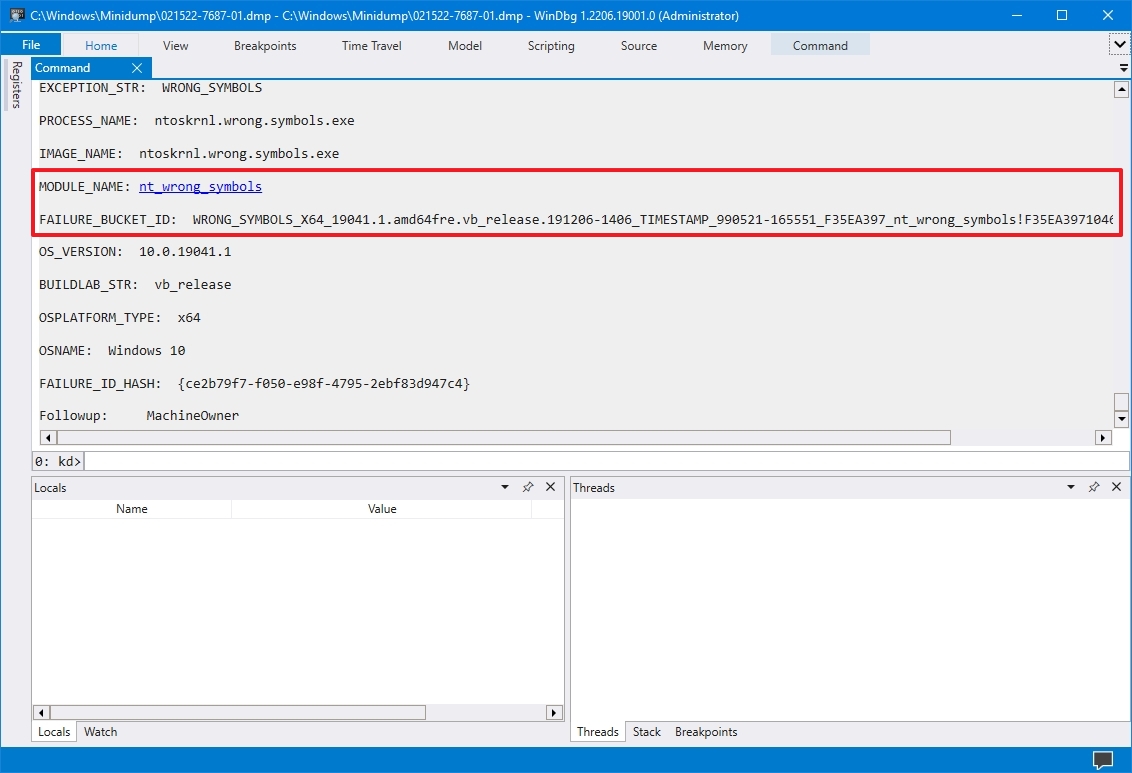
The information can be overwhelming since it is not meant for regular users. If your computer keeps crashing, you can use this tool to get an idea of the problem. If you cannot figure it out, you can use the hints in the report to search online for more information.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.
Все способы:
- Что это такое
- Вариант 1: Удаление мусорных файлов
- Вариант 2: Отключение дампа памяти
- Вариант 3: Исправление ошибки дампа памяти
- Способ 1: Восстановление системных файлов
- Способ 2: Проверка диска
- Способ 3: Автоматическое восстановление
- Анализ дампа памяти
- Вопросы и ответы: 0
Что это такое
Для начала следует разобраться, что такое дамп памяти и в каких ситуациях пользователи сталкиваются с ним. В зависимости от этого и применяются различные способы устранения неполадки. Дамп памяти – это файл, который автоматически создается при возникновении критических ошибок в работе операционной системы.
Если вкратце, наверняка каждый юзер Windows получал «синий экран смерти» (BSOD), который по своей сути является результатом различных сбоев. Он появляется на любой стадии использования ОС, а сама система при возникновении такого экрана автоматически создает один или несколько файлов. Они содержат в себе отладочную информацию о компьютере, включая данные, которые при критической ошибке, повлекшей BSOD, находились в ОЗУ. Такие сведения позволяют понять причину проблемы, которая вызывает «синий экран смерти». То есть система генерирует дамп, а аварийным он называется, потому что формируется при возникновении аварий в работе ОС.
Теперь стоит понять, как нужно действовать при появлении дампа памяти. Например, если рядом с названием диска в утилите «Управление дисками» появляется надпись «Аварийный дамп памяти», тогда это не является ошибкой. Тут указана информация о том, что файлы со сведениями о системной проблеме попросту хранятся на этом томе. Соответственно, исправлений никаких не требуется, но можно убрать данную надпись, о чем мы написали в Вариантах 1 и 2.
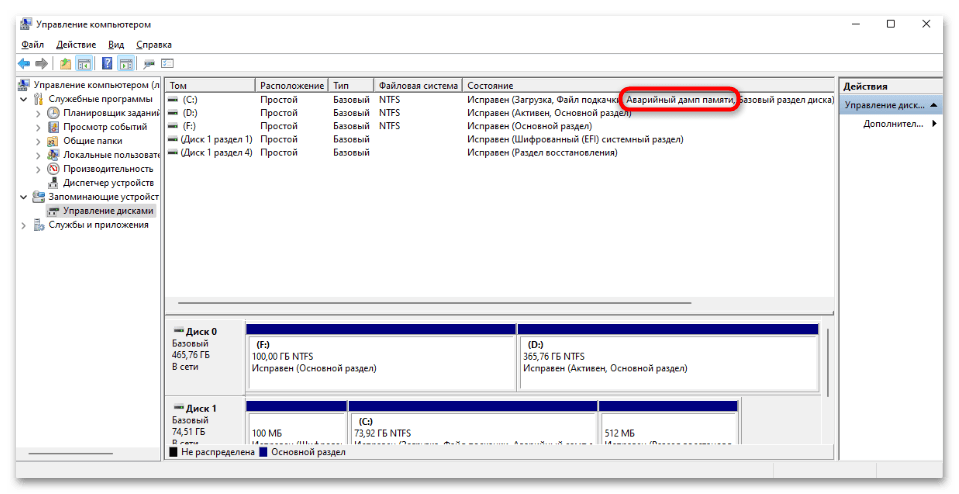
В случае если BSOD появляется периодически, тогда может потребоваться решение проблемы на системном уровне, а дамп памяти лишь поможет выяснить, что случилось. В Варианте 3 мы рассмотрели наиболее распространенные пути решения (даже когда Windows 10 не запускается), а также привели несколько специализированных программных средств, с помощью которых можно проанализировать дамп памяти.
Вариант 1: Удаление мусорных файлов
Как уже говорилось, при появлении сообщений о дампе памяти, касающихся локального диска, беспокоиться не стоит – это не проблема накопителя, а лишь информация о том, что файлы были созданы именно на этом разделе. Но можно убрать дамп памяти, очистив данный диск.
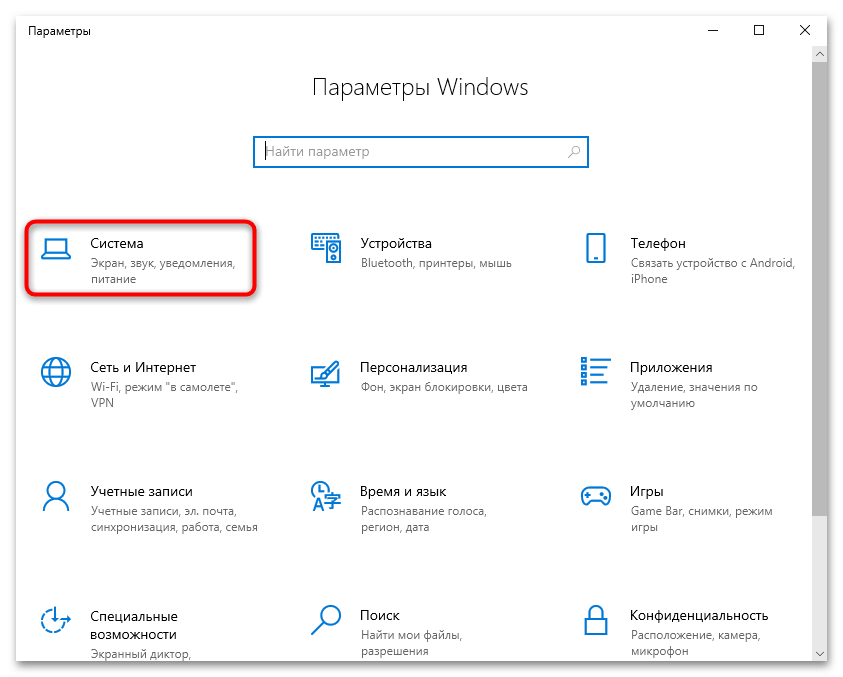
- Нажмите на кнопку «Пуск» и выберите запуск штатных «Параметров».
- Перейдите в раздел «Система».
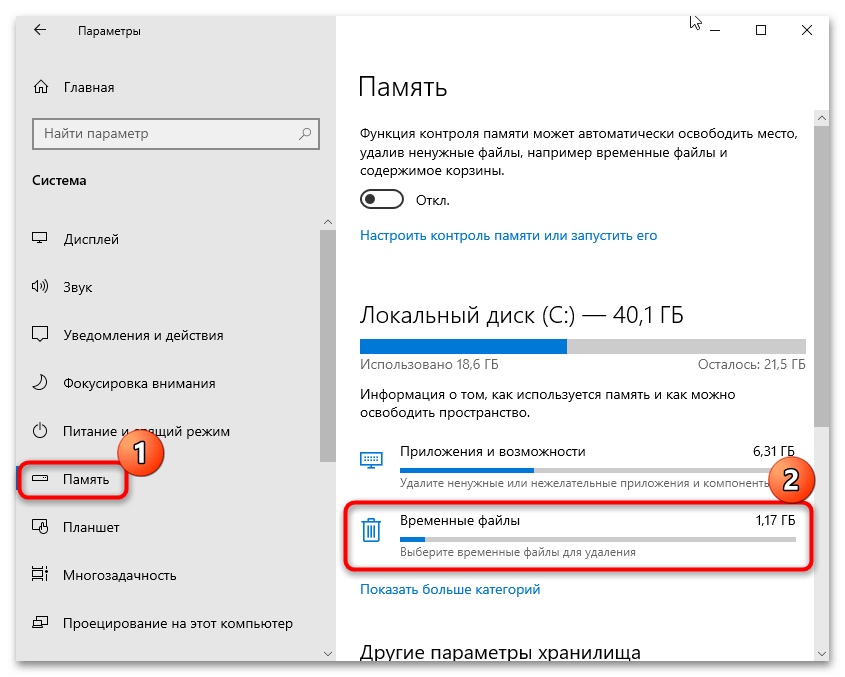
- Через левую панель переключитесь на вкладку «Память», затем в центральной части окна найдите локальный диск, у которого появилось сообщение об аварийном дампе памяти, и нажмите по «Временные файлы».
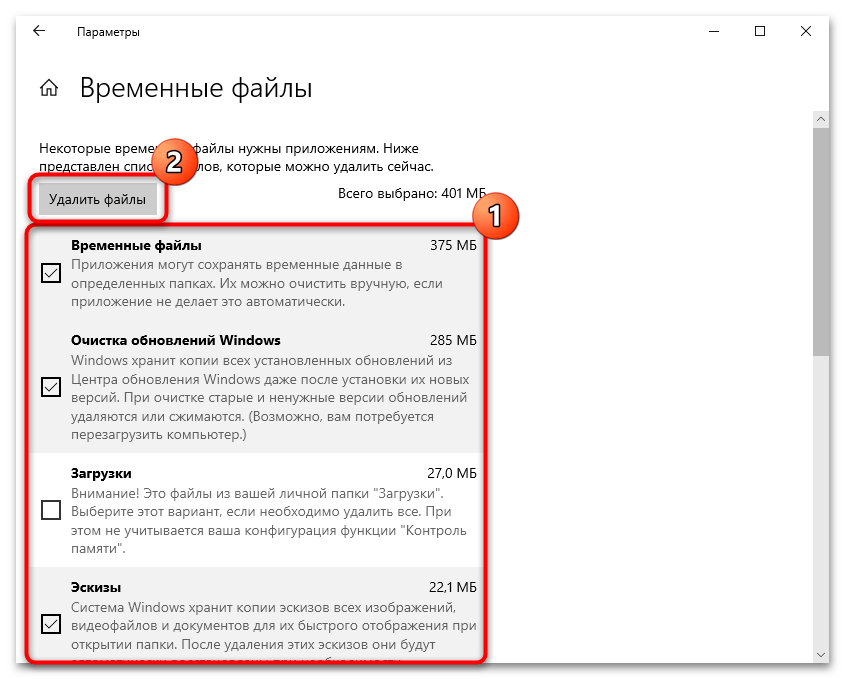
- После сканирования системы отобразятся различные временные файлы. Снимите галочки у всех пунктов, кроме «Файлы дампа памяти для системных ошибок» (впрочем, по желанию можно очистить и другие категории), затем нажмите на кнопку «Удалить файлы», расположенную вверху.
Удалить дампы памяти с локального диска можно и другим способом – вручную через файловую систему. Достаточно запустить «Проводник» и перейти к корневой директории диска. Если это системный раздел, то откройте папку «Windows», где должен располагаться файл под названием «MEMORY.DMP» (это основной дамп памяти), а в каталоге «Minidump» можно найти малые дампы (их размер, как правило, составляет около 1 МБ). Удалите эти данные, но для процедуры потребуются права администратора.
Читайте также: Получение прав Администратора на компьютере с Windows 10
Вариант 2: Отключение дампа памяти
В Windows 10 можно отключить автоматическое создание файла с данными об ошибке – то есть дампа памяти. Конечно, это позволит избежать появления различных предупреждающих надписей и иногда BSOD, но при этом системная ошибка, вызывающая это, исправлена не будет, и, возможно, узнать потом причину ее появления без дампа памяти окажется довольно проблематично.
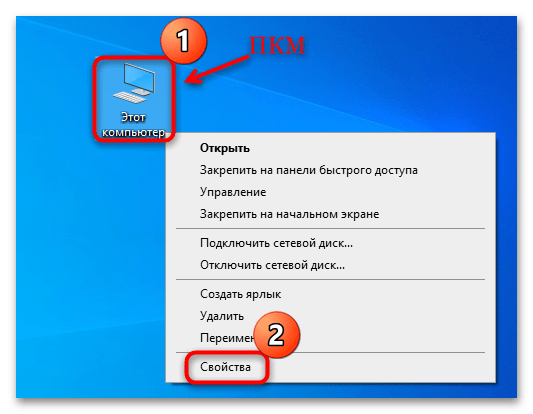
- Кликните правой кнопкой мыши по иконке «Этот компьютер» на рабочем столе и из контекстного меню выберите пункт «Свойства».
- В открывшемся окне штатных «Параметров» кликните по строке «Дополнительные параметры системы» в блоке «Сопутствующие параметры».
- На вкладке «Дополнительно» в разделе «Загрузка и восстановление» щелкните по кнопке «Параметры».
- Из выпадающего меню «Запись отладочной информации» выберите пункт «Нет», чтобы отключить аварийный дамп памяти. Нажмите на «ОК» для сохранения настроек.
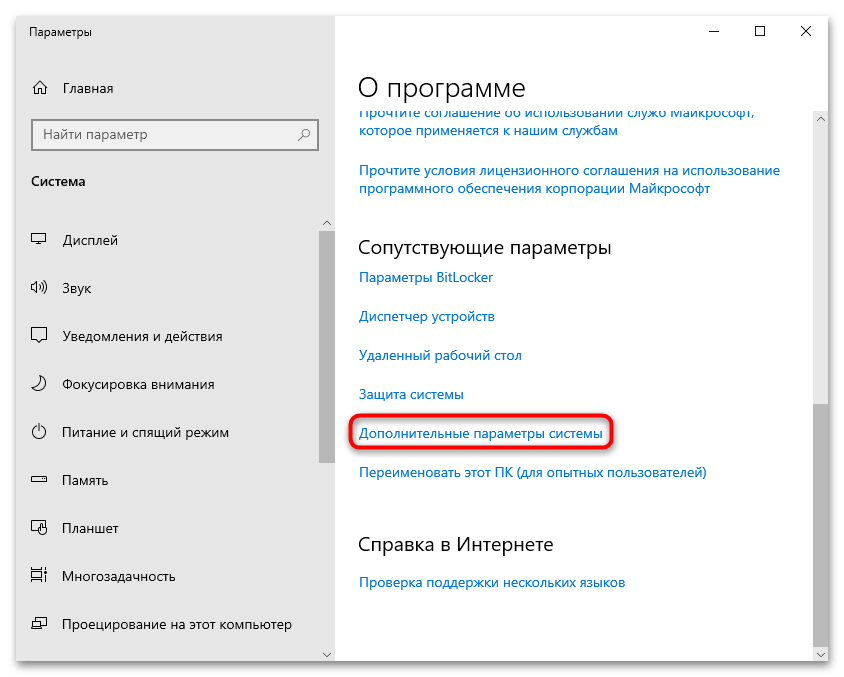
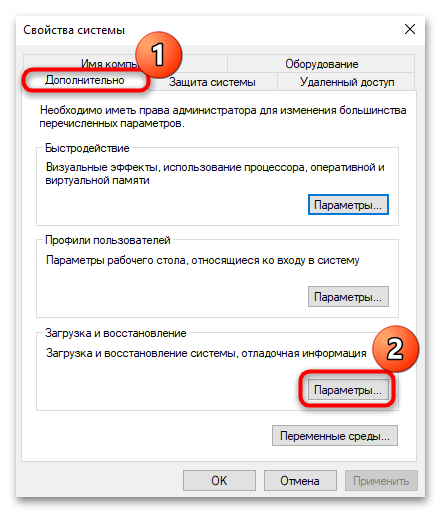
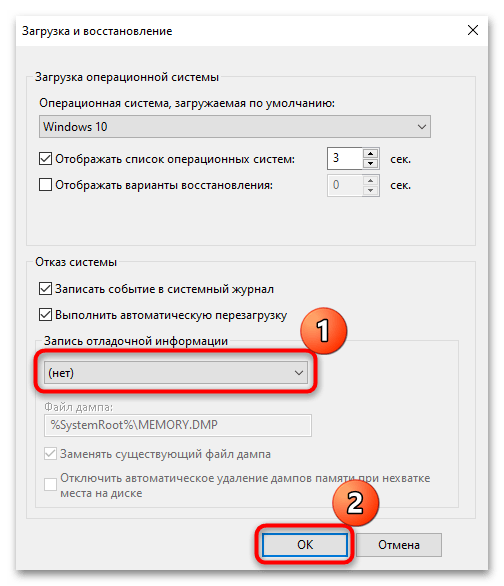
Кстати, изменить путь сохранения для дампа памяти можно здесь же: в текстовом поле «Файл дампа» пропишите нужный адрес.
Вариант 3: Исправление ошибки дампа памяти
Аварийный дамп памяти может быть создан по различным причинам, в частности из-за системных ошибок любого характера. Мы рассмотрим несколько универсальных способов, позволяющих решить многие распространенные неполадки в работе ОС.
Способ 1: Восстановление системных файлов
В первую очередь стоит проверить целостность системных файлов, поскольку синий экран и, соответственно, запись дампа памяти часто возникают именно по этой причине. Системные компоненты повреждаются вследствие разных неполадок в работе ОС, а также в результате вирусных атак, но в «десятке» предусматривается специальное средство для сканирования и восстановления поврежденных файлов Windows. О применении такой утилиты мы писали в отдельном материале.
Подробнее: Как проверить целостность системных файлов в Windows 10
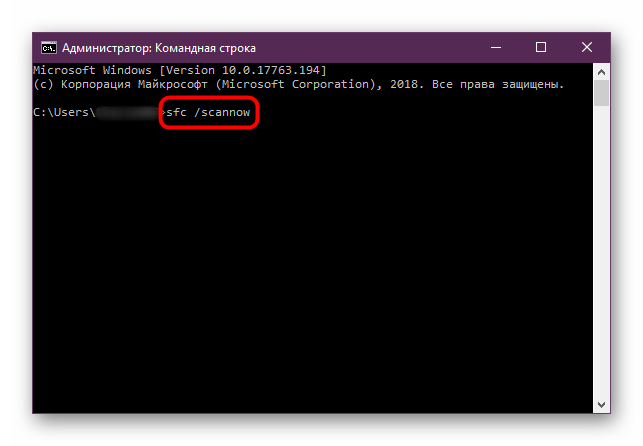
Способ 2: Проверка диска
Также не лишним будет проверить накопитель на наличие ошибок, которые могут стать причиной создания дампа памяти. Для этого предназначен специальный инструмент, который встроен в операционную систему. Можно еще воспользоваться средствами от сторонних разработчиков. Переходите по ссылке ниже, чтобы узнать, как правильно выполнить диагностику диска на компьютере с Windows 10.
Подробнее:
Выполнение диагностики жесткого диска в Windows 10
Проверка работоспособности SSD
Способ 3: Автоматическое восстановление
Если после появления BSOD система не стартует, скорее всего, придется запустить автоматическое восстановление. В Windows 10 реализована специальная среда (WinRE), с помощью которой выполняются различные манипуляции по восстановлению работы ОС, диагностики и использование системных средств, например «Командной строки». Вероятно, важные файлы оказались повреждены, отчего и не получается полноценно пользоваться ОС.
Подробнее: Запускаем автоматическое восстановление в Windows 10
Анализ дампа памяти
Различные ошибки в работе операционной системы требуют правильного подбора методов решения. При создании аварийного дампа памяти важно корректно его проанализировать и найти нужный способ исправления неполадки. Для анализа файла дампа существуют специализированные программы, как правило, устанавливаемые отдельно. Одним из таких инструментов является фирменная утилита от компании Microsoft – WinDbg. С ее помощью можно посмотреть информацию, которая содержится в файле с расширением DMP, созданного после появления BSOD.
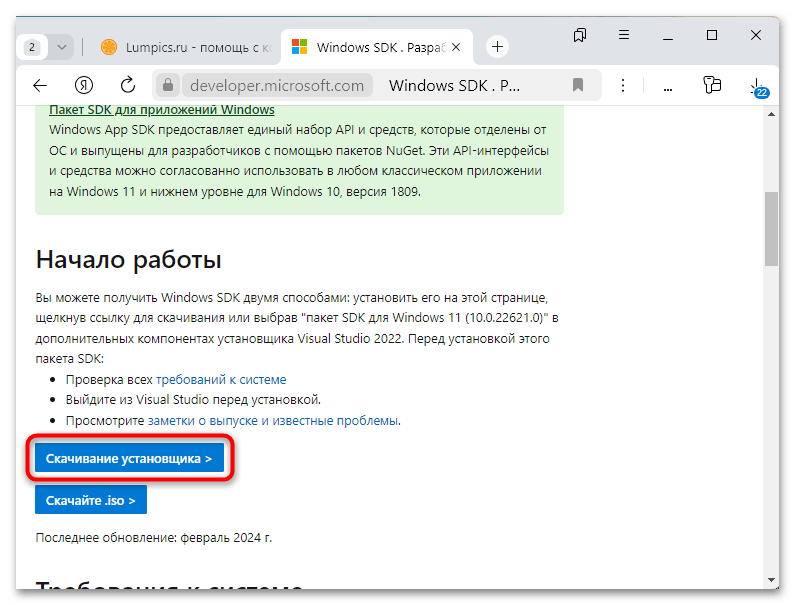
Скачать WinDbg с официального сайта
- Перейдите по ссылке выше и скачайте инсталляционный файл программы, нажав на кнопку «Скачивание установщика».
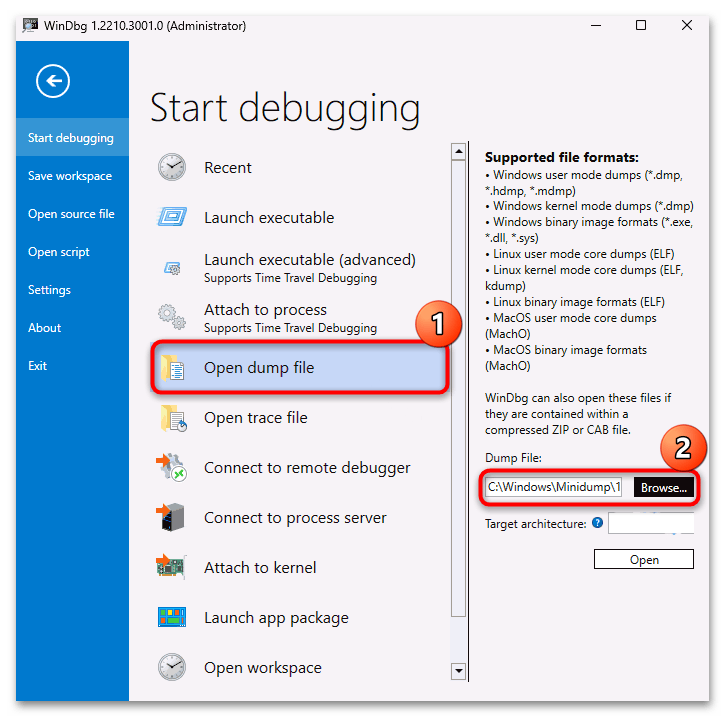
- Далее запустите сохраненный файл и выполните установку на локальный диск. Откройте установленную программу от имени администратора, кликнув правой кнопкой мыши по ярлыку и выбрав нужный тип запуска. В главном окне кликните по строке «Open dump file» и укажите к нему путь (как мы уже упоминали в Варианте 1, он хранится на системном диске в папке «Windows»).
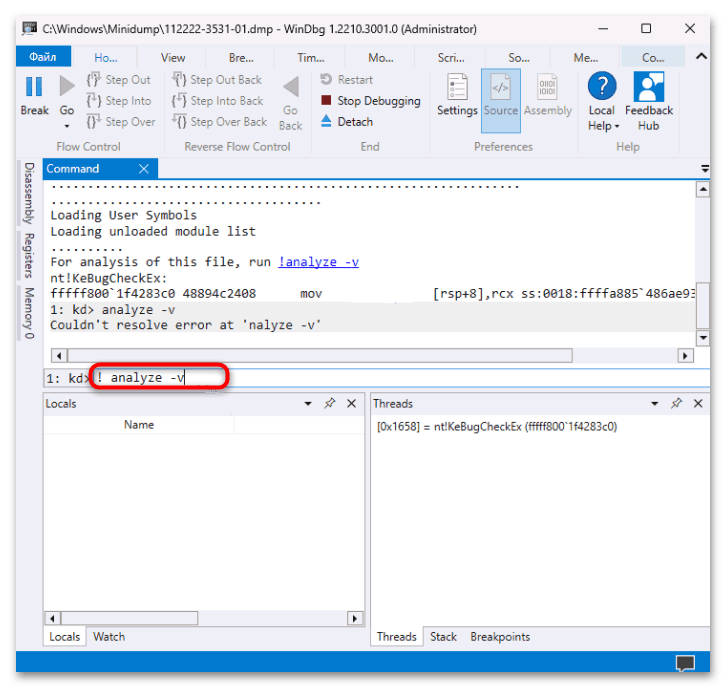
- В текстовом поле панели «Command» введите команду
!analyze -vи нажмите на «Enter» для ее выполнения. - После в основной части окна появится информация об ошибке, вызывавшей сбой. Обратите внимание на строку «PROCESS_NAME», где указано название программы, являющейся причиной появления BSOD и записи дампа памяти.
- Также нужные сведения могут быть связаны с файлом драйвера с расширением SYS (строка «IMAGE_NAME»).
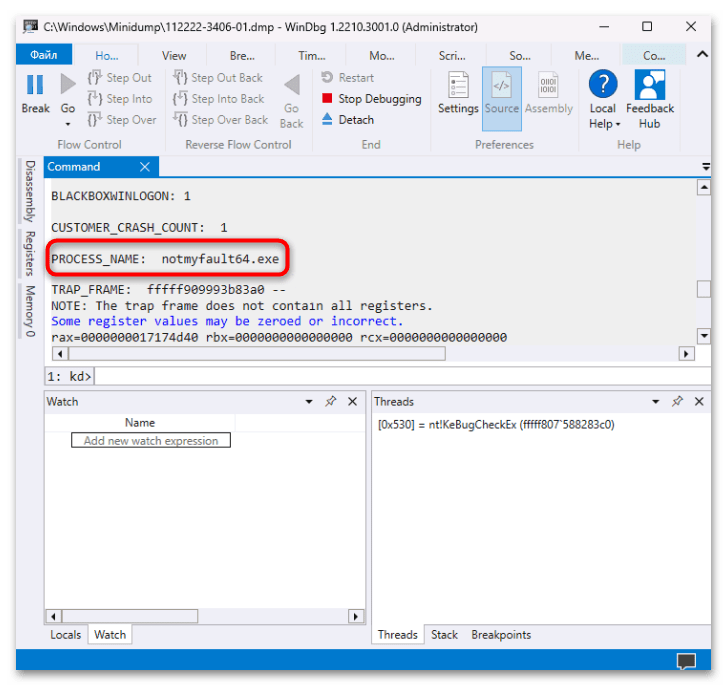
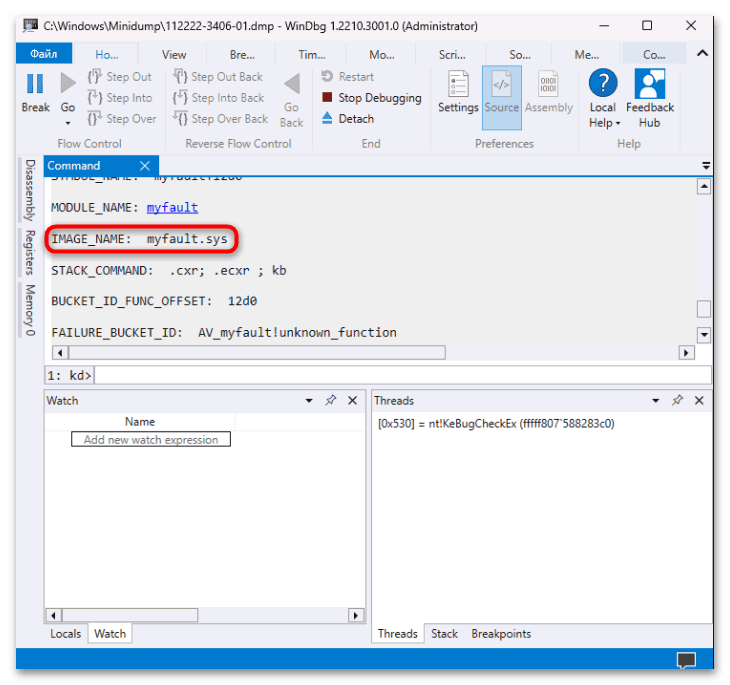
После того как причина создания дампа памяти станет известна, более детальные сведения можно найти в интернете. Например, вы сможете узнать, каким устройствам соответствуют проблемные драйверы, или выяснить назначение процессов, вызвавших сбой в работе ОС.
К примеру, если стало понятно, что проблема кроется в конкретном программном обеспечении, то его может потребоваться переустановить или вовсе удалить и заменить на аналогичный софт. Если же дамп был создан вследствие неполадок с драйвером, его, может быть, понадобится обновить или выполнить переустановку ПО на текущую либо предыдущую версию.
Также для анализа ошибок BSOD есть и другие программы от сторонних разработчиков, например BlueScreenView. Как пользоваться этим софтом, мы писали ранее в отдельном руководстве.
Подробнее: Как пользоваться BlueScreenView в Windows 10
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
Windows 11 (including earlier version), when, encounter a Blue Screen of Death (or BSOD), accumulates all the memory information into a file. Holding Dump file as name it further helps users to identify and debug the cause of the crashes. The files also allow writing the debugging details in different file formats in order to simplify the readability of the data.
Dump file may be of various types depending on the nature of crash and bug check values. These are “Small memory dump (Minidump)”, “Kernel memory dump”, “Complete memory dump”, “Automatic memory dump”, and “Active memory dump”. However, among all these, Windows 10/11 generates Automatic memory dump all by itself as its name suggests. The following section will deal with everything related to Dump File Location Windows 11 or 10.
Dump File Location Windows 10 or 11
Here is the Dump File Location Windows 11 or 10 –
Dump File Location
Instead, you can say Dump file locations so see the following paths to find out the data –
%SystemRoot%memory.dmp which means
C:\Windows\memory.dmp
This is the default location and here, C: refers to the system drive where Windows is installed.
Windows 11/10 can also capture memory dumps that consume a small amount of space. These are created at –
%SystemRoot%Minidump.dmp i.e.,
C:\Window\Minidump.dump
Change Dump File Location Windows 11 or 10
- Go to desktop and right-click on This PC icon. From the available options, choose Properties.
- Click Advanced system settings link that shows up on the top left of the subsequent window.
- Click Settings beneath Startup and Recovery section.
- Locate the Dump File text field and insert the location of the file.
Configure the Type of Memory Dump File
As aforementioned, Windows generates Automatic memory dump files but users can choose to configure the settings as per need. Thankfully, there are certain ways using which a user can change the type of memory dump file that Windows creates.
1]Through Startup and Recovery
- Press “Win logo+R” hotkey to open Run dialog box. System properties wizard will become visible, switch to Advanced tab.
- Here, click Settings just below Startup and Recovery section.
- Click the drop-down under Write debugging information. From the list of dump file types, choose the type that you wish Windows to generate when Windows crashes.
- To apply the changes, click OK.
Note – In case the system crashes a lot, it’s better to deselect the checkbox against the option Overwrite any existing file. Doing this will eventually create incremental dump files that will have a memory dump file for each crash that occurs.
2] Use Elevated Command Prompt
- Fire up taskbar search using Win+S combination of keys. Type in cmd.exe, right-click ok Command Prompt and choose Run as administrator.
- Click Yes on the prompt of UAC to access elevated Command Prompt.
- Once into the black window, insert the applicable command from the list below to change the type of dump file and hit Enter.
| Memory Type | Command Line |
| No memory | wmic RECOVEROS set DebugInfoType = 0 |
| Small memory dump | wmic RECOVEROS set DebugInfoType = 3 |
| Kernel memory dump | wmic RECOVEROS set DebugInfoType = 2 |
| Complete memory dump | wmic RECOVEROS set DebugInfoType = 1 |
| Automatic memory dump | wmic RECOVEROS set DebugInfoType = 7 |
| Active memory dump | wmic RECOVEROS set DebugInfoType = 1 |
- Finally, close the prompt window and Restart Windows 10 PC to make the changes effective.
Note – The Command Prompt also lets you view the current memory dump file. Just open Command Prompt as Administrator and run the following command-line –
wmic RECOVEROS get DebugInfoType
Types of Memory Dump Files
It is important to know the types after finding Dump File Location Windows 11 or 10 –
Small memory dump – It is the type that contains a minimal amount of details. Basically, the file includes the stop code, list of device drivers, parameters. Furthermore, it also contains the current process and informs which kernel thread or process crashed.
Kernel memory dump – This is the most useful and comprehensive one with respect to the kernel. Moreover, this type contains information in connection with programs and drivers in kernel mode. However, the dimension of this dump file completely depends on the amount of kernel-mode memory specified by Windows and drivers. Now, in case a second crash occurs and a kernel memory dump file is generated, the earlier content gets overwritten.
Complete memory dump – A remarkably large file type which is equal to the RAM of the system. It incorporates physical memory allocation that is basically left out in other kernel dumps.
Automatic memory dump – When compared to the kernel memory option, this is quite similar to it in terms of information. The only difference between them is the size of the paging file that Windows sets for them.
Active memory dump – It is comparatively smaller than complete memory dump. This type refines the items that are not influential in spotting the cause of a crash.
That’s all!!!
In this article, we will be showing you the two ways in which you can manually create a Crash Dump file in Windows 11/10. Also known as a Memory dump file or a Windows dump file, a crash dump file holds details concerning a specific application or process crash in Windows.
What is a Crash Dump file?
Commonly used to analyze and troubleshoot an issue, these Memory dump files hold data on the files and processes that were running during a particular crash and also the Kernel-mode stack that stopped. While, for the most part, your computer creates these files on its own, mostly when there is a complication, there may arise a need for you to create them manually sometimes too. The most common scenario would be when an app is not responding on your computer, and you have to send details of its malfunctioning to technical support to resolve the issue.
Broadly speaking, there are three different types of crash dump files, even though all of them serve the same purpose. Dump files are categorized based on their file size and the information they hold. A complete memory dump has the biggest stack of information. It’s the biggest dump file that a system can support, with its size as big as your computer’s RAM. Kernel Memory dump files are smaller, making them easier to transfer around. The third and final type is a small memory dump file, which contains only the most basic information and is normally only 256KB in size.
As mentioned earlier, there are two ways in which you can create a crash dump file. One via the Task Manager, and the other using your Command Prompt.
1] Create Crash Dump files using Task Manager
First things first, open the Task Manager. The simplest way to do it is by clicking on the Taskbar and selecting Task Manager from the context menu. Click on the Processes tab and right-click the app that you want to create the file for. From the list of options that appear, select Create dump file.
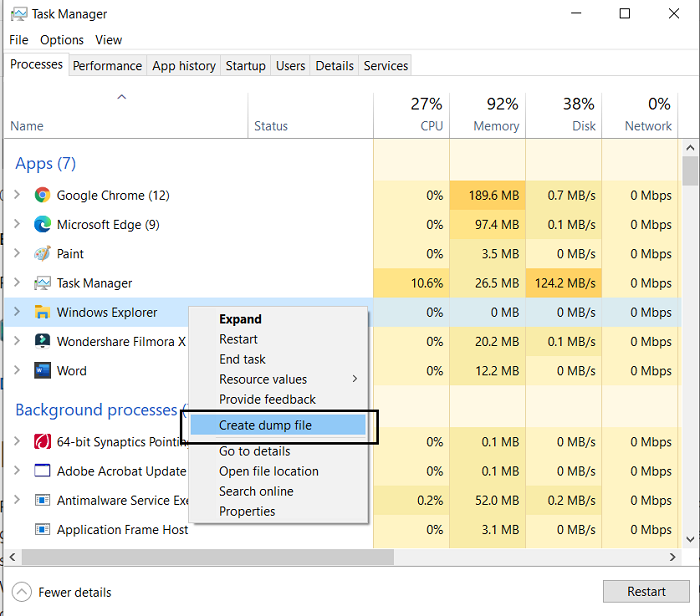
Wait for some time till the process is finished. Once you’re notified that the file has been created, click on Open File location. If you don’t want it to stay where it’s been located by default, you can copy the .dmp file and paste it in the location of your choice.
TIP: You can configure Windows to create Crash Dump Files on Blue Screen.
2] Create Crash Dump files using Command Prompt
To do this, you’ll have to download ProcDump. It’s a command-line utility that helps users keep an application’s CPU spikes in check. It also generates crash dumps during spikes. This tool can be used alongside the command prompt to create crash dump files. Here’s how.
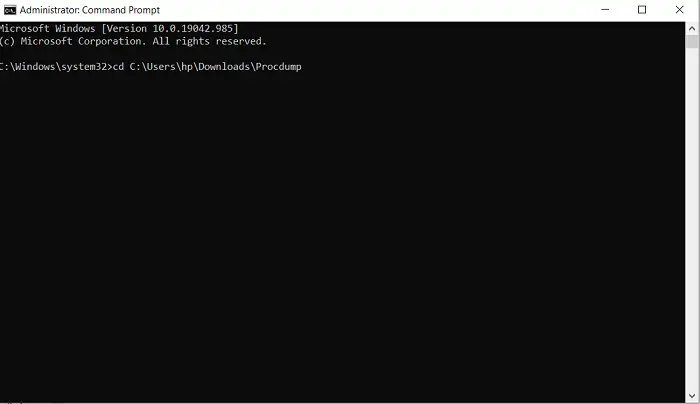
Firstly, download ProcDump from the Windows SysInternals website. The file is in a .zip format, so you will have to extract it. Upon downloading and installing, search for Command Prompt and open it to run it as an administrator.
Type the following command line to open the Procdump folder and press enter.
cd C:\Path\Procdump
You can get the path to the ProcDump app by right-clicking on the app icon and opening its properties.
After that, in order to create a dump file, paste the following command line.
procdump APP-NAME
For example, if you want to create a dump file for File Explorer, then the command line would be:
procdump explorer
This is going to create a mini-dump file for your file explorer. A similar command line can be used to create a dump file by replacing the app name with the Process ID. So, an alternate command line would be
procdump PROCESS-ID
You can easily find the process ID of any particular application by opening Task Manager and visiting the Details tab. Here, you’ll find all the processes running on your PC and their respective PID next to them.
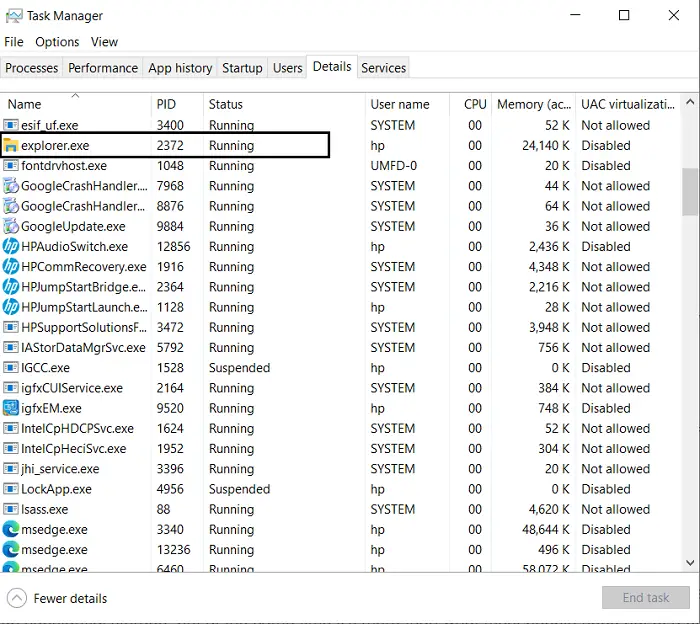
If you want to create a full-size dump file for an application or process, you can make use of the following command.
procdump -ma APP NAME/PROCESS ID
Here too, both the executable name of the program or its process ID will work. As mentioned earlier, a complete dump file stores all the memory information about the app and takes up substantial storage, but at the same time, it’s more than what most people need out of a dump file.
TIPS:
- You can create Live Kernel Memory Dump File using Task Manager
- You can change the number of Memory Dump Files that are created.
Once done, you will find your manually created dump files housed in the same folder as all the other ProcDump files. Here is the link to download the .zip file for ProcDump from Microsoft.com.
We hope that this post was able to bring some clarity about what crash dump files are, why you may need them, and how they can be manually created if need be.
Where is the crash dump file in Windows?
In Windows, crash dump files are typically stored in the C:\Windows\Minidump or C:\Windows\Memory.dmp directories by default. This is where you’ll find the files after a system crash, which can be useful for diagnosing problems.
Related reads:
- Free Crash Dump Analyzer software
- What are System Error Memory Dump Files
- Crash, hang, and cause kernel memory leaks using NotMyFault
- Physical Memory Limits in Crash Dump files
- Machine Memory Dump Collector
- Physical memory allocation and memory status.

Welcome Dear Visitors All;
If you are a windows user, then you may encounter a blue screen of death error message that indicates that “Your Device Ran into a Problem and Needs to Restart”. This blue screen indicates that your windows detected a system or hardware corruption, so the computer restarted as an attempt to protect your hardware or system files from further corruption. In such case, the computer will write a log report into a file called Memory.dmp or minidump file to inform you what is the problem that caused the system to crash or to restart. But the Crash debugging mode should be enabled before this event.
This topic I will show you how to enable Windows crash Memory dump, and how to view or share the file in windows 10 and windows 11 operating systems to get an online support from Microsoft or from ValiumMedia Techs channel on YouTube.
You can configure your system to write a debugging information either into a large file called Memory.dmp stored in windows folder on this path “C:\Windows\Memory.dmp“, or as a small numerically named file with .dmp extension stored inside Minidump folder on this path “C:\Windows\Minidump\“.
How to Check Crash Debugging Status?
You can check whether the crash debugging status is enabled or disabled by using either Command Prompt or using Advanced System Properties, a System Settings panel. Both methods are applicable to Windows 7,Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows 11 or any windows edition.
How to Check Debugging Status from Advanced System Settings?
- Press Windows + R keys from keyboard to open Run tool
- Type SystemPropertiesAdvanced and press Enter to open System Properties settings panel.
- Click on Settings icon under Startup and Recovery field
- If None is the selected option under Write Debugging Information field, then the debugging status is disabled in your computer.
- So select Automatic Memory Dump or Small memory dump or another option to enable the Memory Dump debugging.
- In Advanced Recovery Environment, you can use CMD to open System Properties Advanced after changing the CMD path into System32 folder.
How to Check Debugging Status Using CMD in Windows 11?
- To check debugging status from Command Prompt, do the followings:
- Type CMD into search box and then run the Command Prompt as administrator
- Type the following command and press Enter
- WMIC RECOVEROS Get DebugInfoType
- The seven value indicates that the Debugging is enabled in Automatic Memory Dump mode.
- Note: In Advanced Recovery Environment, you have to change the CMD path into C:\Windows\System32 folder first, in order to check or to enable Crash debugging mode using this command:
- CD /D C:\Windows\System32
- Replace the C with the letter of windows drive in your PC.
- CD /D C:\Windows\System32
You can enable the Crash debugging mode in windows using one of the following methods:
- From System Properties settings
- From Command Prompt
- From Registry Editor
How to Enable Crash Debugging Using System Properties settings:
- Press Windows + R keys from keyboard to open Run tool
- Type SystemPropertiesAdvanced and press Enter from keyboard to open System Properties settings
- Click on Settings icon under Startup and Recovery field
- From Write Debugging Information field, choose Complete Memory Dump, Kernel Memory Dump, Automatic Memory Dump, or Small Memory Dump according to what you want
- After that, click Ok to save changes.
How to Enable Crash debugging Memory File Using CMD?
- To enable Memory dmp or minidump creation using CMD, do the followings:
- Type CMD into Search box and then Run the Command Prompt as administrator
- Execute the following command to enable Complete Memory Dump:
- WMIC RECOVEROS set DebugInfoType = 1
- Execute the following command to enable Kernel Memory Dump:
- WMIC RECOVEROS set DebugInfoType = 2
- Execute the following command to enable Small memory dump (128 KB):
- Execute the following command to enable Automatic memory Dump:
- WMIC RECOVEROS set DebugInfoType = 7
- To disable Crash debugging, execute this command:
- WMIC RECOVEROS set DebugInfoType = 0
- You can also use the same commands to enable the debugging memory files from Windows Recovery Environment, but you have to change the CMD path to System32 folder first using this command:
- CD /D C:\Windows\System32
- Replace the C with the letter of windows drive in your PC.
- CD /D C:\Windows\System32
How to Enable Debugging Memory File Using Registry Editor?
- To enable crash debugging file from registry editor, do the followings
- Press Windows logo + R keys to open Run Tool
- Type Regedit and press Enter to open Registry Editor tool
- Navigate to this key path:
- Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControl
- Right click on CrashDumpEnabled key and then select Modify option
- Change the value data into one of the followings:
- Type 1 to enable Complete Memory Dump
- Type 2 to enable Kernel memory Dump
- Type 3 to enable Small Memory Dump
- Type 7 to enable Automatic Memory Dump
- You can enable debugging from advanced recovery menu using Registry editor as followings:
- Type REGEDIT into command prompt and press Enter to open Registry editor
- Select HKEY LOCAL MACINE
- From File tab, select Load Hive option
- Select your windows and then navigate to Windows\System32\Config folder
- Select System file and then click on Open option
- Type Sys and then click ok to load the system Registry file
- Expand Sys key and then navigate to this path:
- ControlSet\Control\CrashControl
- Right click on CrashDumpEnabled key and select Modify option
- Type three to enable Small Memory Dump, or type Seven to enable Automatic Memory Dump
- Collapse the keys list and then select Sys key
- Click on file tab and then select Unload Hive option
How to Read Memory Dump File?
- To View the memory.dmp or the Minidump file, do the followings:
- Install the WinDbg tool from Microsoft Store or from the official Microsoft website for free
- After installing the debugger tool, locate the tool launcher and start it
- From File tab, select Open Crash Dump option
- Navigate to the windows or Minidump folder and then double click the dump file to load it.
- Click on !analyze -v to start analyzing the crash file
- Note: You have to be connected to the internet in order to download the debugging codes and symbols required to analyze the file.
- You have to have enough experience in coding and in Microsoft symbolsmeanings in order to understand the analyzing result of the Memory.dmp file.
- You can also use free windows memory.dmp viewer from third party source, such as NirSoft BlueScreenView tool. This free tool can also be used while booting into Windows Recovery Environment.
How to Share the Memory Dump File?
- To get an online support, you can upload the memory dump or minidump file as followings:
- Open C:\Windows\ and/or C:\Windows\Minidump\ folder according to debug settings in your computer
- Copy the memory.dmp file or the Minidump file into Documents or another folder so you can compress and share the file without access denied or permission errors, because windows security settings is not allow copy or modification the files in their default paths.
- Right click the Memory.dmp file and then select “Compress to zip File” option to reduce the file size so you can share it faster.
- You can copy both memory.dmp and minidump files if your computer created both files.
- If you have failed to copy the files, you can run the CMD as administrator and then execute one of the following commands to copy the files into Dump folder in the main directory of C partition:
- XCOPY /R /H /i “C:\Windows\Memory.dmp” C:\DUMP
- To copy Memory.dmp file
- XCOPY /R /H /i “C:\Windows\Minidump” C:\DUMP
- To copy Minidump folder or its contents
- XCOPY /R /H /i “C:\Windows\Memory.dmp” C:\DUMP
- To compress the Dump folder using CMD, execute this command;
- Powershell Compress-Archive c:\dump c:\dump.zip
- In Advanced Recovery Menu, you can send the Memory.dmp file into a USB drive, after that, connect the USB drive to your mobile or another computer to upload the file into google drive or into another file hosting website or online cloud.
- After that, copy the link and add it in a comment or into email to get the online help.
How do I upload files to a shared Google Drive?
- To upload the file into your Google Drive, do the followings:
- Click on +New icon in the upper left corner and then select File upload option
- Navigate to the file path and double click it to start uploading
- You can also drag and drop the zip file into the main website page to upload it.
- To all others viewing or downloading the file, hover on the file name and then click on the Share icon, and then change the General Access of the file from “Restricted” to “Anyone with the link” option and click Done to save changes. After that, copy the link and share it to anyone you want to share with.
VIDEO:
For more details about how to enable crash debugging mode, and how to view or share the memory.dmp file to get online support, watch the following video to see everything step by step:
Please follow and like us:
