Download Windows Speedup Tool to fix errors and make PC run faster
Here is the list of command-line tools and the names of almost all common applications that are used by users in the Windows operating system. You can directly run them right from the start menu search bar or the Run box of your Windows 11/10 system. They are mainly used to save time and do the job efficiently.
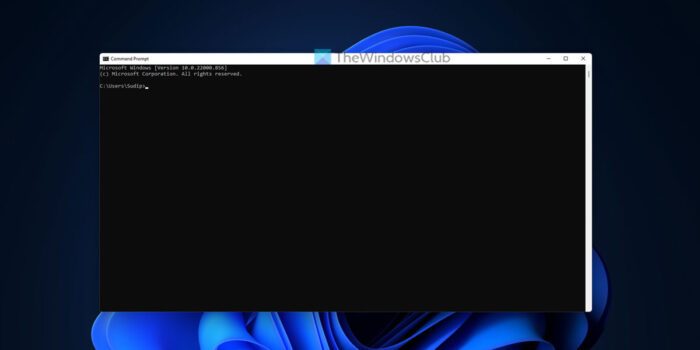
How to use command line tool in Windows 11/10
To use command line tools in Windows 11 or Windows 10, you mainly have two options. First, you can enter the command in the Taskbar search box or Start Menu. Second, you can open the Run prompt and type the command accordingly.
If you want to follow the second method, you need to press Win+R to display the Run prompt on your screen, type the command in the empty box, and press the Enter button or click the OK button.
Common application name and the Executable filename or command line have been mentioned below:
- Accessibility Options – access.cpl
- Accessibility Wizard – accwiz.exe
- Activate Windows – msoobe.exe
- Active Connections Utility – netstat.exe
- Add Hardware Wizard – hdwwiz.cpl
- Add or Remove Programs – appwiz.cpl
- Address Book – wab.exe
- Attrib – attrib.exe
- Backup – ntbackup.exe
- Boot Configuration Manager – bootcfg.exe
- Cabinet (CAB) Maker – makecab.exe, diantz.exe
- Calculator – calc.exe
- Character Map – charmap.exe
- Chkdsk – chkdsk.exe
- Chkntfs – chkntfs.exe
- Clipbook Viewer – clipbrd.exe
- Command Prompt – cmd.exe
- Component Services – dcomcnfg.exe
- Computer Management – compmgmt.msc
- Connection Manager Profile Installer – cmstp.exe
- Control Panel – control.exe
- Create Shared Folder – shrpubw.exe
- Date and Time Properties – timedate.cpl
- DDE Share – ddeshare.exe
- Device Manager – devmgmt.msc
- DirectX Management Tool – dxdiag.exe
- Disk Cleanup – cleanmgr.exe
- Disk Defragmenter – defrag.exe
- DiskPart – diskpart.exe
- Display Properties – desk.cpl
- Dr. Watson – drwatson.exe, drwtsn32.exe
- Driver Verifier Manager- verifier.exe
- DriverQuery – driverquery.exe
- Event Viewer – eventvwr.exe
- FAT to NTFS Conversion Utility – convert.exe
- Fax Console – fxsclnt.exe
- Fax Cover Page Editor – fxscover.exe
- File Compare (comp) – comp.exe
- File Compare (fc) – fc.exe
- File Expansion Utility – expand.exe
- File and Settings Transfer Wizard – migwiz.exe
- Folder Options – control.exe folders
- Font Viewer – fontview.exe
- Fonts Folder – control.exe fonts
- ForceDOS – forcedos.exe
- Format – format.com<%2
What is command line tools?
Command line tools are those which can be opened and used using Command Prompt. However, there is a thin line between a command line tool and a command that opens a tool. The former option works well when you need to open a tool on your Windows computer using the Run prompt. For example, if you want to open the Network Connections panel, you can enter ncpa.cpl command.
How does command line tool work?
The entire tool is already included in your system when you need to opt for a command line tool. It requires you to enter a command to open that tool or script, or program on your Windows 11/10 system. Instead of getting a user-friendly interface, you get all the things in the Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell.
Which is a widely used command line tool?
There are multiple command line tools used widely on Windows 11/10 PC. For example, chkdsk, cmd.exe, etc., are some of the most common commands or command line tools that you often use on your computer. For your information, these tools are included in Windows 10 as well as Windows 11.
Details about some are available here:
Cipher | ChkDsk | Attrib | CMD | Cleanmgr | Diskpart.
Take a look at this Windows Command Line Tools Reference Guide from Microsoft too.
Nitin Agarwal is an MVP alumni and a Pro Blogger. He was awarded as Most Valuable Professional for 3 times by Microsoft in Windows Expert — Consumer category. He is immensely inspired by Bill Gates, Steve Jobs and APJ Abdul Kalam.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, efficiency is key. Whether you’re a developer, system administrator, or power user, having the right tools at your disposal can significantly streamline your workflow. One such category of tools that has been around for decades but continues to be relevant is command line tools for Windows. These efficient command line tools provide users with the ability to interact with the operating system and automate various tasks, ultimately saving time and improving productivity.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, incorporating command line tools into your toolkit can unlock a whole new level of productivity. From file management and system configuration to network troubleshooting and software development, the possibilities are endless. In this blog post, we will explore the best command line tools for Windows, discuss their features, and provide our insights to help you choose the right tool for your needs.
What is Command Line Tool for Windows?
For those unfamiliar, a command line tool, also known as a command-line interface (CLI) tool, is a software program that allows users to interact with the computer’s operating system and perform various tasks using text-based commands. Unlike graphical user interfaces (GUIs) that rely on mouse clicks and visual elements, command line tools rely solely on text commands entered by the user.
Command line tools have been a fundamental part of computing since its early days, and Windows has its fair share of powerful and versatile command line tools. These tools provide a lightweight and efficient way to perform tasks, automate processes, and access system-level functionalities that may not be easily accessible through GUI-based applications.
Many command line tools for Windows are bundled with the operating system itself, making them readily available for use. However, there are also third-party command line tools that offer additional features and functionalities beyond what the built-in tools provide. In the next section, we will delve into the best seven command line tools for Windows that are used and trusted by professionals worldwide.
Video Tutorial:
Best 7 Command Line Tools for Windows Recommendation
1. PowerShell
PowerShell is a versatile and powerful command line tool developed by Microsoft. It provides a command-line shell and scripting language that enables system administrators and power users to automate tasks and manage Windows environments with ease. PowerShell is built on the .NET framework, which allows it to interact with various aspects of the Windows operating system.
With PowerShell, you can perform a wide range of administrative tasks, such as managing files and directories, configuring network settings, managing Windows services, and even controlling other applications through its extensive scripting capabilities. The tool also supports remote management, making it an invaluable asset in managing large-scale Windows environments.
Pros:
– Extensive scripting capabilities
– Seamless integration with other Microsoft products and services
– Excellent support for automation and task scheduling
Cons:
– Steeper learning curve compared to other command line tools
– Certain functionalities might not be available in older versions of Windows
Download Link
2. Cygwin
Cygwin is a unique command line tool that brings the power of Linux tools and utilities to the Windows environment. It provides a large collection of GNU and Open Source tools that allow developers and power users to leverage the familiar Linux command line experience on their Windows machines.
With Cygwin, you can use a wide range of command line utilities and tools, such as Bash, grep, sed, awk, and many others, which are commonly found in Linux distributions. This opens up a whole new world of possibilities for developers who work with both Windows and Linux systems, as they can utilize their existing Linux scripts and workflows seamlessly in the Windows environment.
Pros:
– Provides a wide range of Linux tools and utilities
– Seamless integration between Windows and Linux workflows
– Frequent updates and maintenance
Cons:
– Requires a separate installation and configuration
– Can be overwhelming for users without a Linux background
Download Link
3. Git Bash
Git Bash is a command line tool that is bundled with the popular version control system Git. While its primary purpose is to serve as a command line interface for Git, it also provides a Bash emulation environment for Windows, allowing users to access various Unix utilities and tools.
With Git Bash, you can use familiar Unix commands to navigate the file system, perform advanced text processing, and execute shell scripts. It provides a lightweight and efficient environment for developers, especially those already familiar with Git. Git Bash also comes equipped with other essential tools, such as SSH, which makes it an excellent option for developers working with Git repositories and remote servers.
Pros:
– Comes bundled with Git
– Provides a Bash emulation environment
– Lightweight and easy to use
Cons:
– Limited functionality beyond Git-related tasks
– Lack of advanced features compared to other command line tools
Download Link
4. Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is not just a single command line tool but an entire subsystem that brings a full-fledged Linux environment to Windows. WSL allows you to run a complete Linux distribution, such as Ubuntu or Debian, directly on your Windows machine.
The integration between Windows and Linux is seamless, allowing you to access your Windows files from the Linux environment and vice versa. WSL combines the power of both Windows and Linux, allowing users to leverage the vast array of Linux command line tools and utilities while still having access to Windows applications. This makes it an excellent choice for developers and power users who require the best of both worlds.
Pros:
– Full Linux environment with access to Linux command line tools
– Seamless integration between Windows and Linux workflows
– Direct access to Windows files from Linux environment
Cons:
– May require additional configuration and setup
– Performance can be slower compared to native Linux installations
Download Link
5. PuTTY
PuTTY is a free and open-source terminal emulator, serial console, and network file transfer application that supports various network protocols, including SSH, Telnet, SCP, and SFTP. While primarily known for its SSH client capabilities, PuTTY also includes a command line interface that allows users to interact with remote systems, execute commands, and transfer files.
With PuTTY, you can establish secure connections to remote servers and devices, making it an essential tool for system administrators and network engineers. Its lightweight nature and extensive protocol support make it a popular choice among Windows users requiring secure remote access.
Pros:
– Lightweight and fast
– Extensive network protocol support
– Excellent SSH client capabilities
Cons:
– Limited functionality beyond remote access and file transfer
– User interface might be outdated for some users
Download Link
6. Windows Command Prompt
The Windows Command Prompt, also known as cmd.exe, is the default command line tool included with Windows. While it may not be the most feature-rich or visually appealing tool on this list, it serves as a reliable and familiar option for many Windows users.
The Windows Command Prompt provides access to various system utilities and commands, allowing users to perform tasks such as file management, network diagnostics, and system configuration. While it lacks some advanced features found in other command line tools, it remains a viable option for performing basic tasks and executing simple scripts.
Pros:
– Pre-installed on all Windows systems
– Familiar and straightforward to use
– Lightweight and fast
Cons:
– Limited in terms of advanced features compared to other tools
– Outdated user interface
Download Link
7. Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL 2)
Building upon the success and features of the original Windows Subsystem for Linux, Microsoft introduced WSL 2 with significant improvements. WSL 2 utilizes a lightweight virtual machine running a full Linux kernel, resulting in improved performance and compatibility compared to the previous version.
The inclusion of a full Linux kernel allows WSL 2 to run various Linux distributions with better file system support, improved Docker container integration, and enhanced system call compatibility. This makes WSL 2 an excellent choice for developers and system administrators working with Linux-based tools and workflows on their Windows machines.
Pros:
– Improved performance compared to WSL 1
– Full Linux kernel for better compatibility and file system support
– Enhanced Docker integration
Cons:
– Requires Windows 10 version 2004 or later
– Setup and configuration might be more involved compared to other tools
Download Link
Comprehensive Comparison of Each Software
| Software | Free Trial | Price | Ease-of-Use | Value for Money |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PowerShell | No | Free | Medium | High |
| Cygwin | N/A | Free | Medium | High |
| Git Bash | N/A | Free | Easy | High |
| WSL | N/A | Free | Easy | High |
| PuTTY | N/A | Free | Easy | High |
| Windows Command Prompt | N/A | Free | Easy | High |
| WSL 2 | N/A | Free | Easy | High |
Our Thoughts on Command Line Tool for Windows
Command line tools for Windows offer a powerful way to enhance productivity, automate tasks, and access system-level functionalities. From the options mentioned above, our top recommendations are PowerShell and WSL 2.
PowerShell, being a Microsoft-developed tool, provides deep integration with various aspects of the Windows operating system and extensive scripting capabilities. It excels in managing Windows environments, automating tasks, and working seamlessly with other Microsoft products and services.
WSL 2, on the other hand, offers the best of both Windows and Linux worlds. With its ability to run a full Linux environment on Windows, it opens up endless possibilities for developers and power users to leverage Linux command line tools and workflows without leaving the familiar Windows environment.
Ultimately, the choice of command line tool depends on your specific requirements, familiarity with certain technologies, and level of comfort with command line interfaces. Each tool mentioned in this blog post has its own strengths, and it’s worth exploring them to find the one that best fits your needs.
5 FAQs about Command Line Tool for Windows
Q1: What is the benefit of using command line tools for Windows?
A: Command line tools for Windows provide various benefits, including improved productivity, the ability to automate tasks, access to system-level functionalities, and streamlined workflows for developers and system administrators.
Q2: Are command line tools only suitable for advanced users?
A: While some command line tools may have a steeper learning curve, there are options available that cater to users of all skill levels. Beginners can start with user-friendly tools like PowerShell, while advanced users can explore more powerful tools with extensive scripting capabilities.
Q3: Can I use command line tools for tasks beyond system administration?
A: Absolutely! Command line tools are not limited to system administration tasks. They can be used for a wide range of purposes, including software development, file management, network troubleshooting, and even automation of repetitive tasks.
Q4: Do I need to install additional software to use command line tools?
A: It depends on the specific tool you wish to use. Some command line tools are built-in to the Windows operating system, while others may require separate installations or downloads. Additionally, third-party tools may have dependencies that need to be installed.
Q5: Can I integrate command line tools with other applications and services?
A: Yes, command line tools can be integrated with other applications and services through scripting and automation. For example, PowerShell provides seamless integration with various Microsoft products and services, allowing you to automate tasks and workflows involving those products.
In Conclusion
Command line tools for Windows offer an efficient and powerful way to interact with the operating system, automate tasks, and improve productivity. In this blog post, we explored the best seven command line tools for Windows, including PowerShell, Cygwin, Git Bash, WSL, PuTTY, Windows Command Prompt, and WSL 2.
Each of these tools has its own unique features and capabilities, catering to different user needs and skill levels. Whether you’re a developer, system administrator, or power user, incorporating command line tools into your workflow can greatly enhance your efficiency and streamline your tasks.
Remember, the key to choosing the right command line tool for your needs lies in understanding your requirements, evaluating the features and capabilities of each tool, and experimenting with different options to find the tool that best fits your workflow.
So, why wait? Dive into the world of command line tools for Windows and unlock a whole new level of productivity and efficiency in your daily tasks!
Stay organized with collections
Save and categorize content based on your preferences.
As devs who spend the majority of our time coding on OSX and Linux, we were curious what a modern command-line setup might look like on Windows.
A StackOverflow developer survey reminded us that there are more devs using Windows than any other OS so we were curious if the tooling there was on par with what we were used to in *nix land.
After spending some time evaluating the landscape of Windows CLI tooling, we settled on a set of tools we think gets us 95% of the way there.
At the end of the day, we landed on a combination of:
- PowerShell
- ConEmu
- PSReadLine
- PSGet
- Chocolatey
- Babun (optional)
See below for some more notes on what these different pieces of machinery give you.
PowerShell (shell)
- Significantly closer to a real ‘shell’ than cmd.exe, offering us a powerful scripting environment for task automation. It’s fair to compare it to Bash or zsh.
- Autocompletes directory and filenames
- Autocompletes application names
- Has integrated aliases and commands (called cmdlets — e.g
Select-Stringis likegrep,Invoke-Elevatedis likesudo,Sort-Objectis likesort,Get-Processlists all active processes). If moving from another shell to PS,Set-Aliaslets you map aliases you’re used to to Windows equivalents. For example:Set-Alias server python -m http.server 8000launches a Python server when theserveralias is used. - Aliases can be persisted in a PowerShell profile
- Supports piping, like Unix. Unlike Unix, it pipes objects rather than text streams. This requires getting used to but avoids reparsing when you want to get out a property.
- Supports modules. PSGet is a package manager for PowerShell allowing you to easily extend it.
- Optionally consider Posh-Git, a PowerShell script for git to gain contextual tab-completion.
If you’re interested in trivia, here’s an answer to why MS created PowerShell from the lead architect.
PSReadLine (console editing helpers)
- Significantly improves the console editing experience
- Syntax highlighting whenever you start typing commands. Clearly indicates syntax errors with a red «>» character.
- Highly customizable key bindings
- Bash-style autocompletion
- Bash/zsh interactive history search (Ctrl + R). Powerful command history traversal too. Easily view previous multi-line commands using arrow keys rather than just the last line of the command.
- Proper support for copy/paste/cut (Ctrl+C/X/V should all work just fine)
- Good support for undo/redo
- History saving is automatic
Alternatively, you can use Clink, which has a similar set of features but wasn’t strictly written for PowerShell.
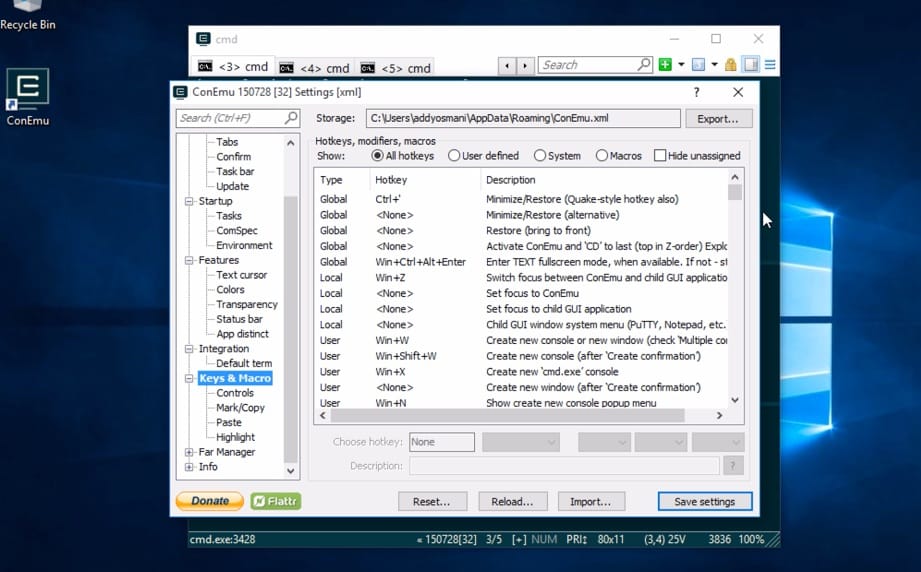
ConEmu (console host)
- An advanced console emulator where you can run your shell of choice.
- Supports opening multiple terminals in different tabs. Makes it trivial to launch terminals as different users.
- Extremely customizable — everything from shortcuts to text selection and status bar colors can be changed.
- Supports a split-screen view
- Simple GUI apps can be run in tabs
- Support for Windows 7+ Jump Lists
- Supports smooth window resizing
- Windows font anti-aliasing
- Starting tabs can be fully customized to start in a particular directory
- Intelligent copy/paste
Some folks still enjoy using Console2 and Scott Hanselman has a blog post written about it.
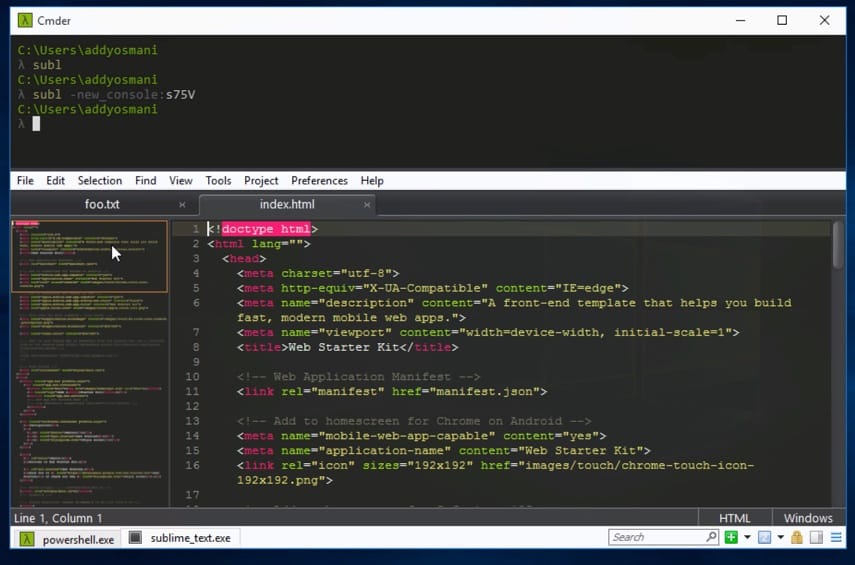
Cmder
Worth a passing note is Cmder — a console emulation package that combines ConEmu, Clink and msysgit — giving you Git helpers. Cmder basically gives you a prettier experience to ConEmu by default via it’s Monokai color scheme.
Cmder also includes some other little benefits, like integration with GUI apps such as Sublime Text.
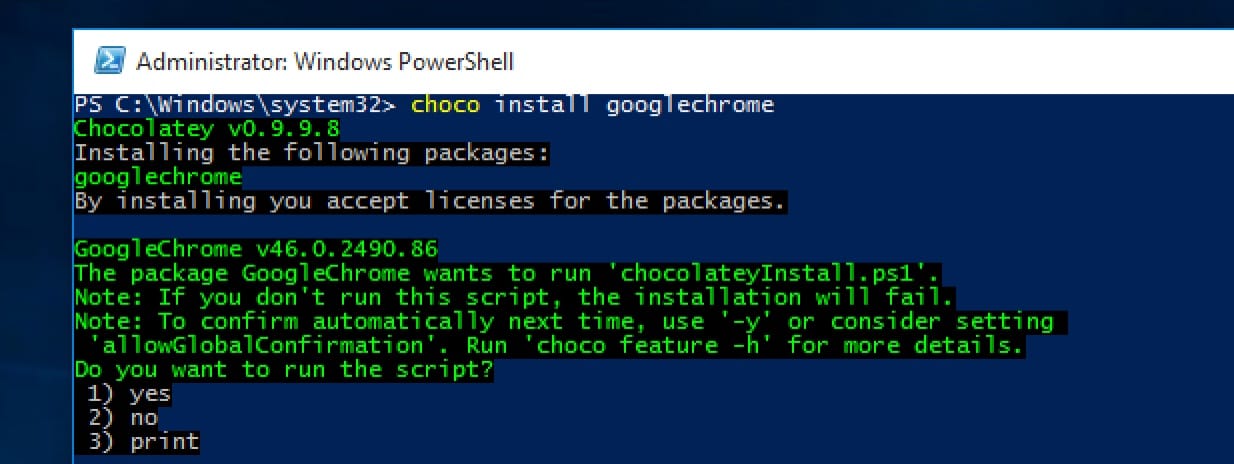
Chocolatey (package manager)
- Basically homebrew for Windows, allowing you to pull in your favorite Windows apps conveniently. There are currently ~3K packages available that can be updated using Chocolatey directly.
- Differs from Nuget. NuGet is for development libraries. Chocolatey is a binary machine package manager and is built on NuGet infrastructure.
- Offers effectively silent builds
You may also be interested in learning about OneGet, Microsoft’s package manager..manager, which should work with Chocolatey under Windows 10.
Babun (Cygwin preconfigured)
- Cygwin (the Linux-like env for Windows) minus some of the historically known quirks. The overall setup is significantly more straight-forward using the Babun installer. If you’re particularly experienced with Unix and would prefer to avoid learning PowerShell, cygwin/Babun are worth considering.
- Includes a package manager called
pact(a little similar tobrew) similar toapt-get. This is a big deal as you currently have to re-run the Cygwin installer when adding packages vs. just using pact. - Vim pre-installed and pre-configured
- Integrated support for oh-my-zsh
- Auto-updates
Further Reading
- Windows command-line experience comparisons
- Windows editors and shells
- Windows command-prompt Redux
- Scott Hanselman’s Ultimate Developer and Power Users Tool List for Windows
Command line might not be the most visually appealing or the simplest feature of Windows 10, but it’s without a doubt the most powerful one. Although Command Prompt is one powerful tool, it still lacks certain features such as tabs.
If you are an average user, you probably don’t use command line that often, but if you are an advanced user, or a developer, you probably use Command Prompt from time to time.
As previously mentioned, one of the biggest drawbacks is that there is no multi tab Command Prompt on Windows 10. However, if you need this feature, we have gathered the best command line tools with tabbed terminal for Windows in this guide.
Console2 – Lightweight tool

Console2 is a simple and lightweight Command Prompt alternative for Windows 10. This tool has been one of the best Command Prompt alternatives for years and even though it hasn’t received any updates recently, it’s still an outstanding tool.
Console2 comes with support for tabbed interface which allows you to simultaneously run different command lines. If you want to differentiate your tabs, you can assign a different name to each tab in order to organize your tabs more easily.
Console2 comes with all sorts of customization options, and it allows you to set the transparency of your console window. One thing we didn’t like about this tool is the lack of support for standard copy and paste shortcuts.
Besides that, Console2 sounds like an amazing alternative to Command Prompt, and if you’re looking for a command line tool that supports tabs, Console2 is one of the tools that you should check out.
⇒ Get Console2
- 6 Ways to Fix the Error Code 42 on Disney Plus
- Start Chrome Incognito From The Command Line [How to]
- How to Start Edge Incognito Using The Command Line
- Celtx Free Download for Windows 10: 2 Safe Methods
PowerCmd – Powerful alternative

PowerCmd is a powerful Command Prompt alternative, but unlike our previous entry, PowerCmd isn’t available for free. However, you can try it free of charge.
Just like the previous tool we mentioned, PowerCmd fully supports a tabbed interface, but it also allows you to organize command line windows by placing them side by side, allowing you to have up to 4 windows available one by another.
Even if you place command line windows one by another, you can still open more tabs if you need to. Another feature worth mentioning is the shell integration.
This means that you can simply right-click any folder, choose the PowerCmd option, and you’ll open a new command line window by using that folder as a currently opened directory.
This feature is extremely useful if you don’t want to enter folder locations manually and if you need quick and instant access to a specific folder.
If you prefer to enter file and folder names manually, PowerCmd will give you suggestions as you type, so you can just select them from the menu.
It’s worth mentioning that this tool also supports Windows-style text editing, thus allowing you to select, cut, copy, and paste into the command line similarly to any text document while using familiar shortcuts.
Another feature we need to mention is the search toolbar that allows you to quickly search for any output in the command line. In fact, PowerCmd will highlight each word from your search query in a different color, thus making it easier for you to find it.
In order to better organize your command line, there’s support for bookmarks, and you can easily navigate between different bookmarks with a single hotkey. In addition, you can also see and search for your input history for any previously used commands.
Lastly, if you heavily use the command line, you’ll be pleased to know that PowerCmd allows you to automatically save the console output log, so you can examine it at any time, even if your PC or application crashes.
⇒ Get PowerCmd
ColorConsole – Small and simple tool

ColorConsole is a rather small and simple command line tool, and although it lacks some advanced features, it fully supports a tabbed interface. In addition to the tabbed interface, it allows you to display command lines side by side.
It’s worth mentioning that this tool supports standard editing shortcuts, so you can easily select, copy and paste in and out of the command line.
We have to mention that ColorConsole comes with a rather simplistic search feature, but at the same time, it allows you to manually select and highlight output in the command line, so you can easily find it when needed.
Another feature is the ability to export your output as HTML or RTF, which some users might find helpful. ColorConsole might not be the most powerful command line tool on this list, but it’s certainly the lightest.
⇒ Get ColorConsole
MobaXterm – Wide range of features

MobaXerm is another advanced command line tool that supports a wide range of features, and it comes in both paid and free versions. It’s worth mentioning that the free version has certain limitations, but for the most part, it should be enough for your needs.
This tool comes with support for Unix commands, and it allows you to launch remote sessions such as SSH, Telnet, FTP, VNC, and many others. Each session is listed in the sidebar on the left, so you can easily create new sessions.
MobaXterm comes with a graphical SFTP browser, so you can easily drag and drop files when you’re using an SFTP connection. In addition, you can also display remote applications directly on your PC while running SSH, TELNET, or RLOGIN/RSH sessions.
If you’re connecting to a remote server using SSH, you can edit remote files directly from MobaXterm by using the built-in MobaTextEditor.
This tool also allows you to remotely control Windows desktop computers by using the RDP protocol. Of course, there’s support for remote Unix desktops by using XDMCP.
MobaXterm is a command line tool with advanced features intended for developers and network administrators, so if you’re just a regular user, you will probably feel overwhelmed by the list of features that this tool offers.
⇒ Get MobaXterm
Terminal Wings – Minimalistic interface

Terminal Wings comes with a minimalistic and visually appealing interface, and just like all the predecessors on this list, it supports a tabbed interface.
This application is simple to use, and it allows you to easily select, copy and paste any input from the command line.
Terminal Wings allows you to set different profiles, and each profile can be customized with different colors, transparency, default directory, or commands that will be executed when you open that profile.
As we mentioned, this tool doesn’t have any advanced features, but if you’re looking for a command line tool with a simple tabbed interface, Terminal Wings might be perfect for you.
⇒ Get Terminal Wings
ConEmu – Free version

ConEmu is another free command line tool with a tabbed interface. This tool comes with a simple user interface, which makes it perfect for basic users.
Despite its simple appearance, ConEmu has a wide range of features hidden in its settings. You can change the visual appearance of the command line, set predefined code to run, and much more.
ConEmu is perfect for both basic and advanced users alike, but if you want to use those advanced features, you’ll have to spend some time in ConEmu’s settings panel.
⇒ Get ConEmu
PowerShell ISE
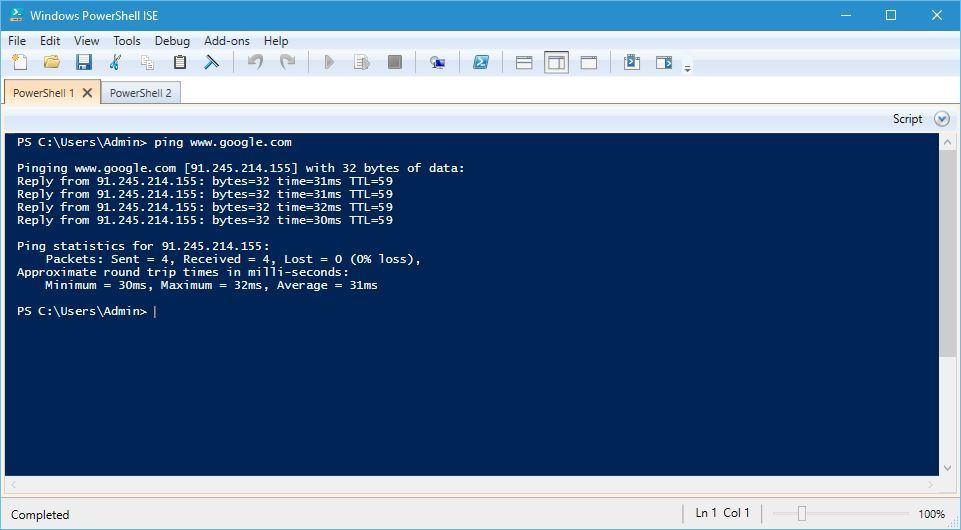
If you want to use the tabbed terminal command line on Windows 10, there’s no need to download alternative tools from the Internet since you can use Microsoft’s PowerShell ISE.
This tool is integrated into Windows 10, and it comes with many features, one of them being a tabbed interface.
Of course, there’s support for a wide range of PowerShell commands, but if you’re not too familiar with PowerShell commands, there’s a list of commands along with additional details about each command available right from the PowerShell ISE.
Although Command Prompt doesn’t support tabs, Windows 10 comes with its own alternative in the form of PowerShell ISE. If you’re looking for a third-party alternative, PowerCmd offers a wide range of features along with a user-friendly interface.
Unfortunately, PowerCmd isn’t available for free, but if you’re looking for a free tabbed command line tool for Windows 10, ConEmu might just be what you need.
EECS 280 Tutorials
The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) runs an Ubuntu Linux guest virtual machine on your Windows host machine.
Upgrade Windows
We recommend Windows 11. Windows 10 version 2004 build 19041 and higher will also work. Here’s how to check your Windows version.
Free Windows upgrades are available for UM students via OnTheHub. If you have an older Windows machine and are not able to upgrade, please reach out to course instructors for assistance.
Pitfall: Make sure Windows Update is enabled and your machine is up-to-date. Search for “Windows Update” in the start menu.
Install WSL
Start PowerShell and run it as administrator. Search for PowerShell in the start menu, then right-click and select “Run as administrator”.
PowerShell is a command-line interface for Windows. Its command prompt ends with a > (e.g. C:\WINDOWS\system32>). To follow the steps below, type the commands that appear after the > and hit enter.
Check if WSL is already installed by running the command wsl -l -v. If you see a list like below, WSL is already installed.
C:\WINDOWS\system32> wsl -l -v
NAME STATE VERSION
* Ubuntu-24.04 Running 2
If the VERSION is 1, you must upgrade to WSL 2.
If you already have an Ubuntu distribution with VERSION 2, skip to Setup Ubuntu below.
Otherwise, WSL is not installed and you’ll see help text similar to the following. (This is expected for most students.)
C:\WINDOWS\system32> wsl -l -v
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Usage: wsl.exe [Argument]
...
Install WSL. We recommend the most recent Ubuntu LTS version from the Microsoft App Store, currently Ubuntu 24.04.
C:\WINDOWS\system32> wsl --install -d Ubuntu-24.04
Pitfall: If you get an error from wsl --install, see the Troubleshooting section below.
Restart your computer.
Start PowerShell as administrator, and check that WSL Ubuntu is now installed with version 2.
C:\WINDOWS\system32> wsl -l -v
NAME STATE VERSION
* Ubuntu-24.04 Running 2
Setup Ubuntu
From the previous section, you have installed WSL and an Ubuntu Linux distribution. You’ll do most C++ development in Ubuntu rather than Windows. Let’s get it set up.
Start an Ubuntu Bash shell. Bash is a command-line interface for Linux. Search for “Ubuntu” (or “Ubuntu 24.04 LTS”) or “bash” in the start menu.
The bash command prompt ends with a $. To follow the steps below, type commands that appear after the $ and hit enter.
First time: create account
The first time you open Ubuntu, you will be prompted to create a Linux username and password. Follow the prompts to create one.
- Choose a username that is all lowercase characters (could be your uniqname).
- While typing your password, the characters are not shown. This is fine.
- You can press Enter to skip fields other than username and password (e.g. “room number”).
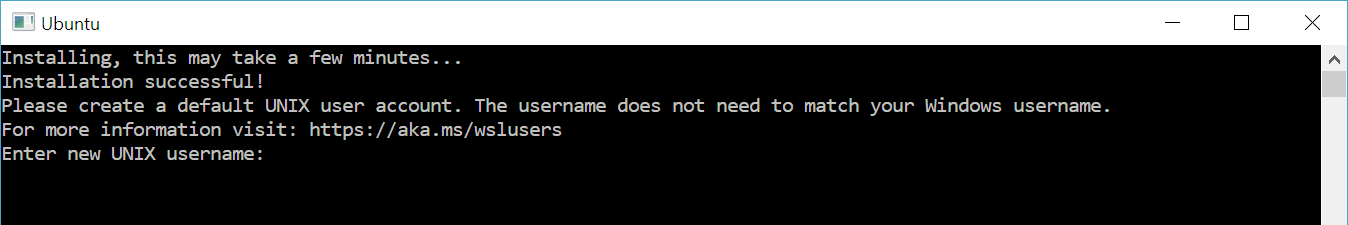
Double check that your user has been created.
$ whoami
awdeorio # this should NOT say root
Pitfall: If you are signed in as root, something has gone wrong.
$ whoami
root # SOMEthiNG IS WRONG
This can happen, for example, if you accidentally closed the terminal window before creating a user account.
We recommend you completely reinstall Ubuntu. (Note this will delete all of the data associated with Ubuntu. If you’ve just installed it, that’s fine.)
Open PowerShell and run it as administrator. Run the commands below. You’ll be prompted to create a user account.
C:\WINDOWS\system32> wsl --unregister Ubuntu-24.04
Unregistering.
The operation completed successfully.
C:\WINDOWS\system32> wsl --install -d Ubuntu-24.04
Ubuntu 24.04 LTS is already installed.
Launching Ubuntu 24.04 LTS...
Installing, this may take a few minutes...
Please create a default UNIX user account. The username does not need to match your Windows username.
For more information visit: https://aka.ms/wslusers
Enter a new UNIX username:
Install CLI tools
From an Ubuntu bash terminal, use the apt package manager to install a few command line programs.
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install g++ make rsync wget git ssh gdb python3 tree
Home Directory
You’ll generally want to store your coding projects in the Linux filesystem, which is separate from your Windows filesystem.
Open an Ubuntu bash terminal and run cd ~. This will take you to your Ubuntu home directory. Running pwd afterward confirms the location. (Your username will be different.)
$ cd ~
$ pwd
/home/jjuett
Create an EECS 280 folder by running mkdir ~/eecs280. Running ls afterward confirms the folder has been created.
$ mkdir ~/eecs280
$ ls
eecs280
We highly recommend you store all coding work for EECS 280 projects and labs here.
Pitfall: Avoid paths that contain spaces. Spaces cause problems with some command line tools.
| Bad Example | Good Example |
|---|---|
EECS 280/ |
eecs280/ |
Project 1 Stats/ |
p1-stats/ |
Pitfall: Linux (Ubuntu) has a separate home directory. Storing code in your Windows home directory can cause slowdowns.
$ pwd
/home/awdeorio ... # Good, Linux home
/c/mnt/Users/awdeorio ... # Bad, Windows home
Access via File Explorer
Even though the files are stored in the Linux filesystem, you can still access them from the Windows file explorer. Run explorer.exe . to open an explorer window in bash’s current directory (Note the extra . at the end, which means “current directory”.)
Right-click on the eecs280 folder and select “Pin to Quick Access”. This adds a shortcut to the left sidebar, which is useful for e.g. finding and submitting your files to the autograder via a web browser.
You can also open a bash terminal in the current directory of your file explorer. Click the blank area to the right of where the directory path is shown. Then, type “bash” (replacing the text already there) and hit enter.
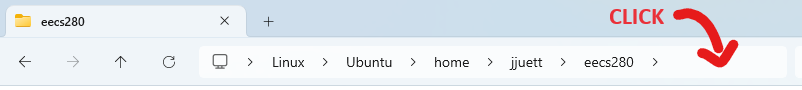

This will open a new bash terminal in the same directory as the file explorer.
CLI Tutorial
Now would be a great time to take a look at our CLI Tutorial.
Pro-tips
Accessing Windows files from Linux
To access Windows files from Linux, navigate to /mnt/c/.
For example, here's how to access your Windows Desktop. Your username will be different.
```console
$ cd /mnt/c/Users
$ ls
'All Users' 'Default User' defaultuser0 awdeorio Default Public defaultuser100000 desktop.ini
$ cd awdeorio
$ ls
... Desktop Downloads ...
$ cd Desktop
Copy/Paste in Terminal
Copy/Paste functionality in your bash terminal may be enabled by default with the usual ctrl + c and ctrl + v keyboard shortcuts.
Or, try ctrl + shift + c and ctrl + shift + v.
If these do not work, right click on the terminal window header. If you see option for “Settings”, go to “Settings” -> “Actions” and add your desired keybindings for copy/paste. If you see an option for “Properties”, go to “Properties” -> “Options” and ensure “Use Ctrl+Shift+C/V as Copy/Paste” box is checked.
Troubleshooting
Enable Virtualization
WSL2 requires virtualization support. Follow the steps below to ensure it is enabled.
Step 1
Launch the task manager by pressing ctrl + shift + esc. Click on the “Performance” tab.
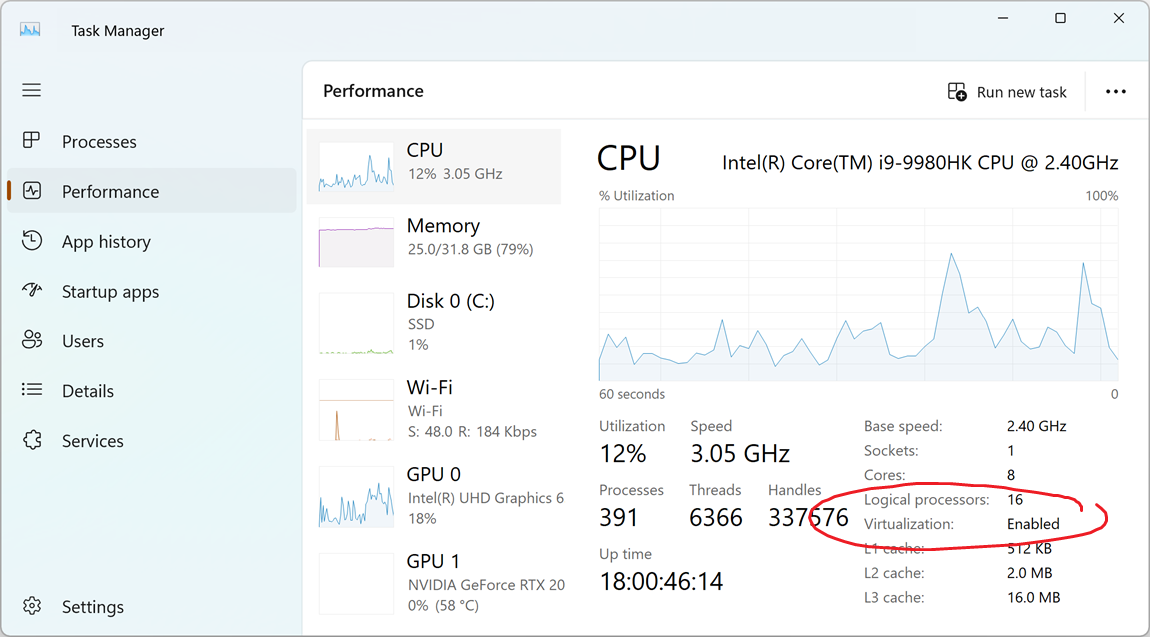
If you see “Virtualization: Enabled”, proceed to step 2. If you don’t see “Virtualization” at all, your computer may not support WSL. (This should only be the case for very old machines.)
If you see “Virtualization: Disabled”, you need to enable virtualization in BIOS settings. The method for doing this varies depending on your computer’s manufacturer, but instructions are generally available online, e.g. here. Once you have restarted into BIOS, navigate the options with your keyboard to find and enable virtualization. Save your changes and restart your computer.
Step 2
Once virtualization is enabled, ensure the “Virtual Machine Platform” feature is enabled in Windows. Search for “Turn Windows features on or off” in the start menu. Scroll down and ensure that “Virtual Machine Platform” is checked. If it is not, check the box and click “OK”. You may be asked to restart your computer.
Attempt to install WSL again, following the instructions at the top of this guide.
Enable Windows Subsystem for Linux
If you’re running commands like wsl -l -v or wsl --install -d Ubuntu-24.04, but it just prints out a generic help message, you may need to enable the Windows Subsystem for Linux feature. Search for “Turn Windows features on or off” in the start menu. Scroll down and ensure that “Windows Subsystem for Linux” is checked. If it is not, check the box and click “OK”. You may be asked to restart your computer.
Microsoft Troubleshooting
Microsoft maintains an extensive troubleshooting page for WSL installation. If you’re getting a specific error code/message, you may be able to match it with a resolution here.
Forgot Password
If you forgot you WSL password, follow the steps here to reset it. Scroll down to the part beginnning with “If you forgot the password for yoru Linux distribution:”.
Manual Installation
If you are running an older version of Windows 10 and unable to update to build 19041 or higher, you may be able to perform a manual installation. Use this only as a last resort option.
Acknowledgments
Original document written by Andrew DeOrio awdeorio@umich.edu.
This document is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 License. You’re free to copy and share this document, but not to sell it. You may not share source code provided with this document.
