From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In computer networking a work group is a collection of computers connected on a LAN that share the common resources and responsibilities. Workgroup is Microsoft’s term for a peer-to-peer local area network. Computers running Microsoft operating systems in the same work group may share files, printers, or Internet connection.[1] Work group contrasts with a domain, in which computers rely on centralized authentication.
- Windows for Workgroups – the earliest version of Windows to allow a work group
- Windows HomeGroup – a feature introduced in Windows 7 and later removed in Windows 10 (Version 1803) that allows work groups to share contents more easily
- Browser service – the service enabled ‘browsing’ all the resources in work groups
- Peer Name Resolution Protocol (PNRP) — IPv6-based dynamic name publication and resolution
- ^ «What Is a Workgroup in Computer Networking?». compnetworking.about.com. Archived from the original on 2014-04-18. Retrieved 2014-04-17.
- Workgroup Server Protocol Program (WSPP)
Низачем не нужна. Просто наследие. Была в 1992 году такая Windows 3.11 для рабочих групп. Потом Windows 95, Windows 95 OSR2, Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, Windows Millenium…
Вот это вот всё…
Идея была в том, что в сети есть сто ПК, ты их распределяешь на десять рабочих групп. Пользователь тыкает на ярлык Network neighborhood (Сетевое окружение) и видит в первую очередь компьютеры из своей рабочей группы. А уж если пользователю приспичит, тогда он дополнительными кликами может увидеть другие рабочие группы. Т.е. примитивная иерархическая структура в сети. Условно «рабочая группа» — это отдел в офисе, и 99% общения на работе происходит в пределах своего отдела.
Сейчаc не актуально, ибо уже не принято расшаривать папки на ПК пользователей, а вместо этого централизовано используется файловый сервер.

Authenticating users in a computer network.
Employees in any organization, big or small, need to log in to their computers at the start of their work day. Logging in gives them access to shared files, folders, printers, critical applications related to work, as well as the internet. Organizations need to authenticate and verify the identity of each user before they gain access to these resources—but how?
The method you use to authenticate and verify users depends on the type of computer network setup in your work environment.
There are two major types of network setups:
- Workgroup environment: This environment is usually found in small offices and home offices.
- Active Directory environment: Larger offices (usually with more than 15 unique users) use Active Directory.
Here we will look at what a workgroup is, how to set one up, and how authentication is managed in a workgroup.
What is a Windows workgroup?
According to Techopedia, a workgroup is a peer-to-peer network setup using Microsoft Windows operating system. It’s a group of computers on a local area network that share common resources and responsibilities. You can easily create a workgroup by connecting two or more PCs without going through a separate server computer.
In a workgroup, each computer on the network is physically connected to a router or switch. Each computer that’s a member of a workgroup can access shared resources in the network, like files or printers, or share their own resources with the group. While a workgroup is a group of computers that are connected to a network, it’s not the same as a network. You can connect a computer to your network without making it a member of a specific workgroup. You can even have multiple workgroups in the same network.
How does a workgroup in a small office or home office work?
Let’s take an example of a small three-person office. John, Amy, and Mark are this small office’s three employees. Every computer on this network will have its own database of usernames and passwords.
Essentially, a workgroup is “every man for themselves,” and there is no central control. Every PC in a workgroup is a server and a client at the same time. A PC will act as a client when it seeks to access a resource in another PC. The PC which needs to provide the access to its resources will act as a server during the process of authentication and authorization.
For instance, if Amy wants to use Mark’s computer, her username and password need to be created on Mark’s computer. And if Mark wants to use Amy’s computer, his username and password need to be created on her computer. If both Amy and Mark want to use John’s computer, both of their usernames and passwords need to be created on John’s computer.
How to set up a Windows 10 workgroup?
Once you’ve set up your network in your small office, you can follow the steps below to connect all your devices to a single Windows workgroup:
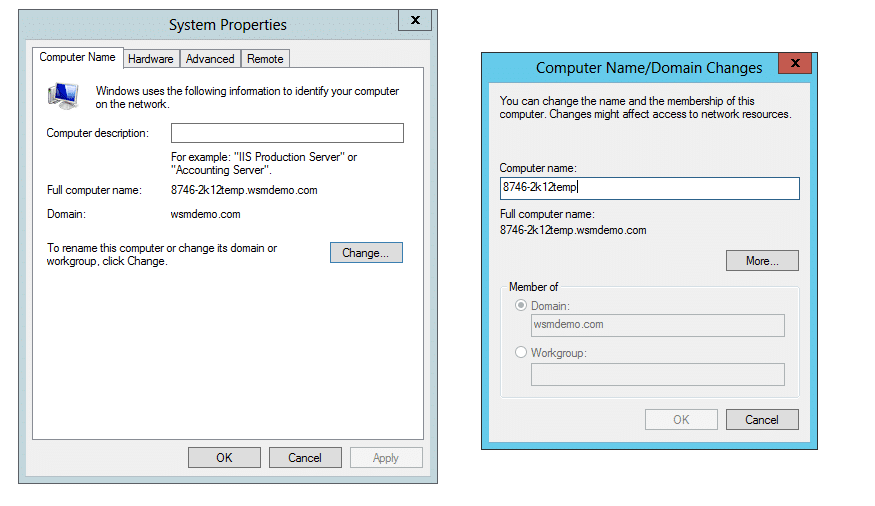
- Navigate to the Control Panel > All Control Panel Items > System. You will get to view basic information about your computer screen.
- Click on Change Settings under Computer name, domain, and workgroup settings to arrive at the System properties pop-up.
- Click on Change to rename this computer.
- Under the Computer Name/Domain Changes pop-up, you’ll have the option to join the workgroup of your choice. Ensure that all the devices you want in a particular workgroup are joined to that workgroup. In this case, the workgroup is named My Workgroup. The following image shows where you can enter the name of the workgroup you want to join.
How do I share files and folders in a workgroup?
Now that you’ve set up a workgroup for your small office, let’s talk about how to share files and folders among different users in a Windows 10 workgroup. Let’s assume that you want to share the My Games folder under Documents.
Follow the steps below to share this folder:
- Right-click My Games.
- Click Properties.
- Click the Sharing tab.
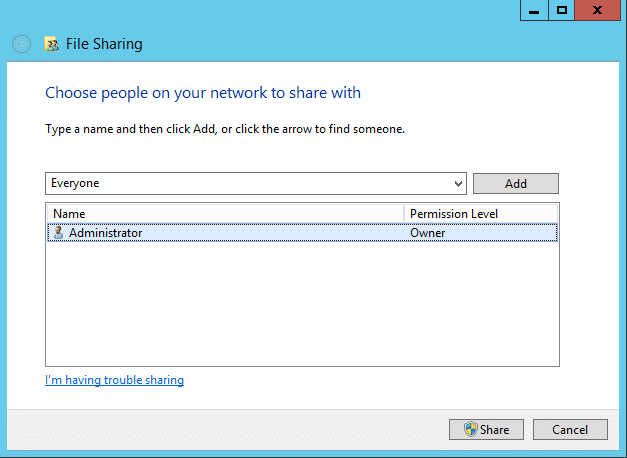
- Click on Share
- Choose the people you want to share the folder with, and select the permission level. The following image shows the screen where you can grant access to other users in the workgroup.
- While granting access to other users, you’ll need to create their usernames and passwords on your own computer. This is the only way these users can be authenticated.
Workgroup challenges for large organizations and the need for Active Directory.
Workgroups are not suitable for larger work environments for two main reasons:
- They don’t scale well: If the network is small, it’s fairly easy to control a workgroup. However, imagine a scenario in which there are more than 15 computers. It would be time-consuming and tedious to create usernames and passwords by visiting each computer. Now imagine a corporation with more than 5,000 computers. It would be next to impossible to manage user accounts through a workgroup.
- Passwords do not sync automatically: If a user has changed their password on their own computer, the change won’t be reflected in the other computers they may try to access on the network. When prompted to enter their username and password when trying to access other computers, they’ll then need to input the old username and password to gain access.
Workgroups are great for smaller networks, but they aren’t efficient for larger ones. For large networks, it’s vital to keep all the usernames and passwords in sync with each other. To do this, you need a centralized database that manages all usernames and passwords, called Active Directory.
Note: A client PC cannot belong to a workgroup and a domain at the same time. If a client joins a domain, its workgroup membership will be automatically removed. The reverse is also true.
Workgroup vs domain
Workgroups are great for small office networks with 15 or less computers. However, they aren’t ideal for larger companies with hundreds or thousands of users, as it will become difficult to access files and folders of one computer with another computer. Simply put, AD workgroups are fine for small offices, but they are not efficient in scaling to big organizations.
So, for big environments, we need to set up a client-server network environment. In Windows, this is achieved by setting up domains. The domain set up ensures better security as we can give varying degrees of permissions for different users or groups of users. Furthermore, we can deploy company-wide policies for easier administration in a domain than a workgroup.
How to change workgroup in Windows 10?
To change a workgroup in Windows 10 and make your computer a part of another workgroup, you can follow these steps:
- Right-click on Start, and click on System.
- Under Computer name, domain, and workgroup settings, select Change Settings
- Under the Computer Name tab in the System Properties window, click on the Change button.
- Under the Member Of tab, change the Workgroup name to the new one.
- Click on OK to confirm your action.
- Reboot your device when prompted.
You computer should now be part of the new workgroup.
A Workgroup (in Windows Networks) is a logical grouping of networked computers that can share resources with each other. These resources might include files, printers, and other devices. A workgroup is often called a peer-to-peer network because all computers in a workgroup are equally important. In other words, no single computer “runs the network,” as in a domain-based model.
How Workgroup Works
Each computer in a workgroup handles security separately using its own local security database, which tracks who can log on to the computer and what rights or permissions users have to resources on the computer. A user who wants to log on to a computer must have an account in that computer’s local security database. A user with an account on one computer doesn’t necessarily have any permissions or rights to resources on other computers.
If a computer in a workgroup is used to provide file, print, or other resources to other computers in the workgroup, that computer is generally called a peer server or a stand-alone server. Because security is local to each computer in a workgroup, a peer server can share resources using share-level security only, which uses passwords to protect access to each resource. Users who know this password can access the resources at the level of access with which it is shared (such as read-only access, full access, and so on).
Workgroups are simple to implement but hard to maintain. Administrators must create accounts on each computer for the users who need access to them. As a result, workgroups are generally used for small networks of 10 or fewer computers in which security and centralized administration are not an issue.
HomeGroup removed from Windows 10
HomeGroup has been removed from Windows 10 (Version 1803). However, even though it has been removed, you can still share printers and files by using features that are built into Windows 10.
- To learn how to share printers in Windows 10, see Share your network printer.
- To learn how to share files, see Share files in File Explorer.
Here’s more info about what’s changed and what hasn’t.
What’s changed?
After you update your PC to Windows 10 (Version 1803):
- HomeGroup won’t appear in File Explorer.
- HomeGroup won’t appear in Control Panel, which means that you can’t create, join, or leave a homegroup.
- HomeGroup won’t appear on the Troubleshoot screen when you go to Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot .
- You won’t be able to share new files and printers using HomeGroup.
The HomeGroup (view) and HomeGroup (view and edit) options still appear in Windows 10 (Version 1803 or later) when you right-click a folder in File Explorer and then point to Give access to. However, neither option does anything. To share a file or folder, select Specific people from the same shortcut menu instead.
What hasn’t changed?
Any folders, files, or printers that you previously shared using HomeGroup will continue to be shared. This means that:
- Shared network folders will still be available. You can open them in File Explorer by typing the name of the PC and the shared folder name in this format: \\homePC\SharedFolderName
- If one user account was set up on a PC for sharing, you can continue using that one account for sharing.
- You can still get to any shared printers through the Print dialog box.
Все способы:
- Шаг 1: Активация и назначение имени рабочей группе
- Шаг 2: Настройка общего доступа
- Шаг 3: Открытие доступа к папкам и файлам
- Вопросы и ответы: 0
Поскольку рабочая группа представляет собой набор сетевых протоколов для взаимодействия устройств в одной сети, название должно совпадать на всех компьютерах, поэтому Шаг 1 необходимо выполнить на всех машинах.
Шаг 1: Активация и назначение имени рабочей группе
Для начала стоит проверить, правильные ли настройки у рабочей группы на всех компьютерах под управлением Windows 10. По умолчанию система задает имя «WORKGROUP», но иногда, вследствие различных действий или вмешательства стороннего ПО, оно оказывается изменено. Также важно активировать саму рабочую группу в настройках:
- Нажмите на клавиши «Win + R» — отобразится диалоговое окно «Выполнить», где в текстовом поле нужно ввести команду
sysdm.cplи нажать на кнопку «ОК» или клавишу «Enter». - На вкладке «Имя компьютера» кликните по кнопке «Изменить».
- В открывшемся окне можно задать имя конкретного компьютера (название у всех устройств должно различаться), а также имя рабочей группы. Если нужно, сначала обязательно активируйте ее, затем введите название или оставьте то, которое выставлено по умолчанию («WORKGROUP»).


Название не должно состоять из одних цифр, а также недопустимы символы, которые запрещены в использовании имен файлов в Windows. Кроме того, если имя состоит из двух или более слов, то между ними не должно быть пробелов. Вместо этого можно разделить их нижним подчеркиванием.
Проверьте имя рабочей группы на всех компьютерах, находящихся в локальной сети, — оно должно быть одинаковым. Если на каком-либо устройстве оно не совпадает, исправьте на то, что установлено на главной машине. Чтобы изменения вступили в силу, необходимо перезагрузить компьютер.
Существует еще один способ переименования рабочей группы, который предполагает использование всего одной команды в консоли «Командная строка», запущенной с расширенными правами.
- Откройте «Командную строку» (или «Windows PowerShell») от имени администратора – можно воспользоваться для этого строкой системного поиска.
- Скопируйте команду
wmic computersystem where name="%computername%" call joindomainorworkgroup name="name_group"и вставьте ее в окно используемой консоли, а для выполнения нажмите на клавишу «Enter». Под сочетанием «name_group» из нашего примера подразумевается ваше имя рабочей группы на латинице с учетом всех рекомендаций о названиях выше.

Те же самые действия понадобится проделать на всех компьютерах, чтобы изменить имя рабочей группы для каждого из них. Но проверить, подключено ли устройство к ней, а не к домену, придется через окно «Свойства системы» (первая инструкция из этого шага).
Шаг 2: Настройка общего доступа
Далее стоит проверить настройки общего доступа, чтобы функции рабочей группы смогли полноценно работать в системе. Следует открыть устройства для обнаружения в локальной сети, соответственно, инструкция ниже актуальна для всех связанных компьютеров:
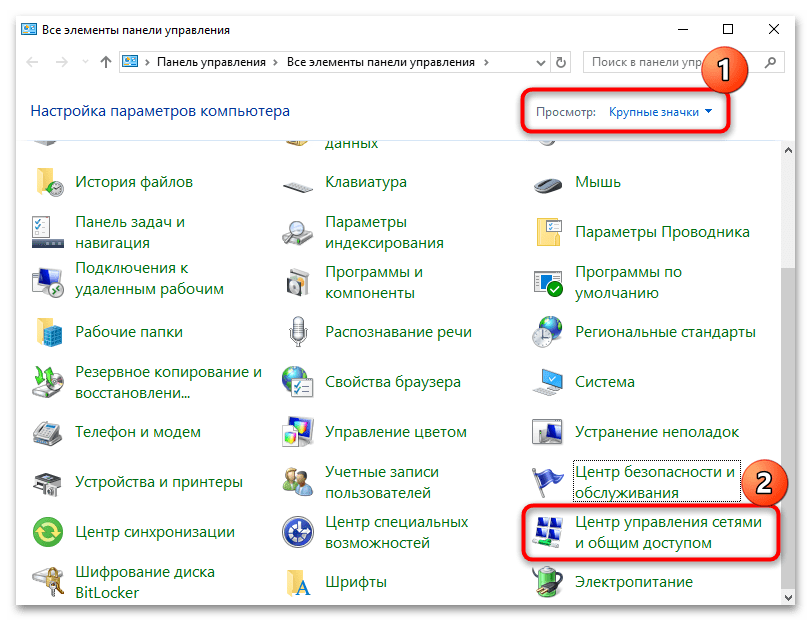
- Запустите стандартное приложение «Панель управления», отыскав его, например, с помощью системного поиска.
- Просмотр разделов выставьте как значки, затем переходите в раздел «Центр управления сетями и общим доступом».
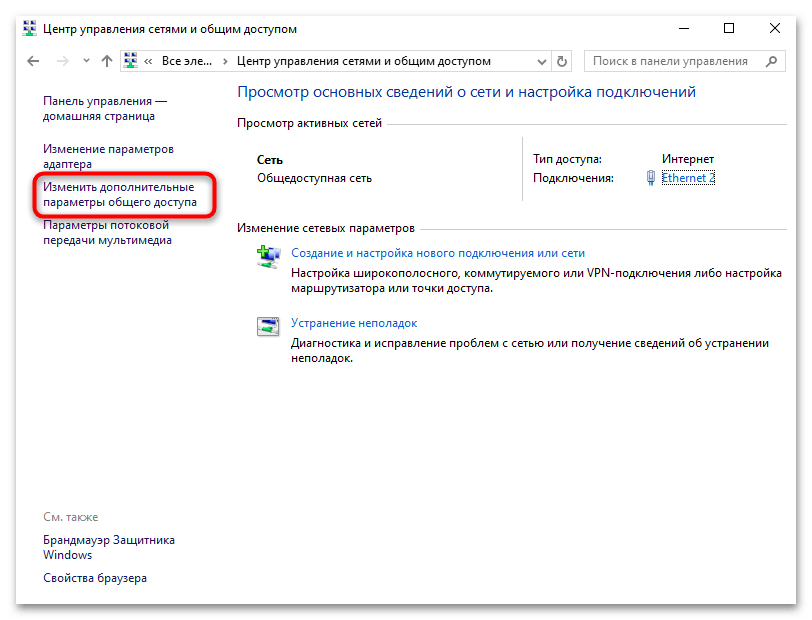
- На панели слева кликните по строке «Изменить дополнительные параметры общего доступа».
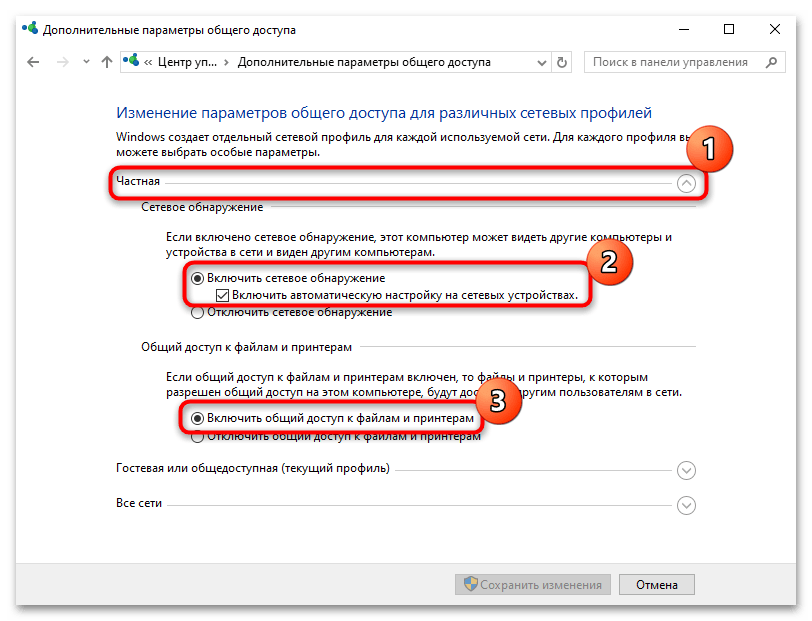
- Разверните меню «Частная» и включите для профиля сетевое обнаружение и общий доступ к файлам и принтерам. Также лучше активировать дополнительную опцию – «Включить автоматическую настройку на сетевых устройствах».
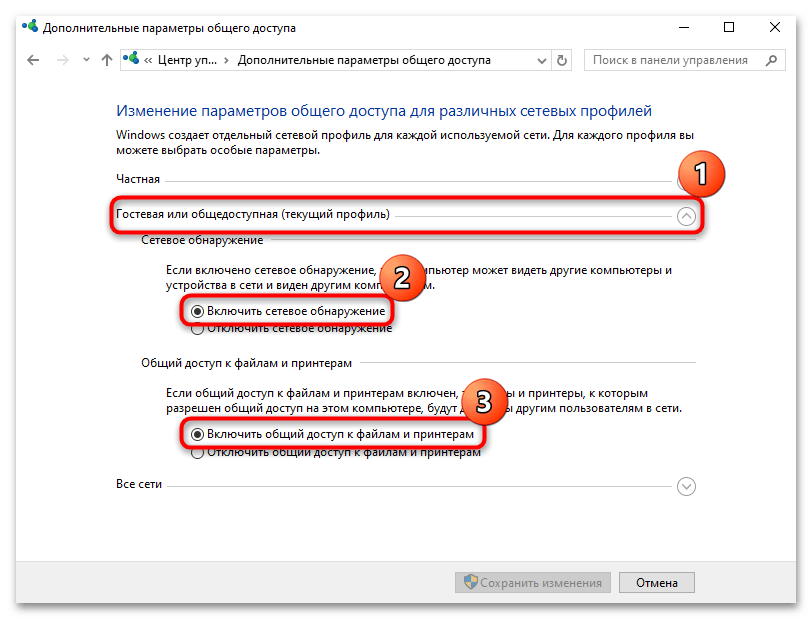
- Те же самые действия проделайте для «Гостевого» профиля.
- В разделе «Все сети», помимо активации общего доступа, также нужно выбрать 128-битное шифрование для защиты подключений общего доступа.
- Сохраните настройки, нажав на соответствующую кнопку внизу.
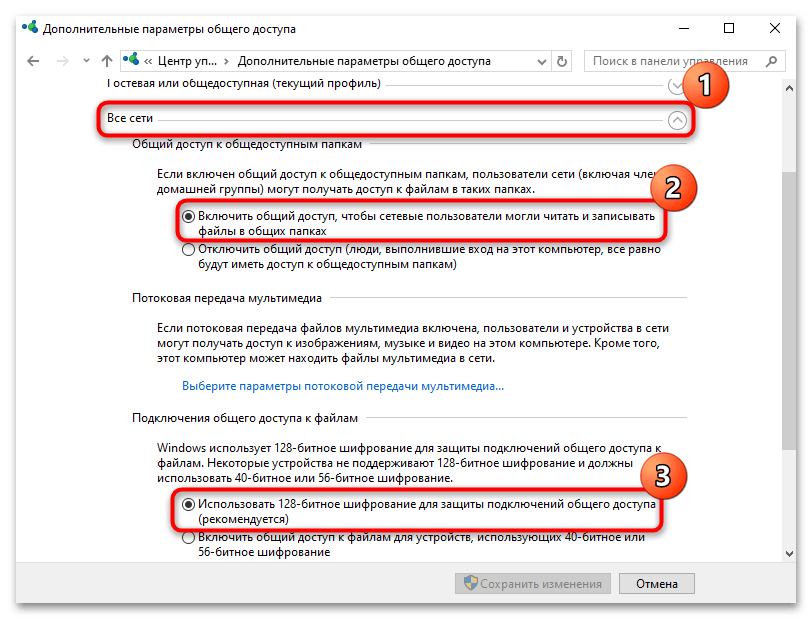
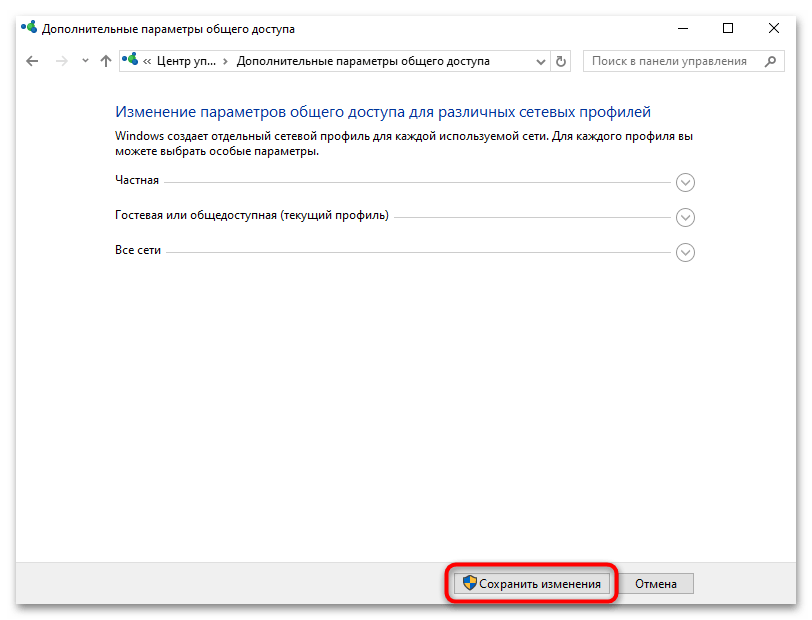
На этом глобальные настройки сетевого обнаружения устройства завершены. Далее при желании можете переходить еще и к открытию доступа к данным на компьютерах в сети.
Шаг 3: Открытие доступа к папкам и файлам
Для того чтобы компьютеры в рабочей группе могли обмениваться файлами или позволять просматривать данные на других устройствах, нужно создать общую папку, то есть каталог, к которому могут получить доступ все машины в сети:
- Кликните правой кнопкой мыши по выбранной/созданной папке и из контекстного меню выберите пункт «Свойства».
- Через вкладку «Доступ» вызовите «Расширенную настройку».
- Поставьте галочку у опции «Открыть общий доступ к этой папке» и нажмите на кнопку «ОК».
- Вернитесь к окну со свойствами папки и перейдите на вкладку «Безопасность», где нужно выбрать «Изменить».
- Далее кликните по кнопке «Добавить».
- В текстовом поле открывшегося окна вручную введите «Все», затем нажмите на «Проверить имена». Если все в порядке, подтвердите новые параметры, кликнув по кнопке «ОК».
- Затем потребуется определиться с разрешениями для пользователей в сети – в соответствующем разделе окна «Разрешения» внизу отметьте пункт «Полный доступ», после чего юзеры из этой рабочей группы смогут не только просматривать файлы, но и копировать, и редактировать их удаленно. Сохраните настройки.
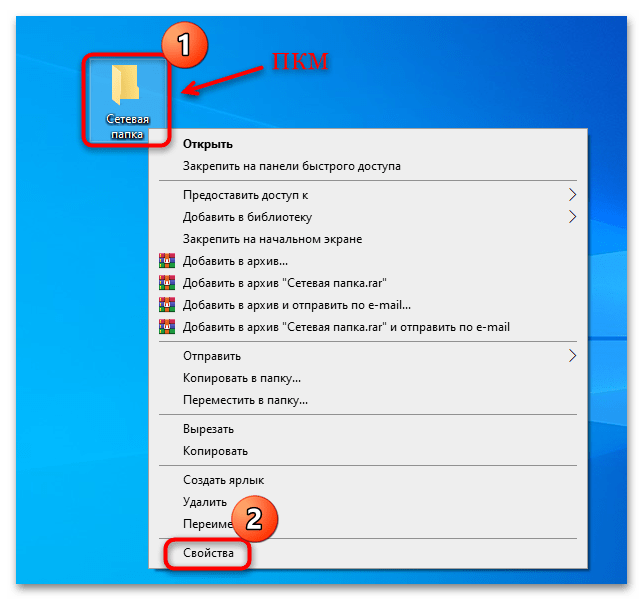

Такие действия можно проделать только на основном компьютере, чтобы другие устройства могли обращаться к выбранной папке в любой момент. Если нужно открыть доступ к файлам на других машинах, проделайте то же самое на каждой из них.
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
