Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
Appearance settings
When you create an enterprise CA on Windows Server, certificates can be generated through a certificate template system.
- What is a certificate template ?
- Certificate template versions
- Certificate template (version 1)
- Certificate template (version 2)
- Certificate template (version 3)
- Certificate template (version 4)
- Choosing the certificate template version
- Certificate templates available on Windows Server
- Certificate template settings
- Create a new certificate template
- Request a certificate for a web server (IIS)
- Installing the web server (IIS)
- Request certificate for IIS web server from mmc console
- Secure the IIS web server with the requested certificate
Certificate templates are sets of rules and settings configured on your enterprise certificate authority on Windows Server.
Warning : the certificate templates only exist on an enterprise certification authority (which is therefore linked to an Active Directory domain) and not on a standalone certification authority (not linked to the Active Directory).

When your certificate authority receives a certificate request, it must apply a set of rules and settings to issue or renew the requested certificate so that it’s valid for the intended use (for example : protecting a web server or proving the identity of a user).
This also ensures that the client will submit a valid certificate request (CSR).
The advantage of a company certificate authority is that it’s linked to the Active Directory.
This means that its certificate and certification templates are also stored in your Active Directory infrastructure. Specifically, in the «Configuration» partition of your Active Directory.
This means that these certificate templates can be used by any CA in your Active Directory forest.
This also allows your company certification authority to retrieve information about the client (user, computer, etc.) who submitted a certificate request directly from your Active Directory infrastructure.
2. Certificate template versions
On Windows Server, there are 4 versions of certificate templates :
- version 1 : version compatible with all certification authorities on Windows Server since Windows 2000.
- version 2 : available from Windows Server 2003 Enterprise and Datacenter
- version 3 : available from Windows Server 2008 Enterprise and Datacenter
- version 4 : available since Windows Server 2012
Note that certificate template versioning has changed since Windows Server 2012.
Important : as you will see below, some versions of certificate templates are editable and others are not.
Nevertheless, we strongly recommend that you don’t modify the pre-installed ones and create a copy of the desired template if you want to modify it.
Indeed, if you modify the pre-installed ones, you may encounter problems when you create certificate templates for third-party professional solutions where their official documentation is based on one of these pre-installed certificate templates.
2.1. Certificate template (version 1)
Certificate templates in version 1 are supported by all certification authorities on Windows Server.
These are installed automatically during your CA installation and therefore can’t be changed or removed.
The certificate templates in version 1 can be :
- Automatically enroll (issue) certificates through custom scripts or through the Computer-only certificate auto-enrollment setting available in Group Policies (GPOs).
- manually enroll (issue) certificates through the Certificates snap-in (via the mmc console) or through the CA web enrollment pages
These version 1 certificate templates are available on Windows Server 2000, 2003, 2003 R2, 2008 and 2008 R2 (all editions) and later.
Important : since you can’t modify a certificate template in version 1, you will have to duplicate it if you want to modify this one.
In addition, the copy of a certificate template in version 1 will become a certificate template in version 2 or 3 which can be modified.
2.2. Certificate template (version 2)
Version 2 certificate templates have been available since Windows Server 2003 and provide support for automatic certificate enrollment.
These certificate templates in version 2 can be :
- enrolled (issued) automatically using custom scripts
- enrolled (issued) automatically on Windows XP Pro, Windows Vista and their equivalents : Windows Server 2003 and 2008
- manually enrolled (issued) using the certificate enrollment wizard or CA web enrollment pages
These version 2 certificate templates are available on Windows Server 2003, 2003 R2, 2008 (Enterprise and Datacenter) and on Windows Server 2008 R2 (all editions) and later.
Important : it’s technically possible to modify most of the certificate template parameters in version 2 without needing to duplicate it.
Nevertheless, as explained before, you should not modify the pre-installed ones, but rather modify a copy of them to avoid.
Indeed, it happens that some third-party solutions require a certificate template that doesn’t exist. In this case, it will suffice to consult the official documentation of this solution to create the new certificate template based on one of the pre-installed certificate templates.
However, if you have modified the pre-installed one, you will not be able to correctly register the certificate you will need.
2.3. Certificate template (version 3)
Version 3 certificate templates have been available since Windows Server 2008 and provide the same features as version 2 certificate templates, as well as automatic certificate enrollment.
In addition to these features, version 3 certificate templates also provide support for Suite B cryptographic algorithms.
Which adds support for key exchange, encryption, digital signatures, and hashing.
These certificate templates in version 3 are available on Windows Server 2008 (Enterprise and Datacenter), 2008 R2 (all editions) and later.
Important : version 3 certificate templates can’t be used to issue certificates via the web interface of your certification authority.
If you wanted to enroll (issue) a certificate using a certificate template in version 3, you can for example do so from the «Certificates» component that you can add in an «mmc» console.
2.4. Certificate template (version 4)
Certificate templates in version 4 are available since Windows Server 2012 and provide new options :
- ability to renew a certificate with the same key.
Which is handy when you want to renew your used keys with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) for system partition encryption/decryption or with BitLocker. - support for CSP (Cryptographic Service Provider) and KSP (Key Storage Provider), as well as the ability to specify providers in order of preference
- allow renewal by key
- activate the issue specified by the caller
Also, since Windows Server 2012, certificate template versioning has changed.
Indeed, previously, you had to select the version of the certificate template that you want to create.
But, since Windows Server 2012, this window will no longer appear and you will have to use the settings available in the «Compatibility» tab.

When you modify the version of the certification authority or the certificate recipient in the «Compatibility» tab of the new template being created, this influences the options that will or will not be available in the other tabs.
When you modify these values, a «Resulting changes» window will appear and tell you which options will be added or removed from the future certificate template.

The «These settings may not prevent earlier operating systems from using this template» message means that changing these compatibility settings will not affect the version of the certificate template.
Although duplicating a version 1 certificate template will always produce a version 2 or 3 certificate template.
On the other hand, from the moment you select «Windows Server 2012» at least for these 2 compatibility settings, a version 4 certificate will be created.
Note that the version of the schema (certificate template) is chosen when the template is created and that it will therefore not change if you try to modify this new certificate template later.
Warning : version 4 certificate templates will not appear on your certification authority’s Web enrollment pages.

2.5. Choosing the certificate template version
If you select «Windows Server 2012» for the «Certification Authority» and «Certificate Recipient» compatibility settings, a version 4 certificate template will be created.
On the other hand, if one of these settings is configured with a value prior to «Windows Server 2012», the version used (2 or 3) will depend on the cryptography provider selected in the «Encryption» tab :
- Key Storage Provider (KSP) : certificate template in version 2.
- cryptographic service provider (CSP) : certificate model in version 3.
This option is available as «Legacy Cryptographic Services Provider / Determined by CSP».
Sources :
- Certificate Template Concepts
- Certificate Template Versions (WS 20008)
- Certificate Template Versions (WS 2008 R2)
- Version 3 (CNG) templates won’t appear in Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 certificate web enrollment
- Windows Server 2012: Certificate Template Versions and Options
3. Certificate templates available on Windows Server
As you can see from the «Certification Authority» console, several certificate templates can be issued by default.
In other words, only these (by default) will be visible from the «Certificate Enrollment» wizard of the «mmc» console, as well as from the web interface of your certification authority (if this web interface is installed).
However, note that you will also have adequate permissions to be able to use them. Also, the web interface may not display all certificate templates (as explained previously).
To see the complete list of certificate templates available on Windows Server, right-click «Manage» on «Certificate Templates».
Note : in business, it may be interesting to remove the templates of certificates to be issued that you don’t wish to use in your case.

As you can see, many certificate templates (33 in the case of Windows Server 2016) are available.
Among the widely used certificate templates, you will find :
- Computer : generally used via the certificates auto-enrollment, this makes it possible to prove the identity of a client workstation (or of a server) when it connects to a server.
- Web Server : generally used to secure access to a website. But, it’s also used generically when server authentication is required.
- User : typically used through certificate auto-enrollment, this helps prove a user’s identity when they connect to a computer or server.
This certificate template can also allow you to encrypt confidential data via the EFS file system or secure your e-mails.
As you can see, there are several schema versions (certificate template versions).
Most are version 1 and will be at least version 2 when you duplicate them (as explained before) and others are version 2 or 3.

As you can see, version 1 templates are not editable (unless you duplicate them to be able to edit the copy of them).

Version 2 certificate templates are editable.
Important : we recommend that you do NOT modify the pre-installed ones, but rather duplicate these if necessary to modify a copy and not the original.
Indeed, as explained previously, it happens that the manufacturer of a professional solution asks you to base yourself on an existing certificate template, then to modify specific settings on the copy of it so that the certificate is valid for this solution.
However, if you have modified the original certificate template, you may have problems in the future.

4. Certificate template settings
As you will see, certificate templates contain a lot of settings, as well as the permissions applied to them.
For the example, we duplicate the «Web Server» certificate template.

To begin with, starting with Windows Server 2012, you will have the option to choose the compatibility of this certificate.
Unlike previous versions of Windows Server where you had to select the certificate template version you wanted to create.
The «Show resulting changes» checkbox simply enables the display of a «Resulting changes» window listing the features added or removed according to the values selected for these compatibility settings.
Warning : as indicated previously, if you select at least «Windows Server 2012» for these 2 compatibility options, a version 4 certificate template will be created.
This means that it will not appear in the web interface of your certification authority (if applicable).
As a workaround, select «Windows Server 2008 R2» for the «Certification Authority» compatibility setting when creating this new certificate template.

In the «General» tab, you can specify :
- the template display name : the name under which it will appear in the list of certificate templates on your certification authority, but also on the client side in the mmc console or in the web interface of your certification authority.
- the template name : the internal name (without space of preference) under which this template will be created.
- the validity period : the length of time the certificate issued (delivered) using this certificate template will be valid.
- the renewal period : indicates when the certificate must be renewed (if automatic renewal is supported by the application that uses this certificate).
- whether to publish certificate in Active Directory : useful if several users or computers must have access to the same certificate, as well as for certificate roaming.
Indeed, if a user obtains a user certificate and this user can connect to several computers and/or servers and the roaming profiles are not configured, this user would obtain as many certificates as there are computers and/or servers where he has logged on. This will quickly become a problem if it’s a user certificate allowing data to be encrypted using EFS, for example.
If you publish the certificate in the Active Directory and you enable certificate roaming, this user will be able to retrieve his unique user certificate, regardless of the computer or server where he connects. - do not automatically reenroll if a duplicate certificate exists in Active Directory : simply allows not to create a new certificate if a valid certificate for the computer, server or user concerned already exists in Active Directory.
Important : for a certificate to be renewed, 80% of its validity period must have passed.
In the example below, our certificate will be valid for 2 years (= 2 x 52 weeks = 104 weeks) and it will be renewed 6 weeks before its expiry date (so at week 98).
If you calculate 80% of 104 weeks, you will see that this corresponds to : 83.2 weeks (104 / 100 x 80).
The renewal will therefore be carried out after the 80% validity of this certificate. Which respects the Microsoft recommendation : Recommended values of validity period and renewal period.

In the «Request Handling» tab, you will find several options allowing for example :
- allow private key to be exported : which is practical to be able to export the certificate in «.pfx» format from the «Personal» store of your computer or server via the mmc console, for example.
- renew with the same key : to renew the certificate using the same key, which allows you to continue signing with the same private key. Client-side verification with the same public key will therefore be possible.
Note that the greyed-out options in this case where an asterisk (*) is displayed correspond to the options that you can’t modify because of the values selected for the compatibility settings present in the «General» tab.
To access it, you will need to increase these values.

In the «Extensions» tab, you will find several advanced options that you will only change if the manufacturer of the solution you want to secure asks you to do so or you know exactly what you are doing.
However, for the «Web Server» certificate template, you will see that the application policy used is : Server authentication.
This allows the client to authenticate the server or in other words to be sure that it connects to the correct server and not that of a hacker who would try to pretend to be the desired server.

In the «Security» tab, you will see that the «Authenticated Users» group only has a «Read» right.
This is necessary so that you can see the certificate templates available through the «mmc» console’s certificate enrollment wizard or in your CA’s web interface.
On the other hand, users will not be able to enroll certificates, because they don’t have the right to enroll (Enroll or autoenroll).

If you select the «Domain Admins» group, you will see that domain administrators can :
- Read : see this certificate template.
- Enroll : enroll certificates using this certificate template.
Warning : you can only enroll certificates from a computer or server allowed to enroll certificates.
Which means that, by default, you will be able to enroll certificates while logged in as the domain admin on your CA, but not remotely through the mmc console (for example).
If you wish to enroll a certificate using this certificate template remotely (via the «mmc» console), you will also need to grant the «Enroll» right for the computer account from which you will attempt to enroll the certificate.
Difference between «Enroll» and «Autoenroll»:
- Enroll : allows you to manually enroll certificates (via the «mmc» console or via the web interface of your certification authority, if applicable).
- Autoenroll : enables certificates to be automatically enrolled through the computer or user certificate auto-enrollment setting available in group policy (GPO).

In the «Subject Name» tab, you can choose whether :
- Supply in the request : the person who wants to enroll a certificate can provide the information when requesting the certificate.
- Build from this Active Directory information : the information used must be retrieved from the Active Directory.
This implies that the request for the certificate is made by the user for whom it’s intended or from the computer or server for which it is intended.

Note: This guide is archived and is no longer updated on this website. For any future updates to this guide, please refer to the version that can be found on docs.mjcb.ca.
6.1 User Certificate Template Creation
The following Certificate Templates will need to be created in the Certification Authority Console on the TFS-CA01 Server:
| Template Name | Validity | Publish in ADDS | Additional Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| TFS Labs User Certificate | 1 Year | Yes |
|
| TFS Labs Workstation Certificate | 1 Year | Yes |
|
| TFS Labs Web Server Certificate | 1 Year | No |
|
These Certificate Templates will be used for issues Certificates to the organization. Some will be issued automatically, and the others can be requested by users or devices. The procedure for creating these Certificate Templates is mostly the same.
6.1.1 User and Workstation Templates
The settings for these templates will vary based on the needs of your organization, and the settings being used in this guide may or may not work for you. Ensure that you understand what the template settings are and how they will affect the users and devices in your organization.
- In the Certification Authority Console on the TFS-CA01 Server, ensure that the TFS Labs Enterprise CA Server is expanded in the Console tree.
- Right-click on Certificate Templates and then click Manage. The Certificate Templates Console window will open and display the Certificate Templates that are currently stored in Active Directory.
- In the details pane, right-click on the User Template and then click Duplicate Template.
- On the Properties of New Template window, click on the General tab. Change the name of the template to TFS Labs User Certificate. Ensure that the Validity Period is set to 1 Year.
- Ensure that the Publish certificate in Active Directory option checkbox is selected, as well as Do not automatically reenroll if a duplicate certificate exists in Active Directory is selected option is selected as well.
- On the Security tab, click the Add button and add the TFS-CA01 Server. Give it the Enroll permission.
- Select the Domain Users group and add the Read, Enroll and Autoenroll permissions.
- Click the OK button to close the Template window.
- Close the Certificate Templates Console window.
- In the Certification Authority Console, right-click on Certificate Templates, then select New and then select Certificate Template to Issue.
- In the Enable Certificate Templates dialog box, click TFS Labs User Certificate and then click OK.
6.1.2 User Certificate Template
Ensure that the user has their e-mail address entered into Active Directory, otherwise this Certificate will not deploy correctly to the User Account.
6.2 Workstation Certificate Template Creation
- In the Certification Authority Console on the TFS-CA01 Server, ensure that the TFS Labs Enterprise CA Server is expanded in the Console tree.
- Right-click on Certificate Templates and then click Manage. The Certificate Templates Console window will open and display the Certificate Templates that are currently stored in Active Directory.
- In the details pane, right-click on the Computer Template and then click Duplicate Template.
- On the Properties of New Template window, click on the General tab. Change the name of the template to TFS Labs Workstation Certificate. Ensure that the Validity Period is set to 1 Year.
- Ensure that the Publish certificate in Active Directory option checkbox is selected.
- On the Security tab, click the Add button and add the TFS-CA01 Server. Give it the Enroll permission.
- Select the Domain Computer group and add the Enroll and Autoenroll permissions.
- Click the OK button to close the Template window.
- Close the Certificate Templates Console window.
- In the Certification Authority Console, right-click on Certificate Templates, then select New and then select Certificate Template to Issue.
- In the Enable Certificate Templates dialog box, click TFS Labs Workstation Certificate and then click OK.
6.3 Web Server Certificate Template Creation
- In the Certification Authority Console on the TFS-CA01 Server, ensure that the TFS Labs Enterprise CA Server is expanded in the Console tree.
- Right-click on Certificate Templates and then click Manage. The Certificate Templates Console window will open and display the Certificate Templates that are currently stored in Active Directory.
- In the details pane, right-click on the Web Server Template and then click Duplicate Template.
- On the Properties of New Template window, click on the General tab. Change the name of the template to TFS Labs Web Server Certificate. Ensure that the Validity Period is set to 1 Year.
- On the Security tab, click the Add button and add the TFS-CA01 Server. Give it the Enroll permission.
- Select the Domain Admins group and add the Enroll and Autoenroll permissions.
- Click the OK button to close the Template window.
- Close the Certificate Templates Console window.
- In the Certification Authority Console, right-click on Certificate Templates, then select New and then select Certificate Template to Issue.
- In the Enable Certificate Templates dialog box, click TFS Labs Web Server Certificate and then click OK.
6.4 Active Directory Certificate Services Web Enrollment
The Active Directory Certificate Services Web Enrollment website is a feature that allows Authenticated Users in the organization the ability to submit Certificate Requests and download the completed Certificates. It can be found by going to the following URL:
http://tfs-ca01.corp.tfslabs.com/CertSrv/
The only minor issue with this is that SSL should be enabled on this site, but we will first need to add an SSL Certificate for it. Fortunately, the Certificate Authority is now able to issue certificates and a proper Certificate can now be requested and applied to this site.
- Open the Certificates Console (certlm.msc) under the Local Computer Account on the TFS-CA01 Server.
- Go to the Certificates > Personal > Certificates Store.
- Right-click on the Certificates folder, go to All Tasks and select Request New Certificate….
- On the Before You Begin screen, click the Next button to continue.
- On the Select Certificate Enrollment Policy screen, click the Next button to continue.
- On the Request Certificates screen, select the TFS Labs Workstation Certificate and click the Enroll button.
- On the Certificate Installation Results screen, click the Finish button to close the wizard.
- Close the Certificates Console.
- Open the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager Console on the TFS-CA01 Server.
- In the Connections pane, select the TFS-CA01 Server and expand Sites.
- Select the Default Web Site and in the Actions pane, select Bindings….
- In the Site Bindings window, click the Add… button.
- In the Add Site Binding window, use the following settings and then click the OK button:
- Type: https
- IP Address: All Unassigned
- Port: 443
- SSL Certificate: TFS-CA01.corp.tfslabs.com
- Expand Default Web Site and select the CertSrv folder.
- In the /CertSrv Home pane, double-click on the SSL Settings icon.
- In the SSL Settings window, select the option for Require SSL and then click the Apply button in the Actions pane.
- You can easily verify that SSL is working correctly on the Enrollment page by opening the http://tfs-ca01.corp.tfslabs.com/CertSrv page (you can login with a Domain Administrator account). It should be secured with SSL.
If you go to the SSL Certificate properties of the web page, you will be able to see that the Certificate has been issued by the TFS Labs Enterprise CA and is valid for only 1 year.
- Introduction
- Part 1 — Offline Root CA Setup
- Part 2 — Subordinate CA Setup
- Part 3 — Deploy Root and Subordinate Certificate
- Part 4 — Certificate Revocation Policies
- Part 5 — Configure Private Key Archive and Recovery
- Part 6 — Certificate Template Deployment
- Part 7 — Certificate Auto-Enrollment
- Part 8 — Final Steps
In this article we will show you how to enable the ‘Web Server’ certificate template option on a Windows Certification Authority (Windows CA) Server. The Web Server option is usually not present in a fresh Windows CA server installation installation which can introduce difficulties for users or administrators who need the option to get their web server certificates signed:
Recommended Article: How to install and configure a Windows CA Server
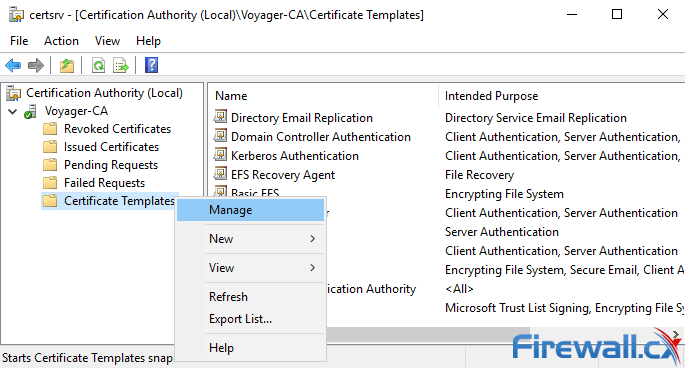
Enabling the Web Server certificate template is a simple and non-disruptive process. From the Administrative Tools, open the Certification Authority tool. Next, right-click on the Certificate Templates folder and select Manage:
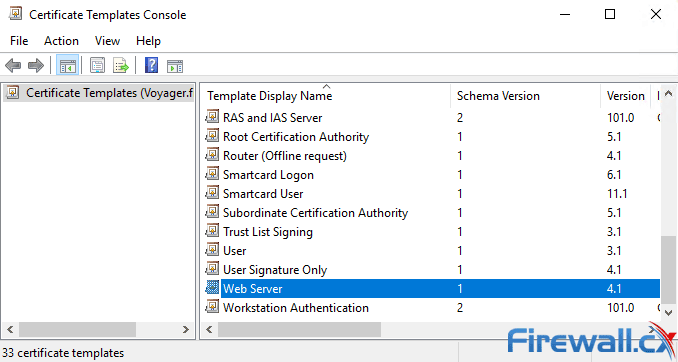
This will open the Certificate Templates Console as shown below. Double-click on the Web Server template:
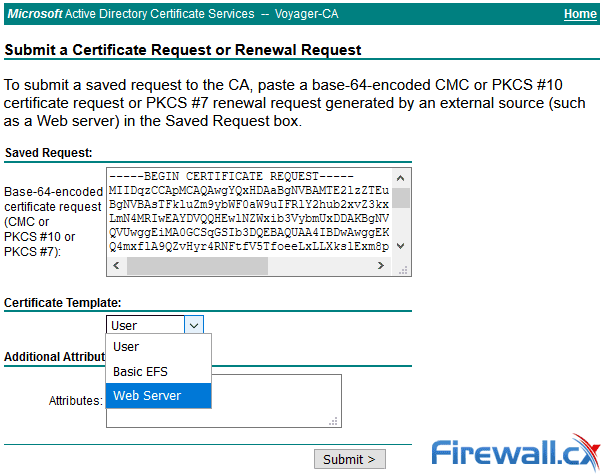
The Web Server Properties window will now appear. Click on the Security tab and select the Authenticated Users from the Group or user names section. In the Permissions for Authenticated Users section tick the Allow action for the Enroll permission. When ready, click on OK:
Congratulations — you’ve now successfully enabled the Web Server certificate template option. Your Windows CA server should now present the previously mission option as shown below:
Summary
This article explained how to enable the Web Server certificate template option on your Windows Certification Authority (Windows CA) Server. We included step-by-step screenshots to ensure its a detailed and yet simple process to follow.
Your IP address:
79.111.214.145
All-in-one protection for Microsoft 365
FREE Hyper-V & VMware Backup
Wi-Fi Key Generator
Generate/Crack any
WEP, WPA, WPA2 Key!
Network and Server Monitoring
Follow Firewall.cx
Cisco Password Crack
Bandwidth Monitor
Free PatchManager
Security Podcast
Firewall Analyzer
Introduction
This document describes a step-by-step procedure to create certificate templates on Windows Server-based Certification Authorities (CA).
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- CUCM version 11.5(1).
- Basic knowledge of Windows Server administration
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- CUCM Version 11.5(1).
- Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 with CA services installed.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background information
These certificate templates are compliant with X.509 extension requirements for every type of Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) certificate.
There are five types of certificates that can be signed by an external CA:
|
Certificate |
Use |
Impacted Services |
|
Callmanager |
Presented at secure device registration and can sign Certificate Trust List (CTL)/Internal Trust List (ITL) files, used for secure interactions with other servers such as secure Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Trunks. |
· Cisco Call Manager · Cisco CTI Manager · Cisco TFTP |
|
tomcat |
Presented for Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTPS) interactions. |
· Cisco Tomcat · Single Sign-On (SSO) · Extension Mobility · Corporate Directory |
|
ipsec |
Used for backup file generation, as well as IP Security (IPsec) interaction with Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) or H323 gateways. |
· Cisco DRF Primary · Cisco DRF Local |
|
CAPF |
Used to generate Locally Significant Certificates (LSC) for phones. |
· Cisco Certificate Authority Proxy Function |
|
TVS |
Used to create a connection to the Trust Verification Service (TVS) when the phones are not able to authenticate an unknown certificate. |
· Cisco Trust Verification Service |
Note: ipsec certificate is not related to Cisco DRF Primary and Cisco DRF Local since 14, in newer versions, Tomcat certificate is used instead. There is no plan to add this change to 12.5 or earlier versions.
Each of these certificates has some X.509 extension requirements that need to be set, otherwise, you can encounter misbehavior on any of the aforementioned services:
|
Certificate |
X.509 Key Usage |
X.509 Extended Key Usage |
|
Callmanager |
· Digital Signature · Key Encipherment · Data Encipherment |
· Web Server Authentication · Web Client Authentication |
|
tomcat |
· Digital Signature · Key Encipherment · Data Encipherment |
· Web Server Authentication · Web Client Authentication |
|
ipsec |
· Digital Signature · Key Encipherment · Data Encipherment |
· Web Server Authentication · Web Client Authentication · IPsec End System |
|
CAPF |
· Digital Signature · Certificate Sign · Key Encipherment |
· Web Server Authentication · Web Client Authentication |
|
TVS |
· Digital Signature · Key Encipherment · Data Encipherment |
· Web Server Authentication · Web Client Authentication |
For more information, reference the Security Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Configure
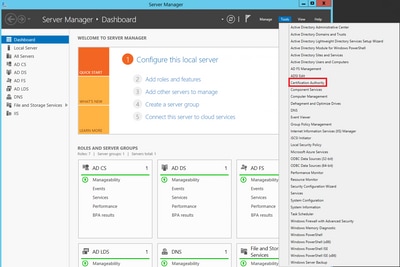
Step 1. On the Windows Server, navigate to Server Manager > Tools > Certification Authority, as shown in the image.
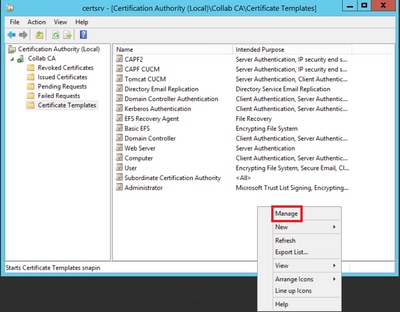
Step 2. Select your CA, then navigate to Certificate Templates, right-click on the list and select Manage, as shown in the image.
Callmanager / Tomcat / TVS Template
The next images display only the creation of the CallManager template; but the same steps can be followed to create the certificate templates for the Tomcat and the TVS services. The only difference is to ensure the respective service name is used for each new template in step 2.
Step 1. Find the Web Server template, right-click on it and select Duplicate Template, as shown in the image.
Step 2. Under General, you can change the certificate template’s name, display name, validity, and some other variables.
Step 3. Navigate to Extensions > Key Usage > Edit, as shown in the image.
Step 4. Select these options and select OK, as shown in the image.
- Digital signature
- Allow key exchange only with key encryption (key encipherment)
- Allow encryption of user data
Step 5. Navigate to Extensions > Application Policies > Edit > Add, as shown in the image.
Step 6. Search for Client Authentication, select it and select OK on both this window and the previous one, as shown in the image.
Step 7. Back on the template, select Apply and then OK.
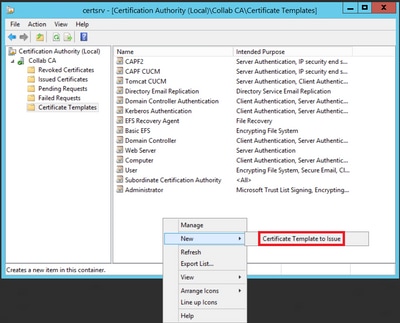
Step 8. Close the Certificate Template Console window, and back on the very first window, navigate to New > Certificate Template to Issue, as shown in the image.
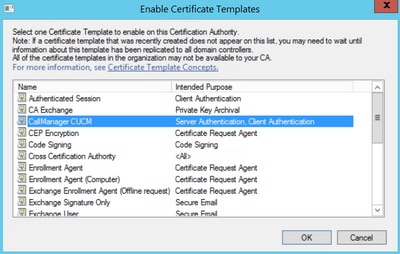
Step 9. Select the new CallManager CUCM template and select OK, as shown in the image.
Step 10. Repeat all previous steps to create certificate templates for the Tomcat and TVS services as needed.
IPsec Template
Step 1. Find the Web Server template, right-click on it and select Duplicate Template, as shown in the image.
Step 2. Under General, you can change the certificate template’s name, display name, validity, and some other vairiables.
Step 3. Navigate to Extensions > Key Usage > Edit, as shown in the image.
Step 4. Select these options and select OK, as shown in the image.
- Digital signature
- Allow key exchange only with key encryption (key encipherment)
- Allow encryption of user data
Step 5. Navigate to Extensions > Application Policies > Edit > Add, as shown in the image.
Step 6. Search for Client Authentication, select it and then OK, as shown in the image.
Step 7. Select Add again, search for IP security end system, select it and then select OK on this and on the previous window as well.
Step 8. Back on the template, select Apply and then OK, as shown in the image.
Step 9. Close the Certificate Templates Console window, and back on the very first window, navigate to New > Certificate Template to Issue, as shown in the image.
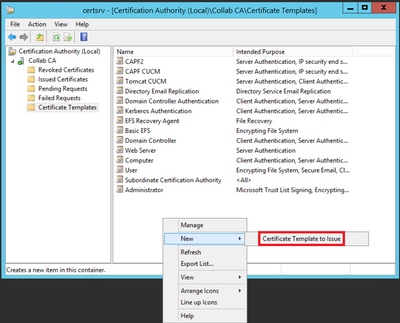
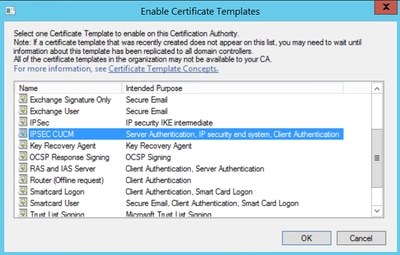
Step 10. Select the new IPSEC CUCM template and select OK, as shown in the image.
CAPF Template
Step 1. Find the Root CA template and right-click on it. Then select Duplicate Template, as shown in the image.
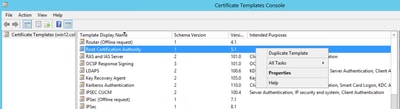
Step 2. Under General, you can change the certificate template’s name, display name, validity, ans some other variables.
Step 3. Navigate to Extensions > Key Usage > Edit, as shown in the image.
Step 4. Select these options and select OK, as shown in the image.
- Digital signature
- Certificate signing
- CRL signing
Step 5. Navigate to Extensions > Application Policies > Edit > Add, as shown in the image.
Step 6. Search for Client Authentication, select it and then select OK, as shown in the image.
Step 7. Select Add again, search for IP security end system, select it and then select OK on this and on the previous window as well, as shown in the image.
Step 8. Back on the template, select Apply and then OK, as shown in the image.
Step 9. Close the Certificate Templates Console window, and back on the very first window, navigate to New > Certificate Template to Issue, as shown in the image.
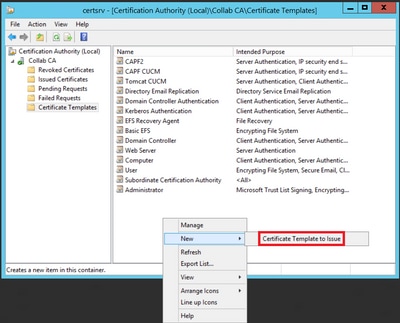
Step 10. Select the new CAPF CUCM template and select OK, as shown in the image.
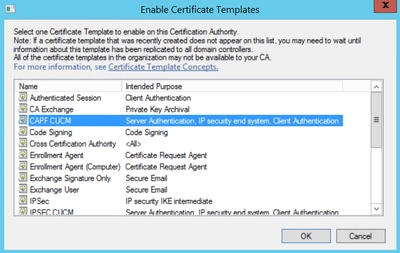
Generate a Certificate Signing Request
Use this example in order to generate a CallManager certificate with the use of the newly created templates. The same procedure can be used for any certificate type, you just need to select the certificate and template types accordingly:
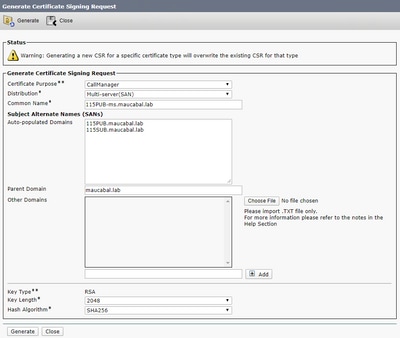
Step 1. On CUCM, navigate to OS Administration > Security > Certificate Management > Generate CSR.
Step 2. Select these options and select Generate, as shown in the image.
- Certificate Purpose: CallManager
- Distribution: <This can either be just for one server or Multi-SAN>
Step 3. A confirmation message is generated, as shown in the image.
Step 4. On the certificate list, look for the entry with type CSR Only and select it, as shown in the image.
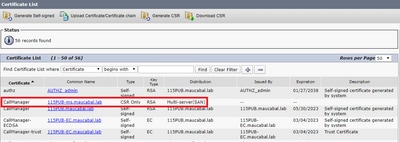
Step 5. On the pop-up window, select Download CSR, and save the file on your computer.
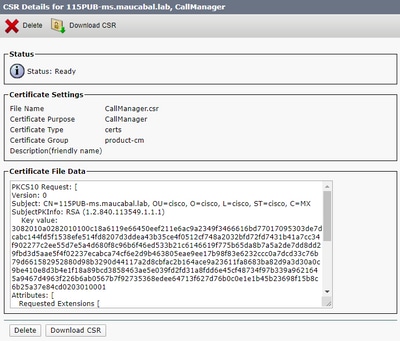
Step 6. On your browser, navigate to this URL, and enter your domain controller administrator credentials: https://<yourWindowsServerIP>/certsrv/.
Step 7. Navigate to Request a certificate > advanced certificate request, as shown in the image.

Step 8. Open the CSR file and copy all its contents:
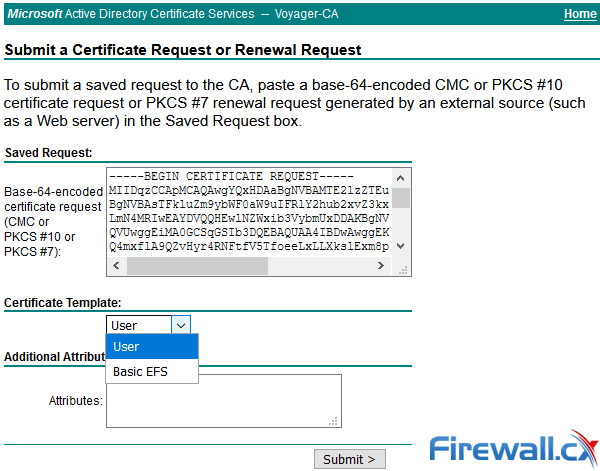
Step 9. Paste the CSR in the Base-64-encoded certificate request field. Under Certificate Template, select the correct template and select Submit, as shown in the image.
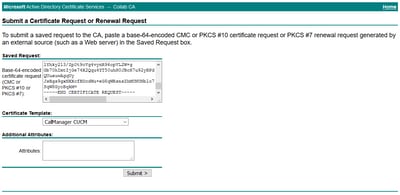
Step 10. Finally, select Base 64 encoded and Download certificate chain. The generated file can now be uploaded to the CUCM.

Verify
The verification procedure is actually part of the configuration process.
Troubleshoot
There is currently no specific troubleshoot information available for this configuration.
