AVRDUDE for Windows
This is a fork of AVRDUDE from https://github.com/avrdudes/avrdude.
The purpose of this fork is to add better support for Windows to bring it on par with the Linux version of AVRDUDE.
Noteable changes include:
- Support Atmel AVR programmers out of the box
- Support Micronucleus bootloader
- Support Teensy HalfKay bootloader
- Support COM port discovery via USB VID/PID
- Support Arduino Leonardo bootloader auto-reset
- Support WinUSB devices via custom libusb
- Support FTDI devices via custom libftdi
- Support HID devices via libhidapi
- Support Visual Studio
- Miscellaneous bug-fixes and patches
The original AVRDUDE project homepage can be found here https://github.com/avrdudes/avrdude.
Documentation
Documentation for current and previous releases is on Github Pages.
Download
To get the latest version of AVRDUDE for Windows, go to the releases folder:
https://github.com/mariusgreuel/avrdude/releases
Feature Details
Support Atmel AVR programmers out of the box
This build contains support for Atmel AVR programmers, such as
- Atmel-ICE (Part Number: ATATMEL-ICE)
- Atmel AVRISP mkII (Part Number: ATAVRISP2)
This build does not rely on libusb drivers. Instead the default Atmel drivers can be used, allowing you to use AVRDUDE and Atmel Studio 7 side-by-side, without switching drivers.
If you previously changed the driver of your programmer to libusb, you should use Windows Device Manager to uninstall the device, and then reinstall using the default Windows drivers.
Support Micronucleus bootloader
This build adds support for the Micronucleus bootloader, so you do no longer need a separate command-line utility when working with devices that use the Micronucleus bootloader.
The Micronucleus bootloader is typically used on small ATtiny boards, such as Digispark (ATtiny85), Digispark Pro (ATtiny167), and the respective clones.
By default, it uses the USB VID/PID 16D0:0753 (MCS Digistump).
Since this bootloader is optimized for size, it implements writing to flash memory only.
As it does not support reading, you need to use the -V option to prevent AVRDUDE from verifing the flash memory. To have AVRDUDE wait for the device to be connected, use the extended option ‘-x wait’.
Example: Flashing a Micronucleus bootloader device
avrdude -c micronucleus -p t85 -x wait -V -U flash:w:main.hex:i
Support Teensy HalfKay bootloader
This build adds support for the Teensy HalfKay bootloader, so you do no longer need a the Teensy Loader tool when working with Teensy devices.
Since this bootloader is optimized for size, it implements writing to flash memory only.
As it does not support reading, you need to use the -V option to prevent AVRDUDE from verifing the flash memory. To have AVRDUDE wait for the device to be connected, use the extended option ‘-x wait’.
Supported devices are:
- Teensy 1.0 (AT90USB162)
- Teensy 2.0 (ATmega32U4)
- Teensy++ 1.0 (AT90USB646)
- Teensy++ 2.0 (AT90USB1286)
Example: Flashing a Teensy 2.0 device
avrdude -c teensy -p m32u4 -x wait -V -U flash:w:main.hex:i
Support COM port discovery via USB VID/PID
Most Arduino boards use a USB-based virtual COM port, which is connected to some sort of bootloader. Since COM port numbers (COM1, COM2, …) are determined by Windows, you first need to use Windows device manager to figure out the COM port before you can use AVRDUDE to flash the board. Alternatively, you may use Windows device manager to assign a COM port of your choice to the USB device. Additionally, the COM port of your Arduino board may change over time, for instance if you plug the device in a different USB port.
To simplify the discovery of your Arduino board, I provided the possibility to specify the USB vendor and product ID instead of the COM port.
For instance, to connect to an Arduino Leonardo, use the following command:
avrdude -c avr109 -P usb:2341:0036 -p m32u4
Since the USB vendor and device ID 2341:0036 is the identical for all Leonardo boards, the command above will work regardless of which COM port was actually assigned to your board.
Note that can cannot use this method if you have more than one device of the same type (i.e. that share the same USB VID/PID) plugged into your computer. Also, some devices ship various versions of firmwares using different VID/PID.
To figure out the USB VID and PID, you may use Windows devices manager (see the Hardware IDs of the Details tab of the USB device), or look it up in the official list of Arduino devices:
https://github.com/arduino/ArduinoCore-avr/blob/master/boards.txt
USB VID/PID pairs for some popular boards and the respective commands are:
- Arduino Uno Rev 3: 2A03:0043 ->
avrdude -c arduino -P usb:2A03:0043 -p m328p - Arduino Micro: 2341:0037 ->
avrdude -c avr109 -P usb:2341:0037 -p m32u4 - Arduino Leonardo: 2341:0036 ->
avrdude -c avr109 -P usb:2341:0036 -p m32u4 - Sparkfun Pro Micro (5V): 1B4F:9205 ->
avrdude -c avr109 -P usb:1B4F:9205 -p m32u4 - Sparkfun Pro Micro (3.3V): 1B4F:9203 ->
avrdude -c avr109 -P usb:1B4F:9203 -p m32u4 - Adafruit Circuit Playground: 239A:0011 ->
avrdude -c avr109 -P usb:239A:0011 -p m32u4
Support Arduino Leonardo bootloader auto-reset
Before any Arduino board may be flashed via the bootloader, you need to kick it into bootloader mode first. This can done manually by pressing the reset button, or automatically via an special auto-reset mechanism: For boards with a USB to serial converter chip (such as Arduino Uno or Nano), the tool needs to pull the DTR signal to low, which will briefly pull the RESET pin of the microcontroller to low. For boards with a direct USB connection (such as Arduino Leonardo or Micro), the sketch typically implements a serial port via a USB composite device with a virtual COM port. To perform the auto-reset, the sketch implements a hack that resets the device into bootloader mode when the COM port is opened with a baudrate of 1200bps. To make matters even more complicated, the bootloader COM port has a different USB VID:PID pair than the sketch COM port, which causes the COM port to change while performing the reset.
To simplify the process of auto-resetting the board, this version will auto-reset the device when AVRDUDE detects that the device is running in sketch mode. Note that the sketch is required to implement a USB composite device with a virtual COM port with a matching USB VID:PID, which is implemented in the Arduino core software.
Support WinUSB devices via custom libusb
Since AVRDUDE originated from Unix, the USB support in AVRDUDE is built upon the Unix-based USB library libusb. In order to support Windows, libusb has been ported to Windows libusb-win32.
The downside of using libusb-win32 is that it requires the user to manually install a kernel-mode driver (libusb0.sys or libusbk.sys) instead of the manufacturer supplied Windows driver. There are several hacks to accomplish this, such as the Zadig driver installation utility, which installs a self-signed root certificate in the Windows driver store due to the lack of proper driver installation packages.
This build contains a custom library called libwinusb, which implements a sub-set of the libusb-win32 API. The libwinusb implementation supports both the winusb.sys driver, and the libusb0.sys driver as well. This patch has a number of advantages, such as
- Many USB devices that ship with WinUSB drivers, such as Atmel programmer, will run out of the box.
- Works with both WinUSB and libusb: You can use either Windows built-in WinUSB driver to access your USB devices, or keep using the libusb drivers if you have them installed already.
- No static dependency to libusb0.dll: You cannot run the original version AVRDUDE, unless you previously installed libusb. On systems where libusb is not installed, this build eliminates the error «The code execution cannot proceed because libusb0.dll was not found. Reinstalling the program may fix this problem».
Microsoft OS descriptors and firmware examples
Windows provides a mechanism to automatically load the built-in WinUSB driver without providing a driver installation package (INF file). The automatic WinUSB driver installation is triggered via a special Microsoft OS descriptor that must be present in the firmware of the USB device.
To demonstrate how this works, I added Microsoft OS descriptors to the following projects:
-
USBasp — USB programmer for Atmel AVR controllers: https://github.com/mariusgreuel/USBasp
-
FabISP a.k.a USBtinyISP — A fab-able in-system programmer: https://github.com/mariusgreuel/FabISP
-
Micronucleus — ATtiny USB bootloader with a strong emphasis on bootloader compactness: https://github.com/mariusgreuel/micronucleus
Support FTDI devices via custom libftdi
In order to support FTDI devices, AVRDUDE uses the Unix-based library libftdi1. Similar to libusb, the libftdi1 library does not play nice on Windows: On Windows, FTDI devices load the manufacturer supplied driver via plug-and-play. The FTDI drivers implement an API via the FTDI D2XX DLLs. However, libftdi1 cannot use the D2XX interface, so it will not work with the plug-and-play drivers.
This build contains a patches library of libftdi. The patches load the D2XX DLLs to support FTDI devices, so FTDI devices will just work.
Support HID devices via libhidapi
This build include the WIN32 version of libhidapi, and some patches, to allow HID devices to work out of the box.
Support Visual Studio
This build adds support for Microsoft Visual Studio. Building AVRDUDE with Microsoft Visual C/C++ will give you the best user and debugging experience while working on Windows.
Miscellaneous bug-fixes and patches
-
This build fixes bug #54159: Buffer overflow in usbtiny.c, which causes AVRDUDE to crash when using the USBtiny programmer.
-
Support new microcontroller: ATtiny167
Releases
You can find the latest releases of AVRDUDE for Windows here:
https://github.com/mariusgreuel/avrdude/releases
Users manual
You can find the original users manual (does not contain AVRDUDE for Windows extras) of AVRDUDE here:
https://www.nongnu.org/avrdude/user-manual/avrdude.html
Build
The build instructions have been moved here:
https://github.com/avrdudes/avrdude/wiki
Building AVRDUDE for Windows using MSVC
Windows Prerequisites
In order to build AVRDUDE on Windows, you need:
- Flex and Bison installed, for instance via Chocolatey
- Microsoft Visual Studio 2019 with Desktop development with C++ and CMake enabled
Windows Build Instructions
To build AVRDUDE on Windows, do the following:
git clone --branch windows https://github.com/mariusgreuel/avrdude- Open the folder avrdude using the menu item File->Open->Folder
- Build the project using the menu item Build->Build All
Linux udev rules
If you intent to use either the Micronucleus or Teensy bootloader, you should edit the udev rules so that you can run AVRDUDE without root.
For instance, if you are on Ubuntu and you installed the avrdude package, you would edit /lib/udev/rules.d/60-avrdude.rules and add the following rules:
# Micronucleus Bootloader SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="16d0", ATTR{idProduct}=="0753", TAG+="uaccess" # Teensy Bootloader SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="16c0", ATTR{idProduct}=="0478", TAG+="uaccess"
Troubleshooting Tips & Tricks
Atmel DFU Device driver broken
The current version of the Atmel DFU drivers that are distributed via the Windows Update are goofed up (@Atmel: It might have something to do with the fact that you commented out the CopyFiles sections!).
Symptoms are:
- You cannot use AVRDUDE to connect to an Atmel DFU device, and you get the error message «No matching USB device found».
- When installing the drivers via Windows Update, you get the error message «Windows encountered a problem installing the drivers for your device» and «A service installation section in this INF is invalid.»
- In Windows Device Manager, the Atmel DFU device shows up as an unknown device.
You should use an older driver package that does not contain this bug.
Outdated libusb0 driver
The most current version of libusb0.sys is 1.2.6.0, signed on 12/17/2012 by Travis Lee Robinson. If you are using an older version (check with Windows Device Manager), you may not be able to connect to your USB devices using the libusb0 driver.
По умолчанию поддерживаемые МК (список МК постоянно расширяется, см. форум):
AT90CAN128, AT90CAN32, AT90CAN64, ATmega128, ATmega1280, ATmega1281, ATmega1284p, ATmega128RFA1, ATmega16, ATmega162, ATmega164p, ATmega168, ATmega169, ATmega2560, ATmega2561, ATmega32, ATmega324p, ATmega325, ATmega3250, ATmega328p, ATmega329, ATmega3290, ATmega329p, ATmega3290p, ATmega32U4, ATmega48, ATmega8, ATmega8515, ATmega8535, ATmega88, ATtiny13, ATtiny2313, ATtiny261.
По умолчанию поддерживаемые программаторы (список программаторов можно самостоятельно расширить, либо скачать с форума):
USBasp, USBtiny, AVR ISP mkII,SI-Prog, AVR910, AVR910, STK200, STK500, STK500 2.X, JTAG ICE mkII, JTAG ICE mkII ISP, JTAG ICE mkII PDI.
Основные отличия от аналогичных программ :
1. Возможность самостоятельного добавления программаторов, настройки скорости программирования и т.п;
2. Возможность самостоятельного добавления МК;
3. Редактирования и настройка отображения Fuses битов;
4. Выбор инверсных или прямых Fuses битов;
5. Окна вывода значений Fuses битов в HEX формате;
6. Сохранение настроек программирования при закрытии программы, т.е. при последующем открытии все настройки восстановятся;
7. «дублирование кнопки» — данная функция выводит на экран кнопку «Программировать», которая является полным функциональным аналогом кнопки «Программировать всё» и всегда будет находиться по верх всех окон. Кнопку можно переместить в удобную для вас зону монитора, свернув AVRDUDE_PROG. Удобна при многочисленном перепрограммировании МК.
Установка.
Разархивируйте файл usbprog.rar в любую удобную папку. Поместите ярлык программы «AVRDUDE_PROG» на рабочий стол. Установка завершена. Можно работать.
Возможности программы.
Настройки оболочки «AVRDUDE_PROG» реализованы в «ini» файлах. Что такое «ini» файлы можно посмотреть тут.
Теперь возможно самостоятельно добавлять и редактировать список микроконтроллеров, программаторов, портов, Fuses бит, добавить различные языки и пр.
Список контроллеров и состояний Fuses бит, редактируется в файле «atmel.ini», список программаторов и портов в файле «programm.ini», список поддерживаемых языков в файле «language.ini».
В файле «atmel.ini», все значения введены по умолчанию в соответствии с datasheet на МК, можете изменить по Вашему усмотрению. Никаких инверсий не требуется, значение по умолчанию вводиться в соответствии с datasheet на МК. В том случае, если МК нет в списке, или при выборе МК во вкладке Fuses везде «error», то Вам необходимо самостоятельно ввести значения в файл «atmel.ini» в соответствии с datasheet и приведённым ниже примером. Либо посмотреть на форуме. Файл «atmel.ini» находится в корневой папке программы.
В файле «programm.ini», введены значения программаторов для командной строки avrdude. В том случае, если используемый Вами программатор отсутствует в списке, либо необходимо изменить какие-либо параметры установленные по умолчанию, то необходимо ввести/редактировать его значения самостоятельно в соответствии с приведённым ниже примером. Либо посмотреть на форуме. Файл «programm.ini» находится в корневой папке программы.
В файле «language.ini», возможно отредактировать на «свой вкус» текстовую информацию оболочки, либо добавить язык программы AVRDUDE_PROG. Тут расписывать ничего не буду, думаю в файле «language.ini» всё понятно.
Добавление/редактирование списка МК. Работа с файлом «atmel.ini».
Окройте в любом текстовом редакторе (рекомендую Notepad++) файл «atmel.ini». Посмотрите как реализован ввод параметров МК, фузе битов и пр. Ниже привожу пример и описание парметров.
Пример на мк AT90CAN128
Заголовок раздела
[AT90CAN128] — имя МК которое появиться в выпадающем списке, «[» и «]» обязательны. В данном случае «AT90CAN128».
Параметр для типа МК
mcuavrdude=c128 // тип мк в avrdude
Значение и описание параметров раздела для Fuse битов
Lock байт
lockbytebit*enabled=0 // «*» — номер бита в Lock байте, «**enabled=0» — невозможно изменение состояния бита, «**enabled=1» — возможно изменение состояния бита. В данном случае изменение бита невозможно. Изменение бита будет недоступно.
lockbytebit*name=NOT USED // «*» — номер бита в Lock байте, «**name = NOT USED» — бит не используется. Если бит используется, вводиться его имя в соответствии с datasheet.
lockbytebit*def=1 // «*» — номер бита в Lock байте, «**def=» — если имя бит бита = «NOT USED», то значение вводится в соответствии с datasheet. В данном случае «1».
High байт
highbytebit*enabled=1 // «*» — номер бита в High байте, «**enabled=0» — невозможно изменение состояния бита, «**enabled=1» — возможно изменение состояния бита. В данном случае изменение бита возможно. Изменение бита будет доступно.
highbytebit*name=OCDEN // «*» — номер бита в High байте, «**name = OCDEN» — имя бита в соответствии с datasheet.
highbytebit*def=1 // «*» — номер бита в High байте, «**def=1» — значение бита по умолчанию, вводиться в соответствии с datasheet. В данном случае значение по умолчанию «1».
Low байт
lowbytebit*enabled=1 // «*» — номер бита в Low байте, «**enabled=0» — невозможно изменение состояния бита, «**enabled=1» — возможно изменение состояния бита. В данном случае изменение бита возможно. Изменение бита будет доступно.
lowbytebit*name=CKDIV8 // «*» — номер бита в Low байте, «**name = CKDIV8» — имя бита в соответствии с datasheet.
lowbytebit*def=0 //»*» — номер бита в Low байте, «**def=0» — значение бита по умолчанию, вводиться в соответствии с datasheet. В данном случае значение по умолчанию «0».
Extended/Fuse/Fuse байт
extendedbytebit*enabled=0 // «*» — номер бита в Extended/Fuse/Fuse байте, «enabled=0» — невозможно изменение состояния бита, «enabled=1» — возможно изменение состояния бита. В данном случае изменение бита невозможно. Изменение бита будет недоступно.
extendedbytebit*name=NOT USED //»*» — номер бита в Extended/Fuse/Fuse байте, «name = NOT USED» — бит не используется. Если бит используется, вводиться его имя в соответствии с datasheet.
extendedbytebit*def=1 // «*» — номер бита в Lock байте, «**def=» — если имя бит бита = «NOT USED», то значение вводится в соответствии с datasheet. В данном случае «1».
Добавление/редактирование списка программаторов. Работа с файлом «programm.ini».
Откройте в любом текстовом редакторе (рекомендую Notepad++) файл «programm.ini». Посмотрите как реализован ввод параметров программаторов. Ниже привожу пример и описание парметров.
Описание переменных файла.
[Name programmator] – имя программатора а выпадающем списке
progisp – программатор для командной строки avrdude
portprog – порт программатора для командной строки avrdude (Usb, com, lpt и пр.)
portenabled – окно изменение порта «1»-доступно, «0» — недоступно
Программатор AVR STK200 с поддержкой LPT.
Для добавления программатора AVR STK200 с поддержкой LPT в файл «programm.ini» можно добавить следующее:
[STK200LPT]
progisp=stk200
portprog=lpt1
portenabled=0
Сохраните файл «programm.ini»
В выпадающем списке «Настройки» -> «Программатор» появиться программатор « STK200LPT » с работой от lpt1 порта.
Всё работает аналогично для других параметров и программаторов, поддерживаемых avrdude.
AVRDUDE_PROG 3.3 (22.01.2021)
ВНИМАНИЕ!!! Обновлена версия avrdude 6.3 (22.01.2021)
Драйвера USBAsp
Основные отличия от предыдущей версии:
— добавлено куча контроллеров, исправлены ошибки файлов «atmel.ini»,»avrdude.conf» — огромное спасибо модератору форума dmibr за проделанную работу!
— исправлены мелкие ошибки.
Если у Вас установлена программа версии 3.1 и выше, то достаточно заменить файл — «AVRDUDEPROG.exe»,»avrdude.exe»,»avrdude.conf»,»atmel.ini» . В этом случае все ранее сохранённые настройки в файлах «ini» не изменяться.
Размер файла: 690КБ
Статус программы: бесплатная
ОС: Windows NT/2000/XP/VISTA/7/10
Интерфейс: русский, english
Разработчик: yourdevice
Версия: 3.3 (22.01.2021)
AVRDUDE_PROG 3.2
ВНИМАНИЕ!!! Актуально для версии 3.2 — ссылка на форум
Основные отличия от предыдущей версии:
— исправлено зависание программы в некоторых случая;
— исправлена ширина выпадающего списка программаторов;
— в диалоговом окне программы состояние avrdude выводиться в режиме онлайн, а не в конце программирования;
— исправлены мелкие ошибки.
Если у Вас установлена программа версии 3.1, то достаточно заменить только «exe» файл. В этом случае все ранее сохранённые настройки в файлах «ini» не изменяться.
Размер файла: 558КБ
Статус программы: бесплатная
ОС: Windows NT/2000/XP/VISTA/WINDOWS 7
Интерфейс: русский, english
Разработчик: yourdevice
Версия: 3.2 (03.08.2013)
Скачать.
AVRDUDE_PROG 3.1
Размер файла: 558КБ
Статус программы: бесплатная
ОС: Windows NT/2000/XP/VISTA/WINDOWS 7
Интерфейс: русский, english
Разработчик: yourdevice
Версия: 3.1 (18.10.2012)
Скачать.
AVRDUDE_PROG 3.0
Размер файла: 558КБ
Статус программы: бесплатная
ОС: Windows NT/2000/XP/VISTA/WINDOWS 7
Интерфейс: русский
Разработчик: yourdevice
Версия: 3.0
Скачать.

- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- Категория: Разное
- Год выпуска: 2022
- Издатель: Боднар
- Платформа: Windows
- Тип издания: лицензия
- Язык интерфейса: русский (RUS) / английский (ENG)
- Версия: 3.3
- Лекарство: не требуется
Скачать AVRDUDE PROG
1 Mb
275 | 205
У нас все желающие могут бесплатно скачать Avrdude. Это программатор для контроллеров AVR.
С его помощью вы сможете программировать широкий перечень микропроцессоров. Приложение достаточно просто в использовании и даже имеет русский интерфейс. Всё чмо вам понадобится – это программатор USBASP, подключаемый через USB порт к компьютеру.
Дальше надо запустить Avrdude Prog и выбрать из списка тип контроллера. Далее задаются FUSE биты и выбирается файл прошивки. Тут надо знать, что делаешь, иначе есть шанс «убить» устройство. Так что лучше изучить гайды и скачивать прошивки с проверенных источников.
Системные требования
ОС: Windows 11 / 10 / 7 / 8
Процессор: Intel или AMD
ОЗУ: 512 Mb
HDD: 10 Mb
Установка AVRDUDE
- Запустить установочный файл
- Установить приложение, следуя его подсказкам
- Начать использование.
Скриншоты
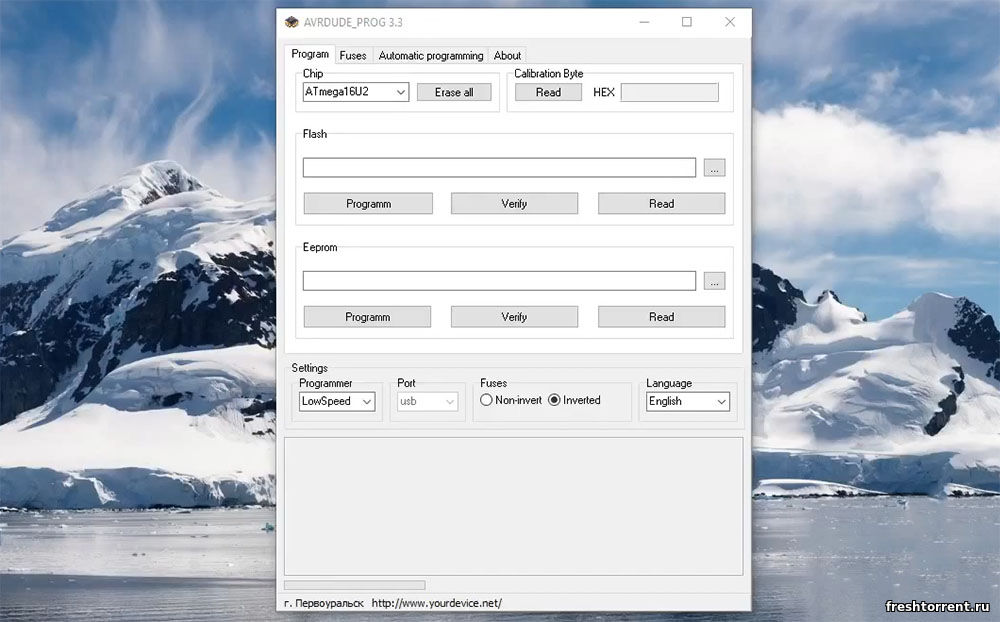
Видеообзор
Похожие файлы
Отзывы: 0
Avrdude 6.3 Windows 8,2/10 6269 votes
Group
If you are using Windows, we recommend downloading WinAVR, which contains the avr-gcc toolchain and a command-line utility called AVRDUDE that can be used to upload programs to the A-Star bootloader. If the version of GNU Make that comes with WinAVR crashes on your computer, we recommend using the Pololu version of GNU Make. Windows avrdude 6.3 (3 files Hide) Release Notes. English; Parallel port does not work anymore for old programmers. If this is needed, create a feature request. Problems with parallel port is realy old computers drive them with 5V, newer old computers drive only. Windows avrdude 6.3 (3 files Hide) Release Notes. English; Parallel port does not work anymore for old programmers. If this is needed, create a feature request. Avrdude-6.1.tar.gz free download. Free motorola razr v3 unlock code generator free. Swiss File Knife Create zip files, extract zip files, replace text in files, search in files using expressions, strea.
Pastebin.com is the number one paste tool since 2002. Pastebin is a website where you can store text online for a set period of time. I’ve developed these instructions on my Windows 10 machine, but they should work for versions of Windows as far back as Windows 7. On older versions, you might want to use WinAVR. WinAVR used to be the preferred way to get this toolchain set up on Windows, even to the point of being semi-official, but has not been maintained in years. Avrdude 6.3 Windows Blackberry Torch 9800 Manual Daemon Tools Windows 7 32 Bit World War 1 Computer Game Nj Drivers License Document Number Backup Exec 2010 R3 Compatibility Invion Gps Map Updates Download Play Free Super Mario Game Pom Qm software download, free Popcorn Movies Youtube Best White Hackle Breeder.
- Main
- Docs
- Submit
- Edit
- Export
- Source code
- Bugs
- Export
- Tasks
- Submit new
- Export
- Patches
- Submit new
- Export
- News
- Submit
- Manage
AVRDUDE 6.3 releasedposted by joerg_wunsch, Tue 16 Feb 2016 10:12:21 PM UTC — 0 replies
AVRDUDE 6.0.1 releasedposted by joerg_wunsch, Tue 17 Sep 2013 10:28:47 PM UTC — 0 replies
AVRDUDE 5.11 relesedposted by joerg_wunsch, Sat 27 Aug 2011 09:38:34 PM UTC — 0 replies
AVRDUDE switched to Subversionposted by joerg_wunsch, Fri 06 Mar 2009 08:04:08 PM UTC — 0 replies
AVRDUDE 5.6 releasedposted by joerg_wunsch, Fri 06 Mar 2009 01:19:21 PM UTC — 1 reply
[Submit News]
[14 news in archive]
AVRDUDE 6.0.1 released
Item posted by Joerg Wunsch <joerg_wunsch> on Tue 17 Sep 2013 10:28:47 PM UTC.
More than two years after the previous release (5.11.1), AVRDUDE 6.0.1
finally made it to go public.
I’d like to thank everyone who has been involved into that release,
both active developers with SVN access as well as numerous users who
contributed bugfixes, improvements and suggestions.
The primary reason for the major version number bump was a changed
syntax of the configuration file (programmer types are now strings
rather than keywords), but that version number change has certainly
also ‘raised the bar’ about many other things that should have been
done before releasing it. Among those are:
. direct reading of ELF files (provided libelf with its header files
is around when ./configure runs)
. keep track of input file contents; when programming just a
bootloader only, nothing else but the bootloader area is touched
. config file can refer to a ‘parent’ device; this dramatically
simplifies the config file as only those things that have been
changed compared to the parent must be specified anew
As an experiment, I’m trying to provide an ‘official’ Win32 binary
release for the first time. It has been compiled using a MinGW32
cross-compilation environment on my FreeBSD host system. If this
turns out to be a complete failure, please tell me, so I can stop this
experiment, and leave Windows binaries to those who know more about
the matter than me. If it works, you might want to tell me
nevertheless, so I might continue that service in future.
Here are the complete release notes for 6.0 (from the NEWS file):
* Major changes compared to the previous version:
— Programmer types in configuration file are no longer keywords but
specified as string.
So you need to change ‘type = XYZ;’ to ‘type = ‘XYZ’;’ in own
config files. (internal: The parser does not need to know all
programmer types now, new programmers will update only the table
in pgm_type.c.)
— The erase cycle counter (formerly options -y / -Y) has been
removed.
— Specifying a -U option without a memory type (short form of
option argument list) now defaults to ‘application’ memory for
Xmega devices, and ‘flash’ for everything else. This ensures
the Xmega bootloader is not accidentally touched.
— For programmers that support it, the default erase method is a
page erase now, rather than a chip erase (Xmega only).
— Keep track of input file contents
Memory segments are being tracked to remember whether they’ve
been actually read from a file. Only segments that came from a
file are being programmed into the device, or considered for
verification. This drastically improves handling speed for
sparse files (e.g. files that have a second bootloader segment),
and it ensures the device contents is actually compared for
everything mentioned in the file (even in case the file has
large 0xFF blocks).
— The -U option now accepts ELF files as input files, and extracts
the appropriate section contents that matches the requested memory
region. To enable this feature, the host system used for the
compilation must have a libelf around, including the respective
header files (i.e., package ‘libelf-devel’ on many Linux systems).
— Programmers and parts lists
They are now sorted at output with ‘-c ?’/’-p ?’. (patch #7671:
Sorting programmers and parts lists for console output)
Programmers and parts lists in documentation generated from lists
mentioned above. (patch #7687: Autogenerating programmers and
parts lists for docs)
Output list of programmer types with ‘-c ?type’, add list to
documentation
— Configuration files now accepts parent parts/programmers, parts
starting with ‘.’ (eg. .xmega) are not included in output parts
list and can be used as abstract parents
(bug #34302: Feature request : device configuration with parent classes)
(patch #7688: Implement parent programmers feature)
— Additional config files which are read after default can be
specified on command line using ‘-C +filename’
(patch #7699 Read additional config files)
— ‘Safemode’ can now be turned off by default from within a
configuration file (like ~/.avrduderc).
— The new option -l logfile allows to redirect diagnostic messages
to a logfile rather than stderr. Useful to record debugging
traces, in particular in environments which do not offer
shell-style redirection functionality for standard streams.
— When leaving debugWIRE mode, immediately retry with ISP rather
than bailing out completely.
— The USBasp programmer implementation now supports detailed traces
with -vvv, and device communication traces with -vvvv.
— The ‘verbose’ terminal mode command allows to query or modify the
verbosity level.
* New devices supported:
— ATmega48P (patch #7629 add support for atmega48p)
— AT90PWM316 (bug #21797: AT90PWM316: New part description)
— ATxmega16D4, ATxmega32D4, ATxmega64D4, ATxmega128D4
— ATmega256RFR2, ATmega128RFR2, ATmega64RFR2, ATmega2564RFR2,
ATmega1284RFR2, ATmega644RFR2
— ATtiny1634
— ATxmega128A1U, ATxmega128A3U, ATxmega128A4U, ATxmega128B1,
ATxmega128B3, ATxmega128C3, ATxmega128D3, ATxmega16A4U,
ATxmega16C4, ATxmega192A3U, ATxmega192C3, ATxmega192D3,
ATxmega256A3BU, ATxmega256A3U, ATxmega256C3, ATxmega256D3,
ATxmega32A4U, ATxmega32C4, ATxmega384C3, ATxmega384D3,
ATxmega64A1U, ATxmega64A3U, ATxmega64A4U, ATxmega64B1,
ATxmega64B3, ATxmega64C3, ATxmega64D3
— ATtiny43U
— ATmega406
— ATxmega8E5, ATxmega16E5, ATxmega32E5
— ATtiny20, ATtiny40
* New programmers supported:
— linuxgpio
+ any (embedded) Linux system with 4 GPIOs available can be used
as a programmer with little or no additional hardware.
— avrftdi
+ o-link (patch #7672 adding support for O-Link (FTDI based
JTAG) as programmer)
+ 4232h (patch #7715 FT4232H support)
— TPI support
+ openmoko (bug #37977 Support for Openmoko Debug Board)
— usbasp
+ nibobee (previously specified as ‘-c usbasp -P nibobee)
+ usbasp-clone (same as usbasp but ignores vendor and product
string, checks only vid/pid)
— ftdi_syncbb (new type for synchronous bitbanging with ft232r/ft245r)
+ ft245r (FT245R Synchronous BitBang, miso = D1, sck = D0, mosi
= D2, reset = D4)
+ ft232r (FT232R Synchronous BitBang, miso = RxD, sck = RTS,
mosi = TxD, reset = DTR)
+ bwmega (BitWizard ftdi_atmega builtin programmer, miso = DSR,
sck = DCD, mosi = CTS, reset = RI)
+ arduino-ft232r (Arduino: FT232R connected to ISP, miso = CTS
X3(1), sck = DSR X3(2), mosi = DCD X3(3), reset = RI X3(4))
+ diecimila (alias for arduino-ft232r)
— pickit2
— Atmel JTAGICE3
— buspirate_bb (TPI programming using the BusPirate in bitbang mode)
* Bugfixes
— bug #34027: avrdude AT90S1200 Problem
— bug #34518: loading intel hex files > 64k using record-type 4
— patch #7667: Minor memory handling fixes
— patch #7680: Fixing timeout problem in ser_recv in ser_win32.c
— patch #7693: Fix config file atmel URLs (+ URLs in
avrdude.texi and avrpart.h)
— bug #21663: AT90PWM efuse incorrect, bug #30438: efuse bits
written as 0 on at90pwmxx parts
— bug #35261: avrftdi uses wrong interface in avrftdi_paged_(write load)
— patch #7437 modifications to Bus Pirate module
— patch #7686 Updating buspirate ascii mode to current firmware,
use AUX as clock generator, and setting of serial receive
timeout
— bug #34768 Proposition: Change the name of the AVR32 devices
— patch #7718: Merge global data of avrftdi in a private data
structure
— bug #35208: avrdude 5.11 on freebsd 8.2-STABLE does not reset
Arduino Uno properly
— bug #34518: loading intel hex files > 64k using record-type 4
(Extended Linear Address Record)
— bug #34027: avrdude AT90S1200 Problem
— bug #30451: Accessing some Xmega memory sections gives not
supported error
— bug #28744: Can’t load bootloader to xmega128a1
— bug #29019: pagel/bs2 warning when uploading using stk500 to xmega
— bug #30756: When setting SUT to 64ms on XMEGA, avrdude doesn’t
read device signature
— bug #37265: wrong page sizes for XMega64xx in avrdude.conf
— bug #37942: Latest SVN can’t program in dragon_jtag mode
— patch #7876 JTAGICE mkII fails to connect to attiny if debugwire
is enabled AND target has a very slow clock
— bug #39893: Verification failure with AVRISPmkII and Xmega
— bug #38713: Compilation of the documentation breaks with texinfo-5
— bug #38023: avrdude doesn’t return an error code when attempting
to upload an invalid Intel HEX file
— bug #39794: warnings when building avrdude 6.0rc1 under CentOS 6.4
— bug #35800: Compilation error on certain systems if parport is disabled
— bug #38307: Can’t write usersig of an xmega256a3
— bug #38580: Current svn head, xmega and fuses, all fuses tied to fuse0
— bug #39691: Buffer overrun when reading EEPROM byte with JTAGICE3
— bug #38951: AVR109 use byte offset instead of word offset
— patch #7769: Write flash fails for AVR910 programmers
— bug #38732: Support for ATtiny1634
— bug #36901: flashing Atmega32U4 EEPROM produces garbage on chip
— bug #28344: chip_erase_delay too short for ATmega324P, 644, 644P, and 1284P
— bug #34277: avrdude reads wrong byte order if using avr911 (aka butterfly)
— bug #35456: The progress bar for STK500V2 programmer is ‘wrong’.
— patch #5708: avrdude should make 10 synchronization attempts instead of just one
— patch #7606: ATtiny43u support
— patch #7657: Add ATmega406 support for avrdude using DRAGON + JTAG
— bug #35474: Feature request: print fuse values in safemode output.
— patch #7710: usb_libusb: Check VID/PID before opening device
— [no-id]: Fix SCK period adjustment for STK500v2
— bug #40040: Support for ATtiny20 and ATtiny40
— bug #40055: AVRDUDE segfaults when writing eeprom
* Internals:
— Restructuring and compacting programmer definition part of
grammar for config file.
— Cleanup of parser code, removing unused definitions/
functions. Using yylex_destroy if available.
— Fixed some more memory leaks, added cleanup code at program exit
(to minimize the number of non-freed memory blocks reported by
valgrind)
— Fixed some findings reported by cppcheck.
/stata-mp-license.html. No messages in AVRDUDE 6.0.1 released
Copyright © 2019 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
Verbatim copying and distribution of this entire articleis permitted in any medium, provided this notice is preserved.
The Levitating,Meditating, Flute-playing Gnu logo is a GNU GPL’ed image providedby the Nevrax Design Team.
Source Code
Avrdude 6.3 Windows 7
Group
- Main
- Docs
- Submit
- Edit
- Export
- Source code
- Bugs
- Export
- Tasks
- Submit new
- Export
- Patches
- Submit new
- Export
- News
- Submit
- Manage
Project Admins:
— Joerg Wunsch
[View Members]
Id: #3904
Name: AVR Downloader/UploaDEr
Avrdude 6.3 Windows
This project is not part of the GNU Project.
AVRDUDE is software for programming Atmel AVR Microcontrollers.
Registration Date: Thu 06 Feb 2003 06:21:20 AM UTC
License: GNU General Public License v2 or later
Development Status: 5 — Production/Stable
AVRDUDE 6.3 released
posted by joerg_wunsch, Tue 16 Feb 2016 10:12:21 PM UTC — 0 replies
Seems like a lot of news was missing here.
So here is a summary of new things since version 6.0.1:
* New devices supported:
— ATmega48PB, ATmega88PB, ATmega168PB
— ATtiny28 (HVPP-only device)
— AT90PWM216 (bug #42310: New part description for AT90PWM216) ..
[Read more]AVRDUDE 6.0.1 released
posted by joerg_wunsch, Tue 17 Sep 2013 10:28:47 PM UTC — 0 replies
More than two years after the previous release (5.11.1), AVRDUDE 6.0.1
finally made it to go public.
I’d like to thank everyone who has been involved into that release,
both active developers with SVN access as well as numerous users who ..
[Read more]AVRDUDE 5.11 relesed
posted by joerg_wunsch, Sat 27 Aug 2011 09:38:34 PM UTC — 0 replies
Finally, more than 1.5 years after the previous release,
AVRDUDE 5.11 is finally done. This is mostly a bugfix
release, but also includes a few enhancements. The two
most important enhancements are:
. TPI (i.e. ATtiny4/5/9/10) programming support for bitbang
programmers.
. FTDI MPSSE (FT2232 etc.) bitbang support.
AVRDUDE switched to Subversion
Avrdude 6.3 Windows 10
posted by joerg_wunsch, Fri 06 Mar 2009 08:04:08 PM UTC — 0 replies
See
https://savannah.nongnu.org/svn/?group=avrdude
[Submit News]
[14 news in archive]
Docs
— Browse docs (External to Savane)
— Browse the cookbook
Mailing Lists (1 public mailing list)
Subversion Repository
— Browse Sources Repository
Bug Tracker (open items: 191, total: 509)
— Browse open items
— Submit a new item
Task Manager (open items: 1, total: 3)
— Browse open items
— Submit a new item
Avrdude 6.3 Windows Xp
Patch Manager (open items: 55, total: 236)
— Browse open items
— Submit a new item
Avrdude 6.3 Windows 10
Copyright © 2019 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
Verbatim copying and distribution of this entire articleis permitted in any medium, provided this notice is preserved.
The Levitating,Meditating, Flute-playing Gnu logo is a GNU GPL’ed image providedby the Nevrax Design Team.
Source Code
Описание
AVRDUDE Prog — это удобная программа с русскоязычным интерфейсом, которая позволяет программировать микроконтроллеры различных типов. Софт является переработанной версией другой утилиты — Usbasp. AVRDUDE Prog совместима с множеством популярных программаторов и выполняет прошивку контроллеров ATmega и ATtiny различных типов. А если загрузить программу на флешку, вы сможете носить мощный инструмент для прошивки микроконтроллеров в своем кармане.
Главное преимущество программы в том, что, если вы не нашли нужный микроконтроллер в меню AVRDUDE Prog, вы можете добавить его самостоятельно. Кроме того, вы можете вручную добавить программатор, настроить скорость программирования и другие параметры. Софт позволяет выбирать инверсные и прямые Fuses биты, настраивать их и редактировать отображение. Значения битов выводятся в HEX формате. А после закрытия окна программы все настройки сохранятся, что избавит пользователя от повторного ввода значений.
Интерфейс программы достаточно прост. Пользователи, знакомые с прошивкой микроконтроллеров, смогут быстро освоить данный софт. Графическая оболочка AVRDUDE Prog примитивна, а элементы управления переведены на русский язык. Дополнительным преимуществом утилиты является то, что она работает в портативном режиме.
Функции и особенности программы AVRDUDE Prog 3.3:
- Прошивка МК ATmega и ATtiny
- Настройка и выбор Fuses битов
- Самостоятельное добавление контроллеров и программаторов
- Интерфейс на русском языке
- Совместимость с 32 и 64 битными системами Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8 и 10
