Note
This module is part of the ansible.windows collection (version 2.8.0).
You might already have this collection installed if you are using the ansible package.
It is not included in ansible-core.
To check whether it is installed, run ansible-galaxy collection list.
To install it, use: ansible-galaxy collection install ansible.windows.
To use it in a playbook, specify: ansible.windows.win_package.
Synopsis
-
Installs or uninstalls software packages for Windows.
-
Supports
.exe,.msi,.msp,.appx,.appxbundle,.msix, and.msixbundle. -
These packages can be sourced from the local file system, network file share or a url.
-
See provider for more info on each package type that is supported.
Parameters
|
Parameter |
Comments |
|---|---|
|
arguments any |
Any arguments the installer needs to either install or uninstall the package. If the package is an MSI do not supply the This is only used for the Can be a list of arguments and the module will escape the arguments as necessary, it is recommended to use a string when dealing with MSI packages due to the unique escaping issues with msiexec. When using a list of arguments each item in the list is considered to be a single argument. As such, if an argument in the list contains a space then Ansible will quote this to ensure that this is seen by Windows as a single argument. Should this behaviour not be what is required, the argument should be split into two separate list items. See the examples section for more detail. |
|
chdir path |
Set the specified path as the current working directory before installing or uninstalling a package. This is only used for the |
|
checksum string added in ansible.windows 2.8.0 |
If a checksum is passed to this parameter, the digest of the package will be calculated before executing it to verify that the path or downloaded file has the expected contents. |
|
checksum_algorithm string added in ansible.windows 2.8.0 |
Specifies the hashing algorithm used when calculating the checksum of the path provided. Choices:
|
|
client_cert string |
The path to the client certificate (.pfx) that is used for X509 authentication. This path can either be the path to the The WinRM connection must be authenticated with Other authentication types can set client_cert_password when the cert is password protected. |
|
client_cert_password string |
The password for client_cert if the cert is password protected. |
|
creates_path path |
Will check the existence of the path specified and use the result to determine whether the package is already installed. You can use this in conjunction with |
|
creates_service string |
Will check the existing of the service specified and use the result to determine whether the package is already installed. You can use this in conjunction with |
|
creates_version string |
Will check the file version property of the file at
You can use this in conjunction with |
|
expected_return_code list / elements=integer |
One or more return codes from the package installation that indicates success. The return codes are read as a signed integer, any values greater than 2147483647 need to be represented as the signed equivalent, i.e. To convert a unsigned number to the signed equivalent you can run “[Int32](“0x{0:X}” -f ([UInt32]3221225477))”. A return code of This is only used for the Default: |
|
follow_redirects string |
Whether or the module should follow redirects.
When following a redirected URL, the Choices:
|
|
force_basic_auth boolean |
By default the authentication header is only sent when a webservice responses to an initial request with a 401 status. Since some basic auth services do not properly send a 401, logins will fail. This option forces the sending of the Basic authentication header upon the original request. Choices:
|
|
dictionary |
Extra headers to set on the request. This should be a dictionary where the key is the header name and the value is the value for that header. |
|
http_agent string |
Header to identify as, generally appears in web server logs. This is set to the Default: |
|
log_path path |
Specifies the path to a log file that is persisted after a package is installed or uninstalled. This is only used for the When omitted, a temporary log file is used instead for those providers. This is only valid for MSI files, use |
|
maximum_redirection integer |
Specify how many times the module will redirect a connection to an alternative URI before the connection fails. If set to Default: |
|
path string |
Location of the package to be installed or uninstalled. This package can either be on the local file system, network share or a url. When If If |
|
product_id string |
The product id of the installed packaged. This is used for checking whether the product is already installed and getting the uninstall information if For msi packages, this is the For msp packages, this is the For msix packages, this is the For registry (exe) packages, this is the registry key name under the registry paths specified in provider. This value is ignored if This SHOULD be set when the package is an |
|
provider string |
Set the package provider to use when searching for a package. The The The The The Choices:
|
|
proxy_password string |
The password for proxy_username. |
|
proxy_url string |
An explicit proxy to use for the request. By default, the request will use the IE defined proxy unless use_proxy is set to |
|
proxy_use_default_credential boolean |
Uses the current user’s credentials when authenticating with a proxy host protected with Proxies that use The module will only have access to the user’s credentials if using If not using Choices:
|
|
proxy_username string |
The username to use for proxy authentication. |
|
state string |
Whether to install or uninstall the package. The module uses product_id to determine whether the package is installed or not. For all providers but Choices:
|
|
url_method string |
The HTTP Method of the request. |
|
url_password string |
The password for url_username. |
|
url_timeout integer |
Specifies how long the request can be pending before it times out (in seconds). Set to Default: |
|
url_username string |
The username to use for authentication. |
|
use_default_credential boolean |
Uses the current user’s credentials when authenticating with a server protected with Sites that use The module will only have access to the user’s credentials if using If not using Choices:
|
|
use_proxy boolean |
If Choices:
|
|
validate_certs boolean |
If This should only be used on personally controlled sites using self-signed certificates. Choices:
|
|
wait_for_children boolean added in ansible.windows 1.3.0 |
The module will wait for the process it spawns to finish but any processes spawned in that child process as ignored. Set to This is useful if the install/uninstaller is just a wrapper which then calls the actual installer as its own child process. When this option is This should not be required for most installers and setting to Requires Windows Server 2012 or Windows 8 or newer to use. Choices:
|
Notes
Note
-
When
state=absentand the product is an exe, the path may be different from what was used to install the package originally. If path is not set then the path used will be what is set underQuietUninstallStringorUninstallStringin the registry for that product_id. -
By default all msi installs and uninstalls will be run with the arguments
/log, /qn, /norestart. -
All the installation checks under
product_idandcreates_*add together, if one fails then the program is considered to be absent.
See Also
Examples
- name: Install the Visual C thingy ansible.windows.win_package: path: http://download.microsoft.com/download/1/6/B/16B06F60-3B20-4FF2-B699-5E9B7962F9AE/VSU_4/vcredist_x64.exe product_id: '{CF2BEA3C-26EA-32F8-AA9B-331F7E34BA97}' arguments: /install /passive /norestart - name: Install Visual C thingy with list of arguments instead of a string ansible.windows.win_package: path: http://download.microsoft.com/download/1/6/B/16B06F60-3B20-4FF2-B699-5E9B7962F9AE/VSU_4/vcredist_x64.exe product_id: '{CF2BEA3C-26EA-32F8-AA9B-331F7E34BA97}' arguments: - /install - /passive - /norestart - name: Install MSBuild thingy with arguments split to prevent quotes ansible.windows.win_package: path: https://download.visualstudio.microsoft.com/download/pr/9665567e-f580-4acd-85f2-bc94a1db745f/vs_BuildTools.exe product_id: '{D1437F51-786A-4F57-A99C-F8E94FBA1BD8}' arguments: - --norestart - --passive - --wait - --add - Microsoft.Net.Component.4.6.1.TargetingPack - --add - Microsoft.Net.Component.4.6.TargetingPack - name: Install Remote Desktop Connection Manager from msi with a permanent log ansible.windows.win_package: path: https://download.microsoft.com/download/A/F/0/AF0071F3-B198-4A35-AA90-C68D103BDCCF/rdcman.msi product_id: '{0240359E-6A4C-4884-9E94-B397A02D893C}' state: present log_path: D:\logs\vcredist_x64-exe-{{lookup('pipe', 'date +%Y%m%dT%H%M%S')}}.log - name: Install Application from msi with multiple properties for installer ansible.windows.win_package: path: C:\temp\Application.msi state: present arguments: >- SERVICE=1 DBNAME=ApplicationDB DBSERVER=.\SQLEXPRESS INSTALLDIR="C:\Program Files (x86)\App lication\App Server" - name: Install Microsoft® SQL Server® 2019 Express (DPAPI example) ansible.windows.win_package: path: C:\temp\SQLEXPR_x64_ENU\SETUP.EXE product_id: Microsoft SQL Server SQL2019 arguments: - SAPWD=VeryHardPassword - /ConfigurationFile=C:\temp\configuration.ini become: true vars: ansible_become_method: runas ansible_become_user: "{{ user }}" ansible_become_pass: "{{ password }}" - name: Uninstall Remote Desktop Connection Manager ansible.windows.win_package: product_id: '{0240359E-6A4C-4884-9E94-B397A02D893C}' state: absent - name: Install Remote Desktop Connection Manager locally omitting the product_id ansible.windows.win_package: path: C:\temp\rdcman.msi state: present - name: Uninstall Remote Desktop Connection Manager from local MSI omitting the product_id ansible.windows.win_package: path: C:\temp\rdcman.msi state: absent # 7-Zip exe doesn't use a guid for the Product ID - name: Install 7zip from a network share with specific credentials ansible.windows.win_package: path: \\domain\programs\7z.exe product_id: 7-Zip arguments: /S state: present become: true become_method: runas become_flags: logon_type=new_credential logon_flags=netcredentials_only vars: ansible_become_user: DOMAIN\User ansible_become_password: Password - name: Install 7zip and use a file version for the installation check ansible.windows.win_package: path: C:\temp\7z.exe creates_path: C:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe creates_version: 16.04 state: present - name: Uninstall 7zip from the exe ansible.windows.win_package: path: C:\Program Files\7-Zip\Uninstall.exe product_id: 7-Zip arguments: /S state: absent - name: Uninstall 7zip without specifying the path ansible.windows.win_package: product_id: 7-Zip arguments: /S state: absent - name: Install application and override expected return codes ansible.windows.win_package: path: https://download.microsoft.com/download/1/6/7/167F0D79-9317-48AE-AEDB-17120579F8E2/NDP451-KB2858728-x86-x64-AllOS-ENU.exe product_id: '{7DEBE4EB-6B40-3766-BB35-5CBBC385DA37}' arguments: '/q /norestart' state: present expected_return_code: [0, 666, 3010] - name: Install a .msp patch ansible.windows.win_package: path: C:\Patches\Product.msp state: present - name: Remove a .msp patch ansible.windows.win_package: product_id: '{AC76BA86-A440-FFFF-A440-0C13154E5D00}' state: absent - name: Enable installation of 3rd party MSIX packages ansible.windows.win_regedit: path: HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\AppModelUnlock name: AllowAllTrustedApps data: 1 type: dword state: present - name: Install an MSIX package for the current user ansible.windows.win_package: path: C:\Installers\Calculator.msix # Can be .appx, .msixbundle, or .appxbundle state: present - name: Uninstall an MSIX package using the product_id ansible.windows.win_package: product_id: InputApp state: absent
Return Values
Common return values are documented here, the following are the fields unique to this module:
|
Key |
Description |
|---|---|
|
checksum string added in ansible.windows 2.8.0 |
<algorithm> checksum of the package Returned: checksum_algorithm is set, package exists, and not check mode Sample: |
|
log string |
The contents of the MSI or MSP log. Returned: installation/uninstallation failure for MSI or MSP packages Sample: |
|
rc integer |
The return code of the package process. Returned: change occurred Sample: |
|
reboot_required boolean |
Whether a reboot is required to finalise package. This is set to true if the executable return code is 3010. Returned: always Sample: |
|
stderr string |
The stderr stream of the package process. Returned: failure during install or uninstall Sample: |
|
stdout string |
The stdout stream of the package process. Returned: failure during install or uninstall Sample: |
Collection links
- Issue Tracker
- Repository (Sources)
To Install an Application on Windows by using Ansible playbook
Introduction:
Ansible is an open-source tool for managing software configurations and deploying applications. Chocolately is a management tool for Windows software.
Master Server Requirements:
ansible
python3-pip
pywinrm (python package
Windows Requirements:
powershell 3+
Dot net 4
Installation Procedure:
Step 1: Search for chocolatey in browser
Step 2: Copy the installation command in chocolatey install page

Step 3: Run Powershell ISE as an administrator

Step 4: Install chocolatey by using the following command
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force;
[System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor 3072; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://community.chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))
Forcing web requests to allow TLS v1.2 (Required for requests to Chocolatey.org)
Getting latest version of the Chocolatey package for download.
Not using proxy.
Getting Chocolatey from https://community.chocolatey.org/api/v2/package/chocolatey/0.11.3.
Downloading https://community.chocolatey.org/api/v2/package/chocolatey/0.11.3 to C:\Users\Admin\AppData\Local\Temp\chocolatey\chocoInstall\chocolatey.zip
Not using proxy.
Extracting C:\Users\Admin\AppData\Local\Temp\chocolatey\chocoInstall\chocolatey.zip to C:\Users\Admin\AppData\Local\Temp\chocolatey\chocoInstall
Installing Chocolatey on the local machine
Creating ChocolateyInstall as an environment variable (targeting 'Machine')
Setting ChocolateyInstall to 'C:\ProgramData\chocolatey'
WARNING: It's very likely you will need to close and reopen your shell
before you can use choco.
Restricting write permissions to Administrators
We are setting up the Chocolatey package repository.
The packages themselves go to 'C:\ProgramData\chocolatey\lib'
(i.e. C:\ProgramData\chocolatey\lib\yourPackageName).
A shim file for the command line goes to 'C:\ProgramData\chocolatey\bin'
and points to an executable in 'C:\ProgramData\chocolatey\lib\yourPackageName'.
Step 5: Check the OS version by using the following command
root@linuxhelp:~# lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 21.04
Release: 21.04
Codename: hirsute
Step 6: Check the availability of Ansible package
root@linuxhelp:~# apt list -a ansible
Listing... Done
ansible/hirsute,hirsute,now 4.8.0-1ppa~hirsute all [installed]
ansible/hirsute,hirsute 2.10.7-1 all
Step 7: Check the availability of python3-pip package
root@linuxhelp:~# apt list -a python3
Listing... Done
python3/hirsute,now 3.9.4-1 amd64 [installed,automatic]
python3/hirsute 3.9.4-1 i386
Step 8: Check the availability of python package pywinrm
root@linuxhelp:~# pip list | grep pywinrm
pywinrm 0.4.2
ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation=ignore
Step 9: Install the plugins of chocolatey for ansible
root@linuxhelp:~# ansible-galaxy collection install chocolatey.chocolatey
Starting galaxy collection install process
Nothing to do. All requested collections are already installed. If you want to reinstall them, consider using `--force`.
Step 10:Create inventory for Windows node system
root@linuxhelp:~# vi /etc/ansible/hosts
[windows]
192.168.2.134
[windows:vars]
ansible_user=Admin
ansible_password=Admin@123
ansible_port=5986
ansible_connection=winrm
Step 11:Create playbook for installing namecoin application
root@linuxhelp:~# vi install.yml
hosts: windows
gather_facts: true
tasks:
- name: install namecoin
win_chocolatey:
name: namecoin
state: present
Step 12: Check the syntax of the install.yml ansible playbook by using the following command
root@linuxhelp:~# ansible-playbook install.yml --syntax-check
playbook: proxyset.yml
Step 13: Run the install.yml playbook by using the following command
root@linuxhelp:~# ansible-playbook install.yml
PLAY [windows] **************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ******************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.2.134]
TASK [install namecoin] *****************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.2.134]
PLAY RECAP ******************************************************************************************
192.168.2.134 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Step 14 : Namecoin application installed on Windows Client system

Step 15: Create playbook for uninstall namecoin application
root@linuxhelp:~# vi uninstall.yml
- hosts: windows
gather_facts: true
tasks:
- name: Uninstall namecoin
win_chocolatey:
name: namecoin
state: absent
~
Step 16: Check the syntax of the uninstall.yml ansible playbook by using the following command
root@linuxhelp:~# ansible-playbook uninstall.yml --syntax-check
playbook: removeproxy.yml
Step 17: Run the uninstall.yml playbook by using the following command
root@linuxhelp:~# ansible-playbook uninstall.yml
PLAY [windows] **************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ******************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.2.134]
TASK [Uninstall namecoin] ***************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.2.134]
PLAY RECAP ******************************************************************************************
192.168.2.134 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Step 18: Namecoin application Uninstalled on Windows Client system

With this installation of an application on Windows by using Ansible comes to an end
By this time most of the readers on this blog know I am an automation junkie and Ansible is my dealer. I started using Chocolatey about 2 years ago as it is an efficient open-source package manager for Windows operating systems similar to what brew is for Mac OS systems. In today’s tutorial, I am going to cover how to use Chocolatey and Ansible together to manage desktop apps on Windows operating systems.
Prerequisite Initial Steps
The initial steps would be to have Ansible set up already and Chocolatey installed on your Windows machine. You can follow the tutorials below to set up Ansible and install Chocolatey:
How To Set Up Ansible Inside A Github Repository And Automate Your Workloads
Ansible is an open-source configuration management and IT automation platform. Let’s jump in and set up our Ansible Github repository and run an example automation playbook.
Opensource GeeksChad Crouch

Installing Chocolatey
Chocolatey is software management automation for Windows that wraps installers, executables, zips, and scripts into compiled packages. Chocolatey integrates w/SCCM, Puppet, Chef, etc. Chocolatey is trusted by businesses to manage software deployments.
Chocolatey Software

Script To Set Ansible Connection To Windows Host Locally Via WSL
WSL also known as Windows Subsystem For Linux is a lightweight virtual machine that you can enable to run Linux on your Windows computer. Ensure that you set up WSL by following these steps:
Install Ubuntu on WSL2 on Windows 10 | Ubuntu
Ubuntu is an open source software operating system that runs from the desktop, to the cloud, to all your internet connected things.
Ubuntu

Once WSL is installed and Ansible and Chocolatey are set up. Copy the Powershell script below and name it windows-host-setup.ps1. Navigate to the directory and run this command to execute the setup that will allow you to access your Windows localhost through WSL — powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -File "windows-host-setup.ps1"
$url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ansible/ansible/devel/examples/scripts/ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1"
$file = "$env:temp\ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1"
(New-Object -TypeName System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile($url, $file)
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -File $file
Set Up Inventory And Playbooks
Once the above script is executed successfully the next steps are to add your inventory file and playbook to manage your desktop apps on your Windows system. Create a directory called choco and add localhost_inventory.yml and desktop_apps.yml and copy the scripts below:
#localhost_inventory.yml
all:
hosts: localhost
vars:
ansible_user: user #add your windows username here
ansible_connection: winrm
ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation: ignore
#desktop_apps.yml
---
- hosts: localhost
connection: local
tasks:
- name: Install/Uninstall/Update Chromium
win_chocolatey:
name:
- chromium
state: absent
- name: Install/Uninstall/Update Slack
win_chocolatey:
name:
- slack
state: present
- name: Install/Uninstall/Update Telegram
win_chocolatey:
name:
- telegram
state: latest
The desktop_apps.yml script can be updated by looking at the chocolatey package website to see which packages are available to install. In this tutorial we are going to uninstall Chromium, ensure that Slack is installed else it will be installed, update Telegram to the latest version if installed, and if not install the latest version. This ansible module states work as follows:
- absent — uninstall package/software
- present — ensure the software is installed and if not install the latest version
- latest — update software to the latest version and if it does not exist install the latest version
Once all the above steps are completed run the following command to execute this Ansible playbook — ansible-playbook choco/desktop_apps.yml -i choco/localhost_inventory.yml --ask-pass --verbose and you will be prompted to input your Windows password.
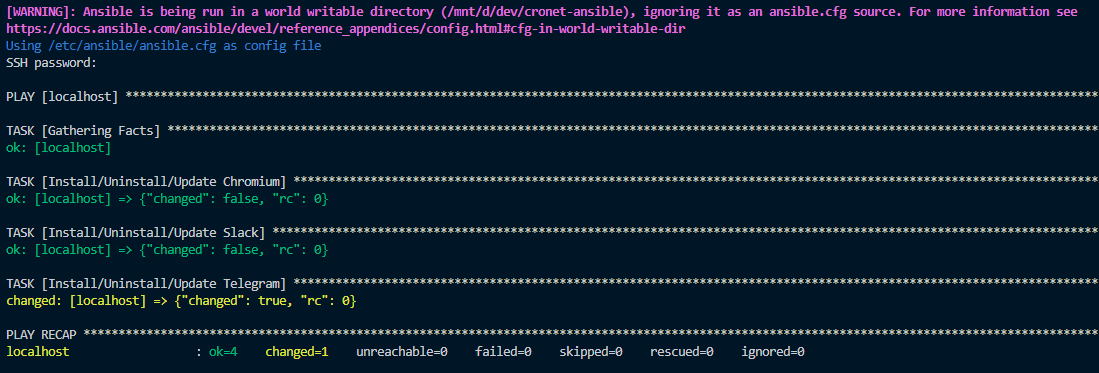
Once successful you can search for the apps and should see that you have installed or updated your desktop apps to the latest version like in this example below.
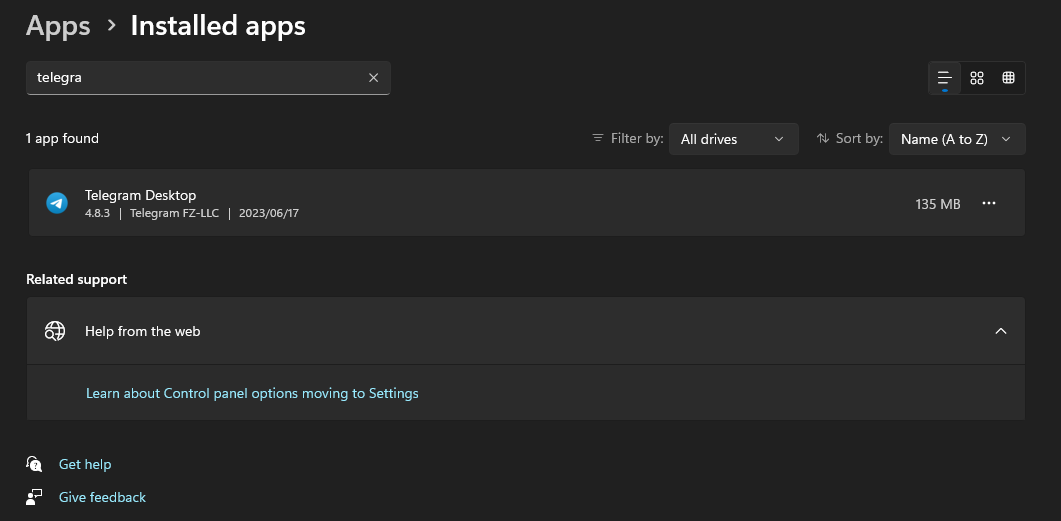
Conclusion
In conclusion, Chocolatey is an awesome open-source package manager for Windows operating systems and has a large community behind it. If you enjoyed this article consider signing up for our newsletter and don’t forget to share it with people that would find it useful. Leave a comment below with a tutorial you would like us to cover.
Всем привет.
Сегодня инсталлируем софт с помощью Ansible. В качестве управляемых хостов берем Windows. Итак, я знаю четыре способа как это сделать: из пакета, прямо из интернета, и с помощью пакетного cmd-файла или PowerShell. В двух последних случаях надо предварительно закинуть на хост сам cmd-файлик или ps1.
Создаем плейбук Ansible.
— name: Windows file example playbook
hosts: all
gather_facts: false
Далее пишем наши задачи. Первый вариант — инсталляция из пакета:
tasks:
— name: Install package
win_package:
path: c:\temp\install\rdcman.msi
product_id: ‘{0240359E-6A4C-4884-9E94-B397A02D893C}’
arguments: /silent /unattended
state: present
Пусть вы желаете раскрутить Adobe Acrobat Reader на штатных хостах Windows, вы можете воспользоваться модулями win_copy или win_get_url для распространения надлежащего установщика, а затем своим модулем win_package для его установки. Однако можно использовать более изящный способ:
— name: Install Acrobat Reader
win_chocolatey:
name: adobereader
state: present
Что касается вариантов пакетного cmd-файла или PowerShell, то для начала создаем предварительно отдельную папку, если не хотим использовать ту же c:\temp (Вдруг она не существует?)
— name: Create a directory using cmd.exe
win_shell: mkdir C:\MasteryCMD
args:
executable: cmd
ИЛИ
— name: Create a directory using PowerShell
win_shell: New-Item -Path C:\MasteryPS -ItemType Directory
далее копируем наш master.cmd на целевой хост:
— name: Copy across a test file
win_copy:
src: ~/src/mastery/master.cmd
dest: ‘C:\MasteryCMD\master.cmd’
и запускаем его на выполнение:
— name: Create a directory using cmd.exe
win_shell: C:\MasteryCMD\master.cmd
args:
executable: cmd
С PowerShell поступаем аналогично.
Удачи.
When using Ansible to manage Windows, many of the syntax and rules that apply
for Unix/Linux hosts also apply to Windows, but there are still some differences
when it comes to components like path separators and OS-specific tasks.
This document covers details specific to using Ansible for Windows.
Use Cases
Ansible can be used to orchestrate a multitude of tasks on Windows servers.
Below are some examples and info about common tasks.
Installing Software
There are three main ways that Ansible can be used to install software:
-
Using the
win_chocolateymodule. This sources the program data from the default
public Chocolatey repository. Internal repositories can
be used instead by setting thesourceoption. -
Using the
win_packagemodule. This installs software using an MSI or .exe installer
from a local/network path or URL. -
Using the
win_commandorwin_shellmodule to run an installer manually.
The win_chocolatey module is recommended since it has the most complete logic for checking to see if a package has already been installed and is up-to-date.
Below are some examples of using all three options to install 7-Zip:
# Install/uninstall with chocolatey - name: Ensure 7-Zip is installed through Chocolatey win_chocolatey: name: 7zip state: present - name: Ensure 7-Zip is not installed through Chocolatey win_chocolatey: name: 7zip state: absent # Install/uninstall with win_package - name: Download the 7-Zip package win_get_url: url: https://www.7-zip.org/a/7z1701-x64.msi dest: C:\temp\7z.msi - name: Ensure 7-Zip is installed through win_package win_package: path: C:\temp\7z.msi state: present - name: Ensure 7-Zip is not installed through win_package win_package: path: C:\temp\7z.msi state: absent # Install/uninstall with win_command - name: Download the 7-Zip package win_get_url: url: https://www.7-zip.org/a/7z1701-x64.msi dest: C:\temp\7z.msi - name: Check if 7-Zip is already installed win_reg_stat: name: HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\{23170F69-40C1-2702-1701-000001000000} register: 7zip_installed - name: Ensure 7-Zip is installed through win_command win_command: C:\Windows\System32\msiexec.exe /i C:\temp\7z.msi /qn /norestart when: 7zip_installed.exists == false - name: Ensure 7-Zip is uninstalled through win_command win_command: C:\Windows\System32\msiexec.exe /x {23170F69-40C1-2702-1701-000001000000} /qn /norestart when: 7zip_installed.exists == true
Some installers like Microsoft Office or SQL Server require credential delegation or
access to components restricted by WinRM. The best method to bypass these
issues is to use become with the task. With become, Ansible will run
the installer as if it were run interactively on the host.
Note
Many installers do not properly pass back error information over WinRM. In these cases, if the install has been verified to work locally the recommended method is to use become.
Note
Some installers restart the WinRM or HTTP services, or cause them to become temporarily unavailable, making Ansible assume the system is unreachable.
Installing Updates
The win_updates and win_hotfix modules can be used to install updates
or hotfixes on a host. The module win_updates is used to install multiple
updates by category, while win_hotfix can be used to install a single
update or hotfix file that has been downloaded locally.
Note
The win_hotfix module has a requirement that the DISM PowerShell cmdlets are
present. These cmdlets were only added by default on Windows Server 2012
and newer and must be installed on older Windows hosts.
The following example shows how win_updates can be used:
- name: Install all critical and security updates win_updates: category_names: - CriticalUpdates - SecurityUpdates state: installed register: update_result - name: Reboot host if required win_reboot: when: update_result.reboot_required
The following example show how win_hotfix can be used to install a single
update or hotfix:
- name: Download KB3172729 for Server 2012 R2 win_get_url: url: http://download.windowsupdate.com/d/msdownload/update/software/secu/2016/07/windows8.1-kb3172729-x64_e8003822a7ef4705cbb65623b72fd3cec73fe222.msu dest: C:\temp\KB3172729.msu - name: Install hotfix win_hotfix: hotfix_kb: KB3172729 source: C:\temp\KB3172729.msu state: present register: hotfix_result - name: Reboot host if required win_reboot: when: hotfix_result.reboot_required
Set Up Users and Groups
Ansible can be used to create Windows users and groups both locally and on a domain.
Local
The modules win_user, win_group and win_group_membership manage
Windows users, groups and group memberships locally.
The following is an example of creating local accounts and groups that can
access a folder on the same host:
- name: Create local group to contain new users win_group: name: LocalGroup description: Allow access to C:\Development folder - name: Create local user win_user: name: '{{ item.name }}' password: '{{ item.password }}' groups: LocalGroup update_password: false password_never_expires: true loop: - name: User1 password: Password1 - name: User2 password: Password2 - name: Create Development folder win_file: path: C:\Development state: directory - name: Set ACL of Development folder win_acl: path: C:\Development rights: FullControl state: present type: allow user: LocalGroup - name: Remove parent inheritance of Development folder win_acl_inheritance: path: C:\Development reorganize: true state: absent
Domain
The modules win_domain_user and win_domain_group manages users and
groups in a domain. The below is an example of ensuring a batch of domain users
are created:
- name: Ensure each account is created win_domain_user: name: '{{ item.name }}' upn: '{{ item.name }}@MY.DOMAIN.COM' password: '{{ item.password }}' password_never_expires: false groups: - Test User - Application company: Ansible update_password: on_create loop: - name: Test User password: Password - name: Admin User password: SuperSecretPass01 - name: Dev User password: '@fvr3IbFBujSRh!3hBg%wgFucD8^x8W5'
Running Commands
In cases where there is no appropriate module available for a task,
a command or script can be run using the win_shell, win_command, raw, and script modules.
The raw module simply executes a Powershell command remotely. Since raw
has none of the wrappers that Ansible typically uses, become, async
and environment variables do not work.
The script module executes a script from the Ansible control node on
one or more Windows hosts. Like raw, script currently does not support
become, async, or environment variables.
The win_command module is used to execute a command which is either an
executable or batch file, while the win_shell module is used to execute commands within a shell.
Choosing Command or Shell
The win_shell and win_command modules can both be used to execute a command or commands.
The win_shell module is run within a shell-like process like PowerShell or cmd, so it has access to shell
operators like <, >, |, ;, &&, and ||. Multi-lined commands can also be run in win_shell.
The win_command module simply runs a process outside of a shell. It can still
run a shell command like mkdir or New-Item by passing the shell commands
to a shell executable like cmd.exe or PowerShell.exe.
Here are some examples of using win_command and win_shell:
- name: Run a command under PowerShell win_shell: Get-Service -Name service | Stop-Service - name: Run a command under cmd win_shell: mkdir C:\temp args: executable: cmd.exe - name: Run a multiple shell commands win_shell: | New-Item -Path C:\temp -ItemType Directory Remove-Item -Path C:\temp -Force -Recurse $path_info = Get-Item -Path C:\temp $path_info.FullName - name: Run an executable using win_command win_command: whoami.exe - name: Run a cmd command win_command: cmd.exe /c mkdir C:\temp - name: Run a vbs script win_command: cscript.exe script.vbs
Note
Some commands like mkdir, del, and copy only exist in
the CMD shell. To run them with win_command they must be
prefixed with cmd.exe /c.
Argument Rules
When running a command through win_command, the standard Windows argument
rules apply:
-
Each argument is delimited by a white space, which can either be a space or a
tab. -
An argument can be surrounded by double quotes
". Anything inside these
quotes is interpreted as a single argument even if it contains whitespace. -
A double quote preceded by a backslash
\is interpreted as just a double
quote"and not as an argument delimiter. -
Backslashes are interpreted literally unless it immediately precedes double
quotes; for example\==\and\"==" -
If an even number of backslashes is followed by a double quote, one
backslash is used in the argument for every pair, and the double quote is
used as a string delimiter for the argument. -
If an odd number of backslashes is followed by a double quote, one backslash
is used in the argument for every pair, and the double quote is escaped and
made a literal double quote in the argument.
With those rules in mind, here are some examples of quoting:
- win_command: C:\temp\executable.exe argument1 "argument 2" "C:\path\with space" "double \"quoted\"" argv[0] = C:\temp\executable.exe argv[1] = argument1 argv[2] = argument 2 argv[3] = C:\path\with space argv[4] = double "quoted" - win_command: '"C:\Program Files\Program\program.exe" "escaped \\\" backslash" unquoted-end-backslash\' argv[0] = C:\Program Files\Program\program.exe argv[1] = escaped \" backslash argv[2] = unquoted-end-backslash\ # Due to YAML and Ansible parsing '\"' must be written as '{% raw %}\\{% endraw %}"' - win_command: C:\temp\executable.exe C:\no\space\path "arg with end \ before end quote{% raw %}\\{% endraw %}" argv[0] = C:\temp\executable.exe argv[1] = C:\no\space\path argv[2] = arg with end \ before end quote\"
For more information, see escaping arguments.
Creating and Running a Scheduled Task
WinRM has some restrictions in place that cause errors when running certain
commands. One way to bypass these restrictions is to run a command through a
scheduled task. A scheduled task is a Windows component that provides the
ability to run an executable on a schedule and under a different account.
Ansible version 2.5 added modules that make it easier to work with scheduled tasks in Windows.
The following is an example of running a script as a scheduled task that deletes itself after
running:
- name: Create scheduled task to run a process win_scheduled_task: name: adhoc-task username: SYSTEM actions: - path: PowerShell.exe arguments: | Start-Sleep -Seconds 30 # This isn't required, just here as a demonstration New-Item -Path C:\temp\test -ItemType Directory # Remove this action if the task shouldn't be deleted on completion - path: cmd.exe arguments: /c schtasks.exe /Delete /TN "adhoc-task" /F triggers: - type: registration - name: Wait for the scheduled task to complete win_scheduled_task_stat: name: adhoc-task register: task_stat until: (task_stat.state is defined and task_stat.state.status != "TASK_STATE_RUNNING") or (task_stat.task_exists == False) retries: 12 delay: 10
Note
The modules used in the above example were updated/added in Ansible
version 2.5.
Path Formatting for Windows
Windows differs from a traditional POSIX operating system in many ways. One of
the major changes is the shift from / as the path separator to \. This
can cause major issues with how playbooks are written, since \ is often used
as an escape character on POSIX systems.
Ansible allows two different styles of syntax; each deals with path separators for Windows differently:
YAML Style
When using the YAML syntax for tasks, the rules are well-defined by the YAML
standard:
-
When using a normal string (without quotes), YAML will not consider the
backslash an escape character. -
When using single quotes
', YAML will not consider the backslash an
escape character. -
When using double quotes
", the backslash is considered an escape
character and needs to escaped with another backslash.
Note
You should only quote strings when it is absolutely
necessary or required by YAML, and then use single quotes.
The YAML specification considers the following escape sequences:
-
\0,\\,\",\_,\a,\b,\e,\f,\n,\r,\t,
\v,\L,\Nand\P– Single character escape -
<TAB>,<SPACE>,<NBSP>,<LNSP>,<PSP>– Special
characters -
\x..– 2-digit hex escape -
\u....– 4-digit hex escape -
\U........– 8-digit hex escape
Here are some examples on how to write Windows paths:
# GOOD tempdir: C:\Windows\Temp # WORKS tempdir: 'C:\Windows\Temp' tempdir: "C:\\Windows\\Temp" # BAD, BUT SOMETIMES WORKS tempdir: C:\\Windows\\Temp tempdir: 'C:\\Windows\\Temp' tempdir: C:/Windows/Temp
This is an example which will fail:
# FAILS tempdir: "C:\Windows\Temp"
This example shows the use of single quotes when they are required:
--- - name: Copy tomcat config win_copy: src: log4j.xml dest: '{{tc_home}}\lib\log4j.xml'
Legacy key=value Style
The legacy key=value syntax is used on the command line for ad hoc commands,
or inside playbooks. The use of this style is discouraged within playbooks
because backslash characters need to be escaped, making playbooks harder to read.
The legacy syntax depends on the specific implementation in Ansible, and quoting
(both single and double) does not have any effect on how it is parsed by
Ansible.
The Ansible key=value parser parse_kv() considers the following escape
sequences:
-
\,',",\a,\b,\f,\n,\r,\tand
\v– Single character escape -
\x..– 2-digit hex escape -
\u....– 4-digit hex escape -
\U........– 8-digit hex escape -
\N{...}– Unicode character by name
This means that the backslash is an escape character for some sequences, and it
is usually safer to escape a backslash when in this form.
Here are some examples of using Windows paths with the key=value style:
# GOOD tempdir=C:\\Windows\\Temp # WORKS tempdir='C:\\Windows\\Temp' tempdir="C:\\Windows\\Temp" # BAD, BUT SOMETIMES WORKS tempdir=C:\Windows\Temp tempdir='C:\Windows\Temp' tempdir="C:\Windows\Temp" tempdir=C:/Windows/Temp # FAILS tempdir=C:\Windows\temp tempdir='C:\Windows\temp' tempdir="C:\Windows\temp"
The failing examples don’t fail outright but will substitute \t with the
<TAB> character resulting in tempdir being C:\Windows<TAB>emp.
Limitations
Some things you cannot do with Ansible and Windows are:
-
Upgrade PowerShell
-
Interact with the WinRM listeners
Because WinRM is reliant on the services being online and running during normal operations, you cannot upgrade PowerShell or interact with WinRM listeners with Ansible. Both of these actions will cause the connection to fail. This can technically be avoided by using async or a scheduled task, but those methods are fragile if the process it runs breaks the underlying connection Ansible uses, and are best left to the bootstrapping process or before an image is
created.
Developing Windows Modules
Because Ansible modules for Windows are written in PowerShell, the development
guides for Windows modules differ substantially from those for standard standard modules. Please see
Windows module development walkthrough for more information.
