Aircrack-ng
Badges
GitHub CI
Others
Repository versions
Description
Aircrack-ng is a complete suite of tools to assess WiFi network security.
It focuses on different areas of WiFi security:
- Monitoring: Packet capture and export of data to text files for further processing by third party tools.
- Attacking: Replay attacks, deauthentication, fake access points and others via packet injection.
- Testing: Checking WiFi cards and driver capabilities (capture and injection).
- Cracking: WEP and WPA PSK (WPA 1 and 2).
All tools are command line which allows for heavy scripting. A lot of GUIs have taken advantage of this feature. It works primarily on Linux but also Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, as well as Solaris and even eComStation 2.
Building
Requirements
- Autoconf
- Automake
- Libtool
- shtool
- OpenSSL development package or libgcrypt development package.
- Airmon-ng (Linux) requires ethtool, usbutils, and often pciutils.
- On Windows, cygwin has to be used and it also requires w32api package.
- On Windows, if using clang, libiconv and libiconv-devel
- Linux: LibNetlink 1 or 3. It can be disabled by passing —disable-libnl to configure.
- pkg-config (pkgconf on FreeBSD, DragonFlyBSD, OpenBSD and NetBSD)
- FreeBSD, DragonFlyBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris and OS X with Macports: gmake
- Linux/Cygwin: make and Standard C++ Library development package (Debian: libstdc++-dev)
Note: Airmon-ng only requires pciutils if the system has a PCI/PCIe bus and it is populated.
Such bus can be present even if not physically visible. For example, it is present,
and populated on the Raspberry Pi 4, therefore pciutils is required on that device.
Optional stuff
- If you want SSID filtering with regular expression in airodump-ng
(—essid-regex) PCRE or PCRE2 development package is required. - If you want to use airolib-ng and ‘-r’ option in aircrack-ng,
SQLite development package >= 3.3.17 (3.6.X version or better is recommended) - If you want to use Airpcap, the ‘developer’ directory from the CD/ISO/SDK is required.
- In order to build
besside-ng,besside-ng-crawler,easside-ng,tkiptun-ngandwesside-ng,
libpcap development package is required (on Cygwin, use the Airpcap SDK instead; see above) - rfkill
- If you want Airodump-ng to log GPS coordinates, gpsd is needed
- For best performance on SMP machines, ensure the hwloc library and headers are installed. It is strongly recommended on high core count systems, it may give a serious speed boost
- CMocka and expect for testing
- For integration testing on Linux only: tcpdump, HostAPd, WPA Supplicant and screen
Installing required and optional dependencies
Below are instructions for installing the basic requirements to build
aircrack-ng for a number of operating systems.
Note: CMocka, tcpdump, screen, HostAPd and WPA Supplicant should not be dependencies when packaging Aircrack-ng.
Linux
Arch Linux
sudo pacman -Sy base-devel libnl openssl ethtool util-linux zlib libpcap sqlite pcre2 hwloc cmocka hostapd wpa_supplicant tcpdump screen iw usbutils pciutils expect
Debian/Ubuntu
sudo apt-get install build-essential autoconf automake libtool pkg-config libnl-3-dev libnl-genl-3-dev libssl-dev ethtool shtool rfkill zlib1g-dev libpcap-dev libsqlite3-dev libpcre2-dev libhwloc-dev libcmocka-dev hostapd wpasupplicant tcpdump screen iw usbutils expect
Fedora
sudo yum install libtool pkgconfig sqlite-devel autoconf automake openssl-devel libpcap-devel pcre2-devel rfkill libnl3-devel gcc gcc-c++ ethtool hwloc-devel libcmocka-devel make file expect hostapd wpa_supplicant iw usbutils tcpdump screen zlib-devel expect
CentOS/RHEL 7
sudo yum install epel-release
sudo ./centos_autotools.sh
# Remove older installation of automake/autoconf
sudo yum remove autoconf automake
sudo yum install sqlite-devel openssl-devel libpcap-devel pcre2-devel rfkill libnl3-devel ethtool hwloc-devel libcmocka-devel make file expect hostapd wpa_supplicant iw usbutils tcpdump screen zlib-devel
Note: autoconf, automake, libtool, and pkgconfig in the repositories are too old. The script centos_autotools.sh automatically installs dependencies to compile then install the tools.
CentOS/RHEL 8
sudo yum config-manager --set-enabled powertools
sudo yum install epel-release
sudo yum install libtool pkgconfig sqlite-devel autoconf automake openssl-devel libpcap-devel pcre2-devel rfkill libnl3-devel gcc gcc-c++ ethtool hwloc-devel libcmocka-devel make file expect hostapd wpa_supplicant iw usbutils tcpdump screen zlib-devel
openSUSE
sudo zypper install autoconf automake libtool pkg-config libnl3-devel libopenssl-1_1-devel zlib-devel libpcap-devel sqlite3-devel pcre2-devel hwloc-devel libcmocka-devel hostapd wpa_supplicant tcpdump screen iw gcc-c++ gcc ethtool pciutils usbutils expect
Mageia
sudo urpmi autoconf automake libtool pkgconfig libnl3-devel libopenssl-devel zlib-devel libpcap-devel sqlite3-devel pcre2-devel hwloc-devel libcmocka-devel hostapd wpa_supplicant tcpdump screen iw gcc-c++ gcc make expect
Alpine
sudo apk add gcc g++ make autoconf automake libtool libnl3-dev openssl-dev ethtool libpcap-dev cmocka-dev hostapd wpa_supplicant tcpdump screen iw pkgconf util-linux sqlite-dev pcre2-dev linux-headers zlib-dev pciutils usbutils expect
Note: Community repository needs to be enabled for iw
Clear Linux
sudo swupd bundle-add c-basic devpkg-openssl devpkg-libgcrypt devpkg-libnl devpkg-hwloc devpkg-libpcap devpkg-pcre2 devpkg-sqlite-autoconf ethtool wget network-basic software-testing sysadmin-basic wpa_supplicant os-testsuite
Note: hostapd must be compiled manually, it is not present in the repository
BSD
FreeBSD
pkg install pkgconf shtool libtool gcc9 automake autoconf pcre2 sqlite3 openssl gmake hwloc cmocka
DragonflyBSD
pkg install pkgconf shtool libtool gcc8 automake autoconf pcre2 sqlite3 libgcrypt gmake cmocka
OpenBSD
pkg_add pkgconf shtool libtool gcc automake autoconf pcre2 sqlite3 openssl gmake cmocka
NetBSD
pkg_add pkgconf libtool gcc7 automake autoconf pcre2 sqlite3 openssl gmake cmocka
macOS
XCode, Xcode command line tools and HomeBrew are required.
brew install autoconf automake libtool openssl shtool pkg-config hwloc pcre2 sqlite3 libpcap cmocka
Windows
Cygwin
Cygwin requires the full path to the setup.exe utility, in order to
automate the installation of the necessary packages. In addition, it
requires the location of your installation, a path to the cached
packages download location, and a mirror URL.
An example of automatically installing all the dependencies
is as follows:
c:\cygwin\setup-x86.exe -qnNdO -R C:/cygwin -s http://cygwin.mirror.constant.com -l C:/cygwin/var/cache/setup -P autoconf -P automake -P bison -P gcc-core -P gcc-g++ -P mingw-runtime -P mingw-binutils -P mingw-gcc-core -P mingw-gcc-g++ -P mingw-pthreads -P mingw-w32api -P libtool -P make -P python -P gettext-devel -P gettext -P intltool -P libiconv -P pkg-config -P git -P wget -P curl -P libpcre2-devel -P libssl-devel -P libsqlite3-devel
MSYS2
pacman -Sy autoconf automake-wrapper libtool msys2-w32api-headers msys2-w32api-runtime gcc pkg-config git python openssl-devel openssl libopenssl msys2-runtime-devel gcc binutils make pcre2-devel libsqlite-devel
GNU/Hurd
Debian
apt-get install build-essential autoconf automake libtool pkg-config libssl-dev shtool zlib1g-dev libpcap-dev libsqlite3-dev libpcre2-dev libhwloc-dev libcmocka-dev screen expect libbsd-dev
Docker containers
We have two repositories on DockerHub:
- aircrackng/release: Each release
- aircrackng/git: every commit in the git repository
Base command for the git version:
sudo docker run --rm -it aircrackng/git
Available platforms/CPU architectures:
- linux/386 (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/amd64 (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/arm/v5 (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/arm/v6 (base image: alpine:3)
- linux/arm/v7 (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/arm64/v8 (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/mips64le (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/ppc64le (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/riscv64 (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
- linux/s390x (base image: debian:unstable-slim)
Compiling
To build aircrack-ng, the Autotools build system is utilized. Autotools replaces
the older method of compilation.
NOTE: If utilizing a developer version, eg: one checked out from source control,
you will need to run a pre-configure script. The script to use is one of the
following: autoreconf -i or env NOCONFIGURE=1 ./autogen.sh.
First, ./configure the project for building with the appropriate options specified
for your environment:
TIP: If the above fails, please see above about developer source control versions.
Next, compile the project (respecting if make or gmake is needed):
-
Compilation:
make -
Compilation on *BSD or Solaris:
gmake
Finally, the additional targets listed below may be of use in your environment:
-
Execute all unit testing:
make check -
Execute all integration testing (requires root):
make integration -
Installing:
make install -
Uninstall:
make uninstall
./configure flags
When configuring, the following flags can be used and combined to adjust the suite
to your choosing:
-
with-airpcap=DIR: needed for supporting airpcap devices on Windows (Cygwin or MSYS2 only).
Replace DIR above with the absolute location to the root of the
extracted source code from the Airpcap CD or downloaded SDK available
online. Required on Windows to buildbesside-ng,besside-ng-crawler,
easside-ng,tkiptun-ngandwesside-ngwhen building experimental tools.
The developer pack (Compatible with version 4.1.1 and 4.1.3) can be downloaded at
https://support.riverbed.com/content/support/software/steelcentral-npm/airpcap.html -
with-experimental: needed to compile
tkiptun-ng,easside-ng,buddy-ng,
buddy-ng-crawler,airventriloquistandwesside-ng.
libpcap development package is also required to compile most of the tools.
If not present, not all experimental tools will be built.
On Cygwin, libpcap is not present and the Airpcap SDK replaces it.
See —with-airpcap option above. -
with-ext-scripts: needed to build
airoscript-ng,versuck-ng,airgraph-ngand
airdrop-ng.
Note: Each script has its own dependencies. -
with-gcrypt: Use libgcrypt crypto library instead of the default OpenSSL.
And also use internal fast sha1 implementation (borrowed from GIT).
Dependency (Debian): libgcrypt20-dev -
with-duma: Compile with DUMA support. DUMA is a library to detect buffer overruns and underruns.
Dependency (Debian): duma -
disable-libnl: Set up the project to be compiled without libnl (1 or 3). Linux option only.
-
without-opt: Do not enable -O3 optimizations.
-
enable-shared: Make OSdep a shared library.
-
disable-shared: When combined with enable-static, it will statically compile Aircrack-ng.
-
with-avx512: On x86, add support for AVX512 instructions in aircrack-ng. Only use it when
the current CPU supports AVX512. -
with-static-simd=: Compile a single optimization in aircrack-ng binary. Useful when compiling
statically and/or for space-constrained devices. Valid SIMD options: x86-sse2,
x86-avx, x86-avx2, x86-avx512, ppc-altivec, ppc-power8, arm-neon, arm-asimd.
Must be used with —enable-static —disable-shared. When using those 2 options, the default
is to compile the generic optimization in the binary. —with-static-simd merely allows
to choose another one. -
enable-maintainer-mode: It is important to enable this flag when developing with Aircrack-ng. This flag enables additional compile warnings and safety features.
Examples:
-
Configure and compiling:
./configure --with-experimental make -
Compiling with gcrypt:
./configure --with-gcrypt make -
Installing:
make install -
Installing (strip binaries):
make install-strip -
Installing, with external scripts:
./configure --with-experimental --with-ext-scripts make make install -
Testing (with sqlite, experimental and pcre2)
./configure --with-experimental make make check -
Compiling on OS X with macports (and all options):
./configure --with-experimental gmake -
Compiling on macOS running on M1/AARCH64 and Homebrew:
autoreconf -vif env CPPFLAGS="-Wno-deprecated-declarations" ./configure --with-experimental make make check -
Compiling on OS X 10.10 with XCode 7.1 and Homebrew:
env CC=gcc-4.9 CXX=g++-4.9 ./configure make make checkNOTE: Older XCode ships with a version of LLVM that does not support CPU feature
detection; which causes the./configureto fail. To work around this older LLVM,
it is required that a different compile suite is used, such as GCC or a newer LLVM
from Homebrew.If you wish to use OpenSSL from Homebrew, you may need to specify the location
to its installation. To figure out where OpenSSL lives, run:brew --prefix opensslUse the output above as the DIR for
--with-openssl=DIRin the./configureline:env CC=gcc-4.9 CXX=g++-4.9 ./configure --with-openssl=DIR make make check -
Compiling on FreeBSD with gcc9
env CC=gcc9 CXX=g++9 MAKE=gmake ./configure gmake -
Compiling on Cygwin with Airpcap (assuming Airpcap devpack is unpacked in Aircrack-ng directory)
cp -vfp Airpcap_Devpack/bin/x86/airpcap.dll src cp -vfp Airpcap_Devpack/bin/x86/airpcap.dll src/aircrack-osdep cp -vfp Airpcap_Devpack/bin/x86/airpcap.dll src/aircrack-crypto cp -vfp Airpcap_Devpack/bin/x86/airpcap.dll src/aircrack-util dlltool -D Airpcap_Devpack/bin/x86/airpcap.dll -d build/airpcap.dll.def -l Airpcap_Devpack/bin/x86/libairpcap.dll.a autoreconf -i ./configure --with-experimental --with-airpcap=$(pwd) make -
Compiling on DragonflyBSD with gcrypt using GCC 8
autoreconf -i env CC=gcc8 CXX=g++8 MAKE=gmake ./configure --with-experimental --with-gcrypt gmake -
Compiling on OpenBSD (with autoconf 2.69 and automake 1.16)
export AUTOCONF_VERSION=2.69 export AUTOMAKE_VERSION=1.16 autoreconf -i env MAKE=gmake CC=cc CXX=c++ ./configure gmake -
Compiling and debugging aircrack-ng
export CFLAGS='-O0 -g' export CXXFLAGS='-O0 -g' ./configure --with-experimental --enable-maintainer-mode --without-opt make LD_LIBRARY_PATH=.libs gdb --args ./aircrack-ng [PARAMETERS]
IDE development
VS Code — devcontainers
A VS Code development environment is provided, as is, for rapid setup of a development environment. This additionally adds support for GitHub Codespaces.
Requirements
The first requirement is a working Docker Engine environment.
Next, an installation of VS Code with the following extension(s):
Remote - Containersby Microsoft.
The «Remote — Containers» extension will refuse to work with OSS Code.
Usage
- Clone this repository to your working folder:
$ git clone --recursive https://github.com/aircrack-ng/aircrack-ng.git
$ cd aircrack-ng
- After cloning this repository, open the folder inside VS Code.
IMPORTANT: You should answer «Yes», if it asks if the folder should be opened inside a remote container. If it does not ask, then press
Ctrl+Shift+Pand typeopen in container. This should bring up the correct command, for which pressing enter will run said command.
- A number of warnings might appear about a missing
compile_commands.jsonfile. These are safe to ignore for a moment, as this file is automatically generated after the initial compilation. - Now build the entire project by pressing
Ctrl+Rand selectingBuild Fullfrom the pop-up menu that appears. - VS Code should detect the
compile_commands.jsonfile and ask if it should be used; selecting «Yes, always» will complete the initial setup of a fully working IDE.
IMPORTANT: If it doesn’t detect the file, pressing
Ctrl+Shift+Pand typingreload windowwill bring up the selection to fully reload the environment.
- At this point, nearly all features of VS Code will function; from Intellisense, auto-completion, live documentation, to code formatting. Additionally, there are pre-configured tasks for builds and tests, as well as an example GDB/LLDB configuration for debugging
aircrack-ng.
Packaging
Automatic detection of CPU optimization is done at run time. This behavior
is desirable when packaging Aircrack-ng (for a Linux or other distribution.)
Also, in some cases it may be desired to provide your own flags completely and
not having the suite auto-detect a number of optimizations. To do this, add
the additional flag --without-opt to the ./configure line:
./configure --without-opt
Using pre-compiled binaries
Linux/BSD
Aircrack-ng is available in most distributions repositories. However, it is not always up-to-date.
Windows
- Install the appropriate «monitor» driver for your card; standard drivers don’t work for capturing data.
- Aircrack-ng suite is command line tools. So, you have to open a command-line
Start menu -> Run... -> cmd.exethen use them - Run the executables without any parameters to have help
Documentation
Some more information is present in the README file.
Documentation, tutorials, … can be found on https://aircrack-ng.org
Support is available in the GitHub Discussions and on IRC (in #aircrack-ng on Libera Chat).
Every tool has its own manpage. For aircrack-ng, man aircrack-ng
Infrastructure sponsors
Table of Contents
Installing Aircrack-ng from Source
Legacy information can be found here.
Requirements
-
Autoconf
-
Automake
-
Libtool
-
shtool
-
OpenSSL development package or libgcrypt development package.
-
pkg-config
Linux
-
Airmon-ng requires ethtool and rfkill
-
If USB bus is present, lsusb
-
If PCI/PCIe bus is present, lspci
-
-
LibNetlink 1 (libnl-dev) or 3 (libnl-3-dev and libnl-genl-3-dev) development packages. It can be disabled by passing –disable-libnl to configure.
-
Kernel headers and gcc as well as make have to be installed on your system (build-essential on Debian based distributions)
-
make and Standard C++ Library development package (Debian: libstdc++-dev)
Windows (Cygwin)
-
w32api is required
-
if using clang, libiconv and libiconv-devel
-
make and Standard C++ Library development package
MacOS
Install the following via Homebrew (brew):
-
autoconf
-
automake
-
libtool
-
openssl
-
shtool
-
pkg-config
-
hwloc
-
pcre
-
sqlite3
-
libpcap
-
cmocka (optional)
FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris
Install the following via pkg:
-
gmake
-
pkgconf
-
pcre
-
sqlite3
-
gcc9 (or better)
Optional stuff
-
If you want SSID filtering with regular expression in airodump-ng (-essid-regex) pcre development package is required.
-
If you want to use airolib-ng and ‘-r’ option in aircrack-ng, SQLite development package >= 3.3.17 (3.6.X version or better is recommended)
-
If you want to use Airpcap, the ‘developer’ directory from the CD is required. It can be downloaded here.
-
For best performance on FreeBSD (50-70% more), install gcc5 via: pkg install gcc5 Then compile with: gmake CC=gcc5 CXX=g++5
-
rfkill
-
CMocka
-
hwloc: strongly recommended, especially on high core count systems where it may give a serious performance boost
Compiling and installing
Notes:
-
On OS X, *BSD and Solaris, use ‘gmake’ instead of ‘make’.
-
In order to compile with clang instead of gcc, add ‘CC=clang CXX=clang++’ to the configure command.
Current version
wget https://download.aircrack-ng.org/aircrack-ng-1.7.tar.gz tar -zxvf aircrack-ng-1.7.tar.gz cd aircrack-ng-1.7 autoreconf -i ./configure --with-experimental make make install ldconfig
Compiling with AirPcap support (cygwin only)
-
Copy ‘developer’ directory from the AirPcap CD at the same level as ‘Aircrack-ng’ directory
-
Append ‘- -with-airpcap=../developer’ parameter to configure:
Compiling on *BSD
Commands are exactly the same as Linux but instead of make, use gmake (with CC=gcc5 CXX=g++5 or any more recent gcc version installed).
Compiling on MacOS
Commands are exactly the same as Linux
Latest Git (development) Sources
Note: Compilation parameters can also be used with the sources from our git repository.
git clone https://github.com/aircrack-ng/aircrack-ng cd aircrack-ng autoreconf -i ./configure --with-experimental make make install ldconfig
./configure flags
When configuring, the following flags can be used and combined to adjust the suite to your choosing:
-
with-airpcap=DIR: needed for supporting airpcap devices on windows (cygwin or msys2 only) Replace DIR above with the absolute location to the root of the extracted source code from the Airpcap CD or downloaded SDK available online. Required on Windows to build besside-ng, besside-ng-crawler, easside-ng, tkiptun-ng and wesside-ng when building experimental tools. The developer pack (Compatible with version 4.1.1 and 4.1.3) can be downloaded at https://support.riverbed.com/content/support/software/steelcentral-npm/airpcap.html
-
with-experimental: needed to compile tkiptun-ng, easside-ng, buddy-ng, buddy-ng-crawler, airventriloquist and wesside-ng. libpcap development package is also required to compile most of the tools. If not present, not all experimental tools will be built. On Cygwin, libpcap is not present and the Airpcap SDK replaces it. See –with-airpcap option above. On debian based distro, install libpcap-dev
-
with-ext-scripts: needed to build airoscript-ng, versuck-ng, airgraph-ng and airdrop-ng. Note: Each script has its own dependencies. Note: It’s only required in install phase.
-
with-gcrypt: Use libgcrypt crypto library instead of the default OpenSSL. And also use internal fast sha1 implementation (borrowed from GIT) Dependency (Debian): libgcrypt20-dev
-
with-duma: Compile with DUMA support. DUMA is a library to detect buffer overruns and under-runs. Dependencies (debian): duma
-
with-xcode: Set this flag to true to compile on OS X with Xcode 7+.
-
disable-libnl: Set-up the project to be compiled without libnl (1 or 3). Linux option only.
-
without-opt: Do not enable stack protector (on GCC 4.9 and above).
-
enable-shared: Make OSdep a shared library.
-
disable-shared: When combined with enable-static, it will statically compile Aircrack-ng.
-
with-avx512: On x86, add support for AVX512 instructions in aircrack-ng. Only use it when the current CPU supports AVX512.
-
with-static-simd=: Compile a single optimization in aircrack-ng binary. Useful when compiling statically and/or for space-constrained devices. Valid SIMD options: x86-sse2, x86-avx, x86-avx2, x86-avx512, ppc-altivec, ppc-power8, arm-neon, arm-asimd. Must be used with –enable-static –disable-shared. When using those 2 options, the default is to compile the generic optimization in the binary. –with-static-simd merely allows to choose another one.
-
enable-maintainer-mode: It is important to enable this flag when developing with Aircrack-ng. This flag enables additional compile warnings and safety features.
Troubleshooting Tips
error while loading shared libraries: libaircrack-ng.so.0
Run ldconfig as root or with “sudo” to solve the issue.
«command not found» error message
After you do “make install” then try to use any of the Aircrack-ng suite commands, you get the error message “command not found” or similar. Your system will look for the Aircrack-ng commands in the directories defined by the PATH command.
Normally, the Aircrack-ng suite programs and man pages are placed in:
/usr/local/bin /usr/local/sbin /usr/local/man
On your system, to determine which directories have the Aircrack-ng programs enter the following. If using “locate” be sure to first run “updatedb”.
locate aircrack-ng locate airmon-ng
or
find / -name aircrack-ng find / -name airmon-ng
Once you know the directories (exclude the source directories) then determine which directories are in your PATH. To see which directories are included in PATH on your particular system enter:
echo $PATH
It should show something like:
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
At this point compare the actual locations with the directories in your PATH. If the directories are missing from your PATH then you have a few options:
-
Add the directories to your PATH. See the one or more of the following web sites for details of how to do this:
https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-print-path-variable/ http://www.troubleshooters.com/linux/prepostpath.htm
-
Change to the particular directory with “cd” and then run the commands from within the directory. Don’t forget to add “./” in front of each command.
-
Specify the full path for each command. So if Aircrack-ng is located in the “/usr/local/bin” directory then run the command as “/usr/local/bin/aircrack-ng”.
Installing pre-compiled binaries
Linux/BSD/OSX
With the exception of Linux penetration testing distributions, packages are usually out of date (MacOS is the exception). In this case, uninstalling the package and installing from sources is the recommended way to go.
On MacOS, install it is via Macports or brew. Simply do “brew install aircrack-ng” or “sudo port install aircrack-ng”
Windows
The Windows version of the Aircrack-ng suite does not have an install program. You must manually install (unzipping archive) the software.
Here are the steps to follow for Windows:
-
Download the latest version of the Aircrack-ng suite for Windows to your computer. The link for the zip file can be found on the Wiki home page.
-
Unzip the contents of the Aircrack-ng zip file into “C:\”. This will create a directory called “aircrack-ng-1.6-win”. This directory name will vary based on the exact version that you downloaded. This main directory contains three subdirectories — “bin”, “src” and “test”.
Prior to using the software, make sure to install the drivers for your particular wireless card. See this link for the instructions. We currently only support Airpcap; other adapters may be supported but require development of your own DLL so the different tools can interact with it.
To now use the Aircrack-ng suite, start Windows Explorer and double click on Aircrack-ng GUI.exe inside “bin” subdirectory. The GUI requires .NET version 4.6.1 to run.
Alternatively, open a command prompt (Start menu → Execute → cmd.exe) and change to the “C:\aircrack-ng-1.6-win\bin” directory and execute the individual commands.
Important notes:
-
Airmon-ng is a Linux/FreeBSD tool only.
-
Remember that Windows only supports a limited subset of the commands.
-
Some troubleshooting tips specific to XP and Vista can be found on this page.
Содержание
- User Tools
- Site Tools
- Table of Contents
- Installing Aircrack-ng from Source
- Requirements
- Linux
- Windows (Cygwin)
- FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris
- Optional stuff
- Compiling and installing
- Current version
- Compiling with AirPcap support (cygwin only)
- Compiling on *BSD
- Compiling on OS X
- Latest Git (development) Sources
- ./configure flags
- Troubleshooting Tips
- error while loading shared libraries: libaircrack-ng.so.0
- «command not found» error message
- Installing pre-compiled binaries
- Linux/BSD/OSX
- Windows
- Подбор пароля Wi-Fi утилитой aircrack-ng
- Введение
- А где же уязвимость?
- Так как же взломать?
- Шаг 1. Определяем интерфейс
- Шаг 2. Переводим сетевой адаптер в режим мониторинга
- Шаг 3. Перехватываем трафик
- Шаг 4. Концентрируем перехват на конкретной точке доступа.
- Шаг 5. Получение handshake
- Шаг 6. Подбираем пароль
- Сколько времени это займёт?
- Как пользоваться Aircrack-NG
- Что это за программа
- Знакомимся с интерфейсом программы
- Как задействовать Aircrack-ng для взлома пароль к Wi-Fi
- Видео инструкция использования программы
- Как Пользоваться AirCrack-NG — Взлом WiFi — Инструкция
- 1. Aircrack-ng: Скачать и Установить
- 2. Airmon-ng: Режим Мониторинга
- 3. Airodump-ng: Перехват Рукопожатия
- 4. Aireplay-ng: Деаутентификации Клиента
- 5. Aircrack-ng: Взлом WiFi Пароля
- Как пользоваться aircrack-ng. WPA и WPA2
- Что такое Aircrack-ng?
- Как будет работать атака на WPA/WPA2?
- Как пользоваться Aircrack-ng для взлома WPA
User Tools
Site Tools
Table of Contents
Installing Aircrack-ng from Source
Legacy information can be found here.
Requirements
Linux
Windows (Cygwin)
Install the following via Homebrew (brew):
FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, Solaris
Install the following via pkg:
Optional stuff
Compiling and installing
Current version
Compiling with AirPcap support (cygwin only)
Compiling on *BSD
Commands are exactly the same as Linux but instead of make, use gmake (with CC=gcc5 CXX=g++5 or any more recent gcc version installed).
Compiling on OS X
Commands are exactly the same as Linux
Latest Git (development) Sources
Note: Compilation parameters can also be used with the sources from our git repository.
./configure flags
When configuring, the following flags can be used and combined to adjust the suite to your choosing:
Troubleshooting Tips
error while loading shared libraries: libaircrack-ng.so.0
Run ldconfig as root or with “sudo” to solve the issue.
«command not found» error message
After you do “make install” then try to use any of the Aircrack-ng suite commands, you get the error message “command not found” or similar. Your system will look for the Aircrack-ng commands in the directories defined by the PATH command.
Normally, the Aircrack-ng suite programs and man pages are placed in:
On your system, to determine which directories have the Aircrack-ng programs enter the following. If using “locate” be sure to first run “updatedb”.
Once you know the directories (exclude the source directories) then determine which directories are in your PATH. To see which directories are included in PATH on your particular system enter:
It should show something like:
At this point compare the actual locations with the directories in your PATH. If the directories are missing from your PATH then you have a few options:
Installing pre-compiled binaries
Linux/BSD/OSX
We offer packages for a number of Linux distributions in 64 bit thanks to PackageCloud.io so you can use your distro’s package manager to install and keep Aircrack-ng up to date:
While most folks want to use our “release” packages, “git” packages are available too for those who decide to use bleeding edge.
More details about them can be found in our blog post.
On OSX, install it is via Macports or brew. Simply do “brew install aircrack-ng” or “sudo ports install aircrack-ng”
Windows
The Windows version of the Aircrack-ng suite does not have an install program. You must manually install (unzipping archive) the software.
Here are the steps to follow for Windows:
Prior to using the software, make sure to install the drivers for your particular wireless card. See this link for the instructions. We currently only support Airpcap; other adapters may be supported but require development of your own DLL so the different tools can interact with it.
Источник
Подбор пароля Wi-Fi утилитой aircrack-ng
Данная статья написана исключительно в ознакомительных и исследовательских целях. Призываем вас соблюдать правила работы с сетями и закон, а также всегда помнить об информационной безопасности.
Введение
В начале 1990-х годов, когда Wi-Fi только появился, был создан алгоритм Wired Equivalent Privacy, который должен был обеспечивать конфиденциальность Wi-Fi сетей. Однако, WEP оказался неэффективным алгоритмом защиты, который легко взломать.
На смену пришел новый алгоритм защиты Wi-Fi Protected Access II, который сегодня применяют большинство точек доступа Wi-Fi. WPA2 использует алгоритм шифрования, AES, взломать который крайне сложно.
А где же уязвимость?
Недостаток WPA2 заключается в том, что зашифрованный пароль передается при подключении пользователей во время так называемого 4-way handshake (4-х стороннего рукопожатия). Если мы поймаем handshake, то узнаем зашифрованный пароль и нам останется лишь расшифровать его. Для этой цели мы воспользуемся aircrack-ng.
Так как же взломать?
Шаг 1. Определяем интерфейс
Для начала нужно узнать, какой сетевой интерфейс нам нужен, для этого вводим команду:
В моем случае всего три интерфейса, два из которых не имеют беспроводных расширений (no wireless extensions). Поэтому нас интересует только wlan0.
Шаг 2. Переводим сетевой адаптер в режим мониторинга
Перевод сетевого адаптера в режим мониторинга позволит нам видеть беспроводной трафик, подходящий рядом с нами. Для того чтобы сделать это, вводим команду:
Обратите внимание, что airmon-ng переименовал ваш интерфейс (у меня он стал называться mon0, но вам, все же, стоит проверить).
Шаг 3. Перехватываем трафик
Теперь, когда наш сетевой адаптер находится в режиме мониторинга, мы можем захватить, подходящий мимо нас трафик, используя команду airodump-ng. Вводим:
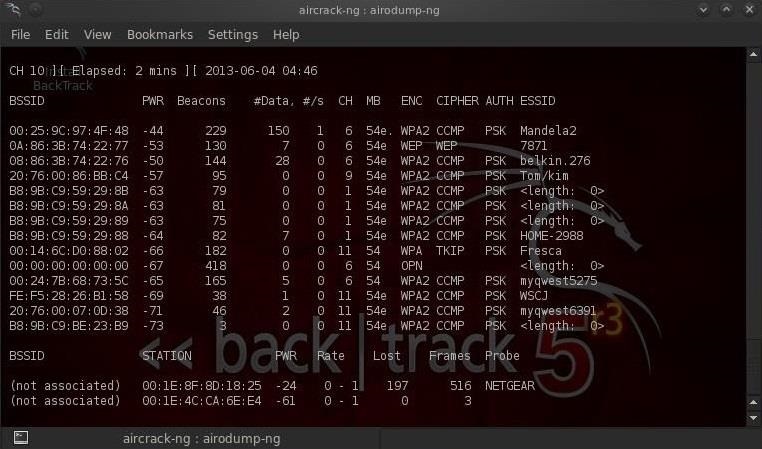
Обратите внимание, что все видимые точки доступа перечислены в верхней части экрана, а клиенты — в нижней части экрана.
Шаг 4. Концентрируем перехват на конкретной точке доступа.
Наш следующий шаг — сосредоточить наши усилия на одной из точек доступа и на ее канале. Нас интересует BSSID и номер канала точки доступа, которую мы будем взламывать. Давайте откроем еще один терминал и введем:
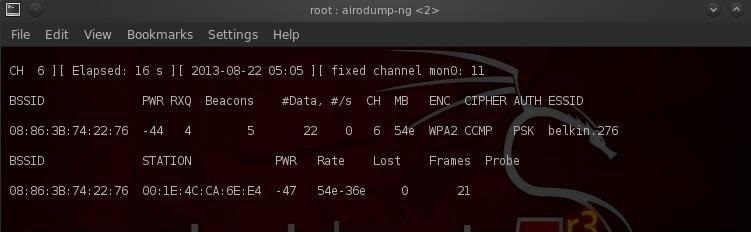
Шаг 5. Получение handshake
Чтобы захватить зашифрованный пароль, нам нужно, чтобы клиент прошел аутентификацию (подключился к Wi-Fi). Если он уже аутентифицирован, мы можем его деаутентифицировать (отключить), тогда система автоматически повторно аутентифицируется (подключится), в результате чего мы можем получить зашифрованный пароль.
То есть нам просто нужно отключить подключенных пользователей, чтобы они подключились снова. Для этого открываем ещё один терминал и вводим:
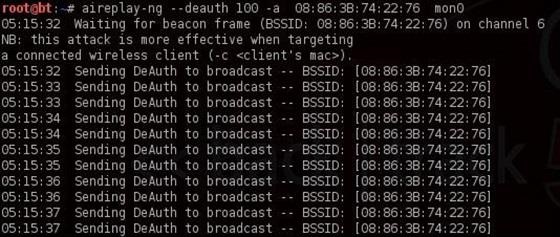
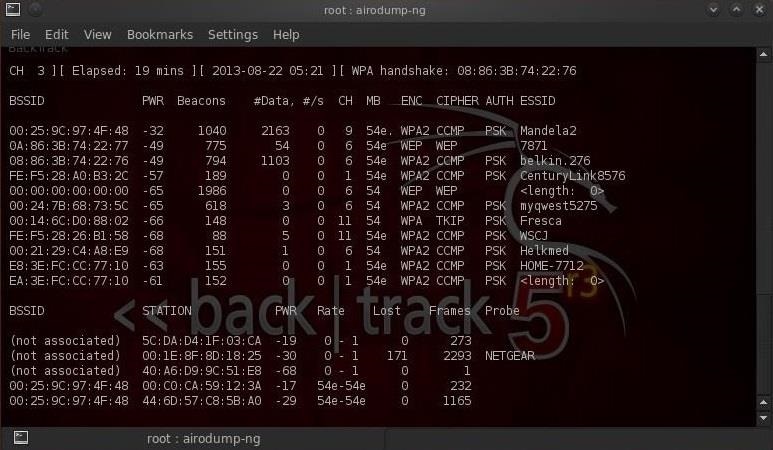
Обратите внимание на верхнюю строку справа, airodump-ng вывел: «Handshake WPA». То есть, мы успешно захватили зашифрованный пароль! Это первый шаг к успеху!
Шаг 6. Подбираем пароль
Теперь, когда у нас есть зашифрованный пароль в нашем файле WPAcrack, мы можем запустить подбор пароля. Но для этого нам нужно иметь список с паролями которые мы хотим использовать. Найти такой список можно за 5 минут в Гугле. Я, же, буду использовать список паролей по умолчанию, включенный в aircrack-ng: BackTrack darkcOde.
Открываем новый терминал и вводим:
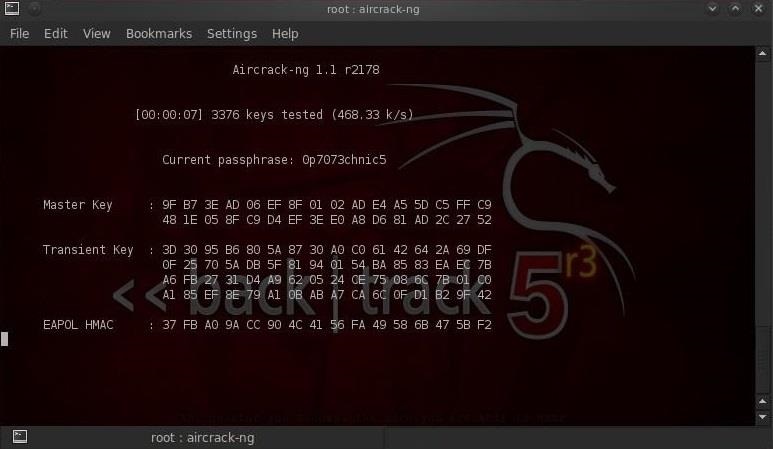
Сколько времени это займёт?
Этот процесс может занять много времени. Все зависит от длины вашего списка паролей, вы можете ждать от нескольких минут до нескольких дней. На моем двухъядерном процессоре Intel aircrack-ng подбирает чуть более 800 паролей в секунду.
Когда пароль будет найден, он появится на вашем экране. Будет ли подбор пароля успешным или нет, зависит от вашего списка. Если у вас не получилось подобрать пароль по одному списку, не отчаивайтесь, попробуйте другой.
Источник
Как пользоваться Aircrack-NG
Что это за программа
Обычно под данным названием понимается набор сетевых программ, предназначенных для обнаружения, анализа, перехвата и взлома беспроводных сетей и соответствующего сетевого трафика. С помощью инструментария, представленного в данном пакете, можно взламывать протоколы безопасности WEP и WPA/WPA2-PSK, тестировать беспроводные сети на уязвимость к внешним атакам (penetration test), проводить проверку стойкости сети и так далее.
Указанный продукт представлен в двух основных вариантах:
При этом работа даже с более простым GUI-вариантом предполагает предварительную подготовку пользователя. Необходимо разобраться с понятийным аппаратом, уяснить специфику алгоритмов шифрования WEP, WPA и WPA2, ознакомиться с вспомогательными программами, которые помогут нам во взломе (к примеру, с комплементарным приложением CommView) и так далее. В статье я расскажу об использовании расшифровщика перехваченного трафика Aircrack-NG.

Знакомимся с интерфейсом программы
Чтобы установить программу скачайте её с официального ресурса https://download.aircrack-ng.org/aircrack-ng-1.2-rc4-win.zip, сохраните архив на жёсткий диск, распакуйте его. Для запуска 32-битной версии архива (под 32-битную ОС) перейдите в распакованный архив по адресу Папка архива\bin\32-bit\ и запустите там файл Aircrack-ng GUI.exe.
Вам откроется окно программы с пятью основными вкладками:
Как задействовать Aircrack-ng для взлома пароль к Wi-Fi
Разберём на простом примере алгоритм взлома пароля соседской вай-фай сети, которая зашифрована протоколом WPA (ныне наиболее популярен) используя Эйркрек-НГ. Для этого выполните следующее:
Надеюсь вы поняли как пользоваться программой, и сумели взломать точку доступа.
Видео инструкция использования программы
Рассмотрев вопрос о том, как работать с Aircrack-NG, обращаем внимание читателя, что полноценное использование указанного продукта, который, de facto, работает на принципах брутфорса, невозможно без дополняющих его функционал сторонних программ (уровня «CommView for WiFi»). Удачный же взлом паролей к сторонним Wi-Fi сетей требует регулярных практических упражнений, позволяющих развивать и совершенствовать свои знания, умения и навыки в выбранном деле (в данном случае, хакинге). Дорогу, как известно, осилит лишь идущий.
Источник
Как Пользоваться AirCrack-NG — Взлом WiFi — Инструкция
С помощью этих команд вы сможете взломать WiFi роутер с WPA/WPA2-PSK (pre-shared key) шифрованием.
Как взломать WiFi — основные шаги:
1. Aircrack-ng: Скачать и Установить
Только Последняя Версия: Если вы действительно хотите взломать WiFi — не стоит устанавливать устаревший aircrack-ng из репозитория ваше операционной системы. Скачайте и скомпилируйте последнюю версию самостоятельно.
Установите необходимы зависимости:
Скачайте и установите последнюю версию aircrack-ng (текущая версия):
Убедитесь что установлена именно последняя версия aircrack-ng :
2. Airmon-ng: Режим Мониторинга
Режим мониторинга позволяет компьютеру с беспроводным сетевым интерфейсом мониторить весь трафик в беспроводной сети.
Что особенно для нас важно, так это то, что режим мониторинга позволяет перехватывать все передающиеся пакеты без непосредственного подключения к какому-либо WiFi роутеру.
Найдите и остановите все процессы, которые могут помешать:
Запустите беспроводной интерфейс в режиме мониторинга:
В приведенном выше примере, airmon-ng создал новый беспроводной интерфейс mon0 и переключил его в режим мониторинга.
Таким образом, mon0 — это правильное имя интерфейса, которое мы будем использовать далее в этом руководстве.
3. Airodump-ng: Перехват Рукопожатия
Теперь, когда беспроводной адаптер переведен в режим мониторинга, у нас появилась возможность видеть весь проходящий мимо нас трафик.
Это можно сделать с помощью команды airodump-ng :
Все видимые точки доступа показаны в верхней части экрана, а подключенные клиенты в нижней:
Для того, чтобы поймать рукопожатие, определите интересующую вас точку доступа и запустите airodump-ng на том же канале с фильтром по BSSID:
Если вы хотите ускорить этот процесс — перейдите к шагу #4 и попытайтесь заставить подключенного беспроводного клиента переподключиться к роутеру.
По прошествию некоторого времени вы должны увидеть сообщение WPA handshake: 00:11:22:33:44:55 в правом верхнем углу экрана.
Это сообщение означает, что airodump-ng успешно перехватил рукопожатие:
4. Aireplay-ng: Деаутентификации Клиента
Дельный Совет: Хотите сохранить анонимность? Узнайте как использовать ПРОКСИ из командной строки в Linux. Читать далее →
Если вы не хотите ждать пока airodump-ng перехватит рукопожатие, вы можете сами попробовать отправить сообщение клиенту, сказав что он больше не подключен к точке доступа.
После этого есть вероятность того, что беспроводной клиент попробует переподключиться и мы сможем перехватил рукопожатие.
Отправить широковещательное deauth сообщение:
Отправить направленное deauth сообщение (атака более эффективна когда направленна на конкретного клиента):
Дельный Совет: Нужно взломать пароль от WiFi? Не тратьте свое время попусту! Используйте «John the Ripper» — самый быстрый взломщик паролей! Читать далее →
5. Aircrack-ng: Взлом WiFi Пароля
Для взлома WiFi необходим словарь с паролями для перебора.
Главное помните, что этот способ взлома настолько хорош, насколько хорош ваш словарь с паролями.
Некоторые словари можно скачать отсюда.
Выполните следующую команду, чтобы взломать WPA/WPA2-PSK:
| Опция | Описание |
|---|---|
| -w | Путь к словарю с паролями |
| -b | MAC адрес точки доступа |
| WPAcrack.cap | Файл, содержащий перехваченное рукопожатие |
Дельный Совет: Взлом пароля часто занимает много времени. Объедините aircrack-ng с «John The Ripper», чтобы иметь возможность ставить перебор на паузу без потери текущего прогресса! Читать далее →
Источник
Как пользоваться aircrack-ng. WPA и WPA2
В наши дни беспроводные сети используются все чаще и чаще, уже в каждом доме где есть интернет, есть и роутер для раздачи Wifi на мобильные устройства и другие гаджеты. Интернет и Wifi стали неотъемлемой частью нашей жизни. Но остался вопрос о безопасности таких сетей. Как показывает история люди всегда находили способы взломать сети, и прекрасное тому подтверждение — протокол WEP, который поддавался взлому буквально за несколько минут, даже при отсутствии подключенных к сети пользователей.
Но, похоже, достучались, люди все реже используют WEP и защищают свои сети с помощью более современных стандартов таких как WPA и WPA2. Но действительно ли они безоговорочно безопасны? В этой статье мы рассмотрим как пользоваться утилитой Aircrack-ng для тестирования безопасности сетей WPA и WPA2. Вы увидите в чем их слабое место и узнаете как защитить себя от взлома.
Что такое Aircrack-ng?
Aircrack-ng — это набор утилит для тестирования безопасности Wifi сетей. Он был разработан группой специалистов с информационной безопасности и в него входят несколько утилит для сканирования сети, передачи пакетов в сеть, настройки интерфейса и непосредственно, перебора пароля. Программы поддерживают взлом WPA, так и WEP сетей.
В пакет Aircrak входит большое количество утилит, но мы рассмотрим только самые основные:
В этой статье мы будем использовать только некоторые из этих утилит. А именно airodump, airmon, aircrhack и besside для попытки автоматического взлома.
Как будет работать атака на WPA/WPA2?
Как я уже говорил протокол шифрования беспроводных сетей WPA тоже имеет свои недочеты. Но большинство из них усугубляет именно пользователь. Если не учитывать недавно открытую уязвимость в работе WPA TKIP, то все остальные проблемы возникают из-за слабого пароля.
Для нашей тестовой атаки будем использовать собственную сеть. Предполагается, что вы к ней не подключены. Рассмотрим в чем состоит суть атаки. Для того чтобы подключиться к сети каждый клиент должен пройти процесс аутентификации с роутером. Я не буду вдаваться в подробности, но между клиентом и маршрутизатором выполняются четыре проверки подлинности на основе MAC адреса, ключа и случайных чисел, если мы их перехватим, то сможем уже на локальном компьютере попробовать перебрать подходящий пароль уже на локальном компьютере.
Суть метода в том, что скорость перебора на компьютере будет намного быстрее, чем при ручной проверке, она будет достигать до 1000 паролей в секунду, а при использовании очень простого и ожидаемого пароля, его можно очень быстро перебрать.
Сначала мы переведем устройство в режим монитора с помощью airmon-ng, затем будем перехватывать все пакеты от этой сети с помощью airodump-ng пока не найдем рукопожатие, затем останется перебрать пароль по словарю с помощью aircrack. А теперь перейдем ближе к практике и рассмотрим насколько просто перебрать ваш пароль если он достаточно простой.
Как пользоваться Aircrack-ng для взлома WPA
Дальше рассмотрим как пользоваться aircrack-ng. Если программа еще не установлена на вашем компьютере, то в Linux вы можете скачать ее из официальных репозиториев. В Ubuntu:
sudo apt install aircrack-ng
А в Red Hat / CentOS:
sudo yum install aircrack-ng
Windows вам придется загрузить установщик из официального сайта. После установки первым делом нужно сделать чтобы нам ничего не мешало. Для этого отключите все сервисы, которые управляют Wifi и тем более отключитесь от Wifi сети, если вы к ней подключены. Если запущен NetworkManager, его нужно отключить:
sudo systemctl stop NetworkManager
Я предполагаю, что у вас уже установлены все необходимые драйвера и вы готовы к работе. Сначала смотрим подключенные к системе интерфейсы:
sudo ls /sys/class/net/
Обычно имя беспроводного интерфейса начинается на w, например, wlp3s0 или wlan0. У меня это wlp3s0b1. Нам нужно перевести сетевой интерфейс WiFi в режим мониторинга. В этом режиме он может захватывать все пакеты, которые летают в сети и даже если ему они не адресованы ему. Вообще, интерфейс и так захватывает все пакеты, но на программном уровне все пакеты, которые не адресованы этому компьютеру отсеиваются, теперь они не будут отсеиваться. Дальше идет инструкция Aircrack-ng.
Для этого воспользуемся утилитой airmon-ng. Ей нужно передать команду start и имя интерфейса:
sudo airmon-ng start wlp0s0b1
После этого будет создан виртуальный интерфейс, который работает в режиме монитора во второй колонке отображено его имя, у меня это wlp3s0b1mon, хотя часто он называется просто mon0. Если какие-либо программы будут мешать программа выдаст их имена и PID:
Их нужно завершить с помощью kill. Дальше нам нужно просканировать эфир и найти нашу сеть, которую мы собираемся тестировать. Для этого используйте команду airodump-ng. В параметрах ей нужно передать только интерфейс. Обратите внимание, что нужно передавать именно виртуальный интерфейс, который работает в режиме монитора:
Почти сразу же вы увидите свою сеть, поскольку она расположена ближе всех. У меня это MyPublicWifi423. Из предоставляемой информации нам понадобится ее BSSID и канал, который можно найти в колонке CH. Дальше мы будем использовать ту же самую утилиту, только теперь нацелим ее именно на нашу сеть, чтобы она не отвлекалась на посторонние и поймала все что нам нужно.
Не закрывайте этот терминал, сейчас выполняется захват и как вы можете видеть к нашей сети подключено два пользователя. Их MAC адреса находятся в колонке STATION. Если сейчас один из них отключится и еще раз подключится, то мы получим необходимые для дальнейшего взлома данные.
Мы можем это сделать со своими устройствами, но в реальной сети у хакера не будет такой возможности, поэтому мы можем принудительно отключить клиента от сети с помощью утилиты aireplay. Если передать ей опцию deauth, то она разошлет широковещательное сообщение от имени маршрутизатора, в котором попросит всех отключиться от сети. Нам нужно только передать в параметрах количество пакетов, которые нужно отправить и BSSID роутера:
Сразу после этого вы сразу же увидите, сообщение WPA handshake: 56:0A:64:17:5D:33 в правом верхнем углу терминала. Вы можете использовать и более простой способ для получения Handshake. Утилита besside позволяет выполнить все действия автоматически нужно только передать BSSID роутера и интерфейс монитора:
Этап, связанный с работой в реальной сети завершен и нам осталось только перебрать все возможные пароли по словарю. Дальше рассмотрим как пользоваться Aircrack-ng для перебора паролей.
Словарь — это обычный текстовый документ со списком возможных паролей. Вы можете составить его сами. Команда будет выглядеть следующим образом:
Дальше начнется перебор ключей и если ключ, который использовался для защиты сети есть в списке, то он обязательно будет найден:
Как видите, aircrack-ng wpa2 psk достаточно быстро может быть взломан. Скорость перебора паролей достигает тысячи вариантов в секунду, а это значит, что на перебор до 100000 паролей уйдет всего только несколько минут. И это на обычном, бюджетном ноутбуке. На более мощном железе использовать Aircrack-ng будет намного быстрее.
Поэтому никогда не используйте простые пароли, состоящие только из цифр, если вы добавите хоть одну букву или символ, то уменьшите шансы на взлом в несколько раз.
Сейчас на сайте 1493 гостя и нет пользователей
Источник
- Airodump Ng For Windows 10
- Aircrack Ng Windows
- Airodump Ng Download
- Airodump Ng For Windows Operating System
Aircrack- ng is a complete suite of tools to assess WiFi network security. All tools are command line which allows for heavy scripting. A lot of GUIs have taken advantage of this feature. It works primarily Linux but also Windows, OS X, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, as well as Solaris and even eComStation 2.
- Aircrack-ng is a complete suite of tools to assess WiFi network security. It focuses on different areas of WiFi security: Monitoring: Packet capture and export of data to text files for further processing by third party tools. Attacking: Replay attacks, deauthentication, fake access points and others via packet injection.
- # airmon-ng check Found 5 processes that could cause trouble. If airodump-ng, aireplay-ng or airtun-ng stops working after a short period of time, you may want to kill (some of) them! PID Name 718 NetworkManager 870 dhclient 1104 avahi-daemon 1105 avahi-daemon 1115 wpasupplicant.
airodump-ng will display a list of detected access points, and also a list of connected clients (“stations”). Here’s an example screenshot:
The first line shows the current channel, elapsed running time, current date and optionally if a WPA/WPA2 handshake was detected. In the example above, “WPA handshake: 00:14:6C:7E:40:80” indicates that a WPA/WPA2 handshake was successfully captured for the BSSID.
In the example above the client rate of “36-24” means:
-
The first number is the last data rate from the AP (BSSID) to the Client (STATION). In this case 36 megabits per second.
-
The second number is the last data rate from Client (STATION) to the AP (BSSID). In this case 24 megabits per second.
-
These rates may potentially change on each packet transmission. It is simply the last speed seen.
-
These rates are only displayed when locked to a single channel, the AP/client transmission speeds are displayed as part of the clients listed at the bottom.
-
NOTE: APs need more then one packet to appear on the screen. APs with a single packet are not displayed.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| BSSID | MAC address of the access point. In the Client section, a BSSID of “(not associated)” means that the client is not associated with any AP. In this unassociated state, it is searching for an AP to connect with. |
| PWR | Signal level reported by the card. Its signification depends on the driver, but as the signal gets higher you get closer to the AP or the station. If the BSSID PWR is -1, then the driver doesn’t support signal level reporting. If the PWR is -1 for a limited number of stations then this is for a packet which came from the AP to the client but the client transmissions are out of range for your card. Meaning you are hearing only 1/2 of the communication. If all clients have PWR as -1 then the driver doesn’t support signal level reporting. |
| RXQ | Receive Quality as measured by the percentage of packets (management and data frames) successfully received over the last 10 seconds. See note below for a more detailed explanation. |
| Beacons | Number of announcements packets sent by the AP. Each access point sends about ten beacons per second at the lowest rate (1M), so they can usually be picked up from very far. |
| # Data | Number of captured data packets (if WEP, unique IV count), including data broadcast packets. |
| #/s | Number of data packets per second measure over the last 10 seconds. |
| CH | Channel number (taken from beacon packets). Note: sometimes packets from other channels are captured even if airodump-ng is not hopping, because of radio interference or overlapping channels. |
| MB | Maximum speed supported by the AP. If MB = 11, it’s 802.11b, if MB = 22 it’s 802.11b+ and up to 54 are 802.11g. Anything higher is 802.11n or 802.11ac. The dot (after 54 above) indicates short preamble is supported. Displays “e” following the MB speed value if the network has QoS enabled. |
| ENC | Encryption algorithm in use. OPN = no encryption,“WEP?” = WEP or higher (not enough data to choose between WEP and WPA/WPA2), WEP (without the question mark) indicates static or dynamic WEP, and WPA, WPA2 or WPA3 if TKIP or CCMP is present (WPA3 with TKIP allows WPA or WPA2 association, pure WPA3 only allows CCMP). OWE is for Opportunistic Wireless Encryption, aka Enhanced Open. |
| CIPHER | The cipher detected. One of CCMP, WRAP, TKIP, WEP, WEP40, or WEP104. Not mandatory, but TKIP is typically used with WPA and CCMP is typically used with WPA2. WEP40 is displayed when the key index is greater then 0. The standard states that the index can be 0-3 for 40bit and should be 0 for 104 bit. |
| AUTH | The authentication protocol used. One of MGT (WPA/WPA2 using a separate authentication server), SKA (shared key for WEP), PSK (pre-shared key for WPA/WPA2), or OPN (open for WEP). |
| ESSID | Shows the wireless network name. The so-called “SSID”, which can be empty if SSID hiding is activated. In this case, airodump-ng will try to recover the SSID from probe responses and association requests. See this section for more information concerning hidden ESSIDs. |
| STATION | MAC address of each associated station or stations searching for an AP to connect with. Clients not currently associated with an AP have a BSSID of “(not associated)”. |
| Rate | Station’s receive rate, followed by transmit rate. Displays “e” following each rate if the network has QoS enabled. |
| Lost | The number of data packets lost over the last 10 seconds based on the sequence number. See note below for a more detailed explanation. |
| Packets | The number of data packets sent by the client. |
| Notes | Additional information about the client, such as captured EAPOL or PMKID. |
| Probes | The ESSIDs probed by the client. These are the networks the client is trying to connect to if it is not currently connected. |
NOTES:
RXQ expanded:
Its measured over all management and data frames. The received frames contain a sequence number which is added by the sending access point. RXQ = 100 means that all packets were received from the access point in numerical sequence and none were missing. That’s the clue, this allows you to read more things out of this value. Lets say you got 100 percent RXQ and all 10 (or whatever the rate) beacons per second coming in. Now all of a sudden the RXQ drops below 90, but you still capture all sent beacons. Thus you know that the AP is sending frames to a client but you can’t hear the client nor the AP sending to the client (need to get closer). Another thing would be, that you got a 11MB card to monitor and capture frames (say a prism2.5) and you have a very good position to the AP. The AP is set to 54MBit and then again the RXQ drops, so you know that there is at least one 54MBit client connected to the AP.
N.B.: RXQ column will only be shown if you are locked on a single channel, not channel hopping.
Quickbooks validation code crack free download. Lost expanded:
It means lost packets coming from the client. To determine the number of packets lost, there is a sequence field on every non-control frame, so you can subtract the second last sequence number from the last sequence number and you know how many packets you have lost.
Possible reasons for lost packets:
-
You cannot send (in case you are sending) and listen at the same time, so every time you send something you can’t hear the packets being transmitted in that interval.
-
You are maybe losing packets due too high transmit power (you may be too close to the AP).
-
There is too much noise on the current channel (other APs, microwave oven, bluetooth…)
To minimize the number of lost packets, vary your physical position, type of antenna used, channel, data rate and/or injection rate.
If you want to know how to hack WiFi access point – just read this step by step aircrack-ng tutorial, run the verified commands and hack WiFi password easily.
With the help a these commands you will be able to hack WiFi AP (access points) that use WPA/WPA2-PSK (pre-shared key) encryption.
The basis of this method of hacking WiFi lies in capturing of the WPA/WPA2 authentication handshake and then cracking the PSK using aircrack-ng.
How to hack WiFi – the action plan:
- Download and install the latest
aircrack-ng - Start the wireless interface in monitor mode using the
airmon-ng - Start the
airodump-ngon AP channel with filter for BSSID to collect authentication handshake - [Optional] Use the
aireplay-ngto deauthenticate the wireless client - Run the
aircrack-ngto hack the WiFi password by cracking the authentication handshake
1. Aircrack-ng: Download and Install
The Latest Version Only: If you really want to hack WiFi – do not install the old aircrack-ng from your OS repositories. Download and compile the latest version manually.
Install the required dependencies:
Download and install the latest aircrack-ng (current version):
Ensure that you have installed the latest version of aircrack-ng:
2. Airmon-ng: Monitor Mode
Now it is required to start the wireless interface in monitor mode.
Monitor mode allows a computer with a wireless network interface to monitor all traffic received from the wireless network.
What is especially important for us – monitor mode allows packets to be captured without having to associate with an access point.
Find and stop all the processes that use the wireless interface and may cause troubles:
Start the wireless interface in monitor mode:
In the example above the airmon-ng has created a new wireless interface called mon0 and enabled on it monitor mode.
So the correct interface name to use in the next parts of this tutorial is the mon0.
3. Airodump-ng: Authentication Handshake
Cool Tip: Want to have some “fun”? Create a Linux fork bomb! One small string that is able to hang the whole system! Read more →
Now, when our wireless adapter is in monitor mode, we have a capability to see all the wireless traffic that passes by in the air.
This can be done with the airodump-ng command:
All of the visible APs are listed in the upper part of the screen and the clients are listed in the lower part of the screen:
Start the airodump-ng on AP channel with the filter for BSSID to collect the authentication handshake for the access point we are interested in:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-c |
The channel for the wireless network |
--bssid |
The MAC address of the access point |
-w |
The file name prefix for the file which will contain authentication handshake |
mon0 |
The wireless interface |
--ignore-negative-one |
Fixes the ‘fixed channel : -1’ error message |
Now wait until airodump-ng captures a handshake.
If you want to speed up this process – go to the step #4 and try to force wireless client reauthentication.
After some time you should see the WPA handshake: 00:11:22:33:44:55 in the top right-hand corner of the screen.
This means that the airodump-ng has successfully captured the handshake:
4. Aireplay-ng: Deauthenticate Client
Cool Tip: Want to stay anonymous? Learn how to use PROXY on the Linux command line. Read more →
Airodump Ng For Windows 10
If you can’t wait till airodump-ng captures a handshake, you can send a message to the wireless client saying that it is no longer associated with the AP.
The wireless client will then hopefully reauthenticate with the AP and we’ll capture the authentication handshake.
Send deauth to broadcast:
Send directed deauth (attack is more effective when it is targeted):
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
--deauth 100 |
The number of de-authenticate frames you want to send (0 for unlimited) |
-a |
The MAC address of the access point |
-c |
The MAC address of the client |
mon0 |
The wireless interface |
--ignore-negative-one |
Fixes the ‘fixed channel : -1’ error message |
Cool Tip: Need to hack WiFi password? Don’t wast your time! Use “John the Ripper” – the fastest password cracker! Read more →
5. Aircrack-ng: Hack WiFi Password
Unfortunately there is no way except brute force to break WPA/WPA2-PSK encryption.
To hack WiFi password, you need a password dictionary.
And remember that this type of attack is only as good as your password dictionary.
You can download some dictionaries from here.
Aircrack Ng Windows
Crack the WPA/WPA2-PSK with the following command:
Airodump Ng Download
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-w |
The name of the dictionary file |
-b |
The MAC address of the access point |
WPAcrack.cap |
The name of the file that contains the authentication handshake |
Airodump Ng For Windows Operating System
Cool Tip: Password cracking often takes time. Combine aircrack-ng with “John The Ripper” to pause/resume cracking whenever you want without loosing the progress! Read more →
Requirements
- Have a Windows computer.
- Have a connection to the internet.
- Download Aircrack-ng: https://download.aircrack-ng.org/aircrack-ng-1.2-win.zip
Steps:
First Step: Download and uncompress the Aircrack-ng file. Personally, I prefer to move the .rar file to the desktop to have a more clear working area. If your web browser does not ask you where to save the file, then just go to your «Downloads» section of your file explorer.
This is how it should look:

Second Step: Determine if your Windows architecture is 64-bit or 32-bit.
You should get something like this:
Third Step: Go to your ‘Local Disk (C:) and open the folder «Program Files» or «Program Files (x86)» depending on your windows architecture. Since my Windows is 64-bit I will choose the ‘Program Files’ folder.

Then, copy and paste the Aircrack-ng folder that you uncompressed before inside the «Program Files» folder.
The Aircrack-ng folder should look like this inside the «Program Files» folder.
After pasting the «Aircrack-ng» folder inside the «Program files» or «Program Files (x86)» you have to go inside of that folder.
Once inside the folder you will have to open the «bin» folder.
Depending on your Windows architecture you will choose the folder according to your Windows. In my case I chose the «64-bit» folder since my Windows architecture is 64-bit.
Once inside your corresponding folder, you will have to copy the address of that folder as it is shown below:

Fourth Step: Now, you will have to go to «This PC» properties once again.
Once you get the window below, you will have to left click on «Advanced system settings» as it is on the picture shown below.
Now you will have to click on the button that says «Environment Variables…»
Once you got inside «Environment Variables» you should get a screen just like this:

Once you got this window, you will have to click the «New» button pointed with the arrow.
In this new window, you have to write (path) inside the «Variable name:» box. Then, you will have to paste the address that you copied before in step #4 inside the «Variable value:» box. All the procedures are shown below.
After that, just click «OK» on all the windows that are open. Also, click on «Apply» if you see the option.
Final Step: Go to your desktop and press the keys «Ctrl + R» to open the «Run» program. Inside «Run» type «cmd» as it is shown below.
Then press «OK»
You should get a window like this one below

Now that you have opened the «cmd» you will have to type «aireplay-ng» inside the «cmd».
Then, press enter.
You should get a set of information just like it is on the picture above.
Now you are done and ready to use it.
